Professional Documents
Culture Documents
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers Chap 10 2nd Ed
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers Chap 10 2nd Ed
Uploaded by
Christian WelshCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers Chap 10 2nd Ed
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers Chap 10 2nd Ed
Uploaded by
Christian WelshCopyright:
Available Formats
.
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
Well Control Certification
Land rigs and Jack-ups (Surface Equipment)
7.1
Ram preventers API Spec 16A
Drift tests
7.1.1 The drift test is required on ram BOP, annular BOP, hydraulic
connectors, drilling spools and adapters.
7.1.2 The equipment size and rated working pressure: TABLE 1-API
16A.
API Size Designation Rated WP (psi)
Drift diam. (inch)
7-1/16
2,000 thru 20,000
7.032
9
2,000 thru 15,000
8.970
11
2,000 thru 20,000 10.790
13-5/8
2,000 thru 15,000 13.595
16-3/4
2,000 thru 10,000 16.720
18-3/4
5,000 thru 15,000 18.720
20-3/4
3,000
20.720
21-1/4
2,000 thru 10,000 21.220
26-3/4
2,000 thru 3,000
26.720
30
2,000 thru 3,000
29.970
API Spec 16A
chapter 7.5.8.4
API Spec 16 A
chapter 4.2.2
7.1.3
Pass a drift mandrel through the bore of the assembly after all API Spec 16 A
pressure testing.
chapter 7.5.8.4.1
7.1.4 The drift mandrel diameter shall be in accordance with the drift API Spec 16 A
diameter in Table 1 with a tolerance of plus 0.010 inch and
chapter
minus 0.000 inch.
7.5.8.4.1.1
7.1.5 The drift mandrel gauge length shall be at least 2 inches longer API Spec 16 A
than any cavity that intersects the bore, but no less than 12
chapter
inches.
7.5.8.4.1.2
Temperature ratings
7.1.6 The minimum temperature is the lowest ambient temperature API Spec 16A
the equipment may be subjected.
chapter 4.2.2
7.1.7 The maximum temperature is the highest temperature of the
API Spec 16A
fluid which may flow through the equipment.
chapter 4.2.2
7.1.8 Equipment shall be designed for metallic parts to operate with API Spec 16A
the temperature shown in Table 2.
chapter 4.2.2.1
Table 2 Temperature ratings for Metallic Materials:
Classification
Operating range (degrees Fahrenheit)
T-75
75F to 250F
T-20
20F to 250F
T-0
0F to 250F
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
7.1.9 The temperature class of the wellbore non metallic components API Spec 16A
shall be as follows:
chapter 8.3.4.2
Lower limit (first digit)
Upper Limit (second digit)
A
-15 F
A
180 F
B
0F
B
200 F
C
10 F
C
220 F
D
20 F
D
250 F
E
30 F
E
300 F
F
40 F
F
350 F
G
other
G
other
X
(see note)
X
(see note)
Note: These components may carry a temperature class of 40
F to 180F without performing temperature verification testing
provided they are marked as temperature verification testing
provided they are marked as temperature class XX.
Example "EB" has a temperature class of 30 F to 200 F.
7.1.10 Temperature Rating Metallic Materials
API Spec 16A
chapter 8.4.2.4
Operating rate
Code DD
from
- 75 F to 250 F
75
from
- 20 F to 250 F
20
from
0 F to 250 F
00
16B hubs
7.1.11 Dimensions for the type 16B integral hubs shall be conform to API Spec 16A
table 5 of page 10 API Spec 16A.
chapter
4.3.4.2.2.2.1
7.1.12 Dimensions for the type 16B hubs blind hubs shall be conform API Spec 16A
Figure 3 page 9 API Spec 16A.
chapter
4.3.4.2.2.2.1
16BX hubs
7.1.13 Dimensions for the type 16BX integral hubs shall be conform API Spec 16A
to table 6.7 or 8 of API Spec 16A.
chapter
4.3.4.2.3.2.1
7.1.14 Dimensions for the type 16BX blind l hubs shall be conform to API Spec 16A
Figure 3 of API Spec 16A.
chapter
4.3.4.2.3.2.1
7.1.15 Dimensions for all ring groves shall conform to Tables 6,7, or 8 API Spec 16A
of API Spec 16A.
chapter
4.3.4.2.3.2.1
7.1.16 Type BX hubs may be manufactured with corrosion resistant API Spec 16A
overlays in the ring grooves. Prior to overlay the ring grooves chapter 4.3.4.2.3.4
shall conform to API Specification 6A.
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
Clamps
7.1.17 All clamps shall have grooves in their bores with 25 (+/-0.25) API Spec 16A
degree angles to fit API 16B and 16BX hubs.
chapter 4.3.5.2.3.3
7.1.18 All 25 degree surfaces in clamp grooves shall have a surface API Spec 16A
finish of 32 RMS or less.
chapter 4.3.5.2.3.4
86
The clamp bore shall provide a minimum of 0.125 inch radial API Spec 16A
7.1.19 clearance around the hub neck in the made up condition on all chapter 4.3.5.2.3.6
hubs it is designed to fit.
7.1.20 Spherical face heavy nuts or spherical washers shall be used to API Spec 16A
minimize potential bending in bolts.
chapter4.3.5.2.3.8
Use of gaskets
7.1.21 Type R, RX and BX ring-joint gaskets are used in flanged,
API Spec 16A
studded and hub connections. Type R and RX gaskets are
chapter 4.3.7.1
interchangeable in type R ring grooves. Only type RX gaskets
are to be used with SR ring grooves. Only type BX gaskets are
to be used with 6BX grooves. Type RX and BX gaskets are not
interchangeable.
Hydrostatic proof testing
7.1.22 Hydrostatic proof testing shall be as shown in Table 18 of API API Spec 16A
Spec 16A.
chapter 7.5.8.6.2.2
7.1.23 Table 18 - Hydrostatic Test Pressure (psi)
API Spec 16A
chapter 7.5.8.6.3.1
Rated WP
API 13-5/8 + smaller
API 16-3/4 + larger.
2,000
4,000
3,000
3,000
6,000
4,500
5,000
10,000
10,000
10,000
15,000
15,000
15,000
22,500
22,500
20,000
30,000
------
7.1.24 The hydrostatic proof test shall consist of three steps:
API Spec 16A
chapter 7.5.8.6.4
a) the initial pressure-holding period of not less than 3 minutes.
b) the reduction of the pressure to zero.
c) the second pressure-holding period of not less than 15
minutes.
7.1.25 The timing of the test shall not start until the test pressure has API Spec 16A
been stabilized within the manufacturer's specified range and chapter 7.5.8.6.4.1
the external surfaces have been thoroughly dried.
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
Hydraulic operating chamber test
7.1.26 The hydraulic operating chamber shall be tested at a minimum API Spec 16A
test pressure equal to 1.5 times the operating chambers rated chapter 7.5.8.6.3.2
working pressure.
Closed preventer test
7.1.27 Each ram and annular blow out preventer shall be subjected to API Spec 16A
a closed preventer test after the hydraulic proof test. The
chapter 7.5.8.7.1.1
hydraulic operating system pressure used shall be equal to or
less than the manufacturer's specified operating pressure.
7.1.28 The timing of all closed preventer tests shall not start until the API Spec 16A
test pressure has stabilized.
chapter 7.5.8.7.1.2
7.1.29 Closed preventer tests shall be performed at low and high
API Spec 16 A
pressure with the low pressure tests always preceding the high chapter 7.5.8.7.1.3
pressure test.
7.1.30 A pressure of 200 to 300 psi shall be applied and held below API Spec 16A
the closed ram or annular packing.
chapter
7.5.8.7.1.3.1
7.1.31 A pressure at least equal to the rated working pressure of the API Spec 16 A
preventer shall be applied and held below the closed ram or
chapter
annular packing unit for a time period of not less than 10
7.5.8.7.1.3.2
minutes after stabilization.
7.1.32 Variable bore rams shall be tested on the minimum and the
API Spec 16A
maximum sizes for their range.
chapter 7.5.8.7.3
API Spec 16A
7.1.33 Each ram preventer equipped with shear blind rams shall be
subjected to a shearing test. As a minimum this test requires chapter 7.5.8.7.4
shearing of a drill pipe as follows: 3-1/2 inch and13.3 lb/ft
grade E for 7-1/16 inch BOPs, 5 inch 19.5 lb/ft grade E for 11
inch BOPs and 5 inch 19.5 lb/ft grade G for 13-5/8 inch BOPs
and all larger BOPs. These tests shall be performed without
tension on the pipe and with zero well bore pressure. Shearing
and sealing shall be achieved in a single operation. The piston
closing pressure shall not exceed the manufacturer's rated
working pressure for the operating system.
7.1.34 Each blow out preventer equipped with a hydraulic ram locking API Spec 16A
system shall be pressure tested with the locking system
chapter 7.5.8.7.5
engaged. The preventer shall be tested in accordance with API
Spec 16 A chapter 7.5.8.7.1.3.1 and chapter 7.5.8.7.1.3.2
after the rams are closed, the locks engaged and then all
operating pressure(s) released.
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
Material requirements
Metallic parts
7.1.35 A written manual specification shall be required for all metallic API Spec 16A
pressure containing or pressure controlling parts.
chapter 5.2.1
The manufacturer's written specified requirements for metallic
materials shall define the following:
a. Material composition with tolerance
b. Material qualification
c. Allowable melting practice(s)
d. Forming practice(s)
e. Heat treatment procedure including cycle type time and
temperature with tolerances, heat treatment equipment and
cooling media
f. NDE requirements
g. Mechanical property requirements.
Non-metallic parts
7.1.36 Each manufacturer shall have written specifications for all
API Spec 16A
elastomeric materials used in the production of drill through
chapter 5.2.2
equipment. These specifications shall include the following
physical test limits for acceptance and control:
a. Hardness per ASTM D2240 or D1415
b. Normal stress-strain properties per ASTM D412 or D1414
c. Compression per ASTM D395 or D1414
d. Immersion test per ASTM D471 0r D1414
Weld repairs
7.1.37 All repair welding shall be done in accordance with the
API Spec 16A
manufacturer's written specification. All major repair welds
chapter 6.2.3.1
performed subsequent to original heat treatment shall be
mapped.
7.1.38 Welding and completed welds shall meet the requirement of
API Spec 16A
chapter 7 of API Spec 16A (Quality Control Requirements).
chapter 6.2.3.2
Measuring and testing equipment
7.1.39 All equipment used to inspect, test or examine material or
API Spec 16A
other equipment shall be identified, controlled, calibrated and chapter 7.2.1
adjusted at specified intervals in accordance with documented
manufacturer's instructions, and shall be consistent with
referenced industry standards to maintain the accuracy
required by this specification.
7.1.40 Dimensional measuring equipment shall be controlled and
API Spec 16A
calibrated by the methods specified in MIL-STD-120 to
chapter 7.2.2
maintain the accurancies specified by API and the
manufacturer's specification. Dimensional measuring
equipment not covered by MIL-STD-120 shall be controlled and
calibrated in accordance with the manufacturer's written
specification.
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
Pressure measuring devices
7.1.41 Test measuring devices shall be either pressure gages or
API Spec 16A
pressure transducers and shall be accurate to at least +/-0.5 chapter 7.2.3.1
percent of full scale range
7.1.42 Pressure gauges shall have a minimum face diameter of 4.5
API Spec 16A
inches. Pressure measurements shall be made at not less than chapter 7.2.3.2
25 percent nor more than 75 percent of the full pressure span
of the gauge
7.1.43 Pressure measuring devices shall be periodically recalibrated
API Spec 16A
with a master pressure measuring device or a dead weight
chapter 7.2.3.3
tester at 25 percent, 50 percent and 75 percent of full scale.
7.1.44 Calibration intervals shall be established for calibrations based API Spec 16A
on repeatability and degree of usage of the pressure measuring chapter 7.2.3.4.1
devices
7.1.45 Calibration intervals shall be a maximum of three months until API Spec 16A
recorded calibration history can be determined by the
chapter 7.2.3.4.2
manufacturer and new intervals established.
Dimensional verification
7.1.46 Critical dimensions as defined by the manufacturer shall be
API Spec 16A
documented for each part and such documentation shall be
chapter 7.5.1.4
retained by the manufacturer in accordance chapter 7.6 API
Spec 16A. The manufacturer shall define and document the
extent to which dimensions shall be verified.
Surface NDE of ferromagnetic materials
7.1.47 All accessible well fluid wetted surfaces and all accessible
API Spec 16A
sealing surfaces of each finished part shall be inspected after chapter 7.5.1.8.1.1
final heat treatment and after final machining operations by
either magnetic particle (MP) or liquid penetrant (LP) method.
Surface NDE of non-ferromagnetic materials
7.1.48 All accessible well fluid wetted surfaces of each finished part API Spec 16A
shall be inspected after final heat treatment and after final
chapter 7.5.1.8.1.2
machining operations by LP method.
7.1.49 MP examination shall be in accordance with procedures
API Spec 16A
specified in ASTM E 709. Prods are not permitted on well fluid chapter 7.5.1.8.2.1
wetted surfaces or sealing surfaces.
7.1.50 LP examination shall be in accordance with procedures
API Spec 16A
specified in ASTM E-165.
chapter 7.5.1.8.2.2
Weld NDE
7.1.51 One hundred percent of all pressure containing welds, repair
API Spec 16A
and weld metal overlay welds and repaired fabrication welds chapter 7.5.1.12.1
shall be examined by either MP or LP methods after all
welding, post weld treatment and machining operations are
completed. The examination shall include 1/2 inch of adjacent
base material on both sides of the weld.
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
7.1.52 All repair welds shall be examined using the same methods and API Spec 16A
acceptance criteria used in examining the base material.
chapter 7.5.1.13.1
Weld NDE volumetric for fabrication
7.1.53 One hundred percent of all pressure containing welds shall be API Spec 16A
chapter 7.5.1.14.1
examined by either radiography, ultrasonic or acoustic
emission methods after all welding and post-weld heat
treatment. All repair welds where the repair is greater than 25
percent of the original wall thickness or 1 inch (whichever is
less) shall be examined by either radiography, ultrasonic or
acoustic emission methods after all welding and post-weld
heat treatment. Examinations shall include at least 1/2- inch
of adjacent base material on all sides of the welds.
7.1.54 Radiographic examinations shall be performed in accordance API Spec 16A
with procedures specified in ASTM E94, to a minimum
chapter
equivalent sensitivity of 2 percent. Both the X-ray and gamma7.5.1.14.2.1
ray radiation sources are acceptable within the inherent
thickness range limitation of each.
7.1.55 Ultrasonic examinations shall be performed in accordance
API Spec 16A
with procedures specified in ASME Boiler and Pressure vessel chapter
Code V, article 5.
7.5.1.14.3.1
7.1.56 Acoustic emission (AE) examinations shall be performed in
API Spec 16A
accordance with procedures specified in ASTM E 569. The
chapter
acoustic emission examination shall be conducted throughout 7.5.1.14.4.1
the duration of the hydrostatic "in-plant" test.
7.1.57 All accessible pressure-containing, non pressure containing
API Spec 16A
and major repairs shall be hardness tested.
chapter 7.5.1.15.1
Recommended Practice API rules RP 53
Surface BOP arrangements
7.1.58 Every installed ram BOP should have, as a minimum, a
API RP 53 chapter
working pressure equal to the maximum anticipated surface 6.2
pressure to be encountered.
7.1.59 Ram type preventers should be equipped with extension hand API RP 53 chapter
wheels or hydraulically operated locks.
6.3
API RP 53 chapter
7.1.60 Drilling spools for BOP stacks should meet the following
6.6.1 a, b and c
minimum qualifications: a. 3K and 5K arrangements should
have two side outlets no smaller than a 2-inch (5.08 cm)
nominal diameter and be flanged, studded, or hubbed. 10K,
15K and 20K arrangements should have two side outlets, one
3-inch (7.62 cm) and one 2-inch (5.08 cm) nominal diameter
as a minimum, and be flanged, studded, or hubbed. b. Have a
vertical bore diameter the same internal diameter as the
mating BOPs and at least equal to the maximum bore of the
uppermost casing/tubing head. c. Have a rated working
pressure equal to the rated working pressure of the installed
ram BOP.
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
7.1.61 For drilling operations, wellhead outlets should not be
API RP 53
employed for choke or kill lines.
6.6.2
7.1.62 All blowout prevention components that may be exposed to API RP 53
well pressure should be tested first to a low pressure of 200 17.3.2.1
to 300 psi (1.38 to 2.1 MPa) and then to a high pressure.
7.1.63 When performing the low pressure test, do not apply a higher API RP 53
pressure and bleed down to the low test pressure. The higher 17.3.2.1
pressure could initiate a seal that may continue to seal after
the pressure is lowered and therefore misrepresenting a low
pressure condition.
7.1.64 A stable low test pressure should be maintained for at least 5 API RP 53
minutes.
17.3.2.1
7.1.65 The initial high pressure test on components that could be
API RP 53
exposed to well pressure (BOP stack, choke manifold, and
17.3.2.2
coke/kill lines) should be to the rated working pressure of the
ram BOPs or to the rated working pressure of the wellhead
that the stack is installed on, whichever is lower.
7.1.66 Initial pressure tests are defined as those tests that should be API RP 53
performed on location before the well is spudded or before
17.3.2.2
the equipment is put into operational service.
7.1.67 Initial pressure tests on hydraulic chambers of ram BOPs and API RP 53
hydraulically operated valves should be to the maximum
17.3.2.4
operating pressure recommended by the manufacturer.
7.1.68 The test should be run on both the opening and the closing API RP 53
chambers.
17.3.2.4
7.1.69 Pressure should be stabilized for at least 5 minutes.
API RP 53
17.3.2.4
7.1.70 Subsequent pressure tests are typically performed on
API RP 53
hydraulic chambers only between wells or when the
17.3.2.4
equipment is reassembled.
7.1.71 The initial pressure test on the closing unit valves, manifolds, API RP 53
gauges, and BOP hydraulic control lines should be to the
17.3.2.5
rated working pressure of the control unit.
7.1.72 Subsequent pressure tests of closing unit systems are
API RP 53
typically performed following the disconnection or repair of
17.3.2.5
any operating pressure containment seal in the closing unit
system, but limited to the affected component.
7.1.73 Pressure tests on the well control equipment should be
API RP 53
conducted at least: a. Prior to spud or upon installation. b.
17.3.3
After the disconnection or repair of any pressure containment
seal in the BOP stack, choke line, or choke manifold, but
limited to the affected component. c. Not to exceed 21 days.
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
7.1.74 Well control equipment should be pressure tested with water. API RP
Air should be removed from the system before test pressure 17.3.5
is applied. Control systems and hydraulic chambers should be
tested using clean control system fluids with lubricity and
corrosion additives for the intended service and operating
temperatures.
7.1.75 Pressure gauges and chart recorders should be used and all API RP
testing results recorded. Pressure measurements should be
17.3.6
made at not less than 25 percent nor more than 75 percent
of the full pressure span of the gauge.
7.1.76 The results of all BOP equipment pressure and function tests API RP
shall be documented and include, as a minimum, the testing 17.3.7
sequence, the low and high test pressures, the duration of
each test, and the results of the respective component tests.
7.1.77 Pressure tests shall be performed with a pressure chart
API RP
recorder or equivalent data acquisition system and signed by 17.3.7
pump operator, contractor's tool pusher, and operating
company representative.
7.1.78 Problems observed during testing and any actions taken to
API RP
remedy the problems should be documented.
17.3.7
7.1.79 Manufacturers should be informed of well control equipment API RP
that fails to perform in the field. (Refer to API Specification
17.3.7
16A).
Surface BOP stack equipment
7.1.80 Fixed bore pipe rams should be tested only on the pipe OD
API RP
size that matches the installed pipe ram blocks.
17.5.4
7.1.81 Variable bore rams should be initially pressure tested on the API RP
largest and smallest OD pipe sizes that may be used during 17.5.5
the well operations.
7.1.82 Blind ram BOPs and blind shear ram BOPs should not be
API RP
tested when pipe is in the stack.
17.5.6
7.1.83 The capability of the shear ram and ram operator should be API RP
verified with the BOP manufacturer for the planned drill
17.5.6
string.
7.1.84 The shear ram and preventer design and/or metallurgical
API RP
differences among drill pipe manufacturers may require high 17.5.6
closing pressures for shear operations.
7.1.85 Prior to testing each ram BOP, the secondary rod seals
API RP
(emergency pack-off assemblies) should be checked to ensure 17.5.7
the seals have not been energized.
7.1.86 Should the ram shaft seal leak during the test, the seal shall API RP
be repaired rather than energizing the secondary packing.
17.5.7
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
7.1.87 Ram BOPs equipped with ram locks should be pressure tested API RP 53
with ram locks in the closed position and closing pressure
17.5.8
bled to zero.
7.1.88 Manual locks either screw clockwise or counter-clockwise, to API RP 53
hold the rams closed.
17.5.8
7.1.89 Hand wheels should be in place and the threads on the ram API RP 53
locking shaft should be in a condition that allows the locks to 17.5.8
be easily operated.
7.1.90 The BOP elastomeric components that may be exposed to
API RP 53
well fluids should be verified by the BOP manufacturer as
17.5.9
appropriate for the drilling fluids to be used and for the
anticipated temperatures to which exposed.
7.1.91 Consideration should be given to the temperature and fluid
API RP 53
conditions during well testing and completion operations.
17.5.9
7.1.92 Manufacturers' markings for BOP elastomeric components
API RP 53
should include the durometer hardness, generic type of
17.5.9.1
compound, date of manufacture, part number, and operating
temperature range of the component.
7.1.93 Consider replacing critical BOP elastomeric components on
API RP 53
well control equipment that has been out of service for six (6) 17.5.9.2
months or longer.
7.1.94 Flexible choke and kill lines should be tested to the same
API RP 53
pressure, frequency, and duration as the ram BOPs.
17.5.10
7.1.95 The drill pipe test joint and casing ram test sub should be
API RP 53
constructed of pipe that can withstand the tensile, collapse, 17.5.12
and internal pressures that will be placed on them during
testing operations.
Major inspections
7.196 After every 3-5 years of service, the BOP stack, choke
API RP 53
17.10.3
manifold and diverter components should be disassembled
and inspected in accordance with the manufacturers
guidelines.
7.1.97 Elastomeric components should be changed out and surface API RP 53
finishes should be examined for wear and corrosion. Critical 17.10.3
dimensions should be checked against the manufacturer's
allowable wear limits. Individual components can be
inspected on a staggered schedule.
7.1.98 A full internal and external inspection of the flexible choke
API RP 53
and kill lines should be performed in accordance with the
17.10.3
equipment manufacturer's guidelines.
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
10
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
7.1.99 Manufacturer's installation, operation, and maintenance (IOM) API RP 53
manuals should be available on the rig for all the BOP
17.11.1
equipment installed on the rig.
7.1.100 Studs and nuts should be checked for proper size and grade. API RP 53
Using the appropriate lubricant, torque should be applied in a 17.11.2
criss-cross manner to the flange studs. All bolts should then
be rechecked for proper torque as prescribed in API
Specification 6A. When making up connections, excessive
force should not be required to bring the connections into
alignment.
7.1.101 Ring gaskets coated with a resilient material such as rubber orAPI RP 53
polyetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) should not be used. Due to the 17.11.2
limited amount of deformation which a groove can make in a
ring as it is compressed during installation, it is not
recommended to reuse ring gaskets.
7.1.102 When making up proprietary clamp hubbed connections, the API RP 53
manufacturer's recommended procedure should be followed. 17.11.2
7.1.103 Spare parts should be designed for their intended use by
API RP 53
industry approved and accepted practices. After spare part
17.11.3
installation, the affected pressure-containing equipment shall
be pressure tested. Elastomeric components shall be stored in
a manner recommended by the equipment manufacturer.
7.1.104 The original equipment manufacturer should be consulted
API RP 53
regarding replacement parts. If replacement parts are acquired 17.11.3
from a nonoriginal equipment manufacturer, the parts shall be
equivalent to or superior to the original equipment and fully
tested, design verified, and supported by traceable
documentation.
7.1.105 Manuals or bulletins containing torque specifications should API RP 53
be available on the rig. As stated in API RP 53 section
17.11.4
17.11.2, torque specifications and the lubricant's coefficient
of friction should be considered when torquing fasteners.
Deviating from the specified lubricant can alter the required
torque.
7.1.106 A planned maintenance system, with equipment identified,
API RP 53
tasks specified, and the time intervals between tasks stated, 17.12.1
should be employed on each rig. Records of maintenance
performed and repairs made should be maintained on file at
the rig site or readily available for the applicable BOP
equipment.
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
11
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
7.1.107 Copies of equipment manufacturers' product alerts or
API RP 53
equipment bulletins should be maintained at the rig site or
17.12.2
readily available for the applicable BOP equipment.
7.1.108 Drawing showing ram space-out and bore of the BOP stack API RP 53
and a drawing of the choke manifold showing the pressure
17.13.1
rating of the components should be on the rig and maintained
up to date. Refer to API RP 53 Figure 19 for an example
drawing.
7.1.109 A bill of material should accompany the equipment drawings API RP 53
to correctly identify the equipment and allow the procurement 17.13.1
of correct replacement parts.
7.1.110 Changes to the BOP control system should be documented. A API RP 53
method should be established to control the drawings,
17.13.1
ensuring that up-to-date documentation is maintained.
7.1.111 Equipment records such as API manufacturing
API RP 53
documentation, NACE certification, and factory acceptance 17.13.2
testing reports should be retained. Where required, copies of
the manufacturer's equipment data book and third party
certification should be available for review.
7.1.112 A maintenance and repair historical file should be maintained API RP 53
by serial number on each major piece of equipment. This file 17.13.3
should follow the equipment when it is transferred.
Equipment malfunctions or failures should be reported in
writing to the equipment manufacturer as stated in API
Specification 16A.
7.1.113 Shop testing after major inspection or equipment weld repairs API RP 53
should be performed according to the manufacturer's written 17.13.4
procedures.
Blowout preventers for hydrogen sulphide service
API RP 53
7.1.114 Where there is reasonable expectation of encountering
hydrogen sulphide gas zones that could potentially result in 20.1
the partial pressure of the hydrogen sulphide exceeding 0.05
psia (0.00034 MPa) in the gas phase at the maximum
anticipated pressure, BOP equipment modifications should be
made. Recommended safety guidelines for conducting drilling
operations in such an environment can be found in API
Recommended Practice 49.
7.1.115 Equipment modifications should be considered since many
API RP 53
metallic materials in a hydrogen sulphide environment (sour 20.2.1
service) are subject to a form of hydrogen embrittlement
known as sulphide stress cracking (SSC).
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
chapter
12
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
7.1.116 This type of spontaneous brittle failure is dependent on the API RP
metallurgical properties of the material, the total stress or
20.2.1
load (either internal or applied), and the corrosive
environment. A list of acceptable materials is given in NACE
Standard MR0175.
7.1.117 A list of specific items to be changed on annular and ram
API RP
type BOPs and valves for service in a hydrogen sulphide
20.2.2
environment should be furnished by the manufacturer.
7.1.118 As a guide, all metallic materials which could be exposed to API RP
hydrogen sulphide under probable operating conditions should 20.2.2
be highly resistant to sulphide stress cracking.
7.1.119 The maximum acceptable harness for all preventer and valve API RP
bodies and spools shall be in accordance with NACE Standard 20.2.3
MR0175.
7.1.120 Ring-joint gaskets should meet the requirements of API
API RP
Specification 16A and be of the material and hardness
20.2.4
specified in API Specification 6A.
7.1.121 All bolts and nuts used in connection with flanges, clamps, API RP
and hubs should be selected in accordance with provisions of 20.2.5
API Specification 6A.
7.1.122 All lines, crosses, valves, and fittings in the choke manifold API RP
system and the drill string safety valve should be constructed 20.2.6
from materials meeting applicable requirements of API
Specification 5L and API Specification 6A.
7.1.123 Heat treating and other applicable requirements, as stipulated API RP
in NACE Standard MR0175 should also be reviewed and
20.2.6
considered. Field welding upstream of the chokes should be
kept to a minimum and, if performed, should meet original
shop construction standards and procedures.
7.1.124 Elastomeric components are also subject to hydrogen sulphideAPI RP
20.2.7
attack. Nitrile elastomeric components which meet other
requirements may be suitable for hydrogen sulphide service
provided drilling fluids are properly treated. Service life
shortens rapidly as temperature increases from 150F to
200F (65.6C to 93C). In the event flow line temperatures
in excess of 200F (93C) are anticipated, the equipment
manufacturer should be consulted. Elastomeric components
should be changed out as soon as possible after exposure to
hydrogen sulphide under pressure.
7.1.125 Changes prescribed by the primary equipment manufacturer API RP
to render equipment acceptable for service in a hydrogen
20.2.8
sulphide environment should not be overlooked in providing
for replacement and repair parts.
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
53 chapter
13
Surface Well Control Equipment Workshop
Chapter 10a - API Legislation - Ram Preventers
Surface Finish of Sealing Surfaces Guidelines
7.1.126 Surface finish is commonly specified in terms of average
deviation from the mean surface expressed in micro-inches
(millionths of an inch) and denoted by the abbreviation RMS.
The RMS value of a surface nay be determined by direct
measurement or by comparison with surfaces of known
roughness. Several surface roughness scales are on the
market and are mostly present at the QM of the
manufacturer. Most roughness scales cover the range from
125RMS to 32 RMS (the higher the figure the rougher the
surface).
Cameron Ram BOPs type U Values (SD-1775)
7.1.127 Face seal grooves finish at the bottom maximum 63 RMS
7.1.128 Face seal grooves finish at the side of the groove maximum
125 RMS.
7.1.129 The sealing surface on the bonnet face maximum 63 RMS.
7.1.130 Intermediate flange surface face maximum 63 RMS.
7.1.131 Ram bore cavities, the upper half at the sealing surface
maximum 125 RMS.
7.1.132 Wedgelock piston maximum 63 RMS.
ModuSpec Engineering (International) B.V.
01.10a API Legisl. Ram Preventers chap 10 2nd ed
14
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- VM 2.5 ManualDocument49 pagesVM 2.5 Manualjeepfreak212185% (20)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Well Completion: Conventional Single Zone CompletionDocument18 pagesWell Completion: Conventional Single Zone CompletionChristian WelshNo ratings yet
- Types of Well Tests: Statutory RequirementDocument19 pagesTypes of Well Tests: Statutory RequirementChristian WelshNo ratings yet
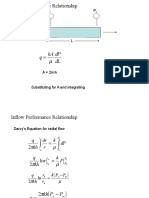
- DL DP Ka Q: Darcy's Equation P PDocument12 pagesDL DP Ka Q: Darcy's Equation P PChristian WelshNo ratings yet
- TrapsDocument10 pagesTrapsChristian WelshNo ratings yet
- LP 1Document2 pagesLP 1Paula BurogNo ratings yet
- BTech CTISDocument3 pagesBTech CTISAbhishek PatilNo ratings yet
- HTB E104 PDFDocument2 pagesHTB E104 PDFWidya Okta UtamiNo ratings yet
- Fujitec Step Chain Remove and ReplaceDocument4 pagesFujitec Step Chain Remove and Replacegeorge_zouridisNo ratings yet
- What Is PhilosophyDocument4 pagesWhat Is PhilosophyLetlie Zoilo SemblanteNo ratings yet
- Confidential: High Efficiency Synchronous Rectifier Boost ConverterDocument15 pagesConfidential: High Efficiency Synchronous Rectifier Boost ConverterkingNo ratings yet
- Petersham Road Noise and Vibration SummaryDocument1 pagePetersham Road Noise and Vibration SummaryOnir XavierNo ratings yet
- SM1001911 ChapterVIIVIIIDocument32 pagesSM1001911 ChapterVIIVIIISURYA KANT PRASADNo ratings yet
- Armored Toyota HiluxDocument1 pageArmored Toyota HiluxDinesh NadarajahNo ratings yet
- Scott Sedam Process and ProfitDocument41 pagesScott Sedam Process and ProfitMark LynchNo ratings yet
- A Review of Rammed Earth ConstructionDocument118 pagesA Review of Rammed Earth ConstructionLuciana Pinto100% (2)
- Ce225 Statistics For Civil Engineers Midterm Examination IDocument2 pagesCe225 Statistics For Civil Engineers Midterm Examination Iznour alyNo ratings yet
- Stone Tool of The Near EastDocument427 pagesStone Tool of The Near EastJa Asi0% (1)
- Hydraulic Turbines and PumpsDocument15 pagesHydraulic Turbines and PumpsSachin Chaturvedi100% (1)
- Solution Manual For Modern Management Concepts and Skills 12 e 12th Edition 0132622610Document13 pagesSolution Manual For Modern Management Concepts and Skills 12 e 12th Edition 0132622610PhilipWoodpsen100% (42)
- Practical Concepts of Quality ControlDocument128 pagesPractical Concepts of Quality ControlSchreiber_DiesesNo ratings yet
- 3 Loop Gain Crossover FrequencyDocument8 pages3 Loop Gain Crossover Frequency양영주No ratings yet
- College Students' Need For Cognition, Academic Motivation, Performance, and Well-Being 2012Document19 pagesCollege Students' Need For Cognition, Academic Motivation, Performance, and Well-Being 2012Vania RamirezNo ratings yet
- 2022-12-15 StrategiesDocument1 page2022-12-15 StrategiesquemilangaNo ratings yet
- Activity Analysis, Cost Behavior, and Cost Estimation: Answers To Review QuestionsDocument84 pagesActivity Analysis, Cost Behavior, and Cost Estimation: Answers To Review QuestionsMuhammad MishbahurrizqiNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Group 3: Cacayan, Grace L. Canlas, Rinalyn O. Celestial, Artchie EDocument9 pagesPresented By: Group 3: Cacayan, Grace L. Canlas, Rinalyn O. Celestial, Artchie EPatrick MakalintalNo ratings yet
- SeaQuantum BrochureDocument12 pagesSeaQuantum BrochureLeo TvrdeNo ratings yet
- 3 Finals-Lesson-1-For-Euthenics-Man-As-A-Social-BeingDocument14 pages3 Finals-Lesson-1-For-Euthenics-Man-As-A-Social-BeingAngela Danielle TanNo ratings yet
- Worldwide Trends in The Burden of Asthma SymptomsDocument12 pagesWorldwide Trends in The Burden of Asthma SymptomsgggNo ratings yet
- ICS Nav6 Navtex v1 ManualDocument79 pagesICS Nav6 Navtex v1 ManualLa Corriente del GolfoNo ratings yet
- New Developments of Near-UV SiPMs at FBK PDFDocument7 pagesNew Developments of Near-UV SiPMs at FBK PDFlaboratorNo ratings yet
- Business Plan of A Water Purification Plant: Hydrapure Technologies 114/A Sector 5 Saltlake City Kolkata-91Document32 pagesBusiness Plan of A Water Purification Plant: Hydrapure Technologies 114/A Sector 5 Saltlake City Kolkata-91Soumen SinhaNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument5 pagesDaftar PustakaAries AndriantoNo ratings yet
- 4a.plant LayoutDocument31 pages4a.plant LayoutSagar PhullNo ratings yet