Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parts of The Cell
Parts of The Cell
Uploaded by
Christine Navarra AcantoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parts of The Cell
Parts of The Cell
Uploaded by
Christine Navarra AcantoCopyright:
Available Formats
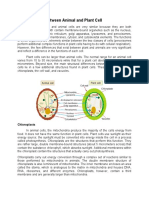
Do All Cells Look the Same?
Cells come in many shapes and sizes. Some cells are covered by a cell wall, other are not, some have slimy coats or
elongated structures that push and pull them through their environment. Some cells have a thick layer surrounding
their cell. This layer is called the capsule and is found in bacteria cells.
In our body there are many different kinds of cells. We are made up of about 200 different types of cells. Our body
also has non- living materials such as hair, finger nails, and the hard part of the bone and teeth. All these materials
are made up of dead cells.
What Are the Parts of the Cell?
Have you ever wondered what the inside of a cell looks like? If you think about the rooms in our homes, the inside of
any animal or plant cell has many similar room-like structures called organelles. Each organelle is a place where
specific jobs are done.
Plant and animal cells have many of the same organelles. But in some cases, the organelles in cells are different. For
example, in plant cells, there are more types of organelles than are found in animal cells. Below are some names and
descriptions of organelles commonly found in cells. There is also an interactive cell viewer and game that can be
used to learn about the parts of animal and plant cells.
Plasma membrane- The membrane enclosing a cell is made up of two
lipid layers called a "bilipid" membrane. The lipids that are present in the
plasma membrane are called "phospholipids."
These lipid layers are made up of a number of fatty acid building blocks.
The fatty acid that makes up this membrane has two different parts to ita small water loving head- hydrophilic head. Hydro stands for water
andphilic means liking or loving. The other part of this fatty acid is a
long water-repelling or water hating tail.
This tail is hydrophobic- Hydro stands for water and phobic means fear.
The plasma membrane is arranged in such a way so that the tails face
each other on the inside and the heads face towards the outside of the
membrane.
back to top
Channels/pores- A channel in the cell's plasma membrane.
Thischannel is made up of certain proteins that control the movement of
molecules, including food and water, into the cell.
back to top
Nucleus- The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It is the largest
organelle in the cell and it contains the DNA of the cell.
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) contains all the information for cells to
live, perform their functions and reproduce.
Inside the nucleus is another organelle called the nucleolus. The
nucleolus is responsible for making ribosomes.
The circles on the surface of the nucleus are the nuclear pores. These are
where ribosomes, and other materials move in and out of the cell.
back to top
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)- It is a network of membranes throughout
the cytoplasm of the cell. There are two types of ER.
When ribosomes are attached it is called rough ER and smooth ER when
there are no ribosomes attached.
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is where most protein synthesis occurs
in the cell. The function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is to
synthesize lipids in the cell. The smooth ER also helps in the
detoxification of harmful substances in the cell.
back to top
Ribosomes- Organelles that help in the synthesis of proteins. Ribosomes
are made up of two parts, called subunits.
Ribosomes are made of one large and one small subunit.
They get their names from their size. One unit is larger than the other so
they are called large and small subunits.
Both these subunits are necessary for protein synthesis in the cell. When
the two units are docked together with a special information unit called
messenger RNA, they make proteins.
Some ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm, but most are attached to the
endoplasmic reticulum. While attached to the ER, ribosomes make
proteins that the cell needs and also ones to be exported from the cell for
work elsewhere in the body.
back to top
Golgi complex- It is the organelle in the cell that is responsible for
sorting and correctly shipping the proteins produced in the ER. Just like
our postal packages, which should have a correct shipping address, the
proteins produced in the ER should be correctly sent to their respective
address. It is a very important step in protein synthesis. If the Golgi
complex makes a mistake in shipping the proteins to the right address,
certain functions in the cell may stop.
This organelle was named after an Italian physician-Camillo Golgi. He
was the first person to describe this organelle in the cell. It is also the
only organelle that is capitalized.
back to top
Mitochondrion- This is the cells powerhouse. This organelle packages
the energy from the food you eat into ATP molecules.
Every type of cell has a different amount of mitochondria (plural). There
are more mitochondria in cells that have to perform lots of work, for
example- your leg muscle cells, heart muscle cells etc. Other cells need
less energy to do their work and have less mitochondria.
back to top
Chloroplast- This is the organelle in which photosynthesis takes place.
In this organelle the light energy of the sun is converted into chemical
energy.
Chloroplasts are found only in plant cells not animal cells. The chemical
energy that is produced by chloroplasts is finally used to make
carbohydrates like starch that get stored in the plant.
Chloroplasts contain tiny pigments called chlorophylls. Chlorophylls are
responsible for trapping the light energy from the sun.
back to top
Vesicles- This term literally means "small vessel". This organelle helps
store and transport products produced by the cell.
The vesicles are the transport and delivery vehicles like our mail and
Federal Express trucks. Some vesicles deliver materials to parts of the
cell and others transport materials outside the cell in a process called
exocytosis.
back to top
Vacuole- Plant cells have what looks like a very large empty space in the
middle. This space is called the vacuole.
Don't be fooled, the vacuole contains large amounts of water and stores
other important materials such as sugars, ions and pigments.
back to top
Cytoplasm- A term for all the contents of a cell other than the nucleus.
Even though the cartoon drawings do not look like it, the cytoplasm
contains mostly water.
Some fun facts about water and the human body:
Adult bodies are about 50 to 65 percent water.
A childs body has a little more water at 75 percent.
The human brain is about 75 percent water.
back to top
Cell wall and Plasmodesmata- In addition to cell membranes, plants
have cell walls. Cell walls provide protection and support for plants. In
land plants, the cell wall is mostly made of cellulose.
Unlike cell membranes, materials cannot get through cell walls. This
would be a problem for plant cells if not for special openings called
plasmodesmata.
These openings are used to communicate and transport materials
between plant cells because the cell membranes are able to touch and
therefore exchange needed materials.
back to top
Peroxisomes- These collect and safely break down chemicals that are
toxic to the cell.
back to top
Centrioles- These are found only in animal cells and come into action
when the cells divide, helping with the organization of chromosomes.
back to top
Lysosomes- Created by the Golgi apparatus, these help break down large
molecules into smaller pieces that the cell can use.
back to top
Cytoskeleton- Made up of filaments and tubules, it helps shape and
support the cell. It also helps move things move around in the cell. For
artistic purposes, the cytoskeleton is shown in just one place when in
reality it is found throughout the entire cell.
back to top
Cite |
Send |
World of Biology
Meet Our Biologists
Listen & Watch
PLOSable
You might also like
- Animal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableDocument16 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableAnnie Lyn Villamor100% (1)
- Review of The Cell and Its OrganellesDocument8 pagesReview of The Cell and Its OrganellesedeceNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and FunctionsKarren Ferrer-Mora Handayan100% (1)
- Cells Parts and It Functions: Vince Emmanuel M. Amandoron Gen. Bio Grade 12 - Stem DDocument6 pagesCells Parts and It Functions: Vince Emmanuel M. Amandoron Gen. Bio Grade 12 - Stem DLuz A. CasipongNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane: Hydro PhilicDocument8 pagesPlasma Membrane: Hydro PhilicAlthea Junsan BernabeNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?Document5 pagesChapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?HeroNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- ADOCS1002 - Course NotesDocument12 pagesADOCS1002 - Course NotesMostafa MansourNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument6 pagesThe CellshaniahNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria Are Known As The Powerhouses of The Cell. They AreDocument12 pagesMitochondria Are Known As The Powerhouses of The Cell. They AreKatrina Marie Chan SalanioNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument26 pagesCellsNairita LetipoNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCell OrganellesMark Kenneth CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology PresentationDocument14 pagesCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459No ratings yet
- 10 CMH Human and Social Biology: CellsDocument28 pages10 CMH Human and Social Biology: CellsScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- 1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellDocument5 pages1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellClint Jhun TabugocNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Science Notes: Plant and Animal CellDocument4 pagesScience Notes: Plant and Animal CellRosalinda LappayNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatDocument7 pagesCell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatSpongie BobNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell DefinitionDocument7 pagesAnimal Cell DefinitionJoanne AlindayoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument29 pagesCell Structure and Functionapi-217439283No ratings yet
- JetDocument14 pagesJetAnnie Lyn VillamorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDHAIRYA KASAR100% (1)
- Pre-Lims ReviewerDocument4 pagesPre-Lims ReviewerANGEL RIZARENo ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellapi-267979304No ratings yet
- Life Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologyDocument16 pagesLife Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologynkllaeNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: Apparatus Proteins Lipids Vesicles Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Nucleus Cells PlantDocument3 pagesCell Membrane: Apparatus Proteins Lipids Vesicles Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Nucleus Cells PlantPauline Grace MontifalconNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsDocument15 pagesPlant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsanyoyoyNo ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- Chapter 2 BotanyDocument6 pagesChapter 2 BotanyLebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- Cell MembranesDocument4 pagesCell MembranesAnju SoniNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells PDFDocument7 pagesPlant Cells PDFMarcus Ben AlgerreNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell - Structure and Functionssidhantm823No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Cell and TissuesDocument13 pagesCell and TissuesJeffrish Doni EzhilNo ratings yet
- Basic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"Document12 pagesBasic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"cbseiscNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell DefinitionDocument10 pagesAnimal Cell DefinitionAngelique VeteNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 2Document10 pagesCell Organelles 2Hardik tyagiNo ratings yet
- Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment No 1Document10 pagesSir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment No 1Ali InamNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Hannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationDocument5 pagesHannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationAngelo AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells - De, Nition, Diagram, Structure & FunctionDocument2 pagesPlant Cells - De, Nition, Diagram, Structure & FunctionJoseph OloruntobaNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDocument13 pagesThe Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDiane CastroNo ratings yet
- O Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsDocument10 pagesO Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsTakudzwa ZvidzaNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument4 pagesPlant CellKenneth FungoNo ratings yet
- The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsDocument6 pagesThe Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsHitesh MoreNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsDocument6 pagesThe Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsYukiNo ratings yet
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 5 NotesSunali BhojwaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceDocument34 pagesChapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceMadhav DayareNo ratings yet
- Byjus Com Biology Cell OrganellesDocument26 pagesByjus Com Biology Cell OrganellesᏗᏕᎥᎷ ᏗᏝᎥNo ratings yet
- All About Animal Cells: Key TakeawaysDocument8 pagesAll About Animal Cells: Key TakeawaysRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Drawing of A Cross Section of A Ligustrum Plant Cell Under A Light MicroscopeDocument4 pagesLab 4 Drawing of A Cross Section of A Ligustrum Plant Cell Under A Light MicroscopeMichael TimsonNo ratings yet
- Only Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus. in Prokaryotic Cells, DNA Is Found in The CytoplasmDocument14 pagesOnly Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus. in Prokaryotic Cells, DNA Is Found in The Cytoplasmrakan ilyasNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument6 pagesCELLSFenny May SebonNo ratings yet
- All About Animal CellsDocument2 pagesAll About Animal CellsJether Marc Palmerola GardoseNo ratings yet
- Organelles in CellsDocument3 pagesOrganelles in CellsSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (2.1)Document13 pagesChapter 2 (2.1)mrtheunknownNo ratings yet