Professional Documents
Culture Documents
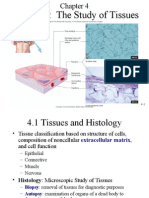
Simple Squamous Simple Cuboidal Non Ciliated: Simple Columnar Ciliated Simple Columnar
Simple Squamous Simple Cuboidal Non Ciliated: Simple Columnar Ciliated Simple Columnar
Uploaded by
Carina ECopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Histology NotesDocument4 pagesHistology NotesThonieroce Apryle Jey Morelos100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology-Intestinal ObstructionDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-Intestinal ObstructionRaisa Robelle Quicho75% (8)
- Cardiovascular System (Anatomy and Physiology)Document93 pagesCardiovascular System (Anatomy and Physiology)Butch Dumdum86% (7)
- Where Hormone Is Produced Hormone Secreted Chemical Class Target Cell Location Hormone FunctionDocument3 pagesWhere Hormone Is Produced Hormone Secreted Chemical Class Target Cell Location Hormone FunctionRNStudent1100% (1)
- Lecture 1: Epithelium and Glands: 1.classification of Epithelial TissueDocument7 pagesLecture 1: Epithelium and Glands: 1.classification of Epithelial TissueMuizz RasaniNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument22 pagesEpithelial TissueMariam HaroonNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Lecture 1Document52 pagesEpithelial Tissue Lecture 1Saphira PramuditaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Veny Larasati, M.Biomed: Bagian Histologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sriwijaya 2016Document52 pagesDr. Veny Larasati, M.Biomed: Bagian Histologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sriwijaya 2016NabilahnurqonitahNo ratings yet
- Histology: BY Alawia Abdalla Mohammed 7 Nov 2021Document23 pagesHistology: BY Alawia Abdalla Mohammed 7 Nov 2021التنين الاحمر العظيمNo ratings yet
- EPITHELIAL TISSUE (Epithelium / Epithelia) : Basement MembraneDocument7 pagesEPITHELIAL TISSUE (Epithelium / Epithelia) : Basement MembraneNanaNo ratings yet
- Epithelium: International Islamic University IslamabadDocument19 pagesEpithelium: International Islamic University IslamabadAsim Bin Arshad 58-FBAS/BSBIO/S19100% (1)
- Epithelial Tissue or Epithelium (Plural Epithelia)Document4 pagesEpithelial Tissue or Epithelium (Plural Epithelia)Charlemagne GuiribaNo ratings yet
- By: Dr. Susianti, M.SCDocument47 pagesBy: Dr. Susianti, M.SCAnityo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- A Epithelial Tissue1!16!12 14Document32 pagesA Epithelial Tissue1!16!12 14Noor SinghNo ratings yet
- A Epithelial - Tissue1 16 12 14Document32 pagesA Epithelial - Tissue1 16 12 14Abdulaziz AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- In The Name of God THE Compassionate The MercifulDocument75 pagesIn The Name of God THE Compassionate The MercifulGaziza MaaroofNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - TissuesDocument3 pagesChapter 4 - TissuesAngelyka CabaloNo ratings yet
- Histology, Frog MusculatureDocument4 pagesHistology, Frog MusculatureAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Tissue Introduction & Epithelial Tissue: PhysiologyDocument22 pagesTissue Introduction & Epithelial Tissue: PhysiologyZahid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Os201 Part 2Document56 pagesOs201 Part 2aa628No ratings yet
- Introduction and Epithelial TissueDocument66 pagesIntroduction and Epithelial Tissueapi-294162496100% (1)
- Ep It HeliumDocument35 pagesEp It Heliumkrazy lrkaNo ratings yet
- EpitheliumDocument25 pagesEpitheliumAsmita BhattNo ratings yet
- ANATOMI - Chapter4TissuesMariebPart1Document23 pagesANATOMI - Chapter4TissuesMariebPart1Adhi TjahyadiNo ratings yet
- General HistologyDocument29 pagesGeneral HistologyShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 Week 1Document35 pagesGenbio2 Week 1Noel Vincent Agonoy100% (1)
- Yy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYDocument64 pagesYy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYsreedam100% (1)
- De Rama - Activity Worksheet #02 - HHIS FINALDocument6 pagesDe Rama - Activity Worksheet #02 - HHIS FINALCHRISTINE JOY DE RAMANo ratings yet
- Lab 7Document25 pagesLab 7202310446No ratings yet
- Biology 112: Chapter 5: TissuesDocument5 pagesBiology 112: Chapter 5: TissuesSwetha GowthamNo ratings yet
- Chapt04 LectureDocument63 pagesChapt04 LecturektbethellNo ratings yet
- Epithelial-Tissues Lect.Document13 pagesEpithelial-Tissues Lect.adelbaneen31No ratings yet
- Simple Squamous: Epithelial Tissue A. Simple /unstratified SINGLE LAYER OF CELLS IDocument5 pagesSimple Squamous: Epithelial Tissue A. Simple /unstratified SINGLE LAYER OF CELLS IMedical HardikNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue (Finale)Document2 pagesEpithelial Tissue (Finale)Adz Na HarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesKenken MijaresNo ratings yet
- Epithelia and GlandsDocument28 pagesEpithelia and GlandsSamuel ArikodNo ratings yet
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: Structure: Function: LocationDocument3 pagesSimple Squamous Epithelium: Structure: Function: LocationdianesamanthaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument27 pagesEpithelial TissueBlodin Zylfiu100% (1)
- 3-Unstratified Epithelium. Definitions and Examples of Squamous, Columnar (Simple, Ciliated, Microvilli, Secretory) and CuboidalDocument2 pages3-Unstratified Epithelium. Definitions and Examples of Squamous, Columnar (Simple, Ciliated, Microvilli, Secretory) and CuboidalAris PaparisNo ratings yet
- Histology of Git and Circulatory SystemDocument45 pagesHistology of Git and Circulatory SystemRan CelNo ratings yet
- 13.histology LectureDocument64 pages13.histology LecturepashaNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument16 pagesHistologyHohai ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- CH 05 TissuesDocument50 pagesCH 05 TissuesAlina Ghe100% (1)
- The Epithelium: By: Maj Rizwan KianiDocument74 pagesThe Epithelium: By: Maj Rizwan Kianiviya7No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument86 pagesEpithelial TissuesElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue PracticeDocument22 pagesEpithelial Tissue Practicemero wowNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#2 MED3Document3 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#2 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument33 pagesEpithelial TissueStnrhalizaNo ratings yet
- Revised of Epithelial TissueDocument24 pagesRevised of Epithelial Tissueiskandar MudaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument1 pageEpithelial Tissuesapi-265736810No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 4: HistologyDocument4 pagesHuman Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 4: HistologySuperjunior8No ratings yet
- Tissue TableDocument4 pagesTissue TableMarcie BooneNo ratings yet
- Histology 1Document82 pagesHistology 1Ramanidhi SNo ratings yet
- Jaringan Hewan Read OnlyDocument28 pagesJaringan Hewan Read OnlylisaNo ratings yet
- lab 9 PDF Epithelial Tissuesم. رشا محمد شاكرDocument12 pageslab 9 PDF Epithelial Tissuesم. رشا محمد شاكرyamanuel25No ratings yet
- Histology of Digestive SystemDocument100 pagesHistology of Digestive SystemFadhila Putri Palupi100% (3)
- Simple Squamous EpitheliumDocument14 pagesSimple Squamous Epitheliumdoubleyouem2003No ratings yet
- Vipin Sharma Digestive SystemDocument41 pagesVipin Sharma Digestive SystemRitvik SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 EpithelialTissueWEBDocument27 pages1 EpithelialTissueWEBJR Rolf NeuqeletNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument31 pagesEpithelial Tissuesmuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Histologi Sistem DigestoriaDocument66 pagesHistologi Sistem DigestoriaPuji Arifianti RamadhanyNo ratings yet
- Glandular Epithelium: Descriptive HistologyDocument23 pagesGlandular Epithelium: Descriptive HistologyIan LubangaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System (Viva)Document46 pagesNervous System (Viva)Mohammed shabekNo ratings yet
- ANAT1005 Eos Exam PDFDocument2 pagesANAT1005 Eos Exam PDFKelvin YipNo ratings yet
- Kel 8 Biology AvesDocument47 pagesKel 8 Biology AvesAbdu RohmanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument18 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseAde Cahyo IslamiNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory Systemapi-250543541No ratings yet
- Intro To Ana Physio RBLDocument69 pagesIntro To Ana Physio RBLHades HadesNo ratings yet
- Emmy Harefa - Tiroid Diksar LIS, 5 Maret 2016Document81 pagesEmmy Harefa - Tiroid Diksar LIS, 5 Maret 2016jcyovelaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 1cdnedlio N Marieb Chapter 12 The LymphaticDocument39 pagesLymphatic System and Body Defenses 1cdnedlio N Marieb Chapter 12 The LymphaticOlalekan OyekunleNo ratings yet
- SSLC Biology (Eng Med) Model Exam 2023 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesSSLC Biology (Eng Med) Model Exam 2023 Answer KeyMuhammad SaidiqNo ratings yet
- CUSHING'S SyndromeDocument9 pagesCUSHING'S SyndromeTheavuthyNo ratings yet
- Kidney Problems and DialysisDocument3 pagesKidney Problems and DialysismarymakinNo ratings yet
- Metamorphisis 2Document6 pagesMetamorphisis 2simran kaurNo ratings yet
- 1031 Autonomic Nervous System-BSDocument20 pages1031 Autonomic Nervous System-BSBunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyGichana ElvisNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 06 Life Processes 11Document13 pages10 Science Notes 06 Life Processes 11rajkumar trivedi100% (3)
- Clumsiness" As They Call It Is Probably Because of An Anomaly in Her CerebellumDocument5 pagesClumsiness" As They Call It Is Probably Because of An Anomaly in Her CerebellumjamielNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument116 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Farm AnimalsJayson BasiagNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument95 pagesReproductionSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Transition: Training of The Trainers Neonatal ResuscitationDocument36 pagesNeonatal Transition: Training of The Trainers Neonatal ResuscitationmitaNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Ahn PDFDocument11 pagesMcqs Ahn PDFMhr AliNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema: (Acute Heart Failure)Document7 pagesPulmonary Edema: (Acute Heart Failure)james garcia100% (5)
- Sci10 LM U3Document131 pagesSci10 LM U3Romel B Agno86% (7)
- Ucpphysio 313 APharm Dfinal F18Document8 pagesUcpphysio 313 APharm Dfinal F18Huzaifa ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Iloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo City Study Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesIloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo City Study Guide Questionseloisa lyn pizNo ratings yet
- How Your Digestive System Works - Emma Bryce - EnglishDocument5 pagesHow Your Digestive System Works - Emma Bryce - EnglishVeronica RamirezNo ratings yet
- Biology Quarter 1 Unit 2 Day 6 Immune System ArticleDocument4 pagesBiology Quarter 1 Unit 2 Day 6 Immune System ArticleTeachTappyNo ratings yet
- Auditory PathwayDocument16 pagesAuditory PathwayDrsreeram ValluriNo ratings yet
Simple Squamous Simple Cuboidal Non Ciliated: Simple Columnar Ciliated Simple Columnar
Simple Squamous Simple Cuboidal Non Ciliated: Simple Columnar Ciliated Simple Columnar
Uploaded by
Carina EOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple Squamous Simple Cuboidal Non Ciliated: Simple Columnar Ciliated Simple Columnar
Simple Squamous Simple Cuboidal Non Ciliated: Simple Columnar Ciliated Simple Columnar
Uploaded by
Carina ECopyright:
Available Formats
Simple Epithelium
Simple Squamous
Anatomy: single layer
of flat cells
Function: rapid
diffusion, filtration,
some secretion
Location: alveoli,
endothelium,
mesothelium of
serous membrane
Stratified
Squamous
Anatomy: multi layer
of flat cells
keratinized: no
nuclei; non
keratinized: nuclei
Function: protet
underlying tissue
Location:
keratinized:
epidermis, scalp or
skin
Non keratinized:oral
cavity, pharynx,
esophagus, anus,
vagina
Simple Cuboidal
Anatomy: Single
layer of cube shaped
cells
Function: Absoprtion,
secretion and
excretion
Location: thryoid
gland, kidney
tubules, ducts of
most exocrine
glands, surface of
ovary
Stratfied
Cuboidal
Anatomy: multi
layer of cube
shaped cells
Function:
protection and
strengthen gland
wall
Location: large
ducts of sweat
glands and parts
of male urethra
Non ciliated: simple
columnar
Anatomy:goblet cells,
microvilli, one layer of
tall cells
Function:absorption and
secretion
Location: small
intestines, GI tract,
digestive tract lining
Ciliated Simple
Columnar
Anatomy: tall single
layer of cells. It will
have cilia and goblet
cells
Function: secrete
mucin, mvement of
mucous and particles
Location: respriatory
and reproductive
system, uterine tubes,
larger bronchioles
Stratified
Epithelium
Stratified
Columnar
Anatomy:multiple
layer of tall cells
Function:protecti
on and secretion
(may run into
goblet cells)
Location: salviary
glands, and male
urethra
Ciliated and Non
Ciliated
Pseudostratified
Columnar:
Anatomy: tall layer of
cells, but layered
appearance of nuclei
- Ciliated: typically has
goblet cells
Function: protection
ciliated: secretes mucin
and causes movement
Location:
Ciliated: respiratory
tract (nasal cavity -->
bronchi)
Nonciliated: epidermis
and male urethra
Transitional:
Anatomy:
polyhedral,
binucleated many
shapes and many
layers cells that
are all stuck
together
Function:
distension, slow
stretch and
relaxation
It needs to expand
and contract
Location: urinary
bladder needs to
expand to fill
bladder then
contract to release,
ureters and part of
urethra
You might also like
- Histology NotesDocument4 pagesHistology NotesThonieroce Apryle Jey Morelos100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology-Intestinal ObstructionDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-Intestinal ObstructionRaisa Robelle Quicho75% (8)
- Cardiovascular System (Anatomy and Physiology)Document93 pagesCardiovascular System (Anatomy and Physiology)Butch Dumdum86% (7)
- Where Hormone Is Produced Hormone Secreted Chemical Class Target Cell Location Hormone FunctionDocument3 pagesWhere Hormone Is Produced Hormone Secreted Chemical Class Target Cell Location Hormone FunctionRNStudent1100% (1)
- Lecture 1: Epithelium and Glands: 1.classification of Epithelial TissueDocument7 pagesLecture 1: Epithelium and Glands: 1.classification of Epithelial TissueMuizz RasaniNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument22 pagesEpithelial TissueMariam HaroonNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Lecture 1Document52 pagesEpithelial Tissue Lecture 1Saphira PramuditaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Veny Larasati, M.Biomed: Bagian Histologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sriwijaya 2016Document52 pagesDr. Veny Larasati, M.Biomed: Bagian Histologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sriwijaya 2016NabilahnurqonitahNo ratings yet
- Histology: BY Alawia Abdalla Mohammed 7 Nov 2021Document23 pagesHistology: BY Alawia Abdalla Mohammed 7 Nov 2021التنين الاحمر العظيمNo ratings yet
- EPITHELIAL TISSUE (Epithelium / Epithelia) : Basement MembraneDocument7 pagesEPITHELIAL TISSUE (Epithelium / Epithelia) : Basement MembraneNanaNo ratings yet
- Epithelium: International Islamic University IslamabadDocument19 pagesEpithelium: International Islamic University IslamabadAsim Bin Arshad 58-FBAS/BSBIO/S19100% (1)
- Epithelial Tissue or Epithelium (Plural Epithelia)Document4 pagesEpithelial Tissue or Epithelium (Plural Epithelia)Charlemagne GuiribaNo ratings yet
- By: Dr. Susianti, M.SCDocument47 pagesBy: Dr. Susianti, M.SCAnityo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- A Epithelial Tissue1!16!12 14Document32 pagesA Epithelial Tissue1!16!12 14Noor SinghNo ratings yet
- A Epithelial - Tissue1 16 12 14Document32 pagesA Epithelial - Tissue1 16 12 14Abdulaziz AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- In The Name of God THE Compassionate The MercifulDocument75 pagesIn The Name of God THE Compassionate The MercifulGaziza MaaroofNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - TissuesDocument3 pagesChapter 4 - TissuesAngelyka CabaloNo ratings yet
- Histology, Frog MusculatureDocument4 pagesHistology, Frog MusculatureAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Tissue Introduction & Epithelial Tissue: PhysiologyDocument22 pagesTissue Introduction & Epithelial Tissue: PhysiologyZahid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Os201 Part 2Document56 pagesOs201 Part 2aa628No ratings yet
- Introduction and Epithelial TissueDocument66 pagesIntroduction and Epithelial Tissueapi-294162496100% (1)
- Ep It HeliumDocument35 pagesEp It Heliumkrazy lrkaNo ratings yet
- EpitheliumDocument25 pagesEpitheliumAsmita BhattNo ratings yet
- ANATOMI - Chapter4TissuesMariebPart1Document23 pagesANATOMI - Chapter4TissuesMariebPart1Adhi TjahyadiNo ratings yet
- General HistologyDocument29 pagesGeneral HistologyShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 Week 1Document35 pagesGenbio2 Week 1Noel Vincent Agonoy100% (1)
- Yy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYDocument64 pagesYy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYsreedam100% (1)
- De Rama - Activity Worksheet #02 - HHIS FINALDocument6 pagesDe Rama - Activity Worksheet #02 - HHIS FINALCHRISTINE JOY DE RAMANo ratings yet
- Lab 7Document25 pagesLab 7202310446No ratings yet
- Biology 112: Chapter 5: TissuesDocument5 pagesBiology 112: Chapter 5: TissuesSwetha GowthamNo ratings yet
- Chapt04 LectureDocument63 pagesChapt04 LecturektbethellNo ratings yet
- Epithelial-Tissues Lect.Document13 pagesEpithelial-Tissues Lect.adelbaneen31No ratings yet
- Simple Squamous: Epithelial Tissue A. Simple /unstratified SINGLE LAYER OF CELLS IDocument5 pagesSimple Squamous: Epithelial Tissue A. Simple /unstratified SINGLE LAYER OF CELLS IMedical HardikNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue (Finale)Document2 pagesEpithelial Tissue (Finale)Adz Na HarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesKenken MijaresNo ratings yet
- Epithelia and GlandsDocument28 pagesEpithelia and GlandsSamuel ArikodNo ratings yet
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: Structure: Function: LocationDocument3 pagesSimple Squamous Epithelium: Structure: Function: LocationdianesamanthaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument27 pagesEpithelial TissueBlodin Zylfiu100% (1)
- 3-Unstratified Epithelium. Definitions and Examples of Squamous, Columnar (Simple, Ciliated, Microvilli, Secretory) and CuboidalDocument2 pages3-Unstratified Epithelium. Definitions and Examples of Squamous, Columnar (Simple, Ciliated, Microvilli, Secretory) and CuboidalAris PaparisNo ratings yet
- Histology of Git and Circulatory SystemDocument45 pagesHistology of Git and Circulatory SystemRan CelNo ratings yet
- 13.histology LectureDocument64 pages13.histology LecturepashaNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument16 pagesHistologyHohai ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- CH 05 TissuesDocument50 pagesCH 05 TissuesAlina Ghe100% (1)
- The Epithelium: By: Maj Rizwan KianiDocument74 pagesThe Epithelium: By: Maj Rizwan Kianiviya7No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument86 pagesEpithelial TissuesElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue PracticeDocument22 pagesEpithelial Tissue Practicemero wowNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#2 MED3Document3 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#2 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument33 pagesEpithelial TissueStnrhalizaNo ratings yet
- Revised of Epithelial TissueDocument24 pagesRevised of Epithelial Tissueiskandar MudaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument1 pageEpithelial Tissuesapi-265736810No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 4: HistologyDocument4 pagesHuman Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 4: HistologySuperjunior8No ratings yet
- Tissue TableDocument4 pagesTissue TableMarcie BooneNo ratings yet
- Histology 1Document82 pagesHistology 1Ramanidhi SNo ratings yet
- Jaringan Hewan Read OnlyDocument28 pagesJaringan Hewan Read OnlylisaNo ratings yet
- lab 9 PDF Epithelial Tissuesم. رشا محمد شاكرDocument12 pageslab 9 PDF Epithelial Tissuesم. رشا محمد شاكرyamanuel25No ratings yet
- Histology of Digestive SystemDocument100 pagesHistology of Digestive SystemFadhila Putri Palupi100% (3)
- Simple Squamous EpitheliumDocument14 pagesSimple Squamous Epitheliumdoubleyouem2003No ratings yet
- Vipin Sharma Digestive SystemDocument41 pagesVipin Sharma Digestive SystemRitvik SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 EpithelialTissueWEBDocument27 pages1 EpithelialTissueWEBJR Rolf NeuqeletNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument31 pagesEpithelial Tissuesmuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Histologi Sistem DigestoriaDocument66 pagesHistologi Sistem DigestoriaPuji Arifianti RamadhanyNo ratings yet
- Glandular Epithelium: Descriptive HistologyDocument23 pagesGlandular Epithelium: Descriptive HistologyIan LubangaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System (Viva)Document46 pagesNervous System (Viva)Mohammed shabekNo ratings yet
- ANAT1005 Eos Exam PDFDocument2 pagesANAT1005 Eos Exam PDFKelvin YipNo ratings yet
- Kel 8 Biology AvesDocument47 pagesKel 8 Biology AvesAbdu RohmanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument18 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseAde Cahyo IslamiNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory Systemapi-250543541No ratings yet
- Intro To Ana Physio RBLDocument69 pagesIntro To Ana Physio RBLHades HadesNo ratings yet
- Emmy Harefa - Tiroid Diksar LIS, 5 Maret 2016Document81 pagesEmmy Harefa - Tiroid Diksar LIS, 5 Maret 2016jcyovelaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 1cdnedlio N Marieb Chapter 12 The LymphaticDocument39 pagesLymphatic System and Body Defenses 1cdnedlio N Marieb Chapter 12 The LymphaticOlalekan OyekunleNo ratings yet
- SSLC Biology (Eng Med) Model Exam 2023 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesSSLC Biology (Eng Med) Model Exam 2023 Answer KeyMuhammad SaidiqNo ratings yet
- CUSHING'S SyndromeDocument9 pagesCUSHING'S SyndromeTheavuthyNo ratings yet
- Kidney Problems and DialysisDocument3 pagesKidney Problems and DialysismarymakinNo ratings yet
- Metamorphisis 2Document6 pagesMetamorphisis 2simran kaurNo ratings yet
- 1031 Autonomic Nervous System-BSDocument20 pages1031 Autonomic Nervous System-BSBunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyGichana ElvisNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 06 Life Processes 11Document13 pages10 Science Notes 06 Life Processes 11rajkumar trivedi100% (3)
- Clumsiness" As They Call It Is Probably Because of An Anomaly in Her CerebellumDocument5 pagesClumsiness" As They Call It Is Probably Because of An Anomaly in Her CerebellumjamielNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument116 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Farm AnimalsJayson BasiagNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument95 pagesReproductionSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Transition: Training of The Trainers Neonatal ResuscitationDocument36 pagesNeonatal Transition: Training of The Trainers Neonatal ResuscitationmitaNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Ahn PDFDocument11 pagesMcqs Ahn PDFMhr AliNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema: (Acute Heart Failure)Document7 pagesPulmonary Edema: (Acute Heart Failure)james garcia100% (5)
- Sci10 LM U3Document131 pagesSci10 LM U3Romel B Agno86% (7)
- Ucpphysio 313 APharm Dfinal F18Document8 pagesUcpphysio 313 APharm Dfinal F18Huzaifa ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Iloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo City Study Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesIloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo City Study Guide Questionseloisa lyn pizNo ratings yet
- How Your Digestive System Works - Emma Bryce - EnglishDocument5 pagesHow Your Digestive System Works - Emma Bryce - EnglishVeronica RamirezNo ratings yet
- Biology Quarter 1 Unit 2 Day 6 Immune System ArticleDocument4 pagesBiology Quarter 1 Unit 2 Day 6 Immune System ArticleTeachTappyNo ratings yet
- Auditory PathwayDocument16 pagesAuditory PathwayDrsreeram ValluriNo ratings yet