Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tut - 02 - DC Machines
Tut - 02 - DC Machines
Uploaded by
Tamy Lorena de SouzaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- DC Generators Problems & Answers-1Document14 pagesDC Generators Problems & Answers-1ahmed Alanazi100% (6)
- Tutorial DC MachinesDocument2 pagesTutorial DC MachinesLucas LeeNo ratings yet
- DC Machine Question BankDocument9 pagesDC Machine Question Bankafasdasd0% (2)
- Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesPractice Problemsdragon_warrior112456804No ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 DC Machines IIDocument2 pagesTutorial 7 DC Machines IIAkshat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 DriveDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 DriveswamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DC MachinesDocument2 pagesTutorial DC MachinesLucas LeeNo ratings yet
- Machine AssignmentDocument2 pagesMachine AssignmentPratik KanjilalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 Questions - 22046Document2 pagesTutorial 7 Questions - 22046anupalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines TutorialsDocument6 pagesElectrical Machines TutorialsAllegro Presto ModeratoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2ShabihNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering, I.I.T. MandiDocument1 pageDepartment of Electrical Engineering, I.I.T. MandiKuldeepNo ratings yet
- Assignments 1, 2, 3Document7 pagesAssignments 1, 2, 3Mude Kishore NaikNo ratings yet
- Finals Machines Ot 2 Lab PDFDocument18 pagesFinals Machines Ot 2 Lab PDFWenzy BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Ps 5Document1 pagePs 5Dawit B Melka100% (1)
- Electrical Machines - IDocument24 pagesElectrical Machines - IEmil Alturk0% (1)
- Assingment No.1 EEE 306Document2 pagesAssingment No.1 EEE 306ashish mathurNo ratings yet
- Machines SheetsDocument7 pagesMachines SheetsSammy BrioNo ratings yet
- Exercise Problems Electrical Machines 291010Document9 pagesExercise Problems Electrical Machines 291010Suleman AshrafNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering, NITR: Electrical Machines (EE 3011) 2 AssignmentDocument2 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering, NITR: Electrical Machines (EE 3011) 2 AssignmentManjitNo ratings yet
- Serie de Sincronas 2013-2Document5 pagesSerie de Sincronas 2013-2Manuel MartínezNo ratings yet
- Training Machines2, Homework in Electrical MachinesDocument5 pagesTraining Machines2, Homework in Electrical MachinesNGOUNENo ratings yet
- Tut 3Document3 pagesTut 3mohanrajgupta1950% (2)
- Assignment I EEE 2214 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Feb 2023 (2) (Original)Document1 pageAssignment I EEE 2214 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Feb 2023 (2) (Original)Jimmy MachariaNo ratings yet
- Tut 3 emDocument2 pagesTut 3 emBishal TiwariNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument12 pagesDC MachinesLevhie Ceasar Raro Ragas Jr.50% (4)
- DC Machines Tutorials (Part Two) : Uba/HTTTC Bambili - EPEDocument4 pagesDC Machines Tutorials (Part Two) : Uba/HTTTC Bambili - EPEGuefack JoanneNo ratings yet
- MakinaDocument51 pagesMakinaFarid RizvanliNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Dc MotorDocument8 pagesBài Tập Dc MotorHai HaNo ratings yet
- Ac Machines Assignment FinalsDocument2 pagesAc Machines Assignment FinalsJoy del RosarioNo ratings yet
- 2Document3 pages2aslamNo ratings yet
- Exercise On DC MachineDocument4 pagesExercise On DC MachineHanan ShayiboNo ratings yet
- AE10Document208 pagesAE10Ahmad Ezzaldeen Balol100% (2)
- Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EE - 101: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 09Document1 pageDepartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EE - 101: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 09Bharat SinghNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.gokulchandruNo ratings yet
- DCM QuestionsDocument2 pagesDCM Questionsljyandrew122122No ratings yet
- حل اسئلة الفصل الثاني مكائن مستمرةDocument4 pagesحل اسئلة الفصل الثاني مكائن مستمرةSetrax .sNo ratings yet
- Question 1: As Shown in Figure 1. A 6-Pole, Long-Shunt Lap-Wound CompoundDocument4 pagesQuestion 1: As Shown in Figure 1. A 6-Pole, Long-Shunt Lap-Wound Compoundالموعظة الحسنه chanelNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorsDocument2 pagesDC Generatorssk11051321No ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - DC MotorsDocument35 pagesLesson 8 - DC MotorsKaelel BilangNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument4 pagesIndian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur Department of Electrical EngineeringKool PrashantNo ratings yet
- Ee 233 DC Motor Prob. For StudentDocument2 pagesEe 233 DC Motor Prob. For StudentchristinejoymelenvillarinNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledMagarsaa Qana'iiNo ratings yet
- Assignment (ELE3307)Document3 pagesAssignment (ELE3307)●●●●●●●1No ratings yet
- Assignment (DC Motors and Measurement)Document1 pageAssignment (DC Motors and Measurement)RoronoaNo ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument4 pagesAssignment Iamith gupta0% (1)
- Dc-Machine 2Document2 pagesDc-Machine 2Bsal SokoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document8 pagesAssignment 2phultushiblsNo ratings yet
- Assignmentsolutionselected 150208132823 Conversion Gate02Document30 pagesAssignmentsolutionselected 150208132823 Conversion Gate02apelokayaNo ratings yet
- Ee311 Test 1Document1 pageEe311 Test 1Efron MdindileNo ratings yet
- Lista de Ejercicios 5a - Intro - Máquinas de InducciónDocument3 pagesLista de Ejercicios 5a - Intro - Máquinas de InducciónStiven Garcia BedoyaNo ratings yet
- Tutorials DC MachinesDocument1 pageTutorials DC MachinesMohd Rashid SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Set No. 1Document5 pagesSet No. 1Geethika VarmaNo ratings yet
- Ej Motor Ess Ín CronosDocument2 pagesEj Motor Ess Ín CronosJunior BolañosNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Question On DC MachinesDocument1 pageAssignment 1 Question On DC MachinesDeepti MishraNo ratings yet
- ASPLDocument3 pagesASPLMohammedNewazNo ratings yet
- Last Date of Submission:07.05.2016Document2 pagesLast Date of Submission:07.05.2016zubbbuNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Doc5 BrocDocument2 pagesDoc5 BrocTamy Lorena de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Doc4 PastaDocument2 pagesDoc4 PastaTamy Lorena de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Doc2 TunaDocument4 pagesDoc2 TunaTamy Lorena de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Project4 15Document43 pagesProject4 15Tamy Lorena de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Ahrs For Adafruits 9 Dof 10 Dof BreakoutDocument24 pagesAhrs For Adafruits 9 Dof 10 Dof BreakoutTamy Lorena de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Doc1 ChickenDocument4 pagesDoc1 ChickenTamy Lorena de SouzaNo ratings yet
Tut - 02 - DC Machines
Tut - 02 - DC Machines
Uploaded by
Tamy Lorena de SouzaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tut - 02 - DC Machines
Tut - 02 - DC Machines
Uploaded by
Tamy Lorena de SouzaCopyright:
Available Formats
The University of Newcastle
School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
ELEC3130 Electric Machines and Power Systems
Tutorial 2 Questions
T. Summers
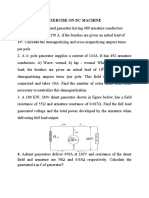
1. When operated at rated voltage, a 230 volt shunt motor runs at 1800 rpm at full load and at no-load. The full load
armature current is 50 amps. The shunt field winding has 1500 turns per pole. The resistance of the armature circuit is
0.2 . The magnetisation characteristic at 1800 rpm is:
generated emf
field current
200
0.53
210
0.59
220
0.65
230
0.73
240
0.81
250
0.95
(a) Compute the demagnetising effect of armature reaction at full load in ampere-turns per pole.
(b) A long shunt cumulative series winding having six turns per pole and a resistance of 0.055 is added to the
machine. Compute the speed at full load current and rated voltage, with the same shunt field circuit resistance as
in part (a).
(c) With the series field winding of part (b) installed, compute the internal starting torque if the starting armature
current is limited to 90 amps and the shunt field current has its nominal value. Assume that the corresponding
demagnetising effect of armature reaction is 230 ampere-turns/pole.
[Answer: (a) 120 At/pole; (b) 1611 rpm; (c) 118.9 Nm]
2.
The open circuit characteristic data of a 25hp, 250 volt, 85 amp shunt motor taken at 1800 rpm is given:
shunt field current (A)
terminal voltage (V)
0.6
150
0.8
185
1.0
214
1.2
237
1.3
245
1.5
260
1.7
270
2.0
280
2.4
290
The resistance of the shunt field circuit, including the field rheostat, is 185 ohms and the resistance of the armature
circuit (including the interpole windings and brushes) is 0.08 ohm. The field winding has 3000 turns per pole. The
demagnetising effect of armature reaction, at rated armature current, is 0.08 amps in terms of the shunt field current.
The friction, windage and core losses (known as the no load rotational losses) are 1500 W and the stray load loss is
assumed as 1% of the output. The field circuit resistance may be assumed to be constant at 185 ohms. Calculate the
following when the motor draws 85 amps from the line:
(a) The speed of the motor.
(b) The electromechanical power
(c) The mechanical output power.
(d) The output torque.
(e) The motor efficiency.
You might also like
- DC Generators Problems & Answers-1Document14 pagesDC Generators Problems & Answers-1ahmed Alanazi100% (6)
- Tutorial DC MachinesDocument2 pagesTutorial DC MachinesLucas LeeNo ratings yet
- DC Machine Question BankDocument9 pagesDC Machine Question Bankafasdasd0% (2)
- Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesPractice Problemsdragon_warrior112456804No ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 DC Machines IIDocument2 pagesTutorial 7 DC Machines IIAkshat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 DriveDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 DriveswamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DC MachinesDocument2 pagesTutorial DC MachinesLucas LeeNo ratings yet
- Machine AssignmentDocument2 pagesMachine AssignmentPratik KanjilalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 Questions - 22046Document2 pagesTutorial 7 Questions - 22046anupalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines TutorialsDocument6 pagesElectrical Machines TutorialsAllegro Presto ModeratoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2ShabihNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering, I.I.T. MandiDocument1 pageDepartment of Electrical Engineering, I.I.T. MandiKuldeepNo ratings yet
- Assignments 1, 2, 3Document7 pagesAssignments 1, 2, 3Mude Kishore NaikNo ratings yet
- Finals Machines Ot 2 Lab PDFDocument18 pagesFinals Machines Ot 2 Lab PDFWenzy BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Ps 5Document1 pagePs 5Dawit B Melka100% (1)
- Electrical Machines - IDocument24 pagesElectrical Machines - IEmil Alturk0% (1)
- Assingment No.1 EEE 306Document2 pagesAssingment No.1 EEE 306ashish mathurNo ratings yet
- Machines SheetsDocument7 pagesMachines SheetsSammy BrioNo ratings yet
- Exercise Problems Electrical Machines 291010Document9 pagesExercise Problems Electrical Machines 291010Suleman AshrafNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering, NITR: Electrical Machines (EE 3011) 2 AssignmentDocument2 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering, NITR: Electrical Machines (EE 3011) 2 AssignmentManjitNo ratings yet
- Serie de Sincronas 2013-2Document5 pagesSerie de Sincronas 2013-2Manuel MartínezNo ratings yet
- Training Machines2, Homework in Electrical MachinesDocument5 pagesTraining Machines2, Homework in Electrical MachinesNGOUNENo ratings yet
- Tut 3Document3 pagesTut 3mohanrajgupta1950% (2)
- Assignment I EEE 2214 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Feb 2023 (2) (Original)Document1 pageAssignment I EEE 2214 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Feb 2023 (2) (Original)Jimmy MachariaNo ratings yet
- Tut 3 emDocument2 pagesTut 3 emBishal TiwariNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument12 pagesDC MachinesLevhie Ceasar Raro Ragas Jr.50% (4)
- DC Machines Tutorials (Part Two) : Uba/HTTTC Bambili - EPEDocument4 pagesDC Machines Tutorials (Part Two) : Uba/HTTTC Bambili - EPEGuefack JoanneNo ratings yet
- MakinaDocument51 pagesMakinaFarid RizvanliNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Dc MotorDocument8 pagesBài Tập Dc MotorHai HaNo ratings yet
- Ac Machines Assignment FinalsDocument2 pagesAc Machines Assignment FinalsJoy del RosarioNo ratings yet
- 2Document3 pages2aslamNo ratings yet
- Exercise On DC MachineDocument4 pagesExercise On DC MachineHanan ShayiboNo ratings yet
- AE10Document208 pagesAE10Ahmad Ezzaldeen Balol100% (2)
- Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EE - 101: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 09Document1 pageDepartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EE - 101: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 09Bharat SinghNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.gokulchandruNo ratings yet
- DCM QuestionsDocument2 pagesDCM Questionsljyandrew122122No ratings yet
- حل اسئلة الفصل الثاني مكائن مستمرةDocument4 pagesحل اسئلة الفصل الثاني مكائن مستمرةSetrax .sNo ratings yet
- Question 1: As Shown in Figure 1. A 6-Pole, Long-Shunt Lap-Wound CompoundDocument4 pagesQuestion 1: As Shown in Figure 1. A 6-Pole, Long-Shunt Lap-Wound Compoundالموعظة الحسنه chanelNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorsDocument2 pagesDC Generatorssk11051321No ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - DC MotorsDocument35 pagesLesson 8 - DC MotorsKaelel BilangNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument4 pagesIndian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur Department of Electrical EngineeringKool PrashantNo ratings yet
- Ee 233 DC Motor Prob. For StudentDocument2 pagesEe 233 DC Motor Prob. For StudentchristinejoymelenvillarinNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledMagarsaa Qana'iiNo ratings yet
- Assignment (ELE3307)Document3 pagesAssignment (ELE3307)●●●●●●●1No ratings yet
- Assignment (DC Motors and Measurement)Document1 pageAssignment (DC Motors and Measurement)RoronoaNo ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument4 pagesAssignment Iamith gupta0% (1)
- Dc-Machine 2Document2 pagesDc-Machine 2Bsal SokoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document8 pagesAssignment 2phultushiblsNo ratings yet
- Assignmentsolutionselected 150208132823 Conversion Gate02Document30 pagesAssignmentsolutionselected 150208132823 Conversion Gate02apelokayaNo ratings yet
- Ee311 Test 1Document1 pageEe311 Test 1Efron MdindileNo ratings yet
- Lista de Ejercicios 5a - Intro - Máquinas de InducciónDocument3 pagesLista de Ejercicios 5a - Intro - Máquinas de InducciónStiven Garcia BedoyaNo ratings yet
- Tutorials DC MachinesDocument1 pageTutorials DC MachinesMohd Rashid SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Set No. 1Document5 pagesSet No. 1Geethika VarmaNo ratings yet
- Ej Motor Ess Ín CronosDocument2 pagesEj Motor Ess Ín CronosJunior BolañosNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Question On DC MachinesDocument1 pageAssignment 1 Question On DC MachinesDeepti MishraNo ratings yet
- ASPLDocument3 pagesASPLMohammedNewazNo ratings yet
- Last Date of Submission:07.05.2016Document2 pagesLast Date of Submission:07.05.2016zubbbuNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Doc5 BrocDocument2 pagesDoc5 BrocTamy Lorena de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Doc4 PastaDocument2 pagesDoc4 PastaTamy Lorena de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Doc2 TunaDocument4 pagesDoc2 TunaTamy Lorena de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Project4 15Document43 pagesProject4 15Tamy Lorena de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Ahrs For Adafruits 9 Dof 10 Dof BreakoutDocument24 pagesAhrs For Adafruits 9 Dof 10 Dof BreakoutTamy Lorena de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Doc1 ChickenDocument4 pagesDoc1 ChickenTamy Lorena de SouzaNo ratings yet