Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Taxation (NIRC Sec 1-36
Taxation (NIRC Sec 1-36
Uploaded by
Angie Louh S. DiosoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Taxation (NIRC Sec 1-36
Taxation (NIRC Sec 1-36
Uploaded by
Angie Louh S. DiosoCopyright:
Available Formats
TAXATION 1-MIDTERM EXAM
DIOSO
BY: ANGIE LOUH S.
TITLE I. ORGANIZATION AND FUNCTION OF THE BUREAU OF INTERNAL REVENUE (BIR)
POWERS AND DUTIES OF THE BIR (ACEEGA)
1) Assessment and Collection of national internal revenue: (a) taxes (b) fees (c) charges
2) Enforcement of all
(a) Forfeitures (b) fines and (c) penalties connected therewith
3) Execution of all judgments decided in BIRs favor By
(a) the Court of Tax Appeals (CTA) and (b) the ordinary courts
4) Give effect to and administer the supervisory and police powers conferred to it by NIRC or by other laws.
(Sec. 2)
In short: 1. Asses and collect 2. Execute 3. Administer 4. Enforce. ( Ae-ae)
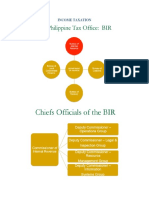
OFFICIALS OF THE BIR
1) one chief ( CIR)Commissioner of Internal Revenue (Commissioner)
2) four assistant chiefs (DCIR) Deputy Commissioners (Sec. 3)
*E.O. 430 (July 28, 1997) designates each of the 4 Deputy Commissioners to head the following functional
groups:
(a) Operations group
(b) Legal Enforcement Group
(c) Information Systems Group
(d) Resource Management Group
NOTE: PER SIR FLORES 6 DEPUTY UNDER PRESENT SET-UP
POWERS OF THE COMMISSIONER
A. Power to interpret tax law and decide tax cases (Sec 4)
1) Interpret provisions of NIRC and other tax laws subject to review by the Secretary of Finance
2) Decide:
(a) Disputed assessments
(b) Refunds of internal revenue taxes, fees and charges
(c) Penalties imposed in relation thereto
(d) other matters arising from NIRC or other laws or portions thereof administered by the BIR subject
to the exclusive appellate jurisdiction of the CTA
B. POWER TO OBTAIN INFORMATION, SUMMON, EXAMINE AND TAKE TESTIMONY OF PERSONS
(SEC.5)
1) For the Commissioner to ascertain:
(a) correctness of any return or in making a return where none has been made
(b) liability of any person for any internal revenue tax or in correcting such liability
(c) tax compliance
The Commissioner is authorized:
2) to Examine any relevant Book, paper, record or other data
3) to Obtain any Information (costs, volume of production, receipts, sales, gross income, etc), on a regular
basis from:
(a) any person other than the person under investigation or
(b) any office or officer of the national/local government, government agencies and instrumentalities
(Bangko Sentral,GOCCs)
4) To Summon (a) the person liable for tax or required to file a return or (b) any officer or employee of such
person or
(c) any person having in his possession/custody/ care 1. the books of accounts 2. accounting records
of entries relating to the business of the person liable for tax or any other person
5) to Produce such books, papers, records and other data and to give testimony
6) to take the Testimony of the person concerned, under oath as may be relevant to the inquiry
7) To cause revenue officers and employees to make a Canvass of any revenue district or region
Note: nothing in Section 5 shall be construed as granting the Commissioner the authority to inquire into bank
deposits other than as provided for under Sec. 6 (F) of the Code (authority to inquire into bank deposits).
C. POWER TO MAKE ASSESSMENTS, PRESCRIBE ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS FOR TAX
ADMINISTRATION AND ENFORCEMENT (SEC. 6)
1) Examination of returns and determination of
(a) After a return has been filed the Commissioner or his representative may authorize
i. the Examination of any taxpayer; and
ii. the Assessment of the correct amount of tax;
TAXATION 1-MIDTERM EXAM
DIOSO
BY: ANGIE LOUH S.
(b) Failure to file a return shall not prevent the Commissioner from authorizing the examination of any
taxpayer;
Any tax or deficiency tax so assessed shall be paid upon notice and demand from the Commissioner
or his representative.
Any return, statement or declaration filed in any authorized office shall not be withdrawn; but within
THREE YEARS from date of filing, the same may be modified, changed or amended; provided that no
notice for audit or investigation of such return, has in the meantime, been actually served upon the
taxpayer.
2) Failure to submit required returns and other documents If a person
(a) fails to file a required return or report at the time prescribed or
(b) Willfully or otherwise files a false or fraudulent return,
The Commissioner shall Make or Amend the return from
(a) his own knowledge or (b) from such information as he can obtain through testimony or otherwise
which shall be prima facie correct and sufficient for all legal purposes
3) Inventory-taking, Surveillance, Presumptive Gross Sales
(a) Commissioner may, at any time during the taxable year
1. order the Inventory taking of goods of any taxpayer; or
2. may place the business operations of any person (natural/juridical) under Observation or
Surveillance if there is reason to believe that such person is not declaring his correct income, sales or
receipts for tax purposes.
The findings may be used as basis for assessing the taxes and shall be deemed prima facie correct.
(b) Commissioner may prescribe a Minimum amount of gross receipts, sales and taxable base (taking into
account the sales and income of other persons engaged in similar business) :
1. When a person has failed to issue receipts as required by Sec. 113 (Invoice requirements for
VATregistered persons) and Sec. 237 (Issuance of Receipts or Commercial Invoices); or
2. When the books of accounts or records do not correctly reflect the declarations made or required to
be made in a return, such minimum amount shall be prima facie correct
4) Terminate taxable period - Commissioner shall declare the tax period ofa taxpayer terminated and send
notice to the taxpayer of such decision with a request for immediate payment of the tax, when it has
come to the knowledge of the Commissioner: (RIRHO)
(a) that a taxpayer is Retiring from business subject to tax or
(b) is Intending to leave the Philippines or
(c) to Remove his property therefrom or
(d) to Hide or conceal his property or
(e) is performing any act tending to Obstruct the proceedings for the collection of tax
5) Prescribe Real Property Values - The Commissioner is authorized to:
(a) divide the Philippines into different zones or areas and
(b) determine the fair market value of real properties located in each zone or area
For tax purposes, the value of the property shall be whichever is higher of:
(a) Fair market value as determined by the Commissioner; or
(b) Fair market value as shown in the schedule of values of the provincial and city assessors.
6) Authority to Inquire into Bank Deposit - Notwithstanding R.A. 1405 (Bank Secrecy Law) the Commissioner
is authorized to inquire into the Bank deposits of:
(a) a decedent to determine his gross estate
(b) a taxpayer who has filed an application to compromise payment of tax liability by reason of financial
incapacity
The taxpayers application for compromise shall not be considered unless he waives in writing his
privilege under RA 1405 and other general or special laws. Such waiver shall authorize the
Commissioner to inquire into his bank deposits.
7) Authority to Register tax agents (a) The Commissioner shall Accredit and Register, individuals and general professional partnerships
and their rep.
who prepare and file tax returns and other papers or who appear before the BIR
(b) The Commissioner shall create national and regional accreditation boards
Those who are denied accreditation may appeal the same to the Sec. of Finance who shall rule on the
appeal within 60 days from receipt of such appeal. Failure of the Sec. of Finance to rule on the appeal
within the said period shall be deemed as approval for accreditation.
TAXATION 1-MIDTERM EXAM
DIOSO
BY: ANGIE LOUH S.
8) Authority to Prescribe Additional RequirementsThe Commissioner may prescribe the manner of compliance with any documentary or procedural
requirement for the submission or preparation of financial statements accompanying tax returns.
D. Authority to delegate power (Sec. 7)
The Commissioner may delegate the powers vested in him to subordinate officials with rank equivalent
to Division Chief or higher, subject to limitations/restrictions imposed under the rules and regulations EXCEPT,
(the following powers shall NOT be delegated): (RIR CoA A)
1) power to Recommend the promulgation of rules and regulations by the Sec. of Finance
2) power to Issue rulings of first impression or to Reverse, revoke, modify any existing rule of the BIR
3) power to Compromise or Abate any tax liability EXCEPT, the regional evaluation board may
compromise:
(a) assessments issued by regional offices involving deficiency taxes of P500,000 or
less; and
(b) minor criminal violations as may be determined by the rules
Regional Evaluation Board is composed of:
i. Regional Director as Chairman
ii. Asst. Regional Director
iii. Heads of the Legal, Assessment and Collection Div.
iv. Revenue District Officer having jurisdiction over the taxpayer
4) power to Assign or reassign internal revenue officers to establishments where articles subject to
excise tax are kept
E. Assignment of Internal Revenue Officers (Secs. 16 &17)
The Commissioner may assign/ reassign internal revenue officers:
1) involved in excise tax functions as often as the exigencies of revenue service may require; provided
that he shall in no case stay in his assignment for more than 2 years (Sec. 16)
2) without change in rank and salary, to other or special duties connected with the enforcement and
administration of internal revenue laws as the exigencies of the service may require; provided that
officers assigned to perform assessment or collection functions shall not remain in the same
assignment for more than 3 years; assignment of officers and employees to special duties shall not
exceed 1 year (Sec. 17)
F. Internal Revenue Districts (Sec. 9)
The Commissioner, with approval of the Sec. of Finance, shall divide the Philippines into such
number of revenue districts for administrative purposes. Each district shall be under the supervision of a
Revenue District Officer.
Duties of the Commissioner: (PASO)
1) To Prescribe, provide and distribute to the proper officials the requisite licenses, internal revenue
stamps, labels, all other forms, certificates, bonds, records, invoices, books, receipts, instruments and
appliances used in administering laws falling within the jurisdiction of BIR
2) To Acknowledge payment of any tax under this Code expressing
a) the amount paid and
b) the particular account for which payment was made (Sec. 8)
3) To Submit reports to the appropriate committee of Congress upon its request and in aid of
legislation, which information or report shall include, but not be limited to:
(a) industry audits
(b) collection performance data
(c) status reports in criminal actions initiated against persons
(d) taxpayers returns provided, any return or information which can be associated with or
identifies, directly or indirectly a particular taxpayer, shall be furnished to the appropriate
committee of Congress only when sitting in Executive Session, unless the taxpayer consents in
writing to such disclosure
4) Submit reports to the Oversight Committee through the Chairman of the Committee on Ways and
Means of the Senate and House of Representatives, on the exercise of his powers of abatement and
compromise of taxes (Sec. 204) every 6 months of each calendar year. (Sec. 20)
TAXATION 1-MIDTERM EXAM
DIOSO
BY: ANGIE LOUH S.
POWERS OF THE COMMISSIONER:
1. To interpret tax laws and to decide tax cases ( sec.4)
2. To obtain information, and to summon, examine and take testimony of persons ( sec.5)
3. To make assessments and prescribes additional requirements for tax administration and
enforcement (sec.6)
4. Authority to delegate power ( sec.7)
5. Duty to ensure the provision and distribution of forms, receipt, certificates and
applicances and the acknowledgement of payment of taxes(sec.8)
SOURCES OF REVENUE: (Sec. 21)
NATIONAL INTERNAL REVENUE TAXES: (I VEE DOO)
1) Income tax- a tax based on income, gross or net
2) Estate and Donors tax
Estate tax - a tax levied, assessed, collected and paid upon the transfer of the net estate of every
decedent whether resident or nonresident of the Philippines, based on the value of such net estate, by
including the value at the time of his death of all the property, real or personal, tangible or intangible,
wherever situated.(sec 84 & 85)
It is an excise tax imposed upon the privilege of transmitting property at the time of
death and on the privilege that a person is given in controlling to a certain extent the
disposition of his property to take effect upon death.
Donors tax- tax levied, assessed, collected and paid upon the transfer oby any person, resident or
nonresident , of the property by gift, whether the transfer is in trust or otherwise whether the gift is direct
or indirect, whether real or personal property,, tangible or intangible,based on the total net gifts made
during the calendar year computed in accordance with the schedule provided for under sec.99 of tax
laws.
3) Value-Added tax - is an indirect tax and the amount of tax may, by law, be shifted or passed on to the buyer,
transferee or lessee of the goods, properties or services. (Sec. 105, NIRC)
It is a tax on the estimated market value added to a product or material at each stage of its manufacture
or distribution, ultimately passed on to the consumer.
VAT is a tax on consumption levied on the sale, barter, exchange, or lease of goods or
properties and services in the Philippines and on importation of goods into the Philippines
The seller is the one statutorily liable for the payment of the tax but the amount of the tax may
be shifted or passed on to the buyer, transferee or lessee of the goods, properties or services.
However, in the case of importation, the importer is the one liable for the VAT. (Sec 4.105-2 RR 162005)
4) Other percentage tax- a business tax imposed on any person who is not vat-registered and who in the
sourse of business or trade,sells barters exchanges lesses goods or properties renderes services but whose
gross annual sales does not exceed 1.5m.
5) Excise tax- applies to tax on goods manufactured or produced in the phil. For domestic sale or consumption
or for any other disposition and to the thing imported which tax shall be in addition to the value-added
tax.specifictax- excise taxes imposed and based on weight or volume capacity or any physical unit of
measurement while advalorem tax based on the selling price or other specified value of the goods.
6) Documentary stamp tax-is a tax levied collected paid for ipon documents instruments loan agreements and
papers .
7) Such Other taxes as are or hereafter may be imposed and collected by the BIR
Title 11. TAX ON INCOME
SECTION 22.definition of terms:
1) Person an individual, a trust, estate or corp.
2) Corporation include partnerships (distinguish between ordinary and general professional partnership)
3) General professional partnership partnerships formed for the sole purpose of exercising their common
profession,
no part of its income being derived from engaging in any trade or business
4) Shares of stock includes shares of stock of a corp., warrants & options to purchase shares of stock, as
well as units of participation in a partnership (except gen. professional partnership), joint stock companies,
joint accounts, joint ventures taxable as corp., associations & recreation or amusement clubs & mutual fund
certificates
5) Taxpayer any person subject to tax
6) Taxable Year can either be calendar year (Jan 1 to Dec 31), or the fiscal year
7) Fiscal Year an accounting period of 12 months ending on the last day of any month other than December
(ex. Feb 1 to Jan 31)
TAXATION 1-MIDTERM EXAM
DIOSO
BY: ANGIE LOUH S.
8) Paid or incurred (cash method) or Paid or accrued (accrual method) payment actually made or if not
paid, actually liable for the expense.
INCOME- It refers to all wealth which flows into the taxpayer other than as mere return of capital. It
includes the forms of income specifically described as gains and profits, including gains derived from the sale
or other disposition of capital assets. (Sec. 36, RR No.2)
Income is a flow of service rendered by capital by payment of money from it or any benefit rendered by a fund
of capital in relation to such fund through a period of time. (Madrigal v. Rafferty, GR 12287, Aug. 8, 1918)
An income is an amount of money coming to a person or corporation within a specified time, whether
as payment for services, interest or profit from investment. Unless otherwise
Income
1. constitutes the investment which is the source of
income
2.Is the wealth
3. Is the tree
Capital
Any wealth which flows into the taxpayer other than a
mere return of capital
Is the service of wealth
Is the fuit
4. Fund
Flow
Definition of income tax.
A tax on all yearly profits arising from property, profession, trade or business, or a tax on persons income,
emoluments, profits and the like. (Fisher v. Trinidad, GR L-19030. Oct. 20, 1922)
the basis of income tax- Income tax is based on income, either gross or net, realized in one taxable year.
the nature of income tax- It is generally regarded as an excise tax. It is not levied upon persons, property,
funds or profits but on the privilege of receiving said income or profit.
the purposes of income tax- To:
1. Provide large amounts of revenue
2. Offset regressive sales and consumption taxes
3. Mitigate the evils arising from the inequality in the distribution of income and wealth which are considered
deterrents to social progress, by a progressive scheme of taxation (Madrigal v. Rafferty, GR 12287, Aug. 8,
1918)
INCOME TAX SYSTEM:
TAXABLE INCOME- The term taxable income means the pertinent items of gross iincome specified in the
NIRC less the deductions and or personal and additiona exemptions if any authorized for such types of
income by the NIRC or other special laws.
Income tax formula
Entire/total income ( legal or illegal)
Less: exclusions and income subj to final
tax(sec.32b)
Equals: gross income(sec 32a)
Less: allowable deductions(sec 34)
Equals: taxable net income(sec 31.)
Multiply by: tax rate (sec 24/27)
Equals: income tax due
Less: tax credit/withholding taxes
Equals: Tax still due/ refundable
TAXATION 1-MIDTERM EXAM
DIOSO
BY: ANGIE LOUH S.
DEFINITION OF GROSS INCOME:SEC 32
- It is a system of taxation where the income is taxed at gross. The taxpayer under this system is not
entitled to any deduction.
All income derived from whatever source, including (but not limited to the following items) (GRIP CARD GPP)
1) Gross income derived from the conduct of trade or business or the exercise of a profession
2) Rent Income
3) Interest Income
4) Prizes & winnings
5) Compensation for services in whatever form paid, including, but not limited to fees, salaries, wages,
commissions & similar items
6) Annuities
7) Royalties
8) Dividend Income
9) Gains derived from dealings in property
10) Pensions
11) Partners distributive share from the net income of the GPP (distributive share from ordinary partnerships
is taxable as dividends; in this case, the ordinary partnership has already been subject to ordinary corporate
income tax)
EXCLUSIONS FROM GROSS INCOME SEC.32.B
1. Life Insurance
( LAGCIRM)
2. Amount Received by Insured as Return of Premium
3. Gifts, Bequests & devises
4. Compensation for Injuries or Sickness
5. Income Exempt under Treaty
6. Retirement Benefits, Pensions, Gratuities
7. Miscellaneous Items
1. Life Insurance Proceeds of life insurance policies paid to the heirs/beneficiaries upon the death of the
insured
If such amounts are held by the insurer under an agreement to pay interest, the interest
payments shall be included in the GI
Insured must die to avail of total exemption. If he survives, there/s only partial exemption to
the extent that the proceeds constitute return of capital (total amount of premiums paid).
2. Amount Received by Insured as Return of Premium
Under life insurance, endowment, or annuity contracts, received either during the term or at the
maturity of the terms or upon surrender of the contract
3. Gifts, Bequests & devises
But, income from such property shall be included in GI
Must be characterized by disinterested generosity and pure liberality
Difficult to establish gift situations if there is an Er-Ee relationship (A bonus/assistance as recognition
of service rendered is not exempt)
If given under
a) constraining force of any moral or legal duty or
b) from the incentive of
c) an anticipated benefit of an economic nature or where it is a return for services rendered,
proceeds cannot qualify as a gift.
Most critical consideration is the givers\ intention or motive.
Can be a gift if given on account of filial relationship.
4. Compensation for Injuries or Sickness
Received through Accident/Health Insurance or Workmens Compensation Act, as compensation for
personal injuries/sickness + amount of damages received on account of such injuries/sickness
TAXATION 1-MIDTERM EXAM
DIOSO
BY: ANGIE LOUH S.
Damages will be exempt only if they arise together with personal injury; however, if damages only
amount to return of capital, it is exempt (Ex. Damages from car accident exempt only if claim includes
compensation for personal injury. If no personal injury, damages for car wreckage will only be exempt
to the extent of the amount of the actual damage return of capital)
Must be physical injury, not injury to rights.
5. ) Income Exempt under Treaty
To the extent required by any treaty obligation binding upon the Phil govt.
6. Retirement Benefits, Pensions, Gratuities
Forms
a) RA 7641 or Reasonable Private Benefit Plan
o See below for rules
b) Amount received as a consequence of separation for any cause beyond control (death,
sickness or other physical disability)
o Sickness must be job threatening
must render taxpayer incapable of working (Ex. Does not include STD)
o Benefits from separation due to retrenchment come under exemption (no choice/option; but if
the Ee avails of an optional early retirement plan, he cannot reason that he was separated for reasons
beyond his control, therefore, he cannot claim exemption of the benefits on this ground but he can
claim under other grounds such as RPBP or RA 7641.
c) Benefits received from a foreign government by resident of non resident citizens or aliens
who reside permanently in the Philippines
d) Veterans benefits
e) Benefits under SSS
f) Benefits received from GSIS
2 Options under paragraph (a), Section 32(B)(6) g) RA 7641
o Conditions: (i) at least 60 years old;
(ii) 5 years of service at time of retirement
o Availed if there is no reasonable private benefit plan (benefits underthis option is less)
o Limted exemption: month salary for every year of service. In RPBP, all is
excludable.
h) Reasonable Private Benefit Plan
o Conditions: (i) at least 50 yrs old; (ii) in the service of same employer for at least 10
years at time of retirement
o Must be approved by BIR
o A pension, gratuity, stock bonus or profit-sharing plan maintained by an ER for the
benefit of some or all of his officials/employees, wherein contributions are made by such ER for
the officials/employees, or both, for the purpose of distributing to such officials & employees the
earnings &
principal of the fund thus accumulated; & provided in the plan that no part of the income shall
be used for/be diverted to any purpose other than for the exclusive benefit of the said officials &
employees
Service must be continuous.
You can avail of the benefits only once (once youve availed of RPBP, you cannot
avail of another RPBP); but you can avail of exemption under another ground
o Ex. A government employee can claim exemption for retirement benefits received from the
GSIS even after availing of RPBP taxpayer can claim RPBP after qualifying as a private employee
then under GSIS proceeds exemption after qualifying as a government employee
o Ex. Employee can claim exemption under RPBP then later claim on the ground that the amount he
received is a
consequence of his separation in a subsequent job for any cause beyond his control
Terminal Leave Pay: amount paid for the commutation of leave credits
TAXATION 1-MIDTERM EXAM
DIOSO
BY: ANGIE LOUH S.
o Excludable only for government employees (this exemption does not find support in NIRC but is
backed by SC decision and BIR Ruling #143-98)
7. Miscellaneous Items
(a) income derived by foreign government (from investments in Philippines in loans, stocks, bonds or
other domestic securities)
Refers only to passive income. If the foreign government engages in trade, income is taxable.
(b) income derived by govt./its political subdivisions (from public utility or exercise\ essential
governmental function)
Key: Income should accrue to government; if the income is retained by the public utility, it is
not exempt look at charter of political subdivision/GOCC to determine whether its income
accrues to the government or not.
(c) prizes, awards in sports competition sanctioned by national sports associations whether held in
Philippines or abroad
Contemplates a particular competition, not a cumulative achievement (Ex. Sportsman of the
year award does not qualify for exemption)
(d) prizes & awards
in recognition of religious, charitable, scientific, educational, artistic, literary or civic
achievement, but only if:
recipient was selected without any action on his part
recipient not required to render substantial future services as a condition of receiving the
prize/award
Example: Nobel prize award
Construed strictly, take note of 7 categories. It does not include athletic achievement.
Contemplates a rational selection process; cannot just be randomly selected.
(e) 13th month pay & other benefits (i.e. productivity incentives & Christmas bonus)
Total exclusion shall not > P30,000
(f) GSIS, SSS, Medicare, Pag-ibig contributions & union dues of individuals
(g) Gains form the sale of bonds, debentures or other certificates of indebtedness with a maturity of
more than 5 years
(h) Gains from redemption of shares in mutual fund
DEDUCTIONS SECTION 34
DEFINITION:
III. DEDUCTION FROM GROSS INCOME
Defined as: Items or amounts which the law allow to be deducted from gross income in order to arrive
at the taxable income.
The basic principle governing deductions from gross income apply to all taxpayers.
Because deductions are strictly construed against the taxpayer, one seeking a deduction must point
to some specific provisions of the statute in which that deduction is authorized & must be able to prove that he
is entitled to the deduction which the law allows.
Adequate records should be kept to support the deductions.
The deduction claimed must have been subjected to withholding tax, if required.
Deductions for income tax purposes partake of the nature of tax exemptions; hence, if tax
exemptions are to be strictly construed, then it follows that deductions must be STRICTLY construed.
He must be able to prove that he is entitled to the deduction authorized or allowed. (Atlas
Consolidated Mining & Devt. Corp. vs. CIR, January 12, 1981)
WHO MAY AVAIL OF THE DEDUCTIONS?
1) Individuals
(a) citizen
(b) resident alien
(c) non-resident alien doing business in the Philippines
(d) member of GPP
2) Corporations
(a) domestic corp.
TAXATION 1-MIDTERM EXAM
DIOSO
BY: ANGIE LOUH S.
(b) resident foreign corp.
(c) proprietary educational institutions & hospitals
(d) GOCCs
WHO CANNOT AVAIL OF DEDUCTIONS FROM GROSS INCOME:
1. Citizens and resident aliens whose income is purely compensation income (except for premium
payments on health and/or hospitalization insurance);
2. Non-resident aliens not engaged in trade or
business in the Philippines; and
3. Non-resident foreign corporation
KINDS OF ALLOWABLE DEDUCTIONS FROM GROSS INCOME sec 34
1. Itemized Deductions: BaD2-TRIP-C-ONEL
a. Bad debts;
b. Depreciation;
c. Depletion;
d. Taxes;
e. Research and development costs;
f. Interest;
g. Pension trust contribution;
h. Charitable and other contributions;
i. Ordinary and Necessary Expenses;
j. Losses.
2. Optional Standard Deduction (OSD)
3. Special Deductions
DISTINGUISH EXCLUSION FROM GROSS INCOME FROM ALLOWABLE DEDUCTIONS FROM GROSS
INCOME.
EXCLUSION
Refers to a flow of wealth which
does not form part of the gross
income because:
1. it is exempted by the
fundamental law;
2. it is exempted by the statute;
3. it does not come within the
definition of income
ALLOWABLE DEDUCTIONS
Refer to amounts which the law allows as
deductions from gross income order to arrive at
net income or taxable income
Material to arrive at gross income Necessary to arrive at net or taxable income
Something earned or received
Something paid or incurred in earning gross
which do not form part of the
income
gross
income
SEC 35. ALLOWANCE OF PERSONAL EXEMPTION FOR INDIVIDUAL TAX PAYERS.
Note: corporation cannot only natural person - 50k annually only is the allowed basic personal
exemption
Note: additional exemption of 25k for each dependent not exceeding 4 children. Only 100k shall be avail.
Requisites of dependents:
1. legitimate child
2. chiefly dependent for support
3. living with the taxpayers (note: if schooling far from the house still included.)
4.not more than 21 years old note: if marries or dies under the same taxable year, still can avail.
Ex. If the 18 year old child married- still becomes dependent at the close of the year/ end.
If below 18 but married- not dependent
5. UNMARRIED NOT GAINFULLY EMPLOYED
6.REGARDLESS OF AGE INCAPABLE OF SELF SUPPORT BECAUSE OF MENTAL OR PHYSICAL DEFECT
GR: all requisites must conquer .IF THE BABY DIED-DEPENDENT UNTIL END OF TAXABLE YEAR.
TAXATION 1-MIDTERM EXAM
DIOSO
BY: ANGIE LOUH S.
ITEMS NOT DEDUCTABLE SEC 36
General rule In computing net income, no deduction shall in any case be allowed in respect to:
1. Personal, living or family expenses these are personal expenses and not related to the conduct of
trade or business
2. Any amount paid out for new buildings of for permanent improvements, or betterments made to
increase the value of any property or estate these are capital expenditures added to the cost of the
property and the periodic depreciation is the amount that is considered as deductible expense
Note: Shall not apply to intangible drilling and development costs incurred in petroleum operations which are
deductible under Subsection (G) (1) of Sec. 34 of the NIRC
3. Any amount expended in restoring property or in making good the exhaustion thereof for which an
allowance is or has been made
4. Premiums paid on any life insurance policy covering the life of any officer or employee, or of any
person financially interested in any trade or business carried on by the taxpayer, individual or corporate,
when the taxpayer is directly or indirectly a beneficiary under such policy (Sec. 36 [A], NIRC)
5. Losses from sales or exchanges of property between related parties (Sec. 36 [B], NIRC)
6. Interest expense, bad debts, and losses from sales of property between related parties
7. Non-deductible interest
8. Non-deductible taxes
9. Non-deductible losses
10. Losses from wash sales of stock or securities
KINDS OF TAX PAYERS:
1. individual
1. citizen
1. Resident
citizen
2. non- RC
2. ALIEN
1.resident alien
2. non ra
WITHIN
WITH OUT
RATE
2.corporation
3.estate.
GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF INCOME TAXATION ON INDIVIDUALS. Sec. 23
Except when otherwise provided in the NIRC:
1. A citizen of the Philippines residing therein is taxable on all income derived from sources within and
without the Philippines;
2. A non-resident citizen is only taxable on income derived from sources within the Philippines
3. An individual citizen of the Philippines who is working and deriving income from abroad as an OFW is
taxable only on income derived from sources within the Philippines: Provided, that a seaman who is a
citizen of the Philippines and who receives compensation for services rendered abroad as a member of
the complement of a vessel engaged exclusively in international trade shall be treated as an OFW
4. An alien individual, whether a resident or not of the Philippines, is taxable only on income derived
from sources within the Philippines (Sec. 23, NIRC)
TAX ON INDIVIDUALS (chapter 3, NIRC)
TAXATION 1-MIDTERM EXAM
DIOSO
BY: ANGIE LOUH S.
TAX ON CORPORATIONS( CHAPTER IV, NIRC)
SPECIAL TREATMENT OF FRINGE BENEFIT
A. Fringe Benefit
Any good, service or other benefit furnished or granted in cash or in kind by an employer to an individual
employee (except rank and file employees) such as, but not limited to the ff:
1) housing
2) expense account
3) vehicle of any kind
4) household personnel (such as maid, driver & others)
5) interest on loan at less than market rate to the extent of the difference between the market rate & actual rate
granted
6) membership fees, dues & other expenses borne by the employer for the employee in social & athletic clubs
or other similar organizations
7) expenses for foreign travel
8) holiday & vacation expenses
9) educational assistance to the employee or his dependents
10) life or health insurance & other non-life insurance premiums or similar amounts in excess of what the law
allows
You might also like
- Form A Fund ManagementDocument88 pagesForm A Fund ManagementAh MhiNo ratings yet
- Milagros Dela CruzFina'Document7 pagesMilagros Dela CruzFina'angelli45No ratings yet
- MM Project On TanishqDocument23 pagesMM Project On Tanishqgpathak826No ratings yet
- SSGC Internship ReportDocument68 pagesSSGC Internship ReportMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Different Authorities in Imposing Tax in The Philippines: TingzonDocument7 pagesDifferent Authorities in Imposing Tax in The Philippines: TingzonDenzelNestorTingzonNo ratings yet
- National Budget Memorandum No. 133 Dated November 29, 2019 PDFDocument87 pagesNational Budget Memorandum No. 133 Dated November 29, 2019 PDFtin cruzNo ratings yet
- Forming An Opinion and Reporting On Financial StatementsDocument68 pagesForming An Opinion and Reporting On Financial StatementsLalaLaniba100% (1)
- Book 4Document60 pagesBook 4Angelynne N. NieveraNo ratings yet
- Income-Tax OutlineDocument41 pagesIncome-Tax OutlineAnonymous YNTVcDNo ratings yet
- Personal Notes On TaxationDocument119 pagesPersonal Notes On Taxationgilbert marimon chattoNo ratings yet
- Concept of Funds-Dr. Loida M. CancinoDocument81 pagesConcept of Funds-Dr. Loida M. CancinoAricirtap Abenoja JoyceNo ratings yet
- LGU NGAS Chapter 1 and 2Document24 pagesLGU NGAS Chapter 1 and 2Lail PDNo ratings yet
- NGAS LectureDocument56 pagesNGAS LectureVenianNo ratings yet
- Fidelity Savings and Mortgage Bank vs. CenzonDocument2 pagesFidelity Savings and Mortgage Bank vs. CenzonAngelo LopezNo ratings yet
- 3 Codal Avenues For Citizen's ParticipationDocument26 pages3 Codal Avenues For Citizen's ParticipationYang RheaNo ratings yet
- Dao 2008-20Document4 pagesDao 2008-20Shenno Lester CoseNo ratings yet
- Rmo 16-2007Document4 pagesRmo 16-2007Jaypee LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Res-991077 HTMLDocument5 pagesRes-991077 HTMLRaissa Almojuela Del ValleNo ratings yet
- Local Treasury Manual 3Document4 pagesLocal Treasury Manual 3Raies JumawanNo ratings yet
- Baar LabelDocument61 pagesBaar LabelJerwin Cases TiamsonNo ratings yet
- Public Budgeting: Introductory Concepts: Gilbert R. HufanaDocument23 pagesPublic Budgeting: Introductory Concepts: Gilbert R. Hufanagilberthufana446877No ratings yet
- National Government Sector Cluster NGS-5-Education and Employment Audit Group R16-C, Audit Team No. R16-C-04Document3 pagesNational Government Sector Cluster NGS-5-Education and Employment Audit Group R16-C, Audit Team No. R16-C-04Winnie Ann Daquil Lomosad-MisagalNo ratings yet
- Local Budget Circular No. 111 - Manual On The Setting Up and Operation of Local Economic Enterprises (Lees)Document3 pagesLocal Budget Circular No. 111 - Manual On The Setting Up and Operation of Local Economic Enterprises (Lees)Glaiza RafaNo ratings yet
- Coa M2014-009 PDFDocument34 pagesCoa M2014-009 PDFAlvin ComilaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For LgusDocument47 pagesAccounting For LgusPatricia Reyes100% (1)
- Attendance Sheet - Hoa by LawsDocument1 pageAttendance Sheet - Hoa by LawsLisa CalderonNo ratings yet
- Updated Matrices of Documentary Requirements For Budgetary RequestsDocument21 pagesUpdated Matrices of Documentary Requirements For Budgetary RequestsGlaiza RafaNo ratings yet
- Barangay Accounting PlanDocument6 pagesBarangay Accounting PlanGaytri Garcia Sangha100% (1)
- The Accounting Policies: Government Accounting Manual For Local Government UnitsDocument259 pagesThe Accounting Policies: Government Accounting Manual For Local Government UnitsKyla Ramos Diamsay100% (1)
- Procurement Timeline - Updated 2016 IRR-RA9184 - 31 March 2021 103Document1 pageProcurement Timeline - Updated 2016 IRR-RA9184 - 31 March 2021 103John Oliver GuiangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Income TaxDocument54 pagesChapter 5 Income TaxGirlie Kaye Onongen PagtamaNo ratings yet
- Quiz NegoDocument3 pagesQuiz NegoMarlon CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Bir Ruling No. 108-93Document2 pagesBir Ruling No. 108-93saintkarriNo ratings yet
- Property Summary Co Ownership EasementsDocument38 pagesProperty Summary Co Ownership EasementsKatharina CantaNo ratings yet
- Warehouse ReceiptDocument30 pagesWarehouse ReceiptShane Fernandez JardinicoNo ratings yet
- Page 584 Cir Vs KepcoDocument2 pagesPage 584 Cir Vs KepcoDaniel GalzoteNo ratings yet
- Form 10 Cash Advances For Field Activity and Intelligence - Confidential ExpensesDocument1 pageForm 10 Cash Advances For Field Activity and Intelligence - Confidential ExpensesShaira BalindongNo ratings yet
- Local TaxesDocument19 pagesLocal TaxesKennethQueRaymundoNo ratings yet
- LGU-NGAS TableofContentsVol1Document6 pagesLGU-NGAS TableofContentsVol1Pee-Jay Inigo UlitaNo ratings yet
- Quarry Permit: Provincial/City Mining Regulatory Board (P/CMRB)Document5 pagesQuarry Permit: Provincial/City Mining Regulatory Board (P/CMRB)cris kuNo ratings yet
- SLUP Checklist of Requirements PDFDocument1 pageSLUP Checklist of Requirements PDFelton jay amilaNo ratings yet
- Local Budget Memorandum No. 75 PDFDocument21 pagesLocal Budget Memorandum No. 75 PDFsuzyNo ratings yet
- TMAP - DOF-BLGF Policy UpdatesDocument35 pagesTMAP - DOF-BLGF Policy UpdatesPena Tn100% (1)
- Features of The Government Accounting Manual For National Government AgenciesDocument30 pagesFeatures of The Government Accounting Manual For National Government AgenciesMay Joy ManagdagNo ratings yet
- Steps in Transfer of TitleDocument2 pagesSteps in Transfer of TitleApril Joy Ortilano- CajiloNo ratings yet
- NTC Memorandum Circular No 9-8-91 IDocument4 pagesNTC Memorandum Circular No 9-8-91 Inyan nyan nyanNo ratings yet
- Property Tax Reform DOF SlidesDocument25 pagesProperty Tax Reform DOF SlidesClarissa DegamoNo ratings yet
- The Local Government CodeDocument176 pagesThe Local Government CodeGracelyn Enriquez BellinganNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory ReviewerDocument9 pagesAuditing Theory ReviewerChristian MaritoNo ratings yet
- Bangko Sentral NG Pilipinas: History BSP Vision and Mission Overview of Functions and OperationsDocument17 pagesBangko Sentral NG Pilipinas: History BSP Vision and Mission Overview of Functions and OperationsMichelle GoNo ratings yet
- AA 4102 1st Hand OutDocument9 pagesAA 4102 1st Hand OutMana XDNo ratings yet
- Estate Tax: 86, NIRC)Document15 pagesEstate Tax: 86, NIRC)Cesyl Patricia BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Withholding Taxes 2Document20 pagesWithholding Taxes 2hildaNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 213500: Office of The Ombudsman Vs EspinaDocument12 pagesG.R. No. 213500: Office of The Ombudsman Vs EspinacharmssatellNo ratings yet
- COA Key Services Procedural Flow - pdf-437299431Document74 pagesCOA Key Services Procedural Flow - pdf-437299431Ruth JacksonNo ratings yet
- CSC Memo Cir No. 2-2005Document35 pagesCSC Memo Cir No. 2-2005daniel besina jrNo ratings yet
- Revised IRR of EO 146Document9 pagesRevised IRR of EO 146Lhadymae ChavezNo ratings yet
- Law On Sales Module 16 17Document29 pagesLaw On Sales Module 16 17Mairene CastroNo ratings yet
- Taxation Law SummerDocument6 pagesTaxation Law SummerAnita Solano BoholNo ratings yet
- Summary NIRCDocument44 pagesSummary NIRCbebs CachoNo ratings yet
- Power of The Bir and Cir-Income Taxation 101-02.23.20Document4 pagesPower of The Bir and Cir-Income Taxation 101-02.23.20Dhierissa LeeNo ratings yet
- Title I: Organization and Function of The BirDocument14 pagesTitle I: Organization and Function of The BirPJ HongNo ratings yet
- The Bureau of Internal Revenue Powers and Duties of The Bureau of Internal RevenueDocument5 pagesThe Bureau of Internal Revenue Powers and Duties of The Bureau of Internal RevenueLyca VNo ratings yet
- R.A. 3019 Anti GraftDocument3 pagesR.A. 3019 Anti GraftAngie Louh S. DiosoNo ratings yet
- Let Reviewergeneral EducationDocument19 pagesLet Reviewergeneral EducationAngie Louh S. DiosoNo ratings yet
- Taxation (NIRC Sec 1-36Document11 pagesTaxation (NIRC Sec 1-36Angie Louh S. DiosoNo ratings yet
- General Principles Lecture Notes (1) TAXATION 1Document9 pagesGeneral Principles Lecture Notes (1) TAXATION 1Angie Louh S. Dioso100% (4)
- Why Standardization in Accounting?Document5 pagesWhy Standardization in Accounting?nrpcsNo ratings yet
- LexisNexis Concepts in Customer Due DiligenceDocument11 pagesLexisNexis Concepts in Customer Due DiligenceLexisNexis Risk Division100% (2)
- Exim Policy of IndiaDocument10 pagesExim Policy of IndiaYash BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Mid Term 2022 Company LawDocument4 pagesMid Term 2022 Company Lawpradeep ranaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On HRMDocument8 pagesAssignment On HRMPoorni PereraNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Aizuddin Aizat Bin Jumhari: Contact InformationDocument4 pagesMuhammad Aizuddin Aizat Bin Jumhari: Contact InformationAndres ShaonNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics GhellaDocument28 pagesCode of Ethics GhellaMassimilianoTerenziNo ratings yet
- ALDANA AESOS Act5Document2 pagesALDANA AESOS Act5Aeriel AldanaNo ratings yet
- On Bajaj Vs Hero HondaDocument17 pagesOn Bajaj Vs Hero HondaketansanwalNo ratings yet
- JfefhehfejhfnyryryyyyyrryyrDocument3 pagesJfefhehfejhfnyryryyyyyrryyrAtulit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan: 1: Define Your BusinessDocument12 pagesMarketing Plan: 1: Define Your Businessdrken3No ratings yet
- Customer Master Record: Smartbooks Operations Management With Analytics Workbook Exercise 2.1Document8 pagesCustomer Master Record: Smartbooks Operations Management With Analytics Workbook Exercise 2.1jennicaashley.chua.engNo ratings yet
- MKT420 Assignment - Business Analysis On 4P's Mini ReportDocument5 pagesMKT420 Assignment - Business Analysis On 4P's Mini ReportNurdini HusinNo ratings yet
- HRM Assignment - InfosysDocument4 pagesHRM Assignment - Infosyssumit SinghNo ratings yet
- 3rd Yr 2nd Sem Strategic Management Prefinals Quiz 2Document9 pages3rd Yr 2nd Sem Strategic Management Prefinals Quiz 2Alfie Jaicten SyNo ratings yet
- Solution Proposed For Salary Ranges Customisation and AutomationDocument6 pagesSolution Proposed For Salary Ranges Customisation and Automationrahul patelNo ratings yet
- University of GondarDocument18 pagesUniversity of GondarGetie TigetNo ratings yet
- BM ReviewDocument10 pagesBM ReviewFish SuperNo ratings yet
- VSM Current and FutureDocument12 pagesVSM Current and FutureLINH TRẦN NGÔ KHÁNHNo ratings yet
- Status of Kendu Leaves Sale: Jharkhand State Forest Development Corporation LTDDocument11 pagesStatus of Kendu Leaves Sale: Jharkhand State Forest Development Corporation LTDmdNo ratings yet
- Hospice Nurse Job DescriptionDocument5 pagesHospice Nurse Job DescriptionKasia KuzakaNo ratings yet
- Sukhwinder Kaur - Office ManagerDocument4 pagesSukhwinder Kaur - Office ManagerAbhishek aby5No ratings yet
- Annual Financials For Pearson PLCDocument6 pagesAnnual Financials For Pearson PLCMustansar IqbalNo ratings yet
- AbsorptionDocument29 pagesAbsorptionRavi KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Recruitment Process of Coca-Cola CompanyDocument31 pagesRecruitment Process of Coca-Cola CompanySagar SahaNo ratings yet
- PARTCOR NotesDocument19 pagesPARTCOR NotesKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- f9 Paper 2012Document8 pagesf9 Paper 2012Shuja UmerNo ratings yet
- Problems GeneralDocument9 pagesProblems GeneralAmal BharaliNo ratings yet