Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology: Modifiable Non-Modifiable
Pathophysiology: Modifiable Non-Modifiable
Uploaded by
imtheboss0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesGlaucoma is caused by an obstruction of the trabecular meshwork and canal of Schlemm, which blocks the outflow of aqueous humor from the eye. This leads to increased intraocular pressure that damages the optic nerve. Specifically, the high pressure can compress or decrease blood flow through the lamina cribrosa, inhibiting blood supply to the optic nerve and retina. Over time this causes optic nerve damage, cupping and pallor of the optic nerve head, and vision loss including blurry or hazy vision, rainbows around lights, and decreased peripheral vision.
Original Description:
Original Title
PATHO-revised.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGlaucoma is caused by an obstruction of the trabecular meshwork and canal of Schlemm, which blocks the outflow of aqueous humor from the eye. This leads to increased intraocular pressure that damages the optic nerve. Specifically, the high pressure can compress or decrease blood flow through the lamina cribrosa, inhibiting blood supply to the optic nerve and retina. Over time this causes optic nerve damage, cupping and pallor of the optic nerve head, and vision loss including blurry or hazy vision, rainbows around lights, and decreased peripheral vision.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesPathophysiology: Modifiable Non-Modifiable
Pathophysiology: Modifiable Non-Modifiable
Uploaded by
imthebossGlaucoma is caused by an obstruction of the trabecular meshwork and canal of Schlemm, which blocks the outflow of aqueous humor from the eye. This leads to increased intraocular pressure that damages the optic nerve. Specifically, the high pressure can compress or decrease blood flow through the lamina cribrosa, inhibiting blood supply to the optic nerve and retina. Over time this causes optic nerve damage, cupping and pallor of the optic nerve head, and vision loss including blurry or hazy vision, rainbows around lights, and decreased peripheral vision.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
NON-MODIFIABLE
MODIFIABLE
Heredofamilial Hx of Glaucoma (Maternal)
Past History
Increasing age (45-65 yrs.old)
HPN
OBSTRUCTION OCCURS AT THE
TRABECULAR MESHWORK AND THE CANAL
OF SCHLEMM
BLOCKAGE OF ANTERIOR CHAMBER ANGLES
HYPERPRODUCTION OF AQUEOUS HUMOUR
INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE
PUPILLARY DILATION/ IRIS DISPLACE
FORWARD
ANGLE
CLOSURE
INHIBITION OF BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE OPTIC
NERVE & RETINA
OPTIC NERVE DAMAGE AND ISCHEMIA OF
DELICATE TISSUES (IRIS & CILIARY BODY)
OPTIC NERVE CUPPING &
PALLOR (BASED ON
OPTHTHALMOSCOPIC
EXAMINATION)
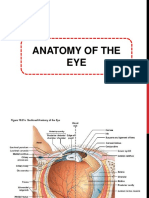
The axons of the optic nerve
leave the eye by passing
through a structure called
the lamina cribrosa, which
is a mesh-like structure
composed of pores or holes
through which the axon
bundles must cross. It is
thought that the site of initial
damage may be to the axons
as they pass through the
lamina cribrosa. Mechanical
compression and/or
decreased blood flow of the
PAIN
AROUND
EYES
Due to
pressure
CLOUDY
VISION
Due to
corneal
edema
HAZY
APPEARING
CORNEA
Due to
corneal
edema
NAUSEA
Result from the
activation of
protective
physiological
mechanisms that
exist in order to
eliminate toxins
from the body.
Increasing IOP
stimulate pain
and causes
nausea.
RAINBOW OF
COLOR
AROUND
LIGHTS
Due to optic
nerve
damage
PERIPHERAL
VISION
A significant
number of nerve
fibers are
damaged; blind
spots develop in
the field of vision
You might also like
- Glaucoma: Pgmi Abadilla Angela MarieDocument29 pagesGlaucoma: Pgmi Abadilla Angela MarieAngel AbadillaNo ratings yet
- Anterior ChamberDocument11 pagesAnterior Chamberhanidya fazwatNo ratings yet
- Full Anatomy CoassDocument74 pagesFull Anatomy CoassKartikaSariNo ratings yet
- VisionDocument199 pagesVisionAshtami Satheesh 2007No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Lecturer: Tatyana V. RyazantsevaDocument70 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Lecturer: Tatyana V. RyazantsevaArif MohammadNo ratings yet
- Dr. Eman Hussein Alwan M.B.CH.B F.I.C.M.S (Ophth) Department of Surgery College of Medicine Hawler Medical UniversityDocument40 pagesDr. Eman Hussein Alwan M.B.CH.B F.I.C.M.S (Ophth) Department of Surgery College of Medicine Hawler Medical UniversityHisham 6ChomanyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: DR - Turlea CristianDocument71 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: DR - Turlea CristianGermanyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy FisiologyDocument44 pagesAnatomy FisiologyLia HaslianiNo ratings yet
- Functional MorphologyDocument12 pagesFunctional MorphologyNelly ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Scalp Ii Layers and Supply Ii Applied Anatomy Ii General AnatomyDocument18 pagesScalp Ii Layers and Supply Ii Applied Anatomy Ii General AnatomyRahul KNo ratings yet
- Anatomy OcularDocument15 pagesAnatomy OcularJessica AlejandraNo ratings yet
- Gonioscopy 2008 01p001-114 Final PDFDocument114 pagesGonioscopy 2008 01p001-114 Final PDFNsk KhanNo ratings yet
- Discuss Physiology of Aqueous Formation and Its Drainage and Relate It To How Intraocular Pressure Is ControlledDocument8 pagesDiscuss Physiology of Aqueous Formation and Its Drainage and Relate It To How Intraocular Pressure Is ControlledPrince ChipunguNo ratings yet
- Secondary Angle Closure Glaucoma: Sristi Thakur 2 Year Resident Lei, NamsDocument96 pagesSecondary Angle Closure Glaucoma: Sristi Thakur 2 Year Resident Lei, NamsSristi ThakurNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy - DCR - Surgical TechniqueDocument11 pagesEndoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy - DCR - Surgical TechniqueLuis De jesus SolanoNo ratings yet
- Vitreous - HemorrhageDocument52 pagesVitreous - HemorrhagenotinsomniacNo ratings yet
- How To Read Fluorescein Angiography (Ophthalmology)Document56 pagesHow To Read Fluorescein Angiography (Ophthalmology)yazan100% (9)
- Introduction To OphthalmologyDocument83 pagesIntroduction To OphthalmologyHassan Raza100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye: Dr. Binto Akturusiano, SPMDocument45 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Eye: Dr. Binto Akturusiano, SPMranz ibonkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 017Document2 pagesChapter 017api-57828209No ratings yet
- Physiology of Aqueous HumorDocument34 pagesPhysiology of Aqueous HumorCindy Seow Sieng TengNo ratings yet
- Full Anatomy CoassDocument74 pagesFull Anatomy CoassAuliaRusdiAllmuttaqienNo ratings yet
- Structure-Function CorrelationDocument1 pageStructure-Function CorrelationrenNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Mata - Rizni FitrianaDocument32 pagesAnatomi Mata - Rizni FitrianaADE SULISTIYANINo ratings yet
- Peripheral Anterior SynechiaDocument11 pagesPeripheral Anterior SynechiaMarisa SukoNo ratings yet
- Bau p1 Mimic and Mastication Muscles 2024Document73 pagesBau p1 Mimic and Mastication Muscles 2024knfxhgqtv8No ratings yet
- Nervous System: Ahmad AminuddinDocument71 pagesNervous System: Ahmad AminuddinSurya Ashri Rahman HNo ratings yet
- Mace WenDocument2 pagesMace WenGerard Paul OrizaNo ratings yet
- Crvo CraoDocument80 pagesCrvo CraoRakshit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma PPT For Final YearDocument57 pagesGlaucoma PPT For Final YearDarshan SinghNo ratings yet
- Sclera AnatomyDocument21 pagesSclera AnatomyMiriam Mwangi100% (1)
- Praktikum Blok 18Document236 pagesPraktikum Blok 18Sherly MydoNo ratings yet
- Print AnaDocument7 pagesPrint AnaAlyssa CastroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EYEDocument117 pagesAnatomy of The EYELancelot BritaniaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrospinal Fluid RhinorrheaDocument4 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid RhinorrheaUlises Villanueva100% (1)
- Pathogenesis of Glaucoma: Determinants of Intraocular PressureDocument17 pagesPathogenesis of Glaucoma: Determinants of Intraocular PressureAdi TriNo ratings yet
- GLAUCOMA DR EunikeDocument47 pagesGLAUCOMA DR EunikeJanet UngNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Brow Lift - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument15 pagesEndoscopic Brow Lift - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelfdrkorn.ophNo ratings yet
- Major Review: Ocular ColobomataDocument20 pagesMajor Review: Ocular ColobomataPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Lacrimal Secretion & Outflow: DR - Nurcahya Ab, SPMDocument51 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Lacrimal Secretion & Outflow: DR - Nurcahya Ab, SPMLianSiahaanNo ratings yet
- Ocular CirculationDocument82 pagesOcular CirculationPrabhjot SinghNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Optic Disc and Congenital AnomalyDocument49 pagesAnatomy of Optic Disc and Congenital AnomalyAdarsh KeshariNo ratings yet
- Visual PathwayDocument63 pagesVisual Pathwaysenny chapagainNo ratings yet
- Assessing EyesDocument33 pagesAssessing Eyesshellacayetano2No ratings yet
- Cavernous Veinous ThrombosisDocument87 pagesCavernous Veinous ThrombosismuksqaziNo ratings yet
- Sclera StructureDocument15 pagesSclera Structureferdi151991No ratings yet
- Angle of Anterior Chamber.Document35 pagesAngle of Anterior Chamber.Vidya KumbarNo ratings yet
- Ophtho GuideDocument24 pagesOphtho GuideNico7234100% (1)
- System Kedaruratan Dan TraumatologyDocument22 pagesSystem Kedaruratan Dan TraumatologyraniNo ratings yet
- Baru Mata 2Document29 pagesBaru Mata 2Ichsan DiazNo ratings yet
- Gonioscopic AnatomyDocument30 pagesGonioscopic AnatomymanognaaaaNo ratings yet
- Cerebro Spinal Fluid and The Meninges: Dr. Setyawati Asih Putri, SPS, M.Kes, FinaDocument30 pagesCerebro Spinal Fluid and The Meninges: Dr. Setyawati Asih Putri, SPS, M.Kes, FinakhairaniNo ratings yet
- GlucomaDocument11 pagesGlucomaAhmed KareemNo ratings yet
- 03 Retinal Vascular Occlution - Dr. Darwan Triyono, SP.MDocument28 pages03 Retinal Vascular Occlution - Dr. Darwan Triyono, SP.MDissa Yulianita SuryaniNo ratings yet
- OphthalmologyDocument5 pagesOphthalmologyGudapati Surendranadhchowdhary100% (1)
- Anatomy-Surg - Clinical Corelates of Vertebral - Meninges and Spinal Cord VasculatureDocument3 pagesAnatomy-Surg - Clinical Corelates of Vertebral - Meninges and Spinal Cord VasculaturecosmoNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY OF SCLERADocument12 pagesANATOMY OF SCLERAjjclara003No ratings yet
- Opthal Summary AnatomyDocument14 pagesOpthal Summary AnatomyNoman ButtNo ratings yet
- H & N 6th Week Eyelids, Lacrimal Apparatus and Ciliary GanglionDocument23 pagesH & N 6th Week Eyelids, Lacrimal Apparatus and Ciliary GanglionAreesha ANo ratings yet
- Suprachoroidal Space InterventionsFrom EverandSuprachoroidal Space InterventionsShohista SaidkasimovaNo ratings yet
- Home Visit Plans: Pregnant Woman Post Partum Well-Baby MorbidDocument1 pageHome Visit Plans: Pregnant Woman Post Partum Well-Baby MorbidimthebossNo ratings yet
- Management Process PlanningDocument4 pagesManagement Process PlanningimthebossNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume R/T Inadequate Fluid Volume Intake Aeb Dry Mucous MembraneDocument2 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume R/T Inadequate Fluid Volume Intake Aeb Dry Mucous MembraneimthebossNo ratings yet
- Audience: Floor Plan: September 2, 2016 at Rooms 207 and 208Document1 pageAudience: Floor Plan: September 2, 2016 at Rooms 207 and 208imthebossNo ratings yet
- Drug Name General Action Specific Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects NSG Responsibilities Acetazolamide 250mg/tab 1 Tab Now Then TIDDocument8 pagesDrug Name General Action Specific Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects NSG Responsibilities Acetazolamide 250mg/tab 1 Tab Now Then TIDimthebossNo ratings yet
- FluphenazineDocument4 pagesFluphenazineimthebossNo ratings yet
- Course in The Ward Date/Time Doctor'S Order Rationale Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesCourse in The Ward Date/Time Doctor'S Order Rationale Nursing ResponsibilitiesimthebossNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goals Nursing Intervention Rationales Evaluation Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goals Nursing Intervention Rationales Evaluation Subjective CuesimthebossNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination and Review of SystemDocument10 pagesPhysical Examination and Review of SystemimthebossNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse and Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse and Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationsimthebossNo ratings yet
- ChlorpromazineDocument1 pageChlorpromazineimthebossNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Therapeutic Class Action Indication Contraindicatio N Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityDocument3 pagesDrug Name Therapeutic Class Action Indication Contraindicatio N Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityimthebossNo ratings yet
- WaverDocument2 pagesWaverimthebossNo ratings yet
- Diarrhe A: Teaching StrategiesDocument12 pagesDiarrhe A: Teaching StrategiesimthebossNo ratings yet
- Jo Marie Ahletea D. Lamsin Neptunites 2017 - P.E 4 Report: Strategy Board Game Halma HexagramDocument3 pagesJo Marie Ahletea D. Lamsin Neptunites 2017 - P.E 4 Report: Strategy Board Game Halma HexagramimthebossNo ratings yet
- Sarsoza BaseyDocument10 pagesSarsoza BaseyimthebossNo ratings yet