Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 8
Chapter 8
Uploaded by
AJ SaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 8
Chapter 8
Uploaded by
AJ SaCopyright:
Available Formats
Alias Jady Santos
2013-11360
HW CE 22 THX
8-2
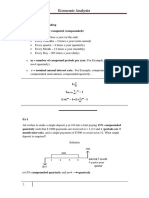
A = $1,000; N = 10
(a) f = 6% per year; ir = 4% per year
In Part (a), the $1,000 is an A$ uniform cash flow (annuity)
im = 0.04 + 0.06 + (0.04)(0.06) = 0.1024, or 10.24% per year
PW(im) = $1,000 (P/A,10.24%,10) = $1,000(6.0817) = $6,082
(b) In Part (b), the $1,000 is a R$ uniform cash flow (annuity) because the A$ cash flow is
$1,000
(1.06)k where 1 k 10; i.e.,
kb
( R $ ) k=( A $ ) k ( 1 ) =$ 1,000(1.06)k (1/(1+1.06))k0=$ 1,000 = $1,000; 1 k 10
1+f
PW(ir) = $1,000 (P/A,4%,10) = $8,111
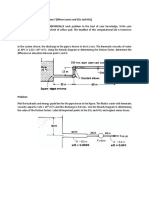
8-6
f = 4% per year; ir = 8% per year; b = 0
Alternative A: Estimates are in actual dollars, so the combined (market) interest rate must be
used to
compute the present worth (PW).
im = ir + f + (ir)(f) = 0.08 + 0.04 + (0.08)(0.04) = 0.1232 or 12.32% per year
PW(12.32%)=$120,000(P/F,12.32%,1)$132,000(P/F,12.32%,2)
$148,000(P/F,12.32%,3)$160,000(P/F,12.32%,4)
=$120,000(0.8903)$132,000(0.7927)$148,000(0.7057)$160,000(0.6283)
=$416,444
Alternative B: Estimates are in real dollars, so the real interest rate must be used to compute the
present
worth (PW).
PW(8%)=$100,000(P/A,8%,4)$10,000(P/G,8%,4)
=$100,000(3.3121)$10,000(4.65)
=$284,710
Alternative B has the least negative equivalent worth in the base time period (a PW value in this
case since b = 0).
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Engineering Economics 4th Edition Park Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesFundamentals of Engineering Economics 4th Edition Park Solutions Manualjadehacr7u100% (24)
- FM09-CH 02Document15 pagesFM09-CH 02دهيرج بهارتي75% (4)
- CFP Exam Calculation Workbook: 400+ Calculations to Prepare for the CFP Exam (2018 Edition)From EverandCFP Exam Calculation Workbook: 400+ Calculations to Prepare for the CFP Exam (2018 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chapter 2 Principles of Corporate FinanceDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Principles of Corporate Financeandreaskarayian8972100% (4)
- Basics of Engineering Economy Every Third Solution PDFDocument75 pagesBasics of Engineering Economy Every Third Solution PDFJoshua ClimacoNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 3 - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocument11 pagesChapter # 3 - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'b84% (19)
- Engineering EconomyDocument7 pagesEngineering EconomyBurn-Man Hiruma Villanueva100% (1)
- 2014 CE 2710 HW 7 SolutionDocument8 pages2014 CE 2710 HW 7 SolutionAJ SaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Solutions Manual To Accompany Fundamentals of Engineering Economics 2Nd Edition 9780132209601 PDFDocument44 pagesFull Download Solutions Manual To Accompany Fundamentals of Engineering Economics 2Nd Edition 9780132209601 PDFdonna.duke560100% (20)
- Sol5 13Document28 pagesSol5 13Val Amiel MirandaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Solution 2013Document10 pages1 - Solution 2013Yamer YusufNo ratings yet
- Si7 - Tarquin (1) 1 9Document9 pagesSi7 - Tarquin (1) 1 9AlvarezMartinNo ratings yet
- Chapter #1 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocument9 pagesChapter #1 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'b100% (10)
- Assignment CH5 SolutionDocument1 pageAssignment CH5 Solutionmk1853828No ratings yet
- Fraser SM ch09Document23 pagesFraser SM ch09Mike ArthursNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Principles of Corporate Finance PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Principles of Corporate Finance PDFchatuuuu123No ratings yet
- 8.2/ Your Rich Aunt Is Going To Give You An End-Of-Year Gift of $1,000 For Each of The Next 10Document1 page8.2/ Your Rich Aunt Is Going To Give You An End-Of-Year Gift of $1,000 For Each of The Next 10abcNo ratings yet
- Math GenDocument3 pagesMath GenRezi Sabutanan AmerilaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Ekonomi Teknik Universitas IndonesiaDocument6 pagesTugas Ekonomi Teknik Universitas IndonesiaInna Ihsani NisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Annual Equivalence Analysis: PF PF PF PFDocument4 pagesChapter 6 Annual Equivalence Analysis: PF PF PF PFGabx TapasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Annual Equivalence Analysis: PF PF PF PFDocument4 pagesChapter 6 Annual Equivalence Analysis: PF PF PF PFshan0214No ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document16 pagesChapter 06coriactrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - How To Calculate Present ValuesDocument15 pagesChapter 02 - How To Calculate Present ValuesShoaibTahirNo ratings yet
- Time Value and Money Page 179 AnswerDocument6 pagesTime Value and Money Page 179 AnswerNINIO B. MANIALAGNo ratings yet
- Solutions Review Problems Chap002Document4 pagesSolutions Review Problems Chap002andreaskarayian8972No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Solutions - Engineering Economy 7 TH Edition. Leland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocument22 pagesChapter 9 Solutions - Engineering Economy 7 TH Edition. Leland Blank and Anthony TarquinYousif AlzarooniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Other Analysis TechniquesDocument33 pagesChapter 9: Other Analysis TechniquesKamNo ratings yet
- Exercises: 1) Acme Borrowed $100,000 From A Local Bank, Which Charges Them An Interest Rate of 7% PerDocument4 pagesExercises: 1) Acme Borrowed $100,000 From A Local Bank, Which Charges Them An Interest Rate of 7% PerIslam MomtazNo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting CH 14, 15Document16 pagesAdvanced Accounting CH 14, 15jessicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 18 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocument26 pagesChapter # 18 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'bNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2Kumar ShivamNo ratings yet
- FINVA100 B TimeValueAnalysis Estares JohnReyDocument6 pagesFINVA100 B TimeValueAnalysis Estares JohnReyJohnRey EstaresNo ratings yet
- Solution Assignment Chapter 9 10 1Document14 pagesSolution Assignment Chapter 9 10 1Huynh Ng Quynh NhuNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 3 - Evaluating A Single ProjectDocument9 pagesASSIGNMENT 3 - Evaluating A Single ProjectKhánh Đoan Lê ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- 313+Exam+1+Discussion+Review+ +solutionsDocument2 pages313+Exam+1+Discussion+Review+ +solutionssuppalerk janechaijitravanitNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument3 pagesSolutionAshish PurohitNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Group 6:: Student ID Full NameDocument9 pagesAssignment 2 Group 6:: Student ID Full NameQuynh Chau TranNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 005 Q AnswersDocument5 pagesProblem Set 005 Q AnswersDennis Korir100% (1)
- EE - Assignment Chapter 5 SolutionDocument10 pagesEE - Assignment Chapter 5 SolutionXuân ThànhNo ratings yet
- Homework 3 Egr OumaimaDocument6 pagesHomework 3 Egr Oumaimaoumaidi123No ratings yet
- Safari - 22 Nov 2022 at 06 - 37Document1 pageSafari - 22 Nov 2022 at 06 - 37Tonie NascentNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Present-Worth Analysis: Identifying Cash Inflows and OutflowsDocument23 pagesChapter 5 Present-Worth Analysis: Identifying Cash Inflows and Outflowsahjhnlol50% (2)
- Chapter 2 PQ FMDocument5 pagesChapter 2 PQ FMRohan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Compound Interest Selina Ans KeyDocument40 pagesCompound Interest Selina Ans KeyMARIAM LEELANo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money I - SolutionsDocument2 pagesTime Value of Money I - SolutionsraymondNo ratings yet
- Check Figures PLL3e FinalDocument23 pagesCheck Figures PLL3e FinalTrần Tuấn AnhNo ratings yet
- Student Solutions CH04 4ceDocument16 pagesStudent Solutions CH04 4ceKOUAMI DONKEE GBOLOHANo ratings yet
- A) Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3Document13 pagesA) Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3Usman KhiljiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Time Value of Money Exercise2Document8 pagesWhat Is The Time Value of Money Exercise2Sadia JuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter+2 3Document14 pagesChapter+2 3kanasanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy Solution of HW2: Exercise 1Document5 pagesEngineering Economy Solution of HW2: Exercise 1Moe ShNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis: 1. Multiple CompoundingDocument7 pagesEconomic Analysis: 1. Multiple CompoundingalibeneshaqNo ratings yet
- MIDS CF Solutions MergedDocument43 pagesMIDS CF Solutions Mergedsohaib.uniqueNo ratings yet
- Solutions On Capital Budgeting AssignmentsDocument3 pagesSolutions On Capital Budgeting AssignmentsjakezzionNo ratings yet
- Time Value MoneyDocument4 pagesTime Value MoneyJulie Ann ZafraNo ratings yet
- AF208 - Revision Package - Test 2 - S1 2021 - SOLUTIONDocument4 pagesAF208 - Revision Package - Test 2 - S1 2021 - SOLUTIONRossie VeremaitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter6E2010 PDFDocument12 pagesChapter6E2010 PDFutcm77No ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Economic & Budget Forecast Workbook: Economic workbook with worksheetFrom EverandEconomic & Budget Forecast Workbook: Economic workbook with worksheetNo ratings yet
- Sample Bs 1377 Part 2Document20 pagesSample Bs 1377 Part 2AJ SaNo ratings yet
- Reporting Template: Introduction and ObjectivesDocument10 pagesReporting Template: Introduction and ObjectivesAJ SaNo ratings yet
- 2001 Foreign Trade Statistics of The Philipines VOLUME II-EXPORTSDocument507 pages2001 Foreign Trade Statistics of The Philipines VOLUME II-EXPORTSAJ SaNo ratings yet
- Trade Jan 2020 - 10 March 2020Document3 pagesTrade Jan 2020 - 10 March 2020AJ SaNo ratings yet
- 4 R 3 ReffffafdafdfdasDocument2 pages4 R 3 ReffffafdafdfdasAJ SaNo ratings yet
- BS 6349-3:2013 Maritime Works. Code of Practice For The Design of Shipyards and Sea Locks Publication YearDocument1 pageBS 6349-3:2013 Maritime Works. Code of Practice For The Design of Shipyards and Sea Locks Publication YearAJ SaNo ratings yet
- Volume II - EXPORTS - FTS 2015 Ebook - As of 05-02-17 PDFDocument664 pagesVolume II - EXPORTS - FTS 2015 Ebook - As of 05-02-17 PDFAJ SaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAJ SaNo ratings yet
- LostDocument2 pagesLostAJ SaNo ratings yet
- Copy - Maritime Industry Authority: Philippine Maritime Maritime Codes StructureDocument3 pagesCopy - Maritime Industry Authority: Philippine Maritime Maritime Codes StructureAJ SaNo ratings yet
- Page Navigation: 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 NextDocument1 pagePage Navigation: 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 NextAJ SaNo ratings yet
- Outreach TarpaulinDocument1 pageOutreach TarpaulinAJ SaNo ratings yet
- Web Results: Specification (Technical Standard) - WikipediaDocument4 pagesWeb Results: Specification (Technical Standard) - WikipediaAJ SaNo ratings yet
- Dao Dao Dao DaoDocument1 pageDao Dao Dao DaoAJ SaNo ratings yet
- LostDocument4 pagesLostAJ SaNo ratings yet
- De-Manufacturing Cost ElementsDocument2 pagesDe-Manufacturing Cost ElementsAJ SaNo ratings yet
- RA CIVILENG MANILA Nov2018 PDFDocument353 pagesRA CIVILENG MANILA Nov2018 PDFPhilBoardResultsNo ratings yet
- NSCP Moment CoefficientsDocument4 pagesNSCP Moment CoefficientsAJ SaNo ratings yet
- PosterContent CE197 ProjectDocument2 pagesPosterContent CE197 ProjectAJ SaNo ratings yet
- CE 111 Quiz 1 August 2012Document2 pagesCE 111 Quiz 1 August 2012AJ SaNo ratings yet
- Closed Conduit Flow: Monroe L. Weber-Shirk S Civil Environmental EngineeringDocument44 pagesClosed Conduit Flow: Monroe L. Weber-Shirk S Civil Environmental EngineeringAJ SaNo ratings yet
- Take Home Lab 7Document1 pageTake Home Lab 7AJ SaNo ratings yet
- Regression Analysis For Transport Trip Generation EvaluationDocument6 pagesRegression Analysis For Transport Trip Generation EvaluationAJ SaNo ratings yet