Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Duration Formulas and Calculations
Duration Formulas and Calculations
Uploaded by
SitiFarhanaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Duration Formulas and Calculations
Duration Formulas and Calculations
Uploaded by
SitiFarhanaCopyright:
Available Formats
Duration: Formulas and Calculations
W.L. Silber
1.
Definition
n
D=
Ct
(1 + r )
t =1
n
(t )
Ct
(1 + r )
t =1
2.
Explicit Sample Calculations
(a)
For an 8% coupon (annual pay) four-year bond with a yield to maturity of 10%,
we have:
80
80
80
1080
(1) +
( 2) +
(3 ) +
( 4)
2
3
1.10
(1.10)
(1.10)
(1.10) 4
D =
80
80
80
1080
+
+
+
2
3
1.10 (1.10)
(1.10)
(1.10) 4
D = 3.56
(b)
If the coupon were 4% rather than 8%, the formula would be:
40
40
40
1040
(1) +
( 2) +
(3 ) +
( 4)
2
3
1.10
(1.10)
(1.10)
(1.10) 4
D =
40
40
40
1040
+
+
+
2
3
1.10 (1.10)
(1.10)
(1.10) 4
D = 3.75
(c)
Finally, for a zero coupon bond with four years to maturity we have:
1080
( 4)
(1.10) 4
D=
=4
1080
(1.10) 4
3.
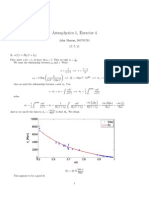
Duration Table for an 11.75% Coupon Bond
(1)
(2)
(3)
(3a)
(4)
(4a)
Coupon
MAT
YTM
DUR
YTM
DUR
11.75
3YR
11.75
2.70
6.75
2.71
11.75
11.75
5.14
6.75
5.36
11.75
10
11.75
6.38
6.75
6.90
11.75
20
11.75
8.48
6.75
10.43
11.75
30
11.75
9.17
6.75
12.54
Notes:
(1) Column 3a shows duration increasing with maturity, but less than proportionately
(2) Column 4a compared with 3a shows that a decline in yield to maturity (from
11.75% to 6.75%) increases duration, especially for the longer maturities.
You might also like
- Theory of Interest-Stephen Kellison-Solutions ManualDocument159 pagesTheory of Interest-Stephen Kellison-Solutions ManualGeOrGe GhOsT KoKKiNaKiS84% (43)
- CQF Exam 3 Questions and GuideDocument8 pagesCQF Exam 3 Questions and GuideTerry Law100% (1)
- Signals and Systems Kuestion (EE) PDFDocument48 pagesSignals and Systems Kuestion (EE) PDFsanthoshNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONs Introduction Dynamic Macroeconomic TheoryDocument9 pagesSOLUTIONs Introduction Dynamic Macroeconomic TheoryAdelaido García AndrésNo ratings yet
- Finance Exam Nr. 9 PDFDocument3 pagesFinance Exam Nr. 9 PDFGretaNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument14 pagesFinalHowardASmithNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics and Control SolutionsDocument22 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control Solutionsciotti620988% (8)
- Useful PropertiesDocument1 pageUseful PropertieschristopherovertonNo ratings yet
- Laplace TransformDocument1 pageLaplace Transformkhaleel_anwar2000No ratings yet
- 1st HWDocument9 pages1st HWrajesh.sha2378No ratings yet
- Class X A.PDocument39 pagesClass X A.PVivek Singh RanaNo ratings yet
- Targate'16: Answer Keys: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10Document19 pagesTargate'16: Answer Keys: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10Mahesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Sample Solutions For A Concise Introduction To MATLAB by William J. Palm IIIDocument12 pagesSample Solutions For A Concise Introduction To MATLAB by William J. Palm IIIMZSHBNo ratings yet
- Assignment SolutionDocument2 pagesAssignment SolutionMuhammad ArbazNo ratings yet
- FIN 630.assignmentDocument2 pagesFIN 630.assignmentMuhammad ArbazNo ratings yet
- FIN 630.assignmentDocument2 pagesFIN 630.assignmentMuhammad ArbazNo ratings yet
- Grupo4 TrabDeMatLabDocument4 pagesGrupo4 TrabDeMatLabVictor Luiz MattozoNo ratings yet
- HW1 PreviewDocument3 pagesHW1 PreviewDan DevlinNo ratings yet
- ECNG2011 Signals and Systems: 0 Number Real Any For, 1) (0 T 0) (Document12 pagesECNG2011 Signals and Systems: 0 Number Real Any For, 1) (0 T 0) (Marlon BoucaudNo ratings yet
- Solutions To The Problems in Introduction To Dynamic Macroeconomic TheoryDocument9 pagesSolutions To The Problems in Introduction To Dynamic Macroeconomic TheoryYutUyiNo ratings yet
- Derivation and Log-Linearization of Otsu (2007) 'S Small Open Economy ModelDocument46 pagesDerivation and Log-Linearization of Otsu (2007) 'S Small Open Economy ModelkeyyongparkNo ratings yet
- 13 19 (A, B, C, D)Document6 pages13 19 (A, B, C, D)Daun_ManggaNo ratings yet
- Astro 4 SolDocument6 pagesAstro 4 SolAdar SharonNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods For Differential Equations: Euler MethodDocument27 pagesNumerical Methods For Differential Equations: Euler Methodmicky kololuNo ratings yet
- F T Is A Periodic Function With A Period of 2Document5 pagesF T Is A Periodic Function With A Period of 2Jaclyn WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - IJMCAR-Common Fixed Point Theorem of Four MappingDocument6 pagesMathematics - IJMCAR-Common Fixed Point Theorem of Four MappingTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- TRIAL STPM Mathematics M 2 (JOHOR) SMK TunHussienOnnDocument8 pagesTRIAL STPM Mathematics M 2 (JOHOR) SMK TunHussienOnnSKNo ratings yet
- Theory of Interest Kellison Solutions Chapter 011Document15 pagesTheory of Interest Kellison Solutions Chapter 011Virna Cristina Lazo100% (1)
- CM1 Specimen Questions and SolutionsDocument4 pagesCM1 Specimen Questions and SolutionsarunNo ratings yet
- BSM DerivationDocument40 pagesBSM DerivationnasrullohNo ratings yet
- Pset Bond Pricing SolDocument4 pagesPset Bond Pricing Solankit banikNo ratings yet
- Hw1 Mfe Au14 SolutionDocument5 pagesHw1 Mfe Au14 SolutionWenn ZhangNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 SolutionsDocument8 pagesAssignment 3 SolutionsAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Answer Key 1: Tri Vi Dang Columbia University Corporate Finance Fall 2012Document4 pagesAnswer Key 1: Tri Vi Dang Columbia University Corporate Finance Fall 2012sykim657No ratings yet
- Unsolved Example of Coughanowr IPCDocument20 pagesUnsolved Example of Coughanowr IPCNeel PatelNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus BC 2016 Scoring GuidelinesDocument7 pagesAP Calculus BC 2016 Scoring Guidelines고봉기No ratings yet
- !probleme ST 2020Document16 pages!probleme ST 2020Marcela DobreNo ratings yet
- ST226 2012 SolutionsDocument5 pagesST226 2012 SolutionsGeorge WashNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Cit1101 Sequence & SericesDocument3 pagesMathematics Cit1101 Sequence & SericesGeorge KomehNo ratings yet
- Gate 2022 inDocument58 pagesGate 2022 inAlwisNo ratings yet
- 2008 CAPE Physics Unit 1Document4 pages2008 CAPE Physics Unit 1mondy1234No ratings yet
- Permutations & Combinations: Selected ExercisesDocument24 pagesPermutations & Combinations: Selected Exercisestalhaaftab728No ratings yet
- .CS (302) BC200413677 - 1639298941000Document4 pages.CS (302) BC200413677 - 1639298941000bc200413677No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SequencesDocument24 pagesChapter 3 SequencesIvan EphraimNo ratings yet
- Revision 2 MCQDocument7 pagesRevision 2 MCQSharmeen SayyadNo ratings yet
- Dupire Local VolatilityDocument15 pagesDupire Local VolatilityJohn MclaughlinNo ratings yet
- Gmatday 1Document27 pagesGmatday 1Long DinhNo ratings yet
- Some Spot Rate and Term Structure Models 8.1 Spot Rate ModelsDocument7 pagesSome Spot Rate and Term Structure Models 8.1 Spot Rate ModelsowltbigNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Discrete Fourier Analysis and Wavelets: Applications to Signal and Image ProcessingFrom EverandDiscrete Fourier Analysis and Wavelets: Applications to Signal and Image ProcessingNo ratings yet
- Solving Partial Differential Equation Applications with PDE2DFrom EverandSolving Partial Differential Equation Applications with PDE2DNo ratings yet