Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physical State: Gaseous E.G. Water Gas, LPG
Physical State: Gaseous E.G. Water Gas, LPG
Uploaded by
PritamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical State: Gaseous E.G. Water Gas, LPG
Physical State: Gaseous E.G. Water Gas, LPG
Uploaded by
PritamCopyright:
Available Formats
Why Study Fuels?
1. Fuels are the resources which had played on important role in the development of
human being since their discovery.
2. As an engineer we will make advancements in our respective field. If the technology
we are working on require fuels to run them then paper knowledge of fuels is
required.
3. Thus for us to have fair knowledge about various aspects of fuels is required.
Definition
1. Fuels are defined as, substances which undergo combustion in the presence of air
to produce a large amount of heat that can be used economically for domestic and
industrial purpose.
2. This definition does not include unclear fuel because it cannot be used by common
man
3. The various fuels are wood, coal, kerosene, petrol etc.
4. The fossil fuels are wood, vegetable oils etc which burn to produce heat are known
as chemical fuels.
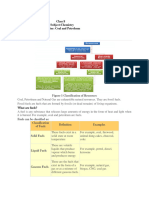
Classification of Chemical Fuels
The diagram given below shows the classification of chemical fuels
Solid
E.g. Wood, Coal, dung
Primary Physical
Or Natural
State
Liquid
E.g. Crude Oil, Vegeta
Gaseous
E.g. Natural G
Chemical
Origin
Fuels
Solid
E.g. Charcoal, Coke, Pulverized coke etc.
Secondary Physical
Or Derived
State
Liquid E.g. Alcohol, Petrol, diesel
Characteristic Properties of Good Fuels
An ideal fuel should possess following properties.
Gaseous
E.g. Water gas, LPG
1. Colorific value should be as high as possible (concept of colorific value is discussed
in further modules)
2. Its viscosity should be adequate
3. Moisture content in the fuel should be as low as possible
4. Ash matter in the fuel should be absent
5. Easy transportation should be possible
6. Harmless products should be produced on combustion.
The chemical properties of the fuel include the compositional analysis of the fuel.
This includes
For Solid and Liquid Fuels
1. Percentage of elements like C,H, N, D,S etc,
2. Percentage of moisture
3. Percentage of volatile matter.
For gaseous Fuels
1. Percentage of combustible gases e.g.- CO, CH4,C2H4 etc
2. Percentage of non combustible gases e.g. N2, CO2 etc
You might also like
- Gasifiers Wood Gasification & Off Grid PowerFrom EverandGasifiers Wood Gasification & Off Grid PowerRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Purpose of Making AlloysDocument2 pagesPurpose of Making AlloysPritam100% (1)
- Fuel: Engineering Chemistry and Environmental Studies UNIT IXDocument2 pagesFuel: Engineering Chemistry and Environmental Studies UNIT IXvravisankarNo ratings yet
- Module FormatDocument18 pagesModule Formatnorlin facultadNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument1 pageFuels and CombustionjayctaNo ratings yet
- Study Notes CBSE Class 8th Physics Coal and Petroleum WWW - CbseportalDocument3 pagesStudy Notes CBSE Class 8th Physics Coal and Petroleum WWW - CbseportalArshad Ahmad MasoodiNo ratings yet
- Coal and Petroleum NotesDocument7 pagesCoal and Petroleum NotessaumiliitbombayNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii IiiDocument10 pagesUnit Ii IiiRAGUDO, ELEAZAR O.No ratings yet
- Class 8 - Chapter 5 - Coal and PetroleumDocument9 pagesClass 8 - Chapter 5 - Coal and PetroleumsanaNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection AND Arson Investigation: Mark Lester E. Caranay, RcrimDocument16 pagesFire Protection AND Arson Investigation: Mark Lester E. Caranay, RcrimGemel John CatapNo ratings yet
- 8 ChemistryDocument5 pages8 ChemistryJakia Wahima Class:-6C Rollno.:-38No ratings yet
- Notes Coal and PetroleumDocument6 pagesNotes Coal and PetroleumzaynabNo ratings yet
- Coal and Petroleum Notes Science Chapter 5Document2 pagesCoal and Petroleum Notes Science Chapter 5Ritom SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Coal and Petroleum NotesDocument3 pagesCoal and Petroleum NotesJyotiNo ratings yet
- Coal and PetroleumDocument5 pagesCoal and PetroleumshobhtelixirNo ratings yet
- Combustion of Flame - 8thDocument17 pagesCombustion of Flame - 8thVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 5 - Coal and PetroleumDocument4 pagesRevision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 5 - Coal and PetroleumArpit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6... Combustion & FlameDocument12 pagesChapter 6... Combustion & FlamepandeyklNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CoalDocument4 pagesIntroduction To CoalEvansChombaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Fuel & BoilerDocument17 pagesUnit 4 Fuel & Boilersample useNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Fuels PDFDocument8 pagesModule 4 Fuels PDFDULCE MAY SEMANINGNo ratings yet
- NCERT, Extra Questions For Coal and PetroleumDocument15 pagesNCERT, Extra Questions For Coal and PetroleumSakshi DahiyaNo ratings yet
- CBSE 8 Science CBSE - Coal and Petroleum, Free Test Papers, Sample Questions, HOTS Questions and Notes, CBSE - Coal and PetroleumDocument8 pagesCBSE 8 Science CBSE - Coal and Petroleum, Free Test Papers, Sample Questions, HOTS Questions and Notes, CBSE - Coal and PetroleumR.Shruti 1040-12No ratings yet
- PDF 1697459000143Document8 pagesPDF 1697459000143harshalgajananwaghmodeNo ratings yet
- Class 8 CBSE Exam BoosterDocument33 pagesClass 8 CBSE Exam BoosterHima MashhoodNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Matter and ENERGY: Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesUnit 2 - Matter and ENERGY: Learning ObjectivesRonald GrayNo ratings yet
- Makalah KimiaDocument13 pagesMakalah KimiaKhansa Adiba Nurluthfi6ENo ratings yet
- Short Answer Type QuestionsDocument12 pagesShort Answer Type QuestionsRamakrishna ErrojuNo ratings yet
- Fuels, Furnaces and Refractories R.C. GUPTA-18-100Document83 pagesFuels, Furnaces and Refractories R.C. GUPTA-18-100AFGITA WIANDA0% (1)
- OF Fuel: by Varun Pratap SinghDocument58 pagesOF Fuel: by Varun Pratap Singhduy.ho188No ratings yet
- Coal and Petrolium-FinalDocument18 pagesCoal and Petrolium-FinaljamaluddinNo ratings yet
- CHE-C4E Lecture 4 - FuelsDocument26 pagesCHE-C4E Lecture 4 - FuelssgagustinNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Notes Coal and PetroliumDocument3 pagesClass 8 Notes Coal and Petroliumindrapreet singhNo ratings yet
- Cdi 303 Chapter 3Document102 pagesCdi 303 Chapter 3melmhyrrsagadonNo ratings yet
- 5Document8 pages5abhimanyuk_2No ratings yet
- Notebook Work Coal & PetroleumDocument2 pagesNotebook Work Coal & PetroleumaryanshaindilyaNo ratings yet
- 8-Science-Coal and Petroleum-Notes-VLDocument8 pages8-Science-Coal and Petroleum-Notes-VLTapan PathakNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 4th FuelDocument7 pagesChemistry 4th FuelArpita 18No ratings yet
- Coal and PetroleumDocument6 pagesCoal and Petroleumdivya pathakNo ratings yet
- Fuel EfficiencyDocument3 pagesFuel EfficiencyHdhdhdNo ratings yet
- 8th Science CBSE Test Paper Solved Chapter 5 Coal and PetroleumDocument5 pages8th Science CBSE Test Paper Solved Chapter 5 Coal and PetroleumAnonymous JamqEgqqh1No ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Part 1Document10 pagesChapter - 1 Part 1dinesh PATIALNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 5 - Coal and PetroleumDocument7 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 5 - Coal and Petroleumkumarmadhesh84No ratings yet
- CLASS-8th Chapter-5 Coal and Petroleum: ScienceDocument5 pagesCLASS-8th Chapter-5 Coal and Petroleum: ScienceRahulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum Lesson PlanDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Coal and Petroleum Lesson PlanmisterrpositiveNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Introduction To Petroleum EngineeringDocument14 pagesChapter - 1 Introduction To Petroleum EngineeringayanNo ratings yet
- Fuels and Combustion CHAPTER 4 FUELS AND COMBUSTION 41 Introduction 42 Requirements of A Good FuelDocument84 pagesFuels and Combustion CHAPTER 4 FUELS AND COMBUSTION 41 Introduction 42 Requirements of A Good FuelOcchitya MudgalNo ratings yet
- FUELS DoneDocument5 pagesFUELS Donethercode sampNo ratings yet
- Coal and Petroleum, NotesDocument7 pagesCoal and Petroleum, NotesSubadra BaskarNo ratings yet
- ENERGIESDocument18 pagesENERGIESAshutosh DevkotaNo ratings yet
- Coal and Petroleum: Check Point 1Document10 pagesCoal and Petroleum: Check Point 1abcdefghNo ratings yet
- Viscous LiquidDocument20 pagesViscous LiquiddanishrasoolmirNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii. Fuels: Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pagesUnit Iii. Fuels: Learning ObjectivesIvyy Joyce BuanNo ratings yet
- Seatwork No. 2Document2 pagesSeatwork No. 2Raincel Mae WarnacNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Matter and Energy Fuels: Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pagesUnit 2 - Matter and Energy Fuels: Learning ObjectivesNiña Viaña BinayNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Calorific Power.Document19 pages1.4 Calorific Power.JESUS ALBERTO SANCHEZ GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Shahdara: Chapter - 5 Coal and PetroleumDocument24 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Shahdara: Chapter - 5 Coal and Petroleumcontact.progresscatalystNo ratings yet
- RGIPT MBA Programme 2010-12 Course: Introduction To Oil and GasDocument11 pagesRGIPT MBA Programme 2010-12 Course: Introduction To Oil and GasUdit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas: Economics and Environment: A Handbook for Students of the Natural Gas IndustryFrom EverandNatural Gas: Economics and Environment: A Handbook for Students of the Natural Gas IndustryNo ratings yet
- Numericals On Percent Atom EconomyDocument1 pageNumericals On Percent Atom EconomyPritamNo ratings yet
- Structural Composites or Layered CompositesDocument3 pagesStructural Composites or Layered CompositesPritam100% (1)
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionPritamNo ratings yet
- Bonding Process by AdhesivesDocument2 pagesBonding Process by AdhesivesPritam100% (1)
- Adhesive ActionDocument1 pageAdhesive ActionPritamNo ratings yet
- Theory Questions Q.1 What Are Adhesives ? Q.2 What Are The Factors Which Influence Adhesive Action ? Q.3 Explain Bonding Process by AdhesivesDocument1 pageTheory Questions Q.1 What Are Adhesives ? Q.2 What Are The Factors Which Influence Adhesive Action ? Q.3 Explain Bonding Process by AdhesivesPritamNo ratings yet
- 4.theory QuestionsDocument1 page4.theory QuestionsPritamNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Adhesive ActionDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Adhesive ActionPritam100% (5)
- Particle and Fiber Reinforced CompositesDocument1 pageParticle and Fiber Reinforced CompositesPritamNo ratings yet
- Numerical On Proximate and Ultimate AnalysisDocument1 pageNumerical On Proximate and Ultimate AnalysisPritam83% (6)
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionPritamNo ratings yet
- BiodieselDocument1 pageBiodieselPritamNo ratings yet
- Numericals On Combustion of Solid and Liquid FuelsDocument2 pagesNumericals On Combustion of Solid and Liquid FuelsPritam100% (1)
- Solid FuelsDocument5 pagesSolid FuelsPritamNo ratings yet
- Unsolved Numericals On Dulong's FormulaDocument1 pageUnsolved Numericals On Dulong's FormulaPritam100% (1)
- Antiknocking AgentsDocument3 pagesAntiknocking AgentsPritam100% (1)
- Cracking of Heavy OilDocument4 pagesCracking of Heavy OilPritamNo ratings yet
- Colorific Value of A FuelDocument1 pageColorific Value of A FuelPritamNo ratings yet
- Knocking and Octane Number of PetrolDocument2 pagesKnocking and Octane Number of PetrolPritamNo ratings yet
- Classification of AlloysDocument9 pagesClassification of AlloysPritamNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument8 pagesPowder MetallurgyPritamNo ratings yet
- Alumina Powder (Al O) : C Sic Crystalline Product + 2coDocument2 pagesAlumina Powder (Al O) : C Sic Crystalline Product + 2coPritamNo ratings yet