Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsWorking Principle of Induction Motor
Working Principle of Induction Motor
Uploaded by
muhammad adnannAn induction motor works through electromagnetic induction, where current induced in the rotor's short-circuited windings generates a magnetic field that causes the rotor to rotate. When alternating current is applied to the stator windings, it generates a magnetic flux that cuts the rotor windings, inducing current in them. This induced current in turn creates another magnetic field in the rotor that lags behind the stator field, producing a torque that causes the rotor to rotate at a speed dependent on the alternating current supply.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesLesson PlanKhairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor CharacteristicsDocument14 pagesInduction Motor CharacteristicsAnnaRajNo ratings yet
- How Does An Induction Motor WorkDocument7 pagesHow Does An Induction Motor WorkLeandro CamargoNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument26 pagesElectrical MachinesVaibhav BacchavNo ratings yet
- What Is An Induction MotorDocument3 pagesWhat Is An Induction MotorfarizabintenoorNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Stator ConstructionDocument9 pagesInduction Motor: Stator ConstructionMohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument23 pagesInduction Motorsai netNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor: Rotor (Document3 pagesElectric Motor: Rotor (qwert qwertNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument3 pagesInduction MotorKazuha MinatoNo ratings yet
- AC MotorsDocument48 pagesAC MotorsBrandon SookdeoNo ratings yet
- Torque Equ of Ac MotorDocument13 pagesTorque Equ of Ac MotorAnonymous xaeuoo4No ratings yet
- Ac Motors: (A) Synchronous Motors. (B) Asynchronous MotorsDocument18 pagesAc Motors: (A) Synchronous Motors. (B) Asynchronous MotorsStudy portalNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Induction MotorDocument2 pagesSingle Phase Induction Motorjay shahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Induction Motor: Experiment 11Document4 pagesIntroduction To Induction Motor: Experiment 11Apna VeerNo ratings yet
- DC and Ac Motor Basic PrincipleDocument1 pageDC and Ac Motor Basic Principledan matombeNo ratings yet
- ELE290 Chapter 6Document21 pagesELE290 Chapter 6imfendiNo ratings yet
- EE313 Class10Document9 pagesEE313 Class10Zahid MarwatNo ratings yet
- 1 Phase Induction MotorDocument2 pages1 Phase Induction Motorjay shahNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 - Induction MachineDocument35 pagesMODULE 4 - Induction MachinedamoskidanielNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment 4 PDFmaha saeedNo ratings yet
- AC Synchronous GeneratorDocument8 pagesAC Synchronous Generatoraswardi8756No ratings yet
- Induction Motor: This Article Does NotDocument24 pagesInduction Motor: This Article Does Notyashraj786100% (1)
- Induction Motor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesInduction Motor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJose EvonneNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorsDocument28 pagesInduction MotorsKimsairng CheaNo ratings yet
- Ex 3Document7 pagesEx 3Feras Al-AzzehNo ratings yet
- #5 Module 5Document52 pages#5 Module 5anishdeshmukh108No ratings yet
- EES (Lec20)Document16 pagesEES (Lec20)Muhammad SagheerNo ratings yet
- AC MotorDocument22 pagesAC MotorRavindar_Singh0% (1)
- AC MotorDocument22 pagesAC MotorMoise CristinaNo ratings yet
- Unit - IvDocument24 pagesUnit - Ivdurairajgeetha318No ratings yet
- Document PDFDocument21 pagesDocument PDFHarizx SaufixNo ratings yet
- Lec 5Document15 pagesLec 5Fernando Paez MendizabalNo ratings yet
- Induction, Squirrel Cage Motor - Torque CalculationDocument10 pagesInduction, Squirrel Cage Motor - Torque CalculationAlexandra100% (1)
- Induction MotorDocument4 pagesInduction MotorSenjuti DeNo ratings yet
- L3 - Three Phase Induction Motor-1Document52 pagesL3 - Three Phase Induction Motor-1Proshenjit BaruaNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument13 pagesInduction MotorAsif AhnafNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Navigation SearchDocument8 pagesInduction Motor: Navigation SearchSoni Mishra TiwariNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Induction Motors PDFDocument11 pages3 Phase Induction Motors PDFFauzan Dimas KusyonoNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Induction MotorsDocument10 pages3 Phase Induction MotorsSTIP Teknik BravoNo ratings yet
- Homework 7 Induction Motor 1Document3 pagesHomework 7 Induction Motor 1JamrNo ratings yet
- Skip To ContentDocument17 pagesSkip To Contentkidanemariam teseraNo ratings yet
- 3phase Induction Motor (Sukhpreet)Document17 pages3phase Induction Motor (Sukhpreet)Ankesh KunwarNo ratings yet
- The Meaning of Electric MotorsDocument11 pagesThe Meaning of Electric MotorsMelindaTamrinNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase IMDocument16 pages3-Phase IMk rajendraNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor BalaDocument8 pagesInduction Motor Baladinesh11rNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Ktu Module 6Document36 pagesMechatronics Ktu Module 6Adarsh s nairNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor and Hydropower PlantDocument24 pagesInduction Motor and Hydropower PlantYugalal GurungNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument7 pagesElectrical Machinesusama jabbarNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument21 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorPrianshu Jyosyula100% (2)
- Rewinding M 1 FasaDocument31 pagesRewinding M 1 Fasanurjayaagung44No ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument2 pagesFinal ExamFlicker LoserNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: by WiresDocument3 pagesInduction Motor: by Wireswajeeh shahNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document20 pagesTopic 1Ʋiŋêet ḠåuṯḁmNo ratings yet
- How Does An Alternator WorkDocument3 pagesHow Does An Alternator WorkZaqPoilmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Induction Motor PDFDocument26 pagesChapter 3 Induction Motor PDFNeezam Halim50% (2)
- Electrical Interview Questions With AnswersDocument9 pagesElectrical Interview Questions With AnswersKrishnamoorthi VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Home-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsFrom EverandHome-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- Mechani Calengi Neer: MuhammadadnanDocument2 pagesMechani Calengi Neer: Muhammadadnanmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Weirs & BarragesDocument38 pagesWeirs & Barragesmuhammad adnann100% (1)
- Refe Letter of Professor 5Document1 pageRefe Letter of Professor 5muhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Candidate Student Application Form: UniversityDocument1 pageCandidate Student Application Form: Universitymuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Title: Purpose of Survey Lab Equipment: NameDocument2 pagesTitle: Purpose of Survey Lab Equipment: Namemuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Functional English:: Class:Bsc - Mechanical EngineeringDocument8 pagesFunctional English:: Class:Bsc - Mechanical Engineeringmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Weirs & Barrages 2Document44 pagesWeirs & Barrages 2muhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Creation of PakistanDocument9 pagesCreation of Pakistanmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Name: Muhammad Adnan: Working of Turbo Jet EnginDocument7 pagesName: Muhammad Adnan: Working of Turbo Jet Enginmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- HT & LT Winding Termination - : Power FactorDocument10 pagesHT & LT Winding Termination - : Power Factormuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument13 pagesAssignmentmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Introdu Ction To MS Excel: Name: M.AdnanDocument2 pagesIntrodu Ction To MS Excel: Name: M.Adnanmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Iintroduction To Work Shop Tools: Name: M.AdnanDocument2 pagesIintroduction To Work Shop Tools: Name: M.Adnanmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Functional English:: Class:Bsc - Mechanical EngineeringDocument8 pagesFunctional English:: Class:Bsc - Mechanical Engineeringmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Name: Muhammad Adnan: Working of Turbo Jet EnginDocument7 pagesName: Muhammad Adnan: Working of Turbo Jet Enginmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Introdu Ction To C++: Name: M.AdnanDocument2 pagesIntrodu Ction To C++: Name: M.Adnanmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer ?Document30 pagesWhat Is Computer ?muhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- 06 Auto TransformerDocument19 pages06 Auto TransformerMuhammad NaguibNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Structure and Functions of The EyeDocument12 pagesLesson 2 The Structure and Functions of The EyeNguyễn Gia LộcNo ratings yet
- Lumen Method Worksheet SI v2Document8 pagesLumen Method Worksheet SI v2Hiram Flores100% (1)
- Study Material Class 10Document19 pagesStudy Material Class 10Shivam Tiwari100% (2)
- TDJ 609015DEI 65Fv01Document1 pageTDJ 609015DEI 65Fv01辛凯No ratings yet
- Assignment Cover Page FormatDocument3 pagesAssignment Cover Page FormatMahadi Hasan KhanNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light: Plane MirrorDocument3 pagesReflection of Light: Plane MirrorJaymarie Zabate100% (1)
- Analytical Chemistry - Exp 1Document8 pagesAnalytical Chemistry - Exp 1Zharifah Bari'ah Basa'ah100% (1)
- Unit-Ii (Part-I) : K.Saravanamoorthy Assistant Professor Ece / SsietDocument90 pagesUnit-Ii (Part-I) : K.Saravanamoorthy Assistant Professor Ece / SsietsamNo ratings yet
- Em 474 N 09 02 Cincinnati CL 7a Laser System With PC Control Operation Safety and Maintenance ManualDocument149 pagesEm 474 N 09 02 Cincinnati CL 7a Laser System With PC Control Operation Safety and Maintenance ManualManolo MedranoNo ratings yet
- 1648474629wave OpticsDocument41 pages1648474629wave OpticsNahush sarvaiyaNo ratings yet
- Photorealistic Texturing For Dummies Pt5Document10 pagesPhotorealistic Texturing For Dummies Pt5Miroslav MojicNo ratings yet
- Electrodynamics and Insulating Materials BDocument331 pagesElectrodynamics and Insulating Materials BOnyango OkeloNo ratings yet
- Final Consolidated Expts-18eel46Document55 pagesFinal Consolidated Expts-18eel46AshwiniNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Cambridge: Light Chapter: Refraction of LightDocument5 pagesO Level Physics Cambridge: Light Chapter: Refraction of LightKoushin UnberNo ratings yet
- Kerala SSLC Physics CH 4-6 Easy Note (Eng Med)Document11 pagesKerala SSLC Physics CH 4-6 Easy Note (Eng Med)Asish ThampiNo ratings yet
- S8 Language Worksheets Unit 6Document4 pagesS8 Language Worksheets Unit 6lukescienceteacherNo ratings yet
- ITT American Electric Horizontal Cutoff Luminaire Series 13-14-25-26 Spec Sheet 2-81Document6 pagesITT American Electric Horizontal Cutoff Luminaire Series 13-14-25-26 Spec Sheet 2-81Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- 1 Dipole Antenna: Assignment-2 Write Short Notes On Different Types of Antennas Used in Communication FieldDocument6 pages1 Dipole Antenna: Assignment-2 Write Short Notes On Different Types of Antennas Used in Communication FieldAkmal KhanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science MCQs Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current DPP1Document5 pagesClass 10 Science MCQs Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current DPP1Paarth BansalNo ratings yet
- U1L7 Lab StarSpectraSEDocument3 pagesU1L7 Lab StarSpectraSEjpstep13No ratings yet
- Admin - Contentimages - Op - Light Brochure PDFDocument7 pagesAdmin - Contentimages - Op - Light Brochure PDFRoberto AraujoNo ratings yet
- AP301 Modern Physics I: Prof. Daniel S. P. Lau Daniel - Lau@polyu - Edu.hk Tel: 2766 5679 Office: CD622Document111 pagesAP301 Modern Physics I: Prof. Daniel S. P. Lau Daniel - Lau@polyu - Edu.hk Tel: 2766 5679 Office: CD622doldolzz100% (1)
- Anna University First Year Practical Question Paper GE 6163 Set2 - 2013 RegulationGE 6163Document2 pagesAnna University First Year Practical Question Paper GE 6163 Set2 - 2013 RegulationGE 6163heavendewNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering Lab Report - Experiment-2Document6 pagesMicrowave Engineering Lab Report - Experiment-2GaneshNo ratings yet
- Textbook Nanophotonics and Plasmonics An Integrated View 1St Edition Ching Eng Jason PNG Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Nanophotonics and Plasmonics An Integrated View 1St Edition Ching Eng Jason PNG Ebook All Chapter PDFlouis.oller517100% (13)
- Cebik-A TaleOfThreeLpasDocument98 pagesCebik-A TaleOfThreeLpasAlejandro AlbanesiNo ratings yet
- Technical DataDocument27 pagesTechnical Datasatria ghaniNo ratings yet
Working Principle of Induction Motor
Working Principle of Induction Motor
Uploaded by
muhammad adnann0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageAn induction motor works through electromagnetic induction, where current induced in the rotor's short-circuited windings generates a magnetic field that causes the rotor to rotate. When alternating current is applied to the stator windings, it generates a magnetic flux that cuts the rotor windings, inducing current in them. This induced current in turn creates another magnetic field in the rotor that lags behind the stator field, producing a torque that causes the rotor to rotate at a speed dependent on the alternating current supply.
Original Description:
Original Title
ac motor
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn induction motor works through electromagnetic induction, where current induced in the rotor's short-circuited windings generates a magnetic field that causes the rotor to rotate. When alternating current is applied to the stator windings, it generates a magnetic flux that cuts the rotor windings, inducing current in them. This induced current in turn creates another magnetic field in the rotor that lags behind the stator field, producing a torque that causes the rotor to rotate at a speed dependent on the alternating current supply.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageWorking Principle of Induction Motor
Working Principle of Induction Motor
Uploaded by
muhammad adnannAn induction motor works through electromagnetic induction, where current induced in the rotor's short-circuited windings generates a magnetic field that causes the rotor to rotate. When alternating current is applied to the stator windings, it generates a magnetic flux that cuts the rotor windings, inducing current in them. This induced current in turn creates another magnetic field in the rotor that lags behind the stator field, producing a torque that causes the rotor to rotate at a speed dependent on the alternating current supply.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
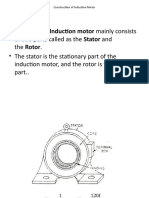
Working Principle of Induction Motor
We need to give double excitation to make a machine to rotate. For example
if we consider a DC motor, we will give one supply to the stator and another
to the rotor through brush arrangement. But in induction motor we give only
one supply, so it is really interesting to know that how it works. It is very
simple, from the name itself we can understand that induction process is
involved. Actually when we are giving the supply to the stator winding, flux
will generate in the coil due to flow of current in the coil. Now the rotor
winding is arranged in such a way that it becomes short circuited in the rotor
itself. The flux from the stator will cut the coil in the rotor and since the rotor
coils are short circuited, according to Faraday's law of electromagnetic
induction, current will start flowing in the coil of the rotor. When the current
will flow, another flux will get generated in the rotor. Now there will be two
flux, one is stator flux and another is rotor flux and the rotor flux will be
lagging w.r.t to the stator flux. Due to this, the rotor will feel a torque which
will make the rotor to rotate in the direction of rotating magnetic flux. So the
speed of the rotor will be depending upon the ac supply and the speed can
be controlled by varying the input supply. This is the working principle of
an induction motor of either type single and three phase. .
You might also like
- Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesLesson PlanKhairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor CharacteristicsDocument14 pagesInduction Motor CharacteristicsAnnaRajNo ratings yet
- How Does An Induction Motor WorkDocument7 pagesHow Does An Induction Motor WorkLeandro CamargoNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument26 pagesElectrical MachinesVaibhav BacchavNo ratings yet
- What Is An Induction MotorDocument3 pagesWhat Is An Induction MotorfarizabintenoorNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Stator ConstructionDocument9 pagesInduction Motor: Stator ConstructionMohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument23 pagesInduction Motorsai netNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor: Rotor (Document3 pagesElectric Motor: Rotor (qwert qwertNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument3 pagesInduction MotorKazuha MinatoNo ratings yet
- AC MotorsDocument48 pagesAC MotorsBrandon SookdeoNo ratings yet
- Torque Equ of Ac MotorDocument13 pagesTorque Equ of Ac MotorAnonymous xaeuoo4No ratings yet
- Ac Motors: (A) Synchronous Motors. (B) Asynchronous MotorsDocument18 pagesAc Motors: (A) Synchronous Motors. (B) Asynchronous MotorsStudy portalNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Induction MotorDocument2 pagesSingle Phase Induction Motorjay shahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Induction Motor: Experiment 11Document4 pagesIntroduction To Induction Motor: Experiment 11Apna VeerNo ratings yet
- DC and Ac Motor Basic PrincipleDocument1 pageDC and Ac Motor Basic Principledan matombeNo ratings yet
- ELE290 Chapter 6Document21 pagesELE290 Chapter 6imfendiNo ratings yet
- EE313 Class10Document9 pagesEE313 Class10Zahid MarwatNo ratings yet
- 1 Phase Induction MotorDocument2 pages1 Phase Induction Motorjay shahNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 - Induction MachineDocument35 pagesMODULE 4 - Induction MachinedamoskidanielNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment 4 PDFmaha saeedNo ratings yet
- AC Synchronous GeneratorDocument8 pagesAC Synchronous Generatoraswardi8756No ratings yet
- Induction Motor: This Article Does NotDocument24 pagesInduction Motor: This Article Does Notyashraj786100% (1)
- Induction Motor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesInduction Motor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJose EvonneNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorsDocument28 pagesInduction MotorsKimsairng CheaNo ratings yet
- Ex 3Document7 pagesEx 3Feras Al-AzzehNo ratings yet
- #5 Module 5Document52 pages#5 Module 5anishdeshmukh108No ratings yet
- EES (Lec20)Document16 pagesEES (Lec20)Muhammad SagheerNo ratings yet
- AC MotorDocument22 pagesAC MotorRavindar_Singh0% (1)
- AC MotorDocument22 pagesAC MotorMoise CristinaNo ratings yet
- Unit - IvDocument24 pagesUnit - Ivdurairajgeetha318No ratings yet
- Document PDFDocument21 pagesDocument PDFHarizx SaufixNo ratings yet
- Lec 5Document15 pagesLec 5Fernando Paez MendizabalNo ratings yet
- Induction, Squirrel Cage Motor - Torque CalculationDocument10 pagesInduction, Squirrel Cage Motor - Torque CalculationAlexandra100% (1)
- Induction MotorDocument4 pagesInduction MotorSenjuti DeNo ratings yet
- L3 - Three Phase Induction Motor-1Document52 pagesL3 - Three Phase Induction Motor-1Proshenjit BaruaNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument13 pagesInduction MotorAsif AhnafNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Navigation SearchDocument8 pagesInduction Motor: Navigation SearchSoni Mishra TiwariNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Induction Motors PDFDocument11 pages3 Phase Induction Motors PDFFauzan Dimas KusyonoNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Induction MotorsDocument10 pages3 Phase Induction MotorsSTIP Teknik BravoNo ratings yet
- Homework 7 Induction Motor 1Document3 pagesHomework 7 Induction Motor 1JamrNo ratings yet
- Skip To ContentDocument17 pagesSkip To Contentkidanemariam teseraNo ratings yet
- 3phase Induction Motor (Sukhpreet)Document17 pages3phase Induction Motor (Sukhpreet)Ankesh KunwarNo ratings yet
- The Meaning of Electric MotorsDocument11 pagesThe Meaning of Electric MotorsMelindaTamrinNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase IMDocument16 pages3-Phase IMk rajendraNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor BalaDocument8 pagesInduction Motor Baladinesh11rNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Ktu Module 6Document36 pagesMechatronics Ktu Module 6Adarsh s nairNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor and Hydropower PlantDocument24 pagesInduction Motor and Hydropower PlantYugalal GurungNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument7 pagesElectrical Machinesusama jabbarNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument21 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorPrianshu Jyosyula100% (2)
- Rewinding M 1 FasaDocument31 pagesRewinding M 1 Fasanurjayaagung44No ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument2 pagesFinal ExamFlicker LoserNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: by WiresDocument3 pagesInduction Motor: by Wireswajeeh shahNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document20 pagesTopic 1Ʋiŋêet ḠåuṯḁmNo ratings yet
- How Does An Alternator WorkDocument3 pagesHow Does An Alternator WorkZaqPoilmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Induction Motor PDFDocument26 pagesChapter 3 Induction Motor PDFNeezam Halim50% (2)
- Electrical Interview Questions With AnswersDocument9 pagesElectrical Interview Questions With AnswersKrishnamoorthi VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Home-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsFrom EverandHome-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- Mechani Calengi Neer: MuhammadadnanDocument2 pagesMechani Calengi Neer: Muhammadadnanmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Weirs & BarragesDocument38 pagesWeirs & Barragesmuhammad adnann100% (1)
- Refe Letter of Professor 5Document1 pageRefe Letter of Professor 5muhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Candidate Student Application Form: UniversityDocument1 pageCandidate Student Application Form: Universitymuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Title: Purpose of Survey Lab Equipment: NameDocument2 pagesTitle: Purpose of Survey Lab Equipment: Namemuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Functional English:: Class:Bsc - Mechanical EngineeringDocument8 pagesFunctional English:: Class:Bsc - Mechanical Engineeringmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Weirs & Barrages 2Document44 pagesWeirs & Barrages 2muhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Creation of PakistanDocument9 pagesCreation of Pakistanmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Name: Muhammad Adnan: Working of Turbo Jet EnginDocument7 pagesName: Muhammad Adnan: Working of Turbo Jet Enginmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- HT & LT Winding Termination - : Power FactorDocument10 pagesHT & LT Winding Termination - : Power Factormuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument13 pagesAssignmentmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Introdu Ction To MS Excel: Name: M.AdnanDocument2 pagesIntrodu Ction To MS Excel: Name: M.Adnanmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Iintroduction To Work Shop Tools: Name: M.AdnanDocument2 pagesIintroduction To Work Shop Tools: Name: M.Adnanmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Functional English:: Class:Bsc - Mechanical EngineeringDocument8 pagesFunctional English:: Class:Bsc - Mechanical Engineeringmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Name: Muhammad Adnan: Working of Turbo Jet EnginDocument7 pagesName: Muhammad Adnan: Working of Turbo Jet Enginmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Introdu Ction To C++: Name: M.AdnanDocument2 pagesIntrodu Ction To C++: Name: M.Adnanmuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer ?Document30 pagesWhat Is Computer ?muhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- 06 Auto TransformerDocument19 pages06 Auto TransformerMuhammad NaguibNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Structure and Functions of The EyeDocument12 pagesLesson 2 The Structure and Functions of The EyeNguyễn Gia LộcNo ratings yet
- Lumen Method Worksheet SI v2Document8 pagesLumen Method Worksheet SI v2Hiram Flores100% (1)
- Study Material Class 10Document19 pagesStudy Material Class 10Shivam Tiwari100% (2)
- TDJ 609015DEI 65Fv01Document1 pageTDJ 609015DEI 65Fv01辛凯No ratings yet
- Assignment Cover Page FormatDocument3 pagesAssignment Cover Page FormatMahadi Hasan KhanNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light: Plane MirrorDocument3 pagesReflection of Light: Plane MirrorJaymarie Zabate100% (1)
- Analytical Chemistry - Exp 1Document8 pagesAnalytical Chemistry - Exp 1Zharifah Bari'ah Basa'ah100% (1)
- Unit-Ii (Part-I) : K.Saravanamoorthy Assistant Professor Ece / SsietDocument90 pagesUnit-Ii (Part-I) : K.Saravanamoorthy Assistant Professor Ece / SsietsamNo ratings yet
- Em 474 N 09 02 Cincinnati CL 7a Laser System With PC Control Operation Safety and Maintenance ManualDocument149 pagesEm 474 N 09 02 Cincinnati CL 7a Laser System With PC Control Operation Safety and Maintenance ManualManolo MedranoNo ratings yet
- 1648474629wave OpticsDocument41 pages1648474629wave OpticsNahush sarvaiyaNo ratings yet
- Photorealistic Texturing For Dummies Pt5Document10 pagesPhotorealistic Texturing For Dummies Pt5Miroslav MojicNo ratings yet
- Electrodynamics and Insulating Materials BDocument331 pagesElectrodynamics and Insulating Materials BOnyango OkeloNo ratings yet
- Final Consolidated Expts-18eel46Document55 pagesFinal Consolidated Expts-18eel46AshwiniNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Cambridge: Light Chapter: Refraction of LightDocument5 pagesO Level Physics Cambridge: Light Chapter: Refraction of LightKoushin UnberNo ratings yet
- Kerala SSLC Physics CH 4-6 Easy Note (Eng Med)Document11 pagesKerala SSLC Physics CH 4-6 Easy Note (Eng Med)Asish ThampiNo ratings yet
- S8 Language Worksheets Unit 6Document4 pagesS8 Language Worksheets Unit 6lukescienceteacherNo ratings yet
- ITT American Electric Horizontal Cutoff Luminaire Series 13-14-25-26 Spec Sheet 2-81Document6 pagesITT American Electric Horizontal Cutoff Luminaire Series 13-14-25-26 Spec Sheet 2-81Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- 1 Dipole Antenna: Assignment-2 Write Short Notes On Different Types of Antennas Used in Communication FieldDocument6 pages1 Dipole Antenna: Assignment-2 Write Short Notes On Different Types of Antennas Used in Communication FieldAkmal KhanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science MCQs Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current DPP1Document5 pagesClass 10 Science MCQs Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current DPP1Paarth BansalNo ratings yet
- U1L7 Lab StarSpectraSEDocument3 pagesU1L7 Lab StarSpectraSEjpstep13No ratings yet
- Admin - Contentimages - Op - Light Brochure PDFDocument7 pagesAdmin - Contentimages - Op - Light Brochure PDFRoberto AraujoNo ratings yet
- AP301 Modern Physics I: Prof. Daniel S. P. Lau Daniel - Lau@polyu - Edu.hk Tel: 2766 5679 Office: CD622Document111 pagesAP301 Modern Physics I: Prof. Daniel S. P. Lau Daniel - Lau@polyu - Edu.hk Tel: 2766 5679 Office: CD622doldolzz100% (1)
- Anna University First Year Practical Question Paper GE 6163 Set2 - 2013 RegulationGE 6163Document2 pagesAnna University First Year Practical Question Paper GE 6163 Set2 - 2013 RegulationGE 6163heavendewNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering Lab Report - Experiment-2Document6 pagesMicrowave Engineering Lab Report - Experiment-2GaneshNo ratings yet
- Textbook Nanophotonics and Plasmonics An Integrated View 1St Edition Ching Eng Jason PNG Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Nanophotonics and Plasmonics An Integrated View 1St Edition Ching Eng Jason PNG Ebook All Chapter PDFlouis.oller517100% (13)
- Cebik-A TaleOfThreeLpasDocument98 pagesCebik-A TaleOfThreeLpasAlejandro AlbanesiNo ratings yet
- Technical DataDocument27 pagesTechnical Datasatria ghaniNo ratings yet