Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The National Income and Product Accounts and Relation To Consumption and Income
The National Income and Product Accounts and Relation To Consumption and Income
Uploaded by
z_k_j_vOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The National Income and Product Accounts and Relation To Consumption and Income
The National Income and Product Accounts and Relation To Consumption and Income
Uploaded by
z_k_j_vCopyright:
Available Formats
The National Income and Product Accounts and Relation to
Consumption and Income
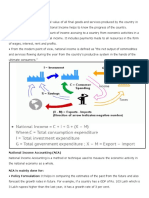
THE ECONOMY
The economy produces goods and services. There are three categories of goods and
services: consumption, investment and intermediate.
People consume consumption goods and services. If consumed by an individual
household, it is private consumption. If consumed collectively, it is public (or
government) consumption.
Investment (or capital) goods are durable and enhance future production possibilities.
They are valued because they make possible greater future production and therefore
consumption.
Intermediate goods and services are produced and used up by businesses in the period
they are produced.
Final goods and services are consumption goods and services and investment (capital)
goods. Final good output is used to judge the current performance of the economy.
NATIONAL PRODUCT ACCOUNT
Definition: Gross National Product (GNP) is the value of all final goods (and services).
Definition: The final goods are the consumption and capital (investment) goods
produced.
Categories of final goods reported in National Product Account:
Accounting
Category
Personal Consumption Expenditures:
C
Durable goods
Non-durable goods
Services
Gross Private Domestic Investment
Net Exports
Government Purchases:
Public Consumption*
Public Investment*
*new in US NIPA
Theory
Category
I
C
C
NE
G
C
I
Question: What is the difference between GNP and GDP?
Answer: GNP = GDP + Net receipts of factor income from the rest of the world.
Question: What is the distinction between nominal and real variables?
Answer: For nominal values, current period prices are used to value current output. For
real values, base year prices are used to value current output.
BUSINESS TRANSACTIONS Production Side
Sales from firm A to firm B are either intermediate goods/services or investment.
Investment if durable (e.g. factory, machine)
Intermediate if used up in the current periods production
Examples:
Computer (investment good)
Desk (investment good)
Car bought for firm use (investment good)
Car leased by a firm for its sales force (intermediate service)
Pencils (intermediate good)
NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNT
Definition: Value added by a business (firm) is the value of production minus the value
of intermediate goods used up. The sum of value added in the economy is equal to its
national product.
Proposition: Total value added equals GNP.
Exercise: Show that, if two firms are consolidated, value added by the consolidated firm
is equal to the sum of value added by the two individual firms.
Definition: Aggregate income is the sum of claims against the value added by
businesses.
Therefore, by definition,
Income = Product
Reason: Every business has a residual claimant. The claim of residual claimant is value
added by that business less the claims of the other claimants. For a corporation, the
residual is corporate profits. For an unincorporated business, the residual is proprietors
income. For an owner occupied dwelling, the owner is treated as a business that rents the
dwelling to the owner. The residual is rental income of the owners.
Major categories of claims against product listed in the National Income Accounts:
Indirect Business Taxes (Property, Sales and Excise Taxes)
Business Transfers
Wages, Salaries, and other Compensation
Profit of Government Enterprises less Subsidies
Net Interest Income (Business Net Interest Payments plus Home Mortgage Interest
Payments)
Capital Consumption Allowances (Depreciation)
Proprietors Income
Rental Income
Corporate Profits
NOTE: The sum of the above categories is equal to GNP.
BUSINESS TRANSACTIONS Income Side
A prime source of national income data is the profit and loss statements of businesses.
Profit and Loss Statement of a Business:
For every firm,
Sales - Intermediate good purchases = Value Added (VA)
Components of Value Added:
Depreciation
Net Interest Payments
Property, Sales and Excise Taxes
Wages, Salaries and other Compensation
Business Transfers (Mostly bad debt)
Profit Residual
NOTE: This residual has different names depending on the nature of the business. It is
called corporate profits if the business is incorporated, proprietors income if
unincorporated, profit of government enterprise if government, and rental income in the
case of owner occupied housing.
OWNER OCCUPIED HOUSING
NOTE: Owner occupied housing is a special case and is treated as a business.
Rents (imputed, this is part of consumption)
- Intermediate goods (e.g. maintenance)
= Value Added (VA)
Components of Value Added:
Depreciation
Mortgage Interest Payments (Net Interest)
Property Taxes
Wages, Salaries, and other Compensation (If any)
Residual (Rental Income)
You might also like
- (Frank - de - Jong, - Barbara - Rindi) - The - Microstructure - of - Financial Markets PDFDocument207 pages(Frank - de - Jong, - Barbara - Rindi) - The - Microstructure - of - Financial Markets PDFz_k_j_v100% (1)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- National Income AccountingDocument36 pagesNational Income AccountingMharck AtienzaNo ratings yet
- National in Come in IndiaDocument41 pagesNational in Come in IndiaSunil SunitaNo ratings yet
- Economics 20161Document9 pagesEconomics 20161chernet bekeleNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Measurements Part 2Document23 pagesMacroeconomic Measurements Part 2Devillz AdvocateNo ratings yet
- Macro Reviewer FinalsDocument9 pagesMacro Reviewer FinalsaltezasarahmaeNo ratings yet
- Computing GNPDocument7 pagesComputing GNPkarton11100% (1)
- Session 2Document40 pagesSession 2Digvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Output, Prices, and Economic Growth: Presenter's Name Presenter's Title DD Month YyyyDocument33 pagesAggregate Output, Prices, and Economic Growth: Presenter's Name Presenter's Title DD Month YyyybingoNo ratings yet
- EC 124 Chap2 Part - II PDFDocument8 pagesEC 124 Chap2 Part - II PDFAnonymous wFIBMUmt100% (1)
- Module - 4 National IncomeDocument64 pagesModule - 4 National Incomelakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- National Income ConceptsDocument22 pagesNational Income ConceptsData AnalystNo ratings yet
- BE 313 - WK 6-7 - Unit Learning C - 1 - 0Document17 pagesBE 313 - WK 6-7 - Unit Learning C - 1 - 0Jessica GerongayNo ratings yet
- Niea NotesDocument5 pagesNiea Notesogonnaakuneme830No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 National Income Complete PDF-2Document67 pagesChapter 3 National Income Complete PDF-2shivam kumarNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Chapter 6:GDP and Real GDPDocument45 pagesMacroeconomics Chapter 6:GDP and Real GDPjrios87No ratings yet
- Seminar 3 - National Income Accounting - ADocument9 pagesSeminar 3 - National Income Accounting - Avivekrabadia0077No ratings yet
- CFA Level 1 - Section 4 MacroEconomicsDocument30 pagesCFA Level 1 - Section 4 MacroEconomicsapi-3763138No ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument16 pagesNational IncomeSamia Irshad ullahNo ratings yet
- Nations WealthDocument49 pagesNations WealthwomabaNo ratings yet
- PGDM (2019-21) Term 2 (September-December) : Dr. Kalpana TokasDocument30 pagesPGDM (2019-21) Term 2 (September-December) : Dr. Kalpana Tokasv_amyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Circular FlowDocument62 pagesUnit 2 Circular Flowk pradeepaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Circular FlowDocument62 pagesUnit 2 Circular FlowAnshumaan PatroNo ratings yet
- GDP:two Measures of National Product Flow of Product Approach. Earning and Cost ApproachDocument53 pagesGDP:two Measures of National Product Flow of Product Approach. Earning and Cost ApproachUmer Farooq MirzaNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Document26 pagesNational Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Asad NaseerNo ratings yet
- GR 11 Economics Covid19 14 AugDocument16 pagesGR 11 Economics Covid19 14 Augboitumelopolori54No ratings yet
- ECO113 Lecture 34 Income Ans ExpDocument47 pagesECO113 Lecture 34 Income Ans ExpShivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Sohail Ahmad Class: Bba 2 Section: B Subject: Macroeconomics Submitted To: Sir Azhar TanoliDocument10 pagesSubmitted By: Sohail Ahmad Class: Bba 2 Section: B Subject: Macroeconomics Submitted To: Sir Azhar TanoliFaisal AwanNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Economic PerformanceDocument14 pagesMeasurement of Economic PerformanceGodfrey RushabureNo ratings yet
- National Income AccountingDocument42 pagesNational Income Accountingraemu26No ratings yet
- CH 21 MacroDocument6 pagesCH 21 MacrowiwideeNo ratings yet
- NI Acounting - FDocument33 pagesNI Acounting - Fmonalishas_1No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 4 NotesBeatriz CanchilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter NIPADocument12 pagesChapter NIPAAdam SmithNo ratings yet
- 2 Theme: Gross Domestic Product and Product AccountsDocument52 pages2 Theme: Gross Domestic Product and Product AccountsShahzod OltiboyevNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 & 3: Measuring Macroeconomic PerformanceDocument34 pagesLecture 2 & 3: Measuring Macroeconomic PerformanceAli zizoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 Summary-14th EditionDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 8 Summary-14th EditionSamerNo ratings yet
- Measuring GDP and Economic GrowthDocument40 pagesMeasuring GDP and Economic GrowthbabrulhasantaponbabulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: The Measurement of National Income: National Output and Value AddedDocument4 pagesChapter 20: The Measurement of National Income: National Output and Value AddedSaaki GaneshNo ratings yet
- ch-7 NewDocument16 pagesch-7 NewSAKIB MD SHAFIUDDINNo ratings yet
- Measuring GDP and Economic Growth: Chapter 21, Michael ParkinDocument21 pagesMeasuring GDP and Economic Growth: Chapter 21, Michael ParkinOyon Nur newazNo ratings yet
- Economics Form Five NotesDocument10 pagesEconomics Form Five NotesMeg PaigeNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Macroeconomics - Lec 5 and 6 - Chapter20Document40 pagesWeek 3 - Macroeconomics - Lec 5 and 6 - Chapter20elserry.comNo ratings yet
- Econ 111 Extended 24 - Summer 17Document48 pagesEcon 111 Extended 24 - Summer 17FatmahNo ratings yet
- GDP: Measuring Total Production and Income: Chapter Summary and Learning ObjectivesDocument22 pagesGDP: Measuring Total Production and Income: Chapter Summary and Learning Objectivesvivianguo23No ratings yet
- ECO 112 - Session 2Document17 pagesECO 112 - Session 2kebaabetswe olebileNo ratings yet
- Economics Class 12Document5 pagesEconomics Class 12Sucheta BhardwajNo ratings yet
- MacroeconomicsDocument35 pagesMacroeconomicsrudraarjunNo ratings yet
- MacroEcon Ch4mylab To ReviseDocument4 pagesMacroEcon Ch4mylab To ReviseJosue VitaleNo ratings yet
- National Income: Amity International Business SchoolDocument13 pagesNational Income: Amity International Business SchoolRatika GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Measurement of National Income Chapter Twenty Principles of Macroeconomics Economics 1202.2BDocument21 pagesThe Measurement of National Income Chapter Twenty Principles of Macroeconomics Economics 1202.2BNayem ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Econ StudyDocument10 pagesEcon Studyc2why985xhNo ratings yet
- MacroeconomicsDocument40 pagesMacroeconomicsLakshmi Harshitha YechuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Cost Revenue Relationship - Prof. Harshad SambhusDocument40 pagesChapter 8 - Cost Revenue Relationship - Prof. Harshad SambhusHitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document70 pagesModule 2PriyankaNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting (NIA)Document8 pagesNational Income Accounting (NIA)Mamta VermaNo ratings yet
- Business Cycle and FlactuationDocument31 pagesBusiness Cycle and FlactuationCheveem Grace EmnaceNo ratings yet
- GDP 2023Document26 pagesGDP 2023Satuti Seth 1545No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Final Exam NotesDocument24 pagesMacroeconomics Final Exam NotesThomas Bryant100% (1)
- KPMG Global Economic Outlook h1 2023 ReportDocument50 pagesKPMG Global Economic Outlook h1 2023 Reportz_k_j_v100% (1)
- Trinity Institute of Professional Studies Affiliated To Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha UniversityDocument1 pageTrinity Institute of Professional Studies Affiliated To Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha Universityz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Tutorials 3Document18 pagesTutorials 3z_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Financial Market Microstructure Theory: The Microstructure of Financial Markets, de Jong and Rindi (2009)Document43 pagesFinancial Market Microstructure Theory: The Microstructure of Financial Markets, de Jong and Rindi (2009)z_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Fin221 End 10Document6 pagesFin221 End 10z_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Weatherwax Hasbrouck NotesDocument60 pagesWeatherwax Hasbrouck Notesz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire: Don't Know Other (Please Specify)Document2 pagesQuestionnaire: Don't Know Other (Please Specify)z_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document8 pagesCH 3z_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document5 pagesCH 2z_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Volatility: 6.1 Basic NotionsDocument10 pagesVolatility: 6.1 Basic Notionsz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Back To Week 1 LessonsDocument2 pagesBack To Week 1 Lessonsz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Interest Rate Derivatives: 4.3 SwaptionsDocument12 pagesChapter 4: Interest Rate Derivatives: 4.3 Swaptionsz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Demestz - The Cost of TransactingDocument14 pagesDemestz - The Cost of Transactingz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Interest Rate Derivatives: 4.2 Caps and FloorsDocument13 pagesChapter 4: Interest Rate Derivatives: 4.2 Caps and Floorsz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Back-Testing of Trading Strategies: 8.1bootstrapDocument12 pagesBack-Testing of Trading Strategies: 8.1bootstrapz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Technical Trading StrategiesDocument16 pagesTechnical Trading Strategiesz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Performance of Trading Strategies: 7.1 Basic ConceptsDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Performance of Trading Strategies: 7.1 Basic Conceptsz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Market Microstructure: Inventory ModelsDocument13 pagesMarket Microstructure: Inventory Modelsz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial MarketsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Financial Marketsz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Market Microstructure: Information-Based ModelsDocument8 pagesMarket Microstructure: Information-Based Modelsz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Models of Limit-Order Markets: 12.1 Cohen, Maier, Schwartz, and Whitcomb (1981)Document8 pagesModels of Limit-Order Markets: 12.1 Cohen, Maier, Schwartz, and Whitcomb (1981)z_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- Empirical Distributions & Prediction of ReturnsDocument14 pagesEmpirical Distributions & Prediction of Returnsz_k_j_vNo ratings yet
- 8 Edition: Steven P. Robbins Mary CoulterDocument43 pages8 Edition: Steven P. Robbins Mary CoulterTeddy León ZegarraNo ratings yet
- Purna Chandra Malik - Tractor - 15 03 22 - CuttackDocument2 pagesPurna Chandra Malik - Tractor - 15 03 22 - CuttacksrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Focus On Destination CompetitivenessDocument3 pagesFocus On Destination Competitivenessapi-360220088No ratings yet
- Company Address Phone Fax E-Mail Contact Value (USD)Document47 pagesCompany Address Phone Fax E-Mail Contact Value (USD)Sharafat AliNo ratings yet
- Kundenrechnung Mit Materialbeschreibung - USI2642020 - 20200309 231033UTC PDFDocument2 pagesKundenrechnung Mit Materialbeschreibung - USI2642020 - 20200309 231033UTC PDFGeovannyValdiviezoNo ratings yet
- CAT - T1 Recording Financial Transactions Mock ExamDocument7 pagesCAT - T1 Recording Financial Transactions Mock ExamACCALIVENo ratings yet
- Microsoft Virtual Labs: Biztalk Server 2009: Building Your First Biztalk Server SolutionDocument18 pagesMicrosoft Virtual Labs: Biztalk Server 2009: Building Your First Biztalk Server SolutionpsycopathaNo ratings yet
- TDRODocument29 pagesTDROAnn ManaloconNo ratings yet
- Fundamentos de La Contabilidad de Coberturas: (Hedge Accounting)Document78 pagesFundamentos de La Contabilidad de Coberturas: (Hedge Accounting)doiNo ratings yet
- AReviewof Modelling Approachesfor Supply Chain Planning Under UncertaintyDocument8 pagesAReviewof Modelling Approachesfor Supply Chain Planning Under UncertaintyHadi P.No ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument24 pagesCapital BudgetingInocencio Tiburcio100% (2)
- Acca BrochureDocument20 pagesAcca BrochureSonuChaudhary0% (1)
- v02 PDFDocument8 pagesv02 PDFMarcelino Navarrete EvaristoNo ratings yet
- ISO 5000 Mapping GuideDocument6 pagesISO 5000 Mapping GuideCamila Guerra0% (1)
- Finova - PD Format Oct 2019Document8 pagesFinova - PD Format Oct 2019Madhusudan ParwalNo ratings yet
- Nomura - Tata MotorsDocument5 pagesNomura - Tata MotorsAshish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Order DataDocument583 pagesOrder DataTosin GeorgeNo ratings yet
- MCK - How Executives GrowDocument8 pagesMCK - How Executives GrowSung Sam100% (2)
- Kelas 176-55726467 AwbDocument1 pageKelas 176-55726467 Awbruslanpermana61No ratings yet
- Overview of Elements of The Financial Report Audit ProcessDocument47 pagesOverview of Elements of The Financial Report Audit ProcessPardeep Ramesh Agarval100% (1)
- Micros CoffeeDocument7 pagesMicros CoffeeBlessy LapinaNo ratings yet
- Kyko Profiling & Management System SolutionsDocument112 pagesKyko Profiling & Management System SolutionsBernard Ah Thau TanNo ratings yet
- Dela Rama Et Al Vs Mao - Ao Sugar - CentralDocument2 pagesDela Rama Et Al Vs Mao - Ao Sugar - CentralJude MaiquezNo ratings yet
- Robert Schmidt v. Bartech Group, Inc., 4th Cir. (2015)Document6 pagesRobert Schmidt v. Bartech Group, Inc., 4th Cir. (2015)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Business Administration PapersDocument36 pagesBusiness Administration Papersinfiniti786No ratings yet
- Week 1Document35 pagesWeek 1flora tasiNo ratings yet
- Field Visit To MsmeDocument10 pagesField Visit To MsmeviswaaruxNo ratings yet
- Rajesh Kumar Sethi - 5+years - Project Control Engineer - Foster Wheeler - SenabiDocument4 pagesRajesh Kumar Sethi - 5+years - Project Control Engineer - Foster Wheeler - SenabiSubrata DuttaNo ratings yet
- The New Business Venture Chapter 3 PDFDocument3 pagesThe New Business Venture Chapter 3 PDFvictorNo ratings yet