Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 viewsElectric Current Electrical Power
Electric Current Electrical Power
Uploaded by
Khoo Ying WeiThe document defines key electrical concepts such as current, charge, power, resistance, and formulas relating them. It states that current is the flow of charge through conductors provided with potential differences, and defines formulas for current (I), power (P), charge (Q), and resistance (R). It provides example calculations applying these formulas to determine values like current, charge, potential difference, resistance, and power in various circuit scenarios.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Electricity: Ohm's LawDocument3 pagesElectricity: Ohm's LawManoj Bhawar PatilNo ratings yet
- NUMERICALS On Electricity-10Document5 pagesNUMERICALS On Electricity-10Tanmay PandeyNo ratings yet
- NUMERICAL - Electricity & Its Effects For (Class X)Document6 pagesNUMERICAL - Electricity & Its Effects For (Class X)Gayathiri SureshNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsDocument8 pagesElectricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- Class-10 Electrycity MCQDocument10 pagesClass-10 Electrycity MCQNuman KhanNo ratings yet
- Electric Current PowerPointDocument46 pagesElectric Current PowerPointPacita Lestojas100% (1)
- Electric NoteDocument6 pagesElectric NoteKucing GemukNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Assignment - 1: PhysicsDocument5 pagesElectricity - Assignment - 1: PhysicsCRUEL HUNTERNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Notes and Worksheets 2023Document27 pagesCurrent Electricity Notes and Worksheets 2023kadynnaidoo7No ratings yet
- ELECTRICITYDocument8 pagesELECTRICITYchandanNo ratings yet
- ElectricDocument40 pagesElectricnishant kumarNo ratings yet
- Bjte2023 WK02Document36 pagesBjte2023 WK02Hafiz khalidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20Document38 pagesChapter 20tonyformedNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class X NotesDocument15 pagesElectricity Class X NotesGrgg Hkhkk100% (5)
- 2.2 Analysing The Relationship Between Electric Current and Potential DifferenceDocument14 pages2.2 Analysing The Relationship Between Electric Current and Potential DifferencesfwongNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity O LevelDocument59 pagesCurrent Electricity O LevelNoah OkitoiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 1Document48 pagesUnit 2 Module 17sky7harveyNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument78 pagesElectricityAryan Kaul CeNtErNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 NotesDocument21 pagesChapter 18 NotesaliNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits 30 JULY 2013: Lesson DescriptionDocument4 pagesElectric Circuits 30 JULY 2013: Lesson DescriptionTosin AbiolaNo ratings yet
- Q1 WEEK 7 Basic ElectricityDocument48 pagesQ1 WEEK 7 Basic ElectricityAileen OcampoNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Electricity NotesDocument12 pagesYear 9 Electricity Notesapi-408461912100% (1)
- GP2 Unit 4Document30 pagesGP2 Unit 4mitchie sierraNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits - Ohms LawDocument11 pagesElectric Circuits - Ohms LawCarmenNo ratings yet
- Physics Ch6&Ch7 EMI&AcDocument4 pagesPhysics Ch6&Ch7 EMI&AclkNo ratings yet
- 13 Electric Circuits Batteries and ResistorsDocument10 pages13 Electric Circuits Batteries and ResistorsrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating CurrentDocument3 pagesAssignment On Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating CurrentAtharav GoyalNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Sheet 3Document1 pagePower Quality Sheet 3ahmed TareqNo ratings yet
- Elex QuexDocument75 pagesElex QuexJHOEMEL TANGO100% (1)
- Electricity Worksheet 1Document2 pagesElectricity Worksheet 1JashNo ratings yet
- Electricity (Main)Document16 pagesElectricity (Main)Sarthak KapoorNo ratings yet
- MathDocument76 pagesMathJHOEMEL TANGONo ratings yet
- Emi and AcDocument3 pagesEmi and Accaptain delhiNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument213 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringchaliebainnocentNo ratings yet
- Voltage Current and ResistanceDocument15 pagesVoltage Current and ResistanceShaniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Part 1 - Lecture PDFDocument34 pagesElectrical Circuits Part 1 - Lecture PDFRyan Cortes0% (1)
- Bee Theory and Nuerical Question BankDocument7 pagesBee Theory and Nuerical Question BankC1 314 Krishna GavaneNo ratings yet
- 4 ElectricityDocument49 pages4 ElectricityKaguya74No ratings yet
- Electricity Notes-XDocument40 pagesElectricity Notes-XArchitaNo ratings yet
- Physics Xii Chapter 4,5,6Document7 pagesPhysics Xii Chapter 4,5,6SatvikNo ratings yet
- Electricity Assignment HHWDocument5 pagesElectricity Assignment HHWAditya GoelNo ratings yet
- Electricity 2 PD and ResistanceDocument18 pagesElectricity 2 PD and ResistanceJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- LXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 23 - Ohms Law - 05aug2014Document6 pagesLXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 23 - Ohms Law - 05aug2014HNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitDocument36 pagesElectric CircuitEzekiel MalazzabNo ratings yet
- Exam-6-Set-A (Print)Document10 pagesExam-6-Set-A (Print)Dummy AccountNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits Note BookDocument44 pagesAC Circuits Note Bookron Joshua QuirapNo ratings yet
- MET-2.2 QuestionsDocument20 pagesMET-2.2 QuestionsApoorv SinghNo ratings yet
- ELECTRIC CURRENT - Improve YourlearningDocument7 pagesELECTRIC CURRENT - Improve Yourlearnings KollaNo ratings yet
- Bee 14 Question BankDocument10 pagesBee 14 Question BankprakashkerurNo ratings yet
- Lesson: ElectricityDocument13 pagesLesson: Electricitybudesasaiaw.v.re32.90No ratings yet
- Electricity: Electric CurrentDocument10 pagesElectricity: Electric CurrentTajiriMollelNo ratings yet
- Emi and Ac AssignmentDocument5 pagesEmi and Ac AssignmentMohammed AmmaarNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL_BASICSDocument78 pagesELECTRICAL_BASICSMichael Adrian BernaldezNo ratings yet
- Electrical Resistance Lecture 2Document5 pagesElectrical Resistance Lecture 2bigbang0% (1)
- Assignment of EeeDocument4 pagesAssignment of EeeHarshilNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit1 (BEEE)Document48 pagesNotes Unit1 (BEEE)Vedashree ShetyeNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- 1994-The Ethnobotany of Citrus and Their RelativesDocument15 pages1994-The Ethnobotany of Citrus and Their RelativesKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Answers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesDocument5 pagesAnswers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Answers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesDocument5 pagesAnswers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Discovery of ViroidsDocument21 pagesDiscovery of ViroidsKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Max Efficiency Dh5 Competent Cells: 9:2, 12. 8:1, 1. Supe44 Λ-Thi-1 Gyra96 Rela1Document4 pagesMax Efficiency Dh5 Competent Cells: 9:2, 12. 8:1, 1. Supe44 Λ-Thi-1 Gyra96 Rela1Khoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Huanglongbing - Pathogen Detection System For Integrated Disease ManagementDocument11 pagesHuanglongbing - Pathogen Detection System For Integrated Disease ManagementKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Boardworks Displacement Velocity and AccelerationDocument8 pagesBoardworks Displacement Velocity and AccelerationKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of Viroid-Host Interactions and Disease Control StrategiesDocument13 pagesMolecular Biology of Viroid-Host Interactions and Disease Control StrategiesKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- C Functions BasicsDocument4 pagesC Functions BasicsKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
Electric Current Electrical Power
Electric Current Electrical Power
Uploaded by
Khoo Ying Wei0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesThe document defines key electrical concepts such as current, charge, power, resistance, and formulas relating them. It states that current is the flow of charge through conductors provided with potential differences, and defines formulas for current (I), power (P), charge (Q), and resistance (R). It provides example calculations applying these formulas to determine values like current, charge, potential difference, resistance, and power in various circuit scenarios.
Original Description:
Physics
Original Title
Electric Current
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines key electrical concepts such as current, charge, power, resistance, and formulas relating them. It states that current is the flow of charge through conductors provided with potential differences, and defines formulas for current (I), power (P), charge (Q), and resistance (R). It provides example calculations applying these formulas to determine values like current, charge, potential difference, resistance, and power in various circuit scenarios.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesElectric Current Electrical Power
Electric Current Electrical Power
Uploaded by
Khoo Ying WeiThe document defines key electrical concepts such as current, charge, power, resistance, and formulas relating them. It states that current is the flow of charge through conductors provided with potential differences, and defines formulas for current (I), power (P), charge (Q), and resistance (R). It provides example calculations applying these formulas to determine values like current, charge, potential difference, resistance, and power in various circuit scenarios.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
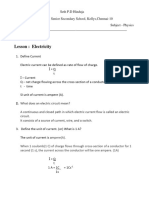
Electric current
Electrical power
Charge is measured in Coulombs (C)
Power- rate at which the energy is transformed
Current flow of charge through conductors provided with potential
differences (PD) between the ends of conductors
Formula:
Current positive side of power supply to negative
Power (W) = PD (V) x current (A)
P = VI
Electron-negative side of power supply to positive
Good conductors free electron to move
Formula:
Energy = power x time
E = VI x t
Charge (C) = current (A) X times (S)
Q=IxT
Resistance
Exercises:
1. A charged of 0.01 C passes a point in a circuit every 0.2 s. What is
the current flowing?
Metals at constant temperature have constant resistant (Ohms, )
Formula:
Resistance () = PD (V) / Current (A)
R = V/ I
The resistance of wire is directly proportional to length of the wire,
inversely proportional to the cross sectional area.
2. How long does it take for a change of 30 C to pass appoint in a
circuit when a current of 0.8 A flows?
3. How much charge will pass appoint in a circuit when a current of
0.5 A flows for.
4. A potential difference of 20 V is required for a current of 0.5 A to
flow through a resistor. What is its resistance?
5. A current of 0.01 A flow a through a resistor 0f 1 k. What is the
potential difference across the resistor?
6. How much current flows when a potential difference of 5 V is
applied to a resistor of 10 ?
7. What is the power of a bulb that allows a current of 1.5 A to flow
when there is a potential difference of 8 V across it?
8. What is the current flowing through a bulb of power 40 W when
there is a potential difference of 200 V across it?
9. What potential difference is required to produce a current of 0.3 A
in a bulb of power 60 W?
You might also like
- Electricity: Ohm's LawDocument3 pagesElectricity: Ohm's LawManoj Bhawar PatilNo ratings yet
- NUMERICALS On Electricity-10Document5 pagesNUMERICALS On Electricity-10Tanmay PandeyNo ratings yet
- NUMERICAL - Electricity & Its Effects For (Class X)Document6 pagesNUMERICAL - Electricity & Its Effects For (Class X)Gayathiri SureshNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsDocument8 pagesElectricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- Class-10 Electrycity MCQDocument10 pagesClass-10 Electrycity MCQNuman KhanNo ratings yet
- Electric Current PowerPointDocument46 pagesElectric Current PowerPointPacita Lestojas100% (1)
- Electric NoteDocument6 pagesElectric NoteKucing GemukNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Assignment - 1: PhysicsDocument5 pagesElectricity - Assignment - 1: PhysicsCRUEL HUNTERNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Notes and Worksheets 2023Document27 pagesCurrent Electricity Notes and Worksheets 2023kadynnaidoo7No ratings yet
- ELECTRICITYDocument8 pagesELECTRICITYchandanNo ratings yet
- ElectricDocument40 pagesElectricnishant kumarNo ratings yet
- Bjte2023 WK02Document36 pagesBjte2023 WK02Hafiz khalidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20Document38 pagesChapter 20tonyformedNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class X NotesDocument15 pagesElectricity Class X NotesGrgg Hkhkk100% (5)
- 2.2 Analysing The Relationship Between Electric Current and Potential DifferenceDocument14 pages2.2 Analysing The Relationship Between Electric Current and Potential DifferencesfwongNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity O LevelDocument59 pagesCurrent Electricity O LevelNoah OkitoiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 1Document48 pagesUnit 2 Module 17sky7harveyNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument78 pagesElectricityAryan Kaul CeNtErNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 NotesDocument21 pagesChapter 18 NotesaliNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits 30 JULY 2013: Lesson DescriptionDocument4 pagesElectric Circuits 30 JULY 2013: Lesson DescriptionTosin AbiolaNo ratings yet
- Q1 WEEK 7 Basic ElectricityDocument48 pagesQ1 WEEK 7 Basic ElectricityAileen OcampoNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Electricity NotesDocument12 pagesYear 9 Electricity Notesapi-408461912100% (1)
- GP2 Unit 4Document30 pagesGP2 Unit 4mitchie sierraNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits - Ohms LawDocument11 pagesElectric Circuits - Ohms LawCarmenNo ratings yet
- Physics Ch6&Ch7 EMI&AcDocument4 pagesPhysics Ch6&Ch7 EMI&AclkNo ratings yet
- 13 Electric Circuits Batteries and ResistorsDocument10 pages13 Electric Circuits Batteries and ResistorsrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating CurrentDocument3 pagesAssignment On Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating CurrentAtharav GoyalNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Sheet 3Document1 pagePower Quality Sheet 3ahmed TareqNo ratings yet
- Elex QuexDocument75 pagesElex QuexJHOEMEL TANGO100% (1)
- Electricity Worksheet 1Document2 pagesElectricity Worksheet 1JashNo ratings yet
- Electricity (Main)Document16 pagesElectricity (Main)Sarthak KapoorNo ratings yet
- MathDocument76 pagesMathJHOEMEL TANGONo ratings yet
- Emi and AcDocument3 pagesEmi and Accaptain delhiNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument213 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringchaliebainnocentNo ratings yet
- Voltage Current and ResistanceDocument15 pagesVoltage Current and ResistanceShaniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Part 1 - Lecture PDFDocument34 pagesElectrical Circuits Part 1 - Lecture PDFRyan Cortes0% (1)
- Bee Theory and Nuerical Question BankDocument7 pagesBee Theory and Nuerical Question BankC1 314 Krishna GavaneNo ratings yet
- 4 ElectricityDocument49 pages4 ElectricityKaguya74No ratings yet
- Electricity Notes-XDocument40 pagesElectricity Notes-XArchitaNo ratings yet
- Physics Xii Chapter 4,5,6Document7 pagesPhysics Xii Chapter 4,5,6SatvikNo ratings yet
- Electricity Assignment HHWDocument5 pagesElectricity Assignment HHWAditya GoelNo ratings yet
- Electricity 2 PD and ResistanceDocument18 pagesElectricity 2 PD and ResistanceJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- LXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 23 - Ohms Law - 05aug2014Document6 pagesLXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 23 - Ohms Law - 05aug2014HNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitDocument36 pagesElectric CircuitEzekiel MalazzabNo ratings yet
- Exam-6-Set-A (Print)Document10 pagesExam-6-Set-A (Print)Dummy AccountNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits Note BookDocument44 pagesAC Circuits Note Bookron Joshua QuirapNo ratings yet
- MET-2.2 QuestionsDocument20 pagesMET-2.2 QuestionsApoorv SinghNo ratings yet
- ELECTRIC CURRENT - Improve YourlearningDocument7 pagesELECTRIC CURRENT - Improve Yourlearnings KollaNo ratings yet
- Bee 14 Question BankDocument10 pagesBee 14 Question BankprakashkerurNo ratings yet
- Lesson: ElectricityDocument13 pagesLesson: Electricitybudesasaiaw.v.re32.90No ratings yet
- Electricity: Electric CurrentDocument10 pagesElectricity: Electric CurrentTajiriMollelNo ratings yet
- Emi and Ac AssignmentDocument5 pagesEmi and Ac AssignmentMohammed AmmaarNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL_BASICSDocument78 pagesELECTRICAL_BASICSMichael Adrian BernaldezNo ratings yet
- Electrical Resistance Lecture 2Document5 pagesElectrical Resistance Lecture 2bigbang0% (1)
- Assignment of EeeDocument4 pagesAssignment of EeeHarshilNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit1 (BEEE)Document48 pagesNotes Unit1 (BEEE)Vedashree ShetyeNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- 1994-The Ethnobotany of Citrus and Their RelativesDocument15 pages1994-The Ethnobotany of Citrus and Their RelativesKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Answers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesDocument5 pagesAnswers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Answers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesDocument5 pagesAnswers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Discovery of ViroidsDocument21 pagesDiscovery of ViroidsKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Max Efficiency Dh5 Competent Cells: 9:2, 12. 8:1, 1. Supe44 Λ-Thi-1 Gyra96 Rela1Document4 pagesMax Efficiency Dh5 Competent Cells: 9:2, 12. 8:1, 1. Supe44 Λ-Thi-1 Gyra96 Rela1Khoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Huanglongbing - Pathogen Detection System For Integrated Disease ManagementDocument11 pagesHuanglongbing - Pathogen Detection System For Integrated Disease ManagementKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Boardworks Displacement Velocity and AccelerationDocument8 pagesBoardworks Displacement Velocity and AccelerationKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of Viroid-Host Interactions and Disease Control StrategiesDocument13 pagesMolecular Biology of Viroid-Host Interactions and Disease Control StrategiesKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- C Functions BasicsDocument4 pagesC Functions BasicsKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet