Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.6 Costing and Scheduling 3.6.1 Costing: Phase Cost
3.6 Costing and Scheduling 3.6.1 Costing: Phase Cost
Uploaded by
vasuCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Software Engineering Module 2Document35 pagesSoftware Engineering Module 2amantNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Find Maintenance Costs Using Cost Drivers of Cocomo Intermediate ModelDocument5 pagesAn Approach To Find Maintenance Costs Using Cost Drivers of Cocomo Intermediate ModelInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- Unit-3 Overview of COCOMODocument5 pagesUnit-3 Overview of COCOMOMs.Manisha ShindeNo ratings yet
- Overview of COCOMO PDFDocument5 pagesOverview of COCOMO PDFfarhadcse30No ratings yet
- Sofware Cost EstimationDocument26 pagesSofware Cost Estimationbedkesachin1No ratings yet
- Brief Summary of The Original COCOMO ModelDocument5 pagesBrief Summary of The Original COCOMO ModelTirthajit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Software Metrics Using Constructive Cost Model: Prepared by Kondam Gopal ReddyDocument9 pagesSoftware Metrics Using Constructive Cost Model: Prepared by Kondam Gopal ReddyhitkNo ratings yet
- Soft Computing Approach For Software Cost EstimationDocument10 pagesSoft Computing Approach For Software Cost EstimationSakthi SankarNo ratings yet
- Bengal College of Engineering and Technology: Report OnDocument11 pagesBengal College of Engineering and Technology: Report OnSouvikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Software Cost EstimationDocument13 pagesChapter 5 Software Cost EstimationYosief DagnachewNo ratings yet
- Sre Assignment 3Document9 pagesSre Assignment 3ALI ANWARNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT NO 11 SenDocument7 pagesEXPERIMENT NO 11 SenVarunNo ratings yet
- Software Cost Estimation: SLOC-based Models and The Function Points ModelDocument16 pagesSoftware Cost Estimation: SLOC-based Models and The Function Points ModelWaqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cocomo IiDocument5 pagesCocomo IiDev ManeNo ratings yet
- Nicolas Garcia Romero: Activity 3 Task SoftwareDocument14 pagesNicolas Garcia Romero: Activity 3 Task SoftwareNicolas Garcia RomeroNo ratings yet
- COCOMO ModelDocument4 pagesCOCOMO ModelSovan SamantaNo ratings yet
- Software Effort Estimation:: Cosmic-FpmDocument3 pagesSoftware Effort Estimation:: Cosmic-FpmRajkumar SivaguruNo ratings yet
- CocomoDocument7 pagesCocomoSanjoy Barman RayNo ratings yet
- Cost Estimates in SPMDocument24 pagesCost Estimates in SPMAbhay SinghNo ratings yet
- My Courses 25848077Document7 pagesMy Courses 25848077beniNo ratings yet
- Unified Modeling LanguageDocument6 pagesUnified Modeling LanguageGopal ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Project Management: EstimationDocument29 pagesProject Management: EstimationDolly ParhawkNo ratings yet
- COCOMO Model: By, Amisha Singh S Ashwin Kumar Rajan Prashant BegwaniDocument8 pagesCOCOMO Model: By, Amisha Singh S Ashwin Kumar Rajan Prashant Begwaniprashant_kr_begwaniNo ratings yet
- Software Project Management: Lecture # 6Document34 pagesSoftware Project Management: Lecture # 6alhassan007No ratings yet
- Mca 4 CocomoDocument56 pagesMca 4 CocomoDiptyankaNo ratings yet
- Cocomo ModelDocument6 pagesCocomo ModelSoundarya MahalingamNo ratings yet
- Mis 03Document7 pagesMis 03Harsh NagNo ratings yet
- Pre SubmissionDocument2 pagesPre SubmissionVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- COCOMO II A Parametric Productivity Model: Software Project Management (KOE-068)Document2 pagesCOCOMO II A Parametric Productivity Model: Software Project Management (KOE-068)pemom29928No ratings yet
- Uint 5 Topic 9 Estimation of Various Parameters Such As Cost Efforts Schedule Duration Constructive Cost ModelDocument57 pagesUint 5 Topic 9 Estimation of Various Parameters Such As Cost Efforts Schedule Duration Constructive Cost ModelRayush JainNo ratings yet
- 5Document20 pages5AndriansyahNo ratings yet
- COnstructive COst MOdel IIDocument3 pagesCOnstructive COst MOdel IIGagandeep Singh AhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 3Document13 pagesUnit-5 3NANDINI PARIHARNo ratings yet
- Unit V - Project Management and EstimationDocument47 pagesUnit V - Project Management and EstimationArshxNo ratings yet
- m3 Project PlaningDocument57 pagesm3 Project PlaningReghu EvNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: UNIT-3Document41 pagesSoftware Engineering: UNIT-3Jayavarapu Karthik JNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 SoftwareCostEstimation Part 2Document8 pagesUnit 4 SoftwareCostEstimation Part 220124011No ratings yet
- Software Cost EstimationDocument42 pagesSoftware Cost EstimationRajiv VesmawalaNo ratings yet
- Cocomo IiDocument7 pagesCocomo Iimeme2001.bashNo ratings yet
- 8.2 - SW Engineering - Effort Estimation - FP - COCOMO Model - NewDocument21 pages8.2 - SW Engineering - Effort Estimation - FP - COCOMO Model - Newkaosar alamNo ratings yet
- CocomoDocument3 pagesCocomonithikali001No ratings yet
- COCOMO ModelDocument2 pagesCOCOMO Modelaarushigarg34788No ratings yet
- SE PPT - PPTX - 20240312 - 180705 - 0000Document27 pagesSE PPT - PPTX - 20240312 - 180705 - 0000anagha.nadig1No ratings yet
- 12 SenDocument2 pages12 SenGanesh EkambeNo ratings yet
- What is a Business CaseDocument10 pagesWhat is a Business Case11 Kadam Gaurav Prakash TycsNo ratings yet
- Basic COCOMO Model Vs DetailedDocument2 pagesBasic COCOMO Model Vs DetailedAryanNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Cocomo ModelDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On Cocomo Modelebjbytvhf100% (1)
- Estimation of Project MetricsDocument4 pagesEstimation of Project MetricsDhanush ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cost Estimation ModelsDocument8 pagesCost Estimation ModelsHussamMohsenNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document76 pagesUnit 2Yash VoraNo ratings yet
- Soft EngineerDocument5 pagesSoft EngineerSalman JavedNo ratings yet
- Exp 5Document10 pagesExp 5chamaar h2No ratings yet
- Cost Estimation ToolsDocument13 pagesCost Estimation Toolsdivya25sep100% (1)
- Experiment No 12: I Practical SignificanceDocument11 pagesExperiment No 12: I Practical SignificanceSatyam MarotheNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering UNIT-2, Ayasha MalikDocument19 pagesSoftware Engineering UNIT-2, Ayasha MalikRisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Putnam Slim ModelDocument13 pagesPutnam Slim Modelsowmya jonnalagaddaNo ratings yet
- Cocomo ModelDocument10 pagesCocomo ModelDr. Sonia Setia (SET Assistant Professor)No ratings yet
- The Constructive Cost ModelDocument4 pagesThe Constructive Cost ModelshirleyNo ratings yet
- COCOMO II ExampleDocument26 pagesCOCOMO II ExampleQuốc ĐạiNo ratings yet
- How to Track Schedules, Costs and Earned Value with Microsoft ProjectFrom EverandHow to Track Schedules, Costs and Earned Value with Microsoft ProjectNo ratings yet
- SGP - 26 12 2017Document185 pagesSGP - 26 12 2017vasuNo ratings yet
- J3 PDFDocument1 pageJ3 PDFvasuNo ratings yet
- Jj4 PDFDocument1 pageJj4 PDFvasuNo ratings yet
- The UuhdhsjdbxbxbhxjzkDocument1 pageThe UuhdhsjdbxbxbhxjzkvasuNo ratings yet
- NCERT History Text: Standard 6 - Ancient India: Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism (NCERT)Document2 pagesNCERT History Text: Standard 6 - Ancient India: Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism (NCERT)vasuNo ratings yet
- Best Books For IPS Mains Exam - (Click To Buy Online)Document9 pagesBest Books For IPS Mains Exam - (Click To Buy Online)vasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- J2 PDFDocument1 pageJ2 PDFvasuNo ratings yet
- Tricks To Solve SimplificationDocument10 pagesTricks To Solve SimplificationvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Permutation and Combination Solved ProblemsDocument9 pagesPermutation and Combination Solved ProblemsvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Permutation and CombinationDocument3 pagesPermutation and CombinationvasuNo ratings yet
- Profit and Loss ShortcutsDocument4 pagesProfit and Loss ShortcutsvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- U20 PDFDocument1 pageU20 PDFvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Danger To Get The This MessageDocument1 pageDanger To Get The This MessagevasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
3.6 Costing and Scheduling 3.6.1 Costing: Phase Cost
3.6 Costing and Scheduling 3.6.1 Costing: Phase Cost
Uploaded by
vasuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3.6 Costing and Scheduling 3.6.1 Costing: Phase Cost
3.6 Costing and Scheduling 3.6.1 Costing: Phase Cost
Uploaded by
vasuCopyright:
Available Formats
3.
6 Costing and Scheduling
3.6.1 Costing
The cost of the project calculated using COCOMO model and it provides
the final cost of this project given below.
COCOMO is an open model, it includes
The underlying cost estimation equations.
Every assumption made in the model.
Every definition.
The costs included in an estimate are explicitly stated. Because
COCOMO is well defined, and because it doesnt rely upon
proprietary estimation algorithms, the advantages to its user:
COCOMO estimates are more objective and repeatable than
estimates made by methods relying on proprietary models.
COCOMO can be calibrated to reflect your software development
environment, and to produce more accurate estimates.
The COCOMO calculations are based on your estimates of a projects size
in Source Lines of Code(SLOC).
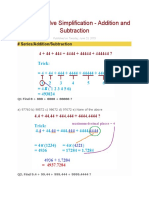
The estimation formulas have the form
Estimation formulas = Li(LOC)exp(Xi)*EAF
Where E is the effort applied in person-months,
Li is the coefficient and exponents Xi are the organic values,
LOC is estimated number of delivered lines of code for the project.
Effort Adjustment Factor(EAF) having the typical values. That range from 0.9 to
1.4
Now
Li=3.2, Lines of code=.215, Xi=1.05 and EAF is the 1.4
Em(Estimation cost per month) = 3.2(.215)(1.05)^1.4 = 736.63
Project coding time = 3 months
Coefficient value = 3 months(90 days) / line of code
=418
Effort Estimation = 0.418*736.63=0.307
Approximation cost = Effort Estimation * Project coding time.
=0.307*3
= 921
Phase
Cost
Direct
17%
156
Resources
Indirect
15%
138
Resources
Manpower
Development
27%
24%
248
221
11%
6%
101
55
921
Costing
Testing
Maintenance
Total Cost
Table1:Cost estimation
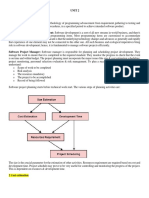
3.6.1 Scheduling
Scheduling is the culmination of a planning activity that is a primary
component of software project management. When combined with estimation
methods and risks analysis, scheduling establishes a road map for the project
manager. Scheduling begins with process decomposition.
COMPLETION
DATE
NO. OF DAYS
11-01-2016
03-02-2016
22
04-02-2016
21-02-2016
07-03-2016
29-03-2016
10-04-2016
20-02-2016
06-03-2016
28-03-2016
09-04-2016
21-04-2016
17
14
20
12
08
96
SCHEDULE
PROPOSED
ACTIVITIES
Requirement
Analysis
Design
Coding
Testing
Implementation
Documentation
Total no of days
DATE
Table2 : Scheduling Table
You might also like
- Software Engineering Module 2Document35 pagesSoftware Engineering Module 2amantNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Find Maintenance Costs Using Cost Drivers of Cocomo Intermediate ModelDocument5 pagesAn Approach To Find Maintenance Costs Using Cost Drivers of Cocomo Intermediate ModelInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- Unit-3 Overview of COCOMODocument5 pagesUnit-3 Overview of COCOMOMs.Manisha ShindeNo ratings yet
- Overview of COCOMO PDFDocument5 pagesOverview of COCOMO PDFfarhadcse30No ratings yet
- Sofware Cost EstimationDocument26 pagesSofware Cost Estimationbedkesachin1No ratings yet
- Brief Summary of The Original COCOMO ModelDocument5 pagesBrief Summary of The Original COCOMO ModelTirthajit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Software Metrics Using Constructive Cost Model: Prepared by Kondam Gopal ReddyDocument9 pagesSoftware Metrics Using Constructive Cost Model: Prepared by Kondam Gopal ReddyhitkNo ratings yet
- Soft Computing Approach For Software Cost EstimationDocument10 pagesSoft Computing Approach For Software Cost EstimationSakthi SankarNo ratings yet
- Bengal College of Engineering and Technology: Report OnDocument11 pagesBengal College of Engineering and Technology: Report OnSouvikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Software Cost EstimationDocument13 pagesChapter 5 Software Cost EstimationYosief DagnachewNo ratings yet
- Sre Assignment 3Document9 pagesSre Assignment 3ALI ANWARNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT NO 11 SenDocument7 pagesEXPERIMENT NO 11 SenVarunNo ratings yet
- Software Cost Estimation: SLOC-based Models and The Function Points ModelDocument16 pagesSoftware Cost Estimation: SLOC-based Models and The Function Points ModelWaqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cocomo IiDocument5 pagesCocomo IiDev ManeNo ratings yet
- Nicolas Garcia Romero: Activity 3 Task SoftwareDocument14 pagesNicolas Garcia Romero: Activity 3 Task SoftwareNicolas Garcia RomeroNo ratings yet
- COCOMO ModelDocument4 pagesCOCOMO ModelSovan SamantaNo ratings yet
- Software Effort Estimation:: Cosmic-FpmDocument3 pagesSoftware Effort Estimation:: Cosmic-FpmRajkumar SivaguruNo ratings yet
- CocomoDocument7 pagesCocomoSanjoy Barman RayNo ratings yet
- Cost Estimates in SPMDocument24 pagesCost Estimates in SPMAbhay SinghNo ratings yet
- My Courses 25848077Document7 pagesMy Courses 25848077beniNo ratings yet
- Unified Modeling LanguageDocument6 pagesUnified Modeling LanguageGopal ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Project Management: EstimationDocument29 pagesProject Management: EstimationDolly ParhawkNo ratings yet
- COCOMO Model: By, Amisha Singh S Ashwin Kumar Rajan Prashant BegwaniDocument8 pagesCOCOMO Model: By, Amisha Singh S Ashwin Kumar Rajan Prashant Begwaniprashant_kr_begwaniNo ratings yet
- Software Project Management: Lecture # 6Document34 pagesSoftware Project Management: Lecture # 6alhassan007No ratings yet
- Mca 4 CocomoDocument56 pagesMca 4 CocomoDiptyankaNo ratings yet
- Cocomo ModelDocument6 pagesCocomo ModelSoundarya MahalingamNo ratings yet
- Mis 03Document7 pagesMis 03Harsh NagNo ratings yet
- Pre SubmissionDocument2 pagesPre SubmissionVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- COCOMO II A Parametric Productivity Model: Software Project Management (KOE-068)Document2 pagesCOCOMO II A Parametric Productivity Model: Software Project Management (KOE-068)pemom29928No ratings yet
- Uint 5 Topic 9 Estimation of Various Parameters Such As Cost Efforts Schedule Duration Constructive Cost ModelDocument57 pagesUint 5 Topic 9 Estimation of Various Parameters Such As Cost Efforts Schedule Duration Constructive Cost ModelRayush JainNo ratings yet
- 5Document20 pages5AndriansyahNo ratings yet
- COnstructive COst MOdel IIDocument3 pagesCOnstructive COst MOdel IIGagandeep Singh AhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 3Document13 pagesUnit-5 3NANDINI PARIHARNo ratings yet
- Unit V - Project Management and EstimationDocument47 pagesUnit V - Project Management and EstimationArshxNo ratings yet
- m3 Project PlaningDocument57 pagesm3 Project PlaningReghu EvNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: UNIT-3Document41 pagesSoftware Engineering: UNIT-3Jayavarapu Karthik JNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 SoftwareCostEstimation Part 2Document8 pagesUnit 4 SoftwareCostEstimation Part 220124011No ratings yet
- Software Cost EstimationDocument42 pagesSoftware Cost EstimationRajiv VesmawalaNo ratings yet
- Cocomo IiDocument7 pagesCocomo Iimeme2001.bashNo ratings yet
- 8.2 - SW Engineering - Effort Estimation - FP - COCOMO Model - NewDocument21 pages8.2 - SW Engineering - Effort Estimation - FP - COCOMO Model - Newkaosar alamNo ratings yet
- CocomoDocument3 pagesCocomonithikali001No ratings yet
- COCOMO ModelDocument2 pagesCOCOMO Modelaarushigarg34788No ratings yet
- SE PPT - PPTX - 20240312 - 180705 - 0000Document27 pagesSE PPT - PPTX - 20240312 - 180705 - 0000anagha.nadig1No ratings yet
- 12 SenDocument2 pages12 SenGanesh EkambeNo ratings yet
- What is a Business CaseDocument10 pagesWhat is a Business Case11 Kadam Gaurav Prakash TycsNo ratings yet
- Basic COCOMO Model Vs DetailedDocument2 pagesBasic COCOMO Model Vs DetailedAryanNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Cocomo ModelDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On Cocomo Modelebjbytvhf100% (1)
- Estimation of Project MetricsDocument4 pagesEstimation of Project MetricsDhanush ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cost Estimation ModelsDocument8 pagesCost Estimation ModelsHussamMohsenNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document76 pagesUnit 2Yash VoraNo ratings yet
- Soft EngineerDocument5 pagesSoft EngineerSalman JavedNo ratings yet
- Exp 5Document10 pagesExp 5chamaar h2No ratings yet
- Cost Estimation ToolsDocument13 pagesCost Estimation Toolsdivya25sep100% (1)
- Experiment No 12: I Practical SignificanceDocument11 pagesExperiment No 12: I Practical SignificanceSatyam MarotheNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering UNIT-2, Ayasha MalikDocument19 pagesSoftware Engineering UNIT-2, Ayasha MalikRisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Putnam Slim ModelDocument13 pagesPutnam Slim Modelsowmya jonnalagaddaNo ratings yet
- Cocomo ModelDocument10 pagesCocomo ModelDr. Sonia Setia (SET Assistant Professor)No ratings yet
- The Constructive Cost ModelDocument4 pagesThe Constructive Cost ModelshirleyNo ratings yet
- COCOMO II ExampleDocument26 pagesCOCOMO II ExampleQuốc ĐạiNo ratings yet
- How to Track Schedules, Costs and Earned Value with Microsoft ProjectFrom EverandHow to Track Schedules, Costs and Earned Value with Microsoft ProjectNo ratings yet
- SGP - 26 12 2017Document185 pagesSGP - 26 12 2017vasuNo ratings yet
- J3 PDFDocument1 pageJ3 PDFvasuNo ratings yet
- Jj4 PDFDocument1 pageJj4 PDFvasuNo ratings yet
- The UuhdhsjdbxbxbhxjzkDocument1 pageThe UuhdhsjdbxbxbhxjzkvasuNo ratings yet
- NCERT History Text: Standard 6 - Ancient India: Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism (NCERT)Document2 pagesNCERT History Text: Standard 6 - Ancient India: Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism (NCERT)vasuNo ratings yet
- Best Books For IPS Mains Exam - (Click To Buy Online)Document9 pagesBest Books For IPS Mains Exam - (Click To Buy Online)vasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- J2 PDFDocument1 pageJ2 PDFvasuNo ratings yet
- Tricks To Solve SimplificationDocument10 pagesTricks To Solve SimplificationvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Permutation and Combination Solved ProblemsDocument9 pagesPermutation and Combination Solved ProblemsvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Permutation and CombinationDocument3 pagesPermutation and CombinationvasuNo ratings yet
- Profit and Loss ShortcutsDocument4 pagesProfit and Loss ShortcutsvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- U20 PDFDocument1 pageU20 PDFvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Danger To Get The This MessageDocument1 pageDanger To Get The This MessagevasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet
- Thanks Again For All The Time To Time andDocument1 pageThanks Again For All The Time To Time andvasuNo ratings yet