Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsR2 4k R3 4k R4 6k R5 9k: 1) Equivalent Circuits/Circuit Reduction
R2 4k R3 4k R4 6k R5 9k: 1) Equivalent Circuits/Circuit Reduction
Uploaded by
JavierThe document contains an assignment on electric circuits with 4 problems:
1) Determining equivalent resistance, current through a voltage source, and current through a resistor in a circuit.
2) Finding an equivalent voltage source, equivalent resistance, and currents for a combined circuit.
3) Using node and mesh analysis to solve for voltages and currents.
4) Using superposition to solve for a voltage across a resistor in a circuit with multiple sources.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Problemas CH6 PDFDocument11 pagesProblemas CH6 PDFJuan227100% (1)
- Leadchip-Lc2127cb5tr C571475Document6 pagesLeadchip-Lc2127cb5tr C571475Oscar Andres Ramirez AmayaNo ratings yet
- GATE EC 10 Volume Set by RK KanodiaDocument629 pagesGATE EC 10 Volume Set by RK KanodiaSiva Prakash89% (44)
- EE 302 Exam 2 and Histogram F11Document3 pagesEE 302 Exam 2 and Histogram F11Perry_Feng_44440% (1)
- Listrik ACDocument79 pagesListrik ACIntan Sari SihombingNo ratings yet
- Problem Set in ELE 001Document8 pagesProblem Set in ELE 001Patrick GarciaNo ratings yet
- Elektroteknik SorularDocument21 pagesElektroteknik Sorularserkan1234No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 For CircuitsDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 For CircuitsAmir EyniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits - Sheets - 1Document13 pagesElectrical Circuits - Sheets - 1محمد عجوة100% (1)
- Due Date: Aug 8, 2016: Basic Components, Voltage & Current Laws, Nodal AnalysisDocument21 pagesDue Date: Aug 8, 2016: Basic Components, Voltage & Current Laws, Nodal Analysisgopika1991No ratings yet
- Ee6201 CT U1 5 QBDocument10 pagesEe6201 CT U1 5 QBsakilakumaresanNo ratings yet
- Tarea #1 3 2017Document4 pagesTarea #1 3 2017BayardoNo ratings yet
- Work SheetDocument8 pagesWork Sheetmehariashfare2012No ratings yet
- Assignment 01Document6 pagesAssignment 01Z S PlaysNo ratings yet
- Recitation#3Document4 pagesRecitation#3William AlikisNo ratings yet
- Report On Basic Ohm S Law Series and Parallel Circuits PDFDocument18 pagesReport On Basic Ohm S Law Series and Parallel Circuits PDFhaikal100% (1)
- T: To Study: Experimen Mesh Method Aim of Experiment: ApparatusDocument3 pagesT: To Study: Experimen Mesh Method Aim of Experiment: ApparatusMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Lec2 BranchCurrentDocument71 pagesLec2 BranchCurrentKuro ShiroNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Question BankDocument18 pagesElectrical Circuits Question BankRacherla Mega RaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment NodalDocument8 pagesExperiment NodalWyndellRioNo ratings yet
- Mesh Solution With 2 SourcesDocument4 pagesMesh Solution With 2 SourcesNATHANIEL OLSEN PARRENASNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Question Bank-21EEE15ADocument18 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Question Bank-21EEE15AG46Anand P KNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Chapter 2: Direct CurrentDocument8 pagesTutorial 2 Chapter 2: Direct CurrentSYAFIQAH ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument12 pagesElectric Circuit AnalysisMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- Eee1 HW 2Document3 pagesEee1 HW 2Averly Jerryl EscotoNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document0 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.aishuvc1822No ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis - I Year ECE - Question BankDocument20 pagesCircuit Analysis - I Year ECE - Question BankPandyselvi Balasubramanian100% (1)
- Elec2091st Semester Ex - 1705355554564Document6 pagesElec2091st Semester Ex - 1705355554564family7482pleaseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Electric Circuits: NameDocument7 pagesChapter 19 Electric Circuits: NameTimothy KurbyNo ratings yet
- CT Assignment IDocument4 pagesCT Assignment ImosesalvinNo ratings yet
- 1basic Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21Document82 pages1basic Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21roberto carlos roberto carlosNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument2 pagesElectricityyashasviupadhyay19No ratings yet
- Final Exam ProblemsDocument23 pagesFinal Exam Problemsakaotaku03No ratings yet
- NAS QuesDocument19 pagesNAS QuesVIVEK AHLAWATNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits ThoeryDocument3 pagesElectrical Circuits ThoerySrini R KNo ratings yet
- Superposition and Norton TheoremDocument24 pagesSuperposition and Norton TheoremMahmudul AlamNo ratings yet
- Electronics I 306a OkDocument3 pagesElectronics I 306a Okparupalli1997No ratings yet
- Ecx3210 Tma2 2010 PDFDocument2 pagesEcx3210 Tma2 2010 PDFThamara Dananjaya GunarathnaNo ratings yet
- CircuitsDocument2 pagesCircuitsEn En BelthereNo ratings yet
- Source Transformation MethodDocument7 pagesSource Transformation MethodChristian CalisinNo ratings yet
- Pset 6Document21 pagesPset 6Anirudth NNo ratings yet
- Assignment CTDocument9 pagesAssignment CTdhinojahimeshNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Exp Series and Parallel Circuit - Group4 (s25)Document14 pagesLab Report Exp Series and Parallel Circuit - Group4 (s25)FARHAH BATRISYIA ABDUL RAHIMNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Resistance Delta - Wye Transformation: Experiment # 4Document12 pagesEquivalent Resistance Delta - Wye Transformation: Experiment # 4John Phillip Lopez MasagcaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1Karamveer SinghNo ratings yet
- 9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument8 pages9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A02305 Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pages9A02305 Electrical CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Part B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisDocument4 pagesPart B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisAnonymous Ndsvh2soNo ratings yet
- Elec3101 HW2Document3 pagesElec3101 HW2asad9akNo ratings yet
- Mid Bee Paper Set 2Document7 pagesMid Bee Paper Set 2raghusabale1No ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 5 (Series-Parallel Circuit)Document6 pagesTUTORIAL 5 (Series-Parallel Circuit)zahirah najihahNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document13 pagesWeek 5Anirudh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On Unit IDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank On Unit IanupamNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Thevenin StevensDocument7 pagesLab 4 Thevenin StevenskarthikhrajvNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Vraj PatelNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 TransformerDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 TransformerGayatri Vedula50% (2)
- Review Questions For Electrical Machines and DrivesDocument14 pagesReview Questions For Electrical Machines and DrivesClifford Mkong100% (1)
- TransformerDocument1 pageTransformertanushitcetNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- MSN, CBR, PSB, VM: PES Institute of Technology and ManagementDocument1 pageMSN, CBR, PSB, VM: PES Institute of Technology and ManagementVishwanath MuddiNo ratings yet
- AX3161 AXEliteDocument12 pagesAX3161 AXEliteCristian CiocoiuNo ratings yet
- cs302 Fall 2009Document45 pagescs302 Fall 2009aamir shahzadNo ratings yet
- AIC Ch12 PDFDocument44 pagesAIC Ch12 PDFAbhilash OSNo ratings yet
- EC8461 - EC II Lab ManualDocument90 pagesEC8461 - EC II Lab ManualKarm Pdk50% (2)
- High-Performance Silicon-Gate CMOS: Semiconductor Technical DataDocument11 pagesHigh-Performance Silicon-Gate CMOS: Semiconductor Technical DataViviana AlbornozNo ratings yet
- DICADocument2 pagesDICAak5775No ratings yet
- 1989 Xilinx Databook PDFDocument380 pages1989 Xilinx Databook PDFztakahashiNo ratings yet
- B.Sc.-Semester - VI: Physics (Paper - II)Document26 pagesB.Sc.-Semester - VI: Physics (Paper - II)Vivek ChardeNo ratings yet
- LSI and VLSI Design and ApplicationDocument15 pagesLSI and VLSI Design and Applicationعہۣۗثہۣۗمہۣۗان الہۣۗضہۣۗاحہۣۗيNo ratings yet
- CmosDocument5 pagesCmosAsif MaharNo ratings yet
- SAED Cell Lib Rev1 4 20 1 PDFDocument100 pagesSAED Cell Lib Rev1 4 20 1 PDFPradeep RoyalNo ratings yet
- Serie SED1530Document37 pagesSerie SED1530Juan Carlos BarandicaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet LVC4245Document8 pagesDatasheet LVC4245AdamTrisnoizeAgustianNo ratings yet
- FSQ510 85947Document15 pagesFSQ510 85947علی امامیNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Technical Data: L SuffixDocument7 pagesSemiconductor Technical Data: L SuffixMerényi OszkárNo ratings yet
- Edc Old PapersDocument36 pagesEdc Old PapersbhagyasrikagithaNo ratings yet
- CMT2210LC en V0.9 20170817Document20 pagesCMT2210LC en V0.9 20170817Ta ToNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital & Digital To Analog ConvertersDocument66 pagesAnalog To Digital & Digital To Analog ConvertersSai Krishna Kodali100% (1)
- SeminarDocument14 pagesSeminarKumar RaviNo ratings yet
- K3596 01L FujiElectricDocument4 pagesK3596 01L FujiElectricLAN JR HOUSENo ratings yet
- Static Timing 1Document27 pagesStatic Timing 1Pradeep BabuNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor KRC110 KRC114: Technical DataDocument4 pagesSemiconductor KRC110 KRC114: Technical DataDabro FabioNo ratings yet
- DicaDocument2 pagesDicaRamesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Problem Set SmithDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Problem Set Smithsatish kNo ratings yet
- Important 16 Mark Questions-19!1!2024Document5 pagesImportant 16 Mark Questions-19!1!2024FLOWERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Micro-Operations: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesChapter 8: Micro-Operations: ObjectivesSteffany RoqueNo ratings yet
- L293 DDocument3 pagesL293 DRonak MananiNo ratings yet
R2 4k R3 4k R4 6k R5 9k: 1) Equivalent Circuits/Circuit Reduction
R2 4k R3 4k R4 6k R5 9k: 1) Equivalent Circuits/Circuit Reduction
Uploaded by
Javier0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesThe document contains an assignment on electric circuits with 4 problems:
1) Determining equivalent resistance, current through a voltage source, and current through a resistor in a circuit.
2) Finding an equivalent voltage source, equivalent resistance, and currents for a combined circuit.
3) Using node and mesh analysis to solve for voltages and currents.
4) Using superposition to solve for a voltage across a resistor in a circuit with multiple sources.
Original Description:
ECSE-2010 HW 2
Original Title
HW02 Circuits
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document contains an assignment on electric circuits with 4 problems:
1) Determining equivalent resistance, current through a voltage source, and current through a resistor in a circuit.
2) Finding an equivalent voltage source, equivalent resistance, and currents for a combined circuit.
3) Using node and mesh analysis to solve for voltages and currents.
4) Using superposition to solve for a voltage across a resistor in a circuit with multiple sources.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesR2 4k R3 4k R4 6k R5 9k: 1) Equivalent Circuits/Circuit Reduction
R2 4k R3 4k R4 6k R5 9k: 1) Equivalent Circuits/Circuit Reduction
Uploaded by
JavierThe document contains an assignment on electric circuits with 4 problems:
1) Determining equivalent resistance, current through a voltage source, and current through a resistor in a circuit.
2) Finding an equivalent voltage source, equivalent resistance, and currents for a combined circuit.
3) Using node and mesh analysis to solve for voltages and currents.
4) Using superposition to solve for a voltage across a resistor in a circuit with multiple sources.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Electric Circuits
HW02
Fall 2016
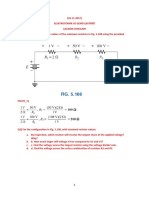
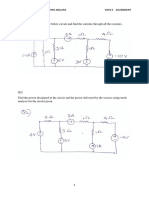
1) Equivalent Circuits/Circuit Reduction
R2
4k
R3
R1
2k
4k
R4
6k
R5
9k
V1
R6
8k
R7
8k
R8
12k
In the above circuit determine:
a. The equivalent resisance seen by the voltage source.
b. Find the current through the voltage source.
c. Find the current through resistor R8.
Electric Circuits
HW02
Fall 2016
2) Equivalent Circuit
R1
4k
R2
2k
V2
5V
R5
10V
V1
3k
R3
6k
R4
2k
R6
8k
In the above circuit determine:
a. An equivalent source (a single voltage source)
b. The equivalent resistance seen by the combined voltage source
c. The current through the voltage souce, V1
d. The current through the resistor R6
Electric Circuits
HW02
V1
3) Node/Mesh Analysis
i1
i2
Fall 2016
V2
i3
a. Apply node analysis to determine V1 and V2
b. Apply mesh analysis to determine i1, i2, and i3
Electric Circuits
HW02
Fall 2016
4) Superposition
R1
2k
V1
8V
R4
R3
V2
6k
3k
10V
R2
4k
I1
0.002
R5
1k
R6
5k
a. Use any method to determine the voltage across R2 (node, mesh, circuit reduction, source transformation...)
b. Find VR2 using superposition. (For each source, draw the schematic).
You might also like
- Problemas CH6 PDFDocument11 pagesProblemas CH6 PDFJuan227100% (1)
- Leadchip-Lc2127cb5tr C571475Document6 pagesLeadchip-Lc2127cb5tr C571475Oscar Andres Ramirez AmayaNo ratings yet
- GATE EC 10 Volume Set by RK KanodiaDocument629 pagesGATE EC 10 Volume Set by RK KanodiaSiva Prakash89% (44)
- EE 302 Exam 2 and Histogram F11Document3 pagesEE 302 Exam 2 and Histogram F11Perry_Feng_44440% (1)
- Listrik ACDocument79 pagesListrik ACIntan Sari SihombingNo ratings yet
- Problem Set in ELE 001Document8 pagesProblem Set in ELE 001Patrick GarciaNo ratings yet
- Elektroteknik SorularDocument21 pagesElektroteknik Sorularserkan1234No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 For CircuitsDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 For CircuitsAmir EyniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits - Sheets - 1Document13 pagesElectrical Circuits - Sheets - 1محمد عجوة100% (1)
- Due Date: Aug 8, 2016: Basic Components, Voltage & Current Laws, Nodal AnalysisDocument21 pagesDue Date: Aug 8, 2016: Basic Components, Voltage & Current Laws, Nodal Analysisgopika1991No ratings yet
- Ee6201 CT U1 5 QBDocument10 pagesEe6201 CT U1 5 QBsakilakumaresanNo ratings yet
- Tarea #1 3 2017Document4 pagesTarea #1 3 2017BayardoNo ratings yet
- Work SheetDocument8 pagesWork Sheetmehariashfare2012No ratings yet
- Assignment 01Document6 pagesAssignment 01Z S PlaysNo ratings yet
- Recitation#3Document4 pagesRecitation#3William AlikisNo ratings yet
- Report On Basic Ohm S Law Series and Parallel Circuits PDFDocument18 pagesReport On Basic Ohm S Law Series and Parallel Circuits PDFhaikal100% (1)
- T: To Study: Experimen Mesh Method Aim of Experiment: ApparatusDocument3 pagesT: To Study: Experimen Mesh Method Aim of Experiment: ApparatusMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Lec2 BranchCurrentDocument71 pagesLec2 BranchCurrentKuro ShiroNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Question BankDocument18 pagesElectrical Circuits Question BankRacherla Mega RaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment NodalDocument8 pagesExperiment NodalWyndellRioNo ratings yet
- Mesh Solution With 2 SourcesDocument4 pagesMesh Solution With 2 SourcesNATHANIEL OLSEN PARRENASNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Question Bank-21EEE15ADocument18 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Question Bank-21EEE15AG46Anand P KNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Chapter 2: Direct CurrentDocument8 pagesTutorial 2 Chapter 2: Direct CurrentSYAFIQAH ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument12 pagesElectric Circuit AnalysisMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- Eee1 HW 2Document3 pagesEee1 HW 2Averly Jerryl EscotoNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document0 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.aishuvc1822No ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis - I Year ECE - Question BankDocument20 pagesCircuit Analysis - I Year ECE - Question BankPandyselvi Balasubramanian100% (1)
- Elec2091st Semester Ex - 1705355554564Document6 pagesElec2091st Semester Ex - 1705355554564family7482pleaseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Electric Circuits: NameDocument7 pagesChapter 19 Electric Circuits: NameTimothy KurbyNo ratings yet
- CT Assignment IDocument4 pagesCT Assignment ImosesalvinNo ratings yet
- 1basic Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21Document82 pages1basic Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21roberto carlos roberto carlosNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument2 pagesElectricityyashasviupadhyay19No ratings yet
- Final Exam ProblemsDocument23 pagesFinal Exam Problemsakaotaku03No ratings yet
- NAS QuesDocument19 pagesNAS QuesVIVEK AHLAWATNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits ThoeryDocument3 pagesElectrical Circuits ThoerySrini R KNo ratings yet
- Superposition and Norton TheoremDocument24 pagesSuperposition and Norton TheoremMahmudul AlamNo ratings yet
- Electronics I 306a OkDocument3 pagesElectronics I 306a Okparupalli1997No ratings yet
- Ecx3210 Tma2 2010 PDFDocument2 pagesEcx3210 Tma2 2010 PDFThamara Dananjaya GunarathnaNo ratings yet
- CircuitsDocument2 pagesCircuitsEn En BelthereNo ratings yet
- Source Transformation MethodDocument7 pagesSource Transformation MethodChristian CalisinNo ratings yet
- Pset 6Document21 pagesPset 6Anirudth NNo ratings yet
- Assignment CTDocument9 pagesAssignment CTdhinojahimeshNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Exp Series and Parallel Circuit - Group4 (s25)Document14 pagesLab Report Exp Series and Parallel Circuit - Group4 (s25)FARHAH BATRISYIA ABDUL RAHIMNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Resistance Delta - Wye Transformation: Experiment # 4Document12 pagesEquivalent Resistance Delta - Wye Transformation: Experiment # 4John Phillip Lopez MasagcaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1Karamveer SinghNo ratings yet
- 9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument8 pages9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A02305 Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pages9A02305 Electrical CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Part B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisDocument4 pagesPart B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisAnonymous Ndsvh2soNo ratings yet
- Elec3101 HW2Document3 pagesElec3101 HW2asad9akNo ratings yet
- Mid Bee Paper Set 2Document7 pagesMid Bee Paper Set 2raghusabale1No ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 5 (Series-Parallel Circuit)Document6 pagesTUTORIAL 5 (Series-Parallel Circuit)zahirah najihahNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document13 pagesWeek 5Anirudh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On Unit IDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank On Unit IanupamNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Thevenin StevensDocument7 pagesLab 4 Thevenin StevenskarthikhrajvNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Vraj PatelNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 TransformerDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 TransformerGayatri Vedula50% (2)
- Review Questions For Electrical Machines and DrivesDocument14 pagesReview Questions For Electrical Machines and DrivesClifford Mkong100% (1)
- TransformerDocument1 pageTransformertanushitcetNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- MSN, CBR, PSB, VM: PES Institute of Technology and ManagementDocument1 pageMSN, CBR, PSB, VM: PES Institute of Technology and ManagementVishwanath MuddiNo ratings yet
- AX3161 AXEliteDocument12 pagesAX3161 AXEliteCristian CiocoiuNo ratings yet
- cs302 Fall 2009Document45 pagescs302 Fall 2009aamir shahzadNo ratings yet
- AIC Ch12 PDFDocument44 pagesAIC Ch12 PDFAbhilash OSNo ratings yet
- EC8461 - EC II Lab ManualDocument90 pagesEC8461 - EC II Lab ManualKarm Pdk50% (2)
- High-Performance Silicon-Gate CMOS: Semiconductor Technical DataDocument11 pagesHigh-Performance Silicon-Gate CMOS: Semiconductor Technical DataViviana AlbornozNo ratings yet
- DICADocument2 pagesDICAak5775No ratings yet
- 1989 Xilinx Databook PDFDocument380 pages1989 Xilinx Databook PDFztakahashiNo ratings yet
- B.Sc.-Semester - VI: Physics (Paper - II)Document26 pagesB.Sc.-Semester - VI: Physics (Paper - II)Vivek ChardeNo ratings yet
- LSI and VLSI Design and ApplicationDocument15 pagesLSI and VLSI Design and Applicationعہۣۗثہۣۗمہۣۗان الہۣۗضہۣۗاحہۣۗيNo ratings yet
- CmosDocument5 pagesCmosAsif MaharNo ratings yet
- SAED Cell Lib Rev1 4 20 1 PDFDocument100 pagesSAED Cell Lib Rev1 4 20 1 PDFPradeep RoyalNo ratings yet
- Serie SED1530Document37 pagesSerie SED1530Juan Carlos BarandicaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet LVC4245Document8 pagesDatasheet LVC4245AdamTrisnoizeAgustianNo ratings yet
- FSQ510 85947Document15 pagesFSQ510 85947علی امامیNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Technical Data: L SuffixDocument7 pagesSemiconductor Technical Data: L SuffixMerényi OszkárNo ratings yet
- Edc Old PapersDocument36 pagesEdc Old PapersbhagyasrikagithaNo ratings yet
- CMT2210LC en V0.9 20170817Document20 pagesCMT2210LC en V0.9 20170817Ta ToNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital & Digital To Analog ConvertersDocument66 pagesAnalog To Digital & Digital To Analog ConvertersSai Krishna Kodali100% (1)
- SeminarDocument14 pagesSeminarKumar RaviNo ratings yet
- K3596 01L FujiElectricDocument4 pagesK3596 01L FujiElectricLAN JR HOUSENo ratings yet
- Static Timing 1Document27 pagesStatic Timing 1Pradeep BabuNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor KRC110 KRC114: Technical DataDocument4 pagesSemiconductor KRC110 KRC114: Technical DataDabro FabioNo ratings yet
- DicaDocument2 pagesDicaRamesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Problem Set SmithDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Problem Set Smithsatish kNo ratings yet
- Important 16 Mark Questions-19!1!2024Document5 pagesImportant 16 Mark Questions-19!1!2024FLOWERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Micro-Operations: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesChapter 8: Micro-Operations: ObjectivesSteffany RoqueNo ratings yet
- L293 DDocument3 pagesL293 DRonak MananiNo ratings yet