Professional Documents
Culture Documents
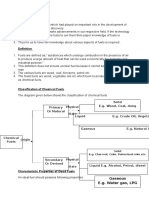
Combustion
Combustion
Uploaded by
PritamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Combustion
Combustion
Uploaded by
PritamCopyright:
Available Formats
Combustion
1) Combustion is a process in which oxygen from the air reacts with the elements or
compounds to liberated heat
2) Sometimes it is required to calculate the minimum amount of oxygen that will be
required for complete combustion of nay compound
3) Commonly involved reactions are as follows
1. C + O2
CO2
2. 2H2 + 02
2H2O
3. S + 02
SO2
4. 2CO + O2
2CO2
5. CH4 + 2O2
CO2 + 2H2O
6. 2C2H6 + 7O2
4CO2 + 6H2O
7. C2H4 + 302
2CO2 +2H2O
8. 2C2H2 +502
4CO2 + 2H2O
9. C4H8 + 602
4CO2 + 4H2O
10. 2C4H10 +13O2
8CO2 + 10H2O
11. 2C3H6 + 9O2
6CO2 + 6H2O
12. C3H8 + 5O2
3CO2 + 4H2O
Calculation of quantity of fuel required for combustion of fuel
By weight and volume
1) Any substance combines with oxygen in definite proportions as per mole concept.
C + O2
By weight 12
32
By volume 1 Vol 1 Vol
2H2 + O2
By weight 4
By volume 2 Vol
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
CO2
44
1 Vol
32
1 Vol
2H2O
36
2 Vol
Nitrogen, ash and CO2 are non combustible
At STP 1 gram mole =22.4 L of gas
Air contains 21% oxygen by volume and 23% oxygen by mass
Molar mass of air is taken as 28.94 gram/ mole
Oxygen required = Theoretical O2 required - O2 already present
When % of elements is given then calculate O 2 quantity as follows
O2 quantity =
32 C
0
+8 H + s
kg
12
8
Quantity of air =
Volume of air =
oxygen quantity
x100kg.
23
Volume of oxygen
21
x 100m3
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Purpose of Making AlloysDocument2 pagesPurpose of Making AlloysPritam100% (1)
- Numericals On Percent Atom EconomyDocument1 pageNumericals On Percent Atom EconomyPritamNo ratings yet
- Structural Composites or Layered CompositesDocument3 pagesStructural Composites or Layered CompositesPritam100% (1)
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionPritamNo ratings yet
- Bonding Process by AdhesivesDocument2 pagesBonding Process by AdhesivesPritam100% (1)
- Adhesive ActionDocument1 pageAdhesive ActionPritamNo ratings yet
- Theory Questions Q.1 What Are Adhesives ? Q.2 What Are The Factors Which Influence Adhesive Action ? Q.3 Explain Bonding Process by AdhesivesDocument1 pageTheory Questions Q.1 What Are Adhesives ? Q.2 What Are The Factors Which Influence Adhesive Action ? Q.3 Explain Bonding Process by AdhesivesPritamNo ratings yet
- 4.theory QuestionsDocument1 page4.theory QuestionsPritamNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Adhesive ActionDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Adhesive ActionPritam100% (5)
- Particle and Fiber Reinforced CompositesDocument1 pageParticle and Fiber Reinforced CompositesPritamNo ratings yet
- Numerical On Proximate and Ultimate AnalysisDocument1 pageNumerical On Proximate and Ultimate AnalysisPritam83% (6)
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionPritamNo ratings yet
- BiodieselDocument1 pageBiodieselPritamNo ratings yet
- Numericals On Combustion of Solid and Liquid FuelsDocument2 pagesNumericals On Combustion of Solid and Liquid FuelsPritam100% (1)
- Solid FuelsDocument5 pagesSolid FuelsPritamNo ratings yet
- Unsolved Numericals On Dulong's FormulaDocument1 pageUnsolved Numericals On Dulong's FormulaPritam100% (1)
- Antiknocking AgentsDocument3 pagesAntiknocking AgentsPritam100% (1)
- Cracking of Heavy OilDocument4 pagesCracking of Heavy OilPritamNo ratings yet
- Colorific Value of A FuelDocument1 pageColorific Value of A FuelPritamNo ratings yet
- Knocking and Octane Number of PetrolDocument2 pagesKnocking and Octane Number of PetrolPritamNo ratings yet
- Physical State: Gaseous E.G. Water Gas, LPGDocument2 pagesPhysical State: Gaseous E.G. Water Gas, LPGPritamNo ratings yet
- Classification of AlloysDocument9 pagesClassification of AlloysPritamNo ratings yet
- Alumina Powder (Al O) : C Sic Crystalline Product + 2coDocument2 pagesAlumina Powder (Al O) : C Sic Crystalline Product + 2coPritamNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument8 pagesPowder MetallurgyPritamNo ratings yet