Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction
Introduction
Uploaded by
PritamCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Purpose of Making AlloysDocument2 pagesPurpose of Making AlloysPritam100% (1)
- Composite Materials: Module I - Introduction Lectures 1 To 2Document8 pagesComposite Materials: Module I - Introduction Lectures 1 To 2Vivek SNo ratings yet
- Study of Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Natural Fiber CompositeDocument5 pagesStudy of Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Natural Fiber CompositeMir Aqib HussainNo ratings yet
- CMS Unit-1 Part-1Document30 pagesCMS Unit-1 Part-1ashok pandiyanNo ratings yet
- Composite Materials Basics: Department of Chemistry University of GujratDocument17 pagesComposite Materials Basics: Department of Chemistry University of GujratArshadNo ratings yet
- Avinash Document ProjectDocument90 pagesAvinash Document ProjectBajibabu IndurthiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 (Second Part) Composites Introduction To CompositesDocument18 pagesModule 4 (Second Part) Composites Introduction To CompositesabhilashNo ratings yet
- Laminated Composite Stiffened Panels Application and BehaviourDocument46 pagesLaminated Composite Stiffened Panels Application and BehaviourHemendra Jain100% (1)
- Composite MaterialsDocument17 pagesComposite MaterialsChiranjaya HulangamuwaNo ratings yet
- Composite+Materials I IIDocument24 pagesComposite+Materials I IIcorleoneeeNo ratings yet
- Coir Fibre Reinforcement and Application in Polymer Composites: A ReviewDocument14 pagesCoir Fibre Reinforcement and Application in Polymer Composites: A ReviewAshokan Keloth100% (1)
- Netaji Subhash University of Technology: Home Assignment OnDocument27 pagesNetaji Subhash University of Technology: Home Assignment OnParshant YadavNo ratings yet
- C 1Document28 pagesC 1mohd nadeemNo ratings yet
- Study of Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Natural Fiber CompositeDocument39 pagesStudy of Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Natural Fiber CompositePeeka Prabhakara RaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument25 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionRandy VidsNo ratings yet
- Composites MaterialDocument47 pagesComposites MaterialNarkedamilli Tulasi RadhaNo ratings yet
- 08 Chapter1Document63 pages08 Chapter1Inam Ul Haq100% (1)
- Walnut Shell A ReviewDocument11 pagesWalnut Shell A ReviewGaneshNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Composite Drive SDocument8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Composite Drive SfrindgeNo ratings yet
- MS Module 5 PDFDocument23 pagesMS Module 5 PDFChidu KNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Water Absorption Behavior of Sisal and Banana Fiber CompositesDocument49 pagesMechanical and Water Absorption Behavior of Sisal and Banana Fiber CompositesKutty AravindNo ratings yet
- Composites: Rohini College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument9 pagesComposites: Rohini College of Engineering and TechnologyalfajNo ratings yet
- Composite MaterialsDocument5 pagesComposite MaterialsIqRa JaVedNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Composite Drive ShaftDocument8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Composite Drive ShaftInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Unit-I TO Composite MaterialsDocument40 pagesUnit-I TO Composite MaterialsSaisurendra VeerlaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NO. 10. Composite MaterialsDocument10 pagesLECTURE NO. 10. Composite MaterialsBizuayehu Tadesse AzeneNo ratings yet
- Flexural Properties Hybrid SFRC PDFDocument16 pagesFlexural Properties Hybrid SFRC PDFAndresEduardoRenjifoRestrepoNo ratings yet
- Project Report PDFDocument38 pagesProject Report PDFLogic Manju71% (14)
- تقرير جديد مواد هندسيهDocument42 pagesتقرير جديد مواد هندسيهداليا شاكر كحيط عامNo ratings yet
- IJEDR1504023Document50 pagesIJEDR1504023prathiksha anchanNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Retrofitted RC T-BEAM Using FRPDocument5 pagesExperimental Study On Retrofitted RC T-BEAM Using FRPInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Composite MaterialsDocument399 pagesComposite MaterialsCharlton S.Inao100% (1)
- Report of Fatigue and Fracture of Structure: Submitted byDocument16 pagesReport of Fatigue and Fracture of Structure: Submitted byameer hamzaNo ratings yet
- ChE 17 Report - CompositesDocument15 pagesChE 17 Report - CompositesZAIRA JOY UDANG SOTARIDONANo ratings yet
- Unit - I Introduction of Composites: Figure (1) : Composite Korean BowDocument61 pagesUnit - I Introduction of Composites: Figure (1) : Composite Korean Bowu2b11517100% (1)
- Efunda - Introduction To Com..Document2 pagesEfunda - Introduction To Com..Sujay DasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CompositeDocument14 pagesIntroduction To CompositeAhmed YASIR JAHINNo ratings yet
- Manuf Project 1usman 2danish-3talha 4izhar...Document10 pagesManuf Project 1usman 2danish-3talha 4izhar...Maria kani MagdaNo ratings yet
- Composite Materials Part 1Document300 pagesComposite Materials Part 1PethurajNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Mechanical Properties of Corn Fiber Reinforced With Biodegradable ResinDocument4 pagesInvestigation of Mechanical Properties of Corn Fiber Reinforced With Biodegradable ResinRaja SajinNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Fibre Project ReportDocument28 pagesBamboo Fibre Project ReportPranabhChowdhury ( mech)No ratings yet
- Hybrid Filament-Wound MaterialsDocument11 pagesHybrid Filament-Wound MaterialsHO LinNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Composite MaterialsDocument27 pagesSeminar On Composite MaterialsNikhilesh Kadukar100% (3)
- Hybrid CompositeDocument91 pagesHybrid Compositemanoharbyalal100% (3)
- Multifunctional MaterialsDocument24 pagesMultifunctional MaterialsGeanina IonescuNo ratings yet
- Anuual Report.1Document8 pagesAnuual Report.1Subhashis SitNo ratings yet
- Module-1: General Introduction M1: General Introduction M1.1 Introduction of CompositesDocument35 pagesModule-1: General Introduction M1: General Introduction M1.1 Introduction of CompositesANo ratings yet
- Industrial Material: Subject NameDocument28 pagesIndustrial Material: Subject NameHamza SaeedNo ratings yet
- A Review On Comparative Study of Polymer Matrix Composites and Metal Matrix CompositesDocument6 pagesA Review On Comparative Study of Polymer Matrix Composites and Metal Matrix CompositesIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Composites Mini ProjectDocument44 pagesComposites Mini ProjectRajaReddyNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Polymer CompositeDocument14 pages01 Introduction To Polymer CompositeMD Sunjin AhsunNo ratings yet
- Materials. The Constituent Materials of A Composite Have Significantly Different Properties. Further, ItDocument18 pagesMaterials. The Constituent Materials of A Composite Have Significantly Different Properties. Further, ItarravindNo ratings yet
- ME518-Part1_introductionDocument27 pagesME518-Part1_introductionRaja DiazNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 2Document57 pages07 Chapter 2namakkamkumarNo ratings yet
- LI ECC - 看图王 PDFDocument38 pagesLI ECC - 看图王 PDFxi.duNo ratings yet
- CompositeDocument20 pagesCompositeSuhbat Ali BozdarNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture Toughness: A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture ToughnessFrom EverandA Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture Toughness: A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture ToughnessNo ratings yet
- Numericals On Percent Atom EconomyDocument1 pageNumericals On Percent Atom EconomyPritamNo ratings yet
- Structural Composites or Layered CompositesDocument3 pagesStructural Composites or Layered CompositesPritam100% (1)
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionPritamNo ratings yet
- Bonding Process by AdhesivesDocument2 pagesBonding Process by AdhesivesPritam100% (1)
- Adhesive ActionDocument1 pageAdhesive ActionPritamNo ratings yet
- Theory Questions Q.1 What Are Adhesives ? Q.2 What Are The Factors Which Influence Adhesive Action ? Q.3 Explain Bonding Process by AdhesivesDocument1 pageTheory Questions Q.1 What Are Adhesives ? Q.2 What Are The Factors Which Influence Adhesive Action ? Q.3 Explain Bonding Process by AdhesivesPritamNo ratings yet
- 4.theory QuestionsDocument1 page4.theory QuestionsPritamNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Adhesive ActionDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Adhesive ActionPritam100% (5)
- Particle and Fiber Reinforced CompositesDocument1 pageParticle and Fiber Reinforced CompositesPritamNo ratings yet
- Numericals On Combustion of Solid and Liquid FuelsDocument2 pagesNumericals On Combustion of Solid and Liquid FuelsPritam100% (1)
- Numerical On Proximate and Ultimate AnalysisDocument1 pageNumerical On Proximate and Ultimate AnalysisPritam83% (6)
- Solid FuelsDocument5 pagesSolid FuelsPritamNo ratings yet
- Unsolved Numericals On Dulong's FormulaDocument1 pageUnsolved Numericals On Dulong's FormulaPritam100% (1)
- Cracking of Heavy OilDocument4 pagesCracking of Heavy OilPritamNo ratings yet
- BiodieselDocument1 pageBiodieselPritamNo ratings yet
- Knocking and Octane Number of PetrolDocument2 pagesKnocking and Octane Number of PetrolPritamNo ratings yet
- Antiknocking AgentsDocument3 pagesAntiknocking AgentsPritam100% (1)
- Physical State: Gaseous E.G. Water Gas, LPGDocument2 pagesPhysical State: Gaseous E.G. Water Gas, LPGPritamNo ratings yet
- Colorific Value of A FuelDocument1 pageColorific Value of A FuelPritamNo ratings yet
- Classification of AlloysDocument9 pagesClassification of AlloysPritamNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument8 pagesPowder MetallurgyPritamNo ratings yet
- Alumina Powder (Al O) : C Sic Crystalline Product + 2coDocument2 pagesAlumina Powder (Al O) : C Sic Crystalline Product + 2coPritamNo ratings yet
Introduction
Introduction
Uploaded by
PritamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction
Introduction
Uploaded by
PritamCopyright:
Available Formats
Composite Materials
Why study composite materials?
Composite materials are one of the important engineering materials which are being
used widely since its discovery. This is because it reduces the cost and on the other
had enhances the property of any structure. Thus it is important for us engineers to
have a comprehensive knowledge about composite materials
Introduction
1) Composite materials are the materials which are the mixture of two or more
materials
2) The constituent materials may or may not be in the same physical state
3) It is a noted property of composite materials that they exhibit the properties which
are totally different from the properties possessed by constituent materials.
4) Most of the properties possessed by composite materials are present in the
enhanced from.
5) Examples of composite materials: -Reinforced Concrete (RCC) Bone, insulating
tape.
Definition
1) Composite materials are engineered materials having enhanced properties made
from which remain separate distinct within given material.
2) The constituent materials used for making composite materials are selected
according to the properties that the composite material should possess
3) Composite materials are having very high strength but very low weight. Thus they
find major applications in various fields of engineering for e.g.
1) Transportation
2) Agriculture
3) Aerospace etc.
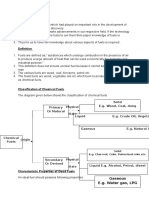
Constitution of Composite Materials.
The constituents of composite materials are as follows: 1) Matrix Phase
2) Dispersed Phase
3) Interface
1) Matrix Phase
1) It is a continuous phase which surrounds dispersed phase
Functions of Matrix Phase:
1) It protects dispersed phase from surface damage
2) It binds dispersed phase together
3) Stress is transmitted and distributed to dispersed through medium of matrix phase
2) Dispersed Phase
Dispersed phase is discontinuous phase which strengthens the matrix phase.
Function:
It provides strength (reinforcement)
3) Interface
It is the boundary between the matrix phase and dispersed phase.
You might also like
- Purpose of Making AlloysDocument2 pagesPurpose of Making AlloysPritam100% (1)
- Composite Materials: Module I - Introduction Lectures 1 To 2Document8 pagesComposite Materials: Module I - Introduction Lectures 1 To 2Vivek SNo ratings yet
- Study of Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Natural Fiber CompositeDocument5 pagesStudy of Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Natural Fiber CompositeMir Aqib HussainNo ratings yet
- CMS Unit-1 Part-1Document30 pagesCMS Unit-1 Part-1ashok pandiyanNo ratings yet
- Composite Materials Basics: Department of Chemistry University of GujratDocument17 pagesComposite Materials Basics: Department of Chemistry University of GujratArshadNo ratings yet
- Avinash Document ProjectDocument90 pagesAvinash Document ProjectBajibabu IndurthiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 (Second Part) Composites Introduction To CompositesDocument18 pagesModule 4 (Second Part) Composites Introduction To CompositesabhilashNo ratings yet
- Laminated Composite Stiffened Panels Application and BehaviourDocument46 pagesLaminated Composite Stiffened Panels Application and BehaviourHemendra Jain100% (1)
- Composite MaterialsDocument17 pagesComposite MaterialsChiranjaya HulangamuwaNo ratings yet
- Composite+Materials I IIDocument24 pagesComposite+Materials I IIcorleoneeeNo ratings yet
- Coir Fibre Reinforcement and Application in Polymer Composites: A ReviewDocument14 pagesCoir Fibre Reinforcement and Application in Polymer Composites: A ReviewAshokan Keloth100% (1)
- Netaji Subhash University of Technology: Home Assignment OnDocument27 pagesNetaji Subhash University of Technology: Home Assignment OnParshant YadavNo ratings yet
- C 1Document28 pagesC 1mohd nadeemNo ratings yet
- Study of Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Natural Fiber CompositeDocument39 pagesStudy of Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Natural Fiber CompositePeeka Prabhakara RaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument25 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionRandy VidsNo ratings yet
- Composites MaterialDocument47 pagesComposites MaterialNarkedamilli Tulasi RadhaNo ratings yet
- 08 Chapter1Document63 pages08 Chapter1Inam Ul Haq100% (1)
- Walnut Shell A ReviewDocument11 pagesWalnut Shell A ReviewGaneshNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Composite Drive SDocument8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Composite Drive SfrindgeNo ratings yet
- MS Module 5 PDFDocument23 pagesMS Module 5 PDFChidu KNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Water Absorption Behavior of Sisal and Banana Fiber CompositesDocument49 pagesMechanical and Water Absorption Behavior of Sisal and Banana Fiber CompositesKutty AravindNo ratings yet
- Composites: Rohini College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument9 pagesComposites: Rohini College of Engineering and TechnologyalfajNo ratings yet
- Composite MaterialsDocument5 pagesComposite MaterialsIqRa JaVedNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Composite Drive ShaftDocument8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Composite Drive ShaftInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Unit-I TO Composite MaterialsDocument40 pagesUnit-I TO Composite MaterialsSaisurendra VeerlaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NO. 10. Composite MaterialsDocument10 pagesLECTURE NO. 10. Composite MaterialsBizuayehu Tadesse AzeneNo ratings yet
- Flexural Properties Hybrid SFRC PDFDocument16 pagesFlexural Properties Hybrid SFRC PDFAndresEduardoRenjifoRestrepoNo ratings yet
- Project Report PDFDocument38 pagesProject Report PDFLogic Manju71% (14)
- تقرير جديد مواد هندسيهDocument42 pagesتقرير جديد مواد هندسيهداليا شاكر كحيط عامNo ratings yet
- IJEDR1504023Document50 pagesIJEDR1504023prathiksha anchanNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Retrofitted RC T-BEAM Using FRPDocument5 pagesExperimental Study On Retrofitted RC T-BEAM Using FRPInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Composite MaterialsDocument399 pagesComposite MaterialsCharlton S.Inao100% (1)
- Report of Fatigue and Fracture of Structure: Submitted byDocument16 pagesReport of Fatigue and Fracture of Structure: Submitted byameer hamzaNo ratings yet
- ChE 17 Report - CompositesDocument15 pagesChE 17 Report - CompositesZAIRA JOY UDANG SOTARIDONANo ratings yet
- Unit - I Introduction of Composites: Figure (1) : Composite Korean BowDocument61 pagesUnit - I Introduction of Composites: Figure (1) : Composite Korean Bowu2b11517100% (1)
- Efunda - Introduction To Com..Document2 pagesEfunda - Introduction To Com..Sujay DasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CompositeDocument14 pagesIntroduction To CompositeAhmed YASIR JAHINNo ratings yet
- Manuf Project 1usman 2danish-3talha 4izhar...Document10 pagesManuf Project 1usman 2danish-3talha 4izhar...Maria kani MagdaNo ratings yet
- Composite Materials Part 1Document300 pagesComposite Materials Part 1PethurajNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Mechanical Properties of Corn Fiber Reinforced With Biodegradable ResinDocument4 pagesInvestigation of Mechanical Properties of Corn Fiber Reinforced With Biodegradable ResinRaja SajinNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Fibre Project ReportDocument28 pagesBamboo Fibre Project ReportPranabhChowdhury ( mech)No ratings yet
- Hybrid Filament-Wound MaterialsDocument11 pagesHybrid Filament-Wound MaterialsHO LinNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Composite MaterialsDocument27 pagesSeminar On Composite MaterialsNikhilesh Kadukar100% (3)
- Hybrid CompositeDocument91 pagesHybrid Compositemanoharbyalal100% (3)
- Multifunctional MaterialsDocument24 pagesMultifunctional MaterialsGeanina IonescuNo ratings yet
- Anuual Report.1Document8 pagesAnuual Report.1Subhashis SitNo ratings yet
- Module-1: General Introduction M1: General Introduction M1.1 Introduction of CompositesDocument35 pagesModule-1: General Introduction M1: General Introduction M1.1 Introduction of CompositesANo ratings yet
- Industrial Material: Subject NameDocument28 pagesIndustrial Material: Subject NameHamza SaeedNo ratings yet
- A Review On Comparative Study of Polymer Matrix Composites and Metal Matrix CompositesDocument6 pagesA Review On Comparative Study of Polymer Matrix Composites and Metal Matrix CompositesIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Composites Mini ProjectDocument44 pagesComposites Mini ProjectRajaReddyNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Polymer CompositeDocument14 pages01 Introduction To Polymer CompositeMD Sunjin AhsunNo ratings yet
- Materials. The Constituent Materials of A Composite Have Significantly Different Properties. Further, ItDocument18 pagesMaterials. The Constituent Materials of A Composite Have Significantly Different Properties. Further, ItarravindNo ratings yet
- ME518-Part1_introductionDocument27 pagesME518-Part1_introductionRaja DiazNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 2Document57 pages07 Chapter 2namakkamkumarNo ratings yet
- LI ECC - 看图王 PDFDocument38 pagesLI ECC - 看图王 PDFxi.duNo ratings yet
- CompositeDocument20 pagesCompositeSuhbat Ali BozdarNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture Toughness: A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture ToughnessFrom EverandA Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture Toughness: A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture ToughnessNo ratings yet
- Numericals On Percent Atom EconomyDocument1 pageNumericals On Percent Atom EconomyPritamNo ratings yet
- Structural Composites or Layered CompositesDocument3 pagesStructural Composites or Layered CompositesPritam100% (1)
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionPritamNo ratings yet
- Bonding Process by AdhesivesDocument2 pagesBonding Process by AdhesivesPritam100% (1)
- Adhesive ActionDocument1 pageAdhesive ActionPritamNo ratings yet
- Theory Questions Q.1 What Are Adhesives ? Q.2 What Are The Factors Which Influence Adhesive Action ? Q.3 Explain Bonding Process by AdhesivesDocument1 pageTheory Questions Q.1 What Are Adhesives ? Q.2 What Are The Factors Which Influence Adhesive Action ? Q.3 Explain Bonding Process by AdhesivesPritamNo ratings yet
- 4.theory QuestionsDocument1 page4.theory QuestionsPritamNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Adhesive ActionDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Adhesive ActionPritam100% (5)
- Particle and Fiber Reinforced CompositesDocument1 pageParticle and Fiber Reinforced CompositesPritamNo ratings yet
- Numericals On Combustion of Solid and Liquid FuelsDocument2 pagesNumericals On Combustion of Solid and Liquid FuelsPritam100% (1)
- Numerical On Proximate and Ultimate AnalysisDocument1 pageNumerical On Proximate and Ultimate AnalysisPritam83% (6)
- Solid FuelsDocument5 pagesSolid FuelsPritamNo ratings yet
- Unsolved Numericals On Dulong's FormulaDocument1 pageUnsolved Numericals On Dulong's FormulaPritam100% (1)
- Cracking of Heavy OilDocument4 pagesCracking of Heavy OilPritamNo ratings yet
- BiodieselDocument1 pageBiodieselPritamNo ratings yet
- Knocking and Octane Number of PetrolDocument2 pagesKnocking and Octane Number of PetrolPritamNo ratings yet
- Antiknocking AgentsDocument3 pagesAntiknocking AgentsPritam100% (1)
- Physical State: Gaseous E.G. Water Gas, LPGDocument2 pagesPhysical State: Gaseous E.G. Water Gas, LPGPritamNo ratings yet
- Colorific Value of A FuelDocument1 pageColorific Value of A FuelPritamNo ratings yet
- Classification of AlloysDocument9 pagesClassification of AlloysPritamNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument8 pagesPowder MetallurgyPritamNo ratings yet
- Alumina Powder (Al O) : C Sic Crystalline Product + 2coDocument2 pagesAlumina Powder (Al O) : C Sic Crystalline Product + 2coPritamNo ratings yet