Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Engineering Thermodynamics Unit Ii Notes 17
Engineering Thermodynamics Unit Ii Notes 17
Uploaded by
amarparimiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Thermodynamics Unit Ii Notes 17
Engineering Thermodynamics Unit Ii Notes 17
Uploaded by
amarparimiCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Thermodynamics
Unit II
Notes 17
Constant volume gas thermometer:-
It consists of two vertical grass tubes connected By a flexible tube. one end of the glass tube is exposed to atmosphere
and the other end is in Communication with the gas bulb to a capillary tube, The gas bulb is filled with any gas like
oxygen, nitro zed, hydrogen and the nanometer is filled with mercury.
Let P0 is the atmospheric pressure p the density of nanometric liquid H is the a differential head Whenever the
gas bulb is exposed to any temperature T (which is unknown) then the pressure D is equals to atmospheric pressure +
pressure due to differential head.
P = P0 + pgh
Now expose the gas bulb to the t ripple point temperature (273.16k) At this instaent the pressure acting on the
gas
PTRP=P0 +Rgh
We know that T oe P
T=CP
T/P=constant
Ttrip / Ptrip = constant
T / P = Ttriple / Ptriple
T = P / Pptriple X Ttriple
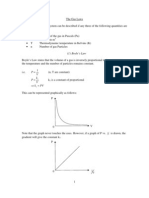
If the a constant volume gas thermometer is operated with different gasses inside the gas bulb at different
instances the variation in temperature w.r to pressure is shown in fig
GMRIT, Rajam.
P. Sai Chaitanya
Engineering Thermodynamics
Unit II
Notes 17
If these threads are extrapolated onto the negative X-axis all the lines are intersect with a common point. Which
indicates the temperature -273.100C i.e. it is the minimum temperature which we can measure using a constant volume
gas thermometer.
Joules experiment:Consider certain mass of water inside and adiabatic
vessel. Which is provided with a pedal wheel and a
thermometer.
Let the initial temperature of water is T1 by
operating the pedal wheel we can stir the water for a period
of time we can find an observable rising temperature (with
the collision of water molecules). Let dw is a elemental
work supply to the system to stir the water.. The
temperature of the water will raise let this is process 1 to 2
If the system is exposed to the atmosphere by removing the
cap, over a finite period of time the system attains thermal
equilibrium condition with the surroundings. Let this is
process 2 to 1 and attains the initial state. During this
process certain quantity of the heat is being rejected to the
atmosphere. The process (1) to (2) and (2) to (1) combindly
executes the cycle. Joule connected thousands of
experiments and the observed that dW oe dQ
dW = J dQ
Where J is the joules constant (or) mechanical
equivalent of the work.
GMRIT, Rajam.
P. Sai Chaitanya
Engineering Thermodynamics
GMRIT, Rajam.
Unit II
Notes 17
P. Sai Chaitanya
You might also like
- Ats Spark Plug Cleaner & TesterDocument2 pagesAts Spark Plug Cleaner & TesteramarparimiNo ratings yet
- Firing Systems in Power PlantsDocument54 pagesFiring Systems in Power PlantsamarparimiNo ratings yet
- Forced ConvectionDocument5 pagesForced ConvectionRahul NairNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GasesDocument49 pagesChapter 5 GasesdeemahhwNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas-Worked ExamplesDocument4 pagesIdeal Gas-Worked ExamplesMuhammad MosaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ThermometryDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Thermometryikaro181083No ratings yet
- Thermal Physics Lecture 27Document8 pagesThermal Physics Lecture 27OmegaUserNo ratings yet
- Chapter4-Lecture No.1Document19 pagesChapter4-Lecture No.1Mohammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- Lab 11: Lab Report Cooling TowerDocument7 pagesLab 11: Lab Report Cooling TowerKhairulAzwanizam100% (2)
- Air Con Refrig Lecture-SlideDocument27 pagesAir Con Refrig Lecture-SlideboonwueNo ratings yet
- Pure SubstancesDocument36 pagesPure SubstancespavanraneNo ratings yet
- CML100 Ar2a PDFDocument34 pagesCML100 Ar2a PDFDivyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower T P ADocument6 pagesCooling Tower T P AZulhisham ZainiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument86 pagesChemical Engineering ThermodynamicsSreedhar BabuNo ratings yet
- TD Module 2Document47 pagesTD Module 2mujeebNo ratings yet
- SCHX1014 - Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics - Unit 3Document17 pagesSCHX1014 - Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics - Unit 3Shanmuga PriyaNo ratings yet
- Entropy Changes & Processes Entropy at A Phase TransitionDocument4 pagesEntropy Changes & Processes Entropy at A Phase TransitionnabilanftNo ratings yet
- Properties of GasesDocument12 pagesProperties of GasesArjun SainiNo ratings yet
- Gas Measurements and Measuring DevicesDocument21 pagesGas Measurements and Measuring DevicesmohamedNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument32 pagesThermodynamicsAsim AnsariNo ratings yet
- PV NRTDocument3 pagesPV NRTthreedlabsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Ideal GasesDocument71 pagesChapter 5 - Ideal GasesRabbitNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro Gases THermodynamics 2022Document15 pages1 Intro Gases THermodynamics 2022Jey BlaQNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument9 pagesGas LawsGineNo ratings yet
- ثرموداينمكDocument10 pagesثرموداينمكabdcivilNo ratings yet
- 1 - Gas Thermometer and Absolute ZeroDocument6 pages1 - Gas Thermometer and Absolute ZeroPeggie ZengNo ratings yet
- Keph 203Document24 pagesKeph 203Ayush JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 12 - ThermodynamicsDocument12 pages12 - Thermodynamicssrujanx360No ratings yet
- ME 161: Introduction To Mechanical Engineering: Asif KabirDocument21 pagesME 161: Introduction To Mechanical Engineering: Asif KabirMohammad Asif KabirNo ratings yet
- Science 10 NotesDocument17 pagesScience 10 NotesDerik Resultay100% (1)
- Thermal PhysicsDocument24 pagesThermal PhysicsSuraj GopaulNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument22 pagesThermodynamicssachiandmarshneelNo ratings yet
- Kennard E.H. - Entropy, Reversible Processes and Thermo-Couples (1932)Document5 pagesKennard E.H. - Entropy, Reversible Processes and Thermo-Couples (1932)Juan Sebastian SánchezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document47 pagesChapter 19maxim santos100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Practice Problems 3Document13 pagesThermodynamics Practice Problems 3Minh Trương PhúcNo ratings yet
- Entropy ChangeDocument13 pagesEntropy ChangeAhmedAmer1No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (PHY)Document103 pagesChapter 2 (PHY)meemaNo ratings yet
- Marcet BoilerDocument9 pagesMarcet BoilerKayfe sayfadeenNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Boyle's Law or The Pressure-Volume Law States That The Volume of A Given AmountDocument9 pagesGas Laws: Boyle's Law or The Pressure-Volume Law States That The Volume of A Given AmountArun KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Natural and Forced Convection ExperimentsDocument12 pagesNatural and Forced Convection ExperimentsOmar Yamil Sanchez Torres25% (4)
- Exp-40 Part2Document22 pagesExp-40 Part2Ahmet Samet ÖzdilekNo ratings yet
- Gas - Vapor Mixtures & Air - ConditioningDocument27 pagesGas - Vapor Mixtures & Air - ConditioningElena Romero ArandaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lab ReportDocument15 pagesThermodynamics Lab ReportFahd Ghuman100% (2)
- 1 Intro Gases THermodynamicsDocument16 pages1 Intro Gases THermodynamicsThabiso GwijiNo ratings yet
- Clausius - Clapeyron Equation and Phase TransitionDocument5 pagesClausius - Clapeyron Equation and Phase TransitionVivek MauryaNo ratings yet
- All The Lecture Notes of ME56Document31 pagesAll The Lecture Notes of ME56Kent NabzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument37 pagesChapter 3 - Laws of Thermodynamicsabdullahmunsi3998No ratings yet
- Basic-Thermodynamics 4Document20 pagesBasic-Thermodynamics 4Bonsay 23No ratings yet
- Lab O2. Variation of Atmospheric Pressure With Altitude: 5 N M Lbs inDocument10 pagesLab O2. Variation of Atmospheric Pressure With Altitude: 5 N M Lbs inAnil PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Joule Thomson ExpansionDocument11 pagesJoule Thomson ExpansionIsabelle Yang100% (2)
- Manual For Experimental Water Cooling TowerDocument7 pagesManual For Experimental Water Cooling TowerBalRam Dhiman100% (1)
- Report PVTDocument17 pagesReport PVTMuhammad Muzamil MazriNo ratings yet
- 5-State of MatterDocument26 pages5-State of MatterAbhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- Ch4 PsychrometricsDocument102 pagesCh4 PsychrometricsJayant SisodiaNo ratings yet
- 5 Temp Ideal Gas-Fall 2022Document22 pages5 Temp Ideal Gas-Fall 2022asakr8481No ratings yet
- Humidification and Cooling Towers - 2nd 2011Document46 pagesHumidification and Cooling Towers - 2nd 2011Vona Sophia MalvarNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 BasicsDocument76 pagesUnit 3 BasicsamarparimiNo ratings yet
- ForgingDocument26 pagesForgingamarparimiNo ratings yet
- Forging Processes: Satya Amarnadh ParimiDocument26 pagesForging Processes: Satya Amarnadh ParimiamarparimiNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes: Multiple Choice 1. A. B. C. DDocument19 pagesManufacturing Processes: Multiple Choice 1. A. B. C. DamarparimiNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document114 pagesModule 1amarparimiNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning EquipmentsDocument44 pagesAir Conditioning Equipmentsamarparimi0% (1)
- WeldingDocument169 pagesWeldingamarparimi100% (1)
- " (R! I.O ,-+e) - ", Ir) : ('I Al FLLT JDocument20 pages" (R! I.O ,-+e) - ", Ir) : ('I Al FLLT JamarparimiNo ratings yet
- R&ac Unit-IiiDocument52 pagesR&ac Unit-Iiiamarparimi100% (1)
- Conclusion and Future ScopeDocument1 pageConclusion and Future ScopeamarparimiNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning PDFDocument276 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning PDFamarparimi100% (1)
- Results and DiscussionsDocument13 pagesResults and DiscussionsamarparimiNo ratings yet
- Grass Cutter 1 PDFDocument4 pagesGrass Cutter 1 PDFamarparimiNo ratings yet
- PCM in Vapour Refrigeration SystemDocument16 pagesPCM in Vapour Refrigeration SystemamarparimiNo ratings yet
- Y.), I b7 'F'': ' F D",-J1 of C/ Ffu. RV 'L' FJ 7:'dDocument34 pagesY.), I b7 'F'': ' F D",-J1 of C/ Ffu. RV 'L' FJ 7:'damarparimiNo ratings yet
- Cnc&Camshort Answer Questions 20161029 0002Document21 pagesCnc&Camshort Answer Questions 20161029 0002amarparimiNo ratings yet
- Lagrange MultiplierDocument5 pagesLagrange MultiplierAdantey MichaelNo ratings yet
- Problems On Boiler Performance.Document1 pageProblems On Boiler Performance.amarparimiNo ratings yet
- IC Engines Amar1Document73 pagesIC Engines Amar1amarparimiNo ratings yet