Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MIDTERM - ECE00 Basic Electronics Engr. Jayde Paolo Castro Mirandilla
MIDTERM - ECE00 Basic Electronics Engr. Jayde Paolo Castro Mirandilla
Uploaded by
Romuel Villanueva Almeyda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageThe document discusses different types of rectifiers used in power supplies. A rectifier uses diodes to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). Half-wave rectifiers only conduct on one half of the AC cycle, resulting in separated DC pulses. Full-wave rectifiers conduct on both halves of the AC cycle, producing continuous DC pulses. Bridge rectifiers are full-wave rectifiers that do not require a center-tapped transformer, allowing their DC output voltage to equal the input voltage from the secondary winding.
Original Description:
rectify
Original Title
Rectifiers
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of rectifiers used in power supplies. A rectifier uses diodes to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). Half-wave rectifiers only conduct on one half of the AC cycle, resulting in separated DC pulses. Full-wave rectifiers conduct on both halves of the AC cycle, producing continuous DC pulses. Bridge rectifiers are full-wave rectifiers that do not require a center-tapped transformer, allowing their DC output voltage to equal the input voltage from the secondary winding.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageMIDTERM - ECE00 Basic Electronics Engr. Jayde Paolo Castro Mirandilla
MIDTERM - ECE00 Basic Electronics Engr. Jayde Paolo Castro Mirandilla
Uploaded by
Romuel Villanueva AlmeydaThe document discusses different types of rectifiers used in power supplies. A rectifier uses diodes to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). Half-wave rectifiers only conduct on one half of the AC cycle, resulting in separated DC pulses. Full-wave rectifiers conduct on both halves of the AC cycle, producing continuous DC pulses. Bridge rectifiers are full-wave rectifiers that do not require a center-tapped transformer, allowing their DC output voltage to equal the input voltage from the secondary winding.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
MIDTERM - ECE00 Basic Electronics
(NEETS)
Engr. Jayde Paolo Castro Mirandilla
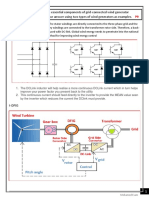
The RECTIFIER is the section of the power supply that contains the secondary windings of the power transformer and the
rectifier circuit. The rectifier uses the ability of a diode to conduct during one half cycle of ac to convert ac to dc.
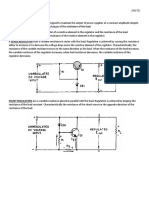
HALF-WAVE RECTIFIERS give an output on only one
half cycle of the input ac. For this reason, the pulses
of dc are separated by a period of one half cycle of
zero potential voltage.
FULL-WAVE RECTIFIERS conduct on both halves of the input ac
cycles. As a result, the dc pulses are not separated from each
other. A characteristic of full-wave rectifiers is the use of a centertapped, high-voltage secondary. Because of the center tap, the
output of the rectifier is limited to one-half of the input voltage of
the high-voltage secondary.
BRIDGE RECTIFIERS are full-wave rectifiers that do not
use a center-tapped, high-voltage secondary. Because
of this, their dc output voltage is equal to the input
voltage from the high-voltage secondary of the power
transformer. Bridge rectifiers use four diodes connected
in a bridge network. Diodes conduct in diagonal pairs to
give a full-wave pulsating dc output.
You might also like
- Gunja EdsDocument10 pagesGunja Edssmritibhardwaz4No ratings yet
- RECTIFIERDocument15 pagesRECTIFIERAni AniNo ratings yet
- Unit II RectifiersDocument37 pagesUnit II Rectifiersdawa penjorNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument13 pagesRectifiersInfidragon GAMINGNo ratings yet
- INDEXDocument12 pagesINDEXMAYIL SHANKARI PNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument13 pagesFull Wave RectifierSundar RajanNo ratings yet
- Physics Project PDF Praveen Class 12Document14 pagesPhysics Project PDF Praveen Class 12ssankar3108No ratings yet
- Derive The Expressions For The Average DC Current, DC Load Voltage, Rectifier Efficiency, Ripple Factor, Piv Rating For The Bridge Rectifier CircuitDocument9 pagesDerive The Expressions For The Average DC Current, DC Load Voltage, Rectifier Efficiency, Ripple Factor, Piv Rating For The Bridge Rectifier CircuitS DispiserNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers, Filters and RegulatoDocument12 pagesRectifiers, Filters and Regulatono.1slytherinprincessNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase RectificationDocument30 pages3 Phase RectificationKobby Brine100% (1)
- Full Wave TheoryDocument6 pagesFull Wave Theorypunjabe2004No ratings yet
- Advantages, Disadvantages of Full Wave Center Tapped and Bridge RectifierDocument1 pageAdvantages, Disadvantages of Full Wave Center Tapped and Bridge RectifierSIAM AL MUJADDEDNo ratings yet
- Basic-Electronics (Rectifier) !Document30 pagesBasic-Electronics (Rectifier) !Rahim AnsariNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier Circuit With WorkingDocument8 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Circuit With WorkingKaran SoniNo ratings yet
- NAVEEN KUMAR CgOLLEGE ROLL NO - 237094034Document22 pagesNAVEEN KUMAR CgOLLEGE ROLL NO - 237094034BARUN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Power SupplyDocument81 pagesLecture On Power SupplyMATE0100% (2)
- Lab Report EcaDocument17 pagesLab Report EcaSYED TAHIR FILMSNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument16 pagesRectifiersJaiom JoshiNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesFull Wave RectifierMurali Krishna GbNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers and FiltersDocument13 pagesRectifiers and FiltersAko si GianNo ratings yet
- Full Wave ContentDocument6 pagesFull Wave ContentAkshaya chandra sekarNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument4 pagesRectifierAngellicaNo ratings yet
- Reectifiers ArjunDocument18 pagesReectifiers Arjunpragya gulatiNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier Circuit With Working TheoryDocument7 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Circuit With Working Theorysuraj vishnoiNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument12 pagesHalf Wave Rectifierutkarsh devNo ratings yet
- Physics Final ReportDocument17 pagesPhysics Final Reportprasannad726No ratings yet
- RACTIFIERDocument19 pagesRACTIFIERDhananjay Aghara100% (1)
- LEARNING GUIDE 02 AC DC RectifierDocument27 pagesLEARNING GUIDE 02 AC DC Rectifiermeseret sisayNo ratings yet
- Half Wave & Full Wave RectifiersDocument19 pagesHalf Wave & Full Wave RectifiersRNKNo ratings yet
- BEEE UNIT IV - Lecture 4 & 5Document32 pagesBEEE UNIT IV - Lecture 4 & 5Girish Shankar MishraNo ratings yet
- Rectifier: BY: Tenie Hayah Jane V. HamocDocument18 pagesRectifier: BY: Tenie Hayah Jane V. HamocKlint Suerte Canilla100% (1)
- Full Wave Rectifier With and Without CapacitorDocument14 pagesFull Wave Rectifier With and Without CapacitorshravanichanikyaNo ratings yet
- Ece Final ProjectDocument19 pagesEce Final ProjectLord JackNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronic Communication: "Rectifier"Document19 pagesDepartment of Electronic Communication: "Rectifier"Bhupendra PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Physics Project01Document12 pagesPhysics Project01nilu royNo ratings yet
- EEE Semester Final PreparationDocument32 pagesEEE Semester Final PreparationMHM MahinNo ratings yet
- A Full Wave Rectifier Is A Circuit Arrangement Which Makes Use of Both Half Cycles of Input Alternating CurrentDocument9 pagesA Full Wave Rectifier Is A Circuit Arrangement Which Makes Use of Both Half Cycles of Input Alternating CurrentKaran SoniNo ratings yet
- Basic Rectifier CircuitsDocument8 pagesBasic Rectifier CircuitssensitivesensesNo ratings yet
- Rect Ific AdoresDocument9 pagesRect Ific AdoresegmNo ratings yet
- PN Junction HW and FWDocument15 pagesPN Junction HW and FWSHIVANSH SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument12 pagesUntitled Documentaadietya11129No ratings yet
- What Is Half Wave Rectifier DeepuDocument15 pagesWhat Is Half Wave Rectifier Deepuharshvardhan singhNo ratings yet
- Tom & JerryDocument13 pagesTom & Jerryhp200615No ratings yet
- Lab Report 03Document8 pagesLab Report 03fkhan201160No ratings yet
- Power Supply CircuitDocument4 pagesPower Supply CircuitMohamed HammadNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument10 pagesRectifiersjipaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Ass 2 Wind0.02Document25 pagesAss 2 Wind0.02Šämęh ËšśämNo ratings yet
- 'What Is A Rectifier:-: Types of RectifiersDocument10 pages'What Is A Rectifier:-: Types of RectifiersRutvikNo ratings yet
- Tripura Institute of Technology: A Presentation OnDocument17 pagesTripura Institute of Technology: A Presentation OnsridharchandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Application of DiodesDocument35 pagesUnit 2-Application of DiodesradsradNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Bridge Rectifier Circuit Over CenterDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Bridge Rectifier Circuit Over CenterLemuel C. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifierNavneet PatelNo ratings yet
- VIVA Question-RectifierDocument3 pagesVIVA Question-RectifierMaheswariRVNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge Rectifier: Experiment No. 6Document5 pagesFull Wave Bridge Rectifier: Experiment No. 6Mohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Single-Phase Supply Three-Phase Supply: Half-Wave RectificationDocument3 pagesSingle-Phase Supply Three-Phase Supply: Half-Wave RectificationKhushbakht KhushiNo ratings yet
- DC Regulated Power SupplyDocument14 pagesDC Regulated Power SupplyMegha Projects100% (2)
- Analog Module 2-Rectifiers PPTDocument35 pagesAnalog Module 2-Rectifiers PPTsanjit0907_982377739No ratings yet
- SCR Rectifiers IVDocument4 pagesSCR Rectifiers IVDhiraj kumawatNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- MIDTERM - ECE00 Basic Electronics: (Neets)Document1 pageMIDTERM - ECE00 Basic Electronics: (Neets)Romuel Villanueva AlmeydaNo ratings yet
- Wine Brochure 2Document3 pagesWine Brochure 2Romuel Villanueva AlmeydaNo ratings yet
- Switches: Prepared By: Engr. Maria Nieves D. ElarcoDocument18 pagesSwitches: Prepared By: Engr. Maria Nieves D. ElarcoRomuel Villanueva AlmeydaNo ratings yet
- Engr. Jayde Paolo Castro Mirandilla Batteries: MIDTERM - ECE00 Basic ElectronicsDocument5 pagesEngr. Jayde Paolo Castro Mirandilla Batteries: MIDTERM - ECE00 Basic ElectronicsRomuel Villanueva AlmeydaNo ratings yet
- IOSH Managing Safely - Course Mar 31 - Apr 03, 2014Document5 pagesIOSH Managing Safely - Course Mar 31 - Apr 03, 2014Romuel Villanueva AlmeydaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of Engineering MaterialsDocument29 pagesChemical Properties of Engineering MaterialsRomuel Villanueva AlmeydaNo ratings yet