Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Copd Exacerbatio N Period: Chronic Cough That Produces Sputum That May Be Clear, White, Yellow or Greenish
Copd Exacerbatio N Period: Chronic Cough That Produces Sputum That May Be Clear, White, Yellow or Greenish
Uploaded by
Nicole FelicianoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Copd Exacerbatio N Period: Chronic Cough That Produces Sputum That May Be Clear, White, Yellow or Greenish
Copd Exacerbatio N Period: Chronic Cough That Produces Sputum That May Be Clear, White, Yellow or Greenish
Uploaded by
Nicole FelicianoCopyright:
Available Formats
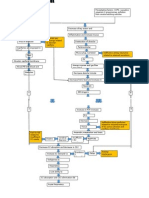
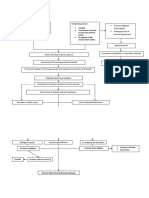
Risk Factors:
Irritants (cement dust, gases and fumes from factory), cigarette
smoking, secondhand smoking from co-workers, inappropriate use
Entry of irritants through
inhalation
Increased
respiratory effort
a.m.b tachypnea,
increased RR,
S.O.B.
Prolonged exposure to particles
Chronic irritation
Decreased Lung
Compliance and
increased airway
Inflammation of bronchial walls
Hypertrophy of submucosal glands in larger
airways and increase in goblet cells in smaller
airways
If prolonged,
fibrosis of
bronchial walls
and scar
Increase in mucus secretion
Accumulation of mucus in airways
Obstruction
with
parenchymal
damage
Narrowing of lumen and plugging
Decrease
in
circulatin
g oxygen
Impaired
ciliary function
Increased
susceptibility to
infection
Chronic
Bronchitis
Obstruction of
airflow which
leads to V/Q
mismatch
Progressive coughing
a.m.b. chronic cough that
produces sputum that
may be clear, white,
yellow or greenish.
COPD
Exacerbatio
n
period
Dyspnea
Alveolar tissue
destruction
If cannot
compensate,
Hypoxemia,
hypercapnia,
COPD
Decrease in
surface area
for gas
exchange
Increase in RBC
production
Polycythemia a.m.b.
plethora, cyanosis,
warm moist skin
Higher blood
viscocity
Increased heart
workload
Manifestations:
Progressive decrease in
exercise tolerance,
prolonged expiration,
expiratory wheezes and
crackles, chest tightness
Hypoxic
pulmonary
vasoconstriction
Increased pulmonary
vascular resistance
Pulmonary
hypertension
Ventilation
-Perfusion
coupling
Manifestations:
S.O.B, venous
congestion,
peripheral
edema, chest
pain, fatigue,
excessive
coughing, and
abnormal heart
Cor
pulmonale
Increased right
ventricular
afterload
Right
ventricular
hypertophy
Right
ventricular
failure
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaGeevine Cansino92% (12)
- PN21 Health and Healing - Pre-Class Activities - Test 2 PDFDocument33 pagesPN21 Health and Healing - Pre-Class Activities - Test 2 PDFRachel HomesNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument9 pagesChronic BronchitisRaiganNo ratings yet
- Airway ObstructionDocument16 pagesAirway ObstructionMubarak AzizNo ratings yet
- Airway Obstruction: TraumaDocument16 pagesAirway Obstruction: TraumaSamuel Hotma Rotua SinagaNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument6 pagesChronic BronchitisN P VNo ratings yet
- Copd 200412082048Document139 pagesCopd 200412082048Richard ArceNo ratings yet
- Bio Lung DiseasesDocument2 pagesBio Lung DiseasesbartieNo ratings yet
- Copd PBL Sept 13Document2 pagesCopd PBL Sept 13Tareq SawanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Viruses Noxious GasesDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Viruses Noxious GasesJessa BorreNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument9 pagesChronic BronchitisSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Christine Loren T. Laya BSN 3-1Document41 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Christine Loren T. Laya BSN 3-1Kristine CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureKimberly Regacho88% (8)
- Schematic Diagram of COPDDocument2 pagesSchematic Diagram of COPDCes CaabayNo ratings yet
- Airway Obstruction: TraumaDocument16 pagesAirway Obstruction: Traumaaeryll1305No ratings yet
- Airway ObstructionDocument16 pagesAirway ObstructionHassaan ShahidNo ratings yet
- "Bronchitis": Respiratory DisorderDocument40 pages"Bronchitis": Respiratory Disorderaswin379No ratings yet
- Obstructive Pulmonary DiseasesDocument55 pagesObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesAbdirashidNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDocument3 pagesPredisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsYujenNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument2 pagesPa Tho PhysiologyBobbie SisonNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary PathologyDocument134 pagesPulmonary PathologyFor ChristNo ratings yet
- GS Bronchial Asthma Bronchiectasis EmphysemaDocument68 pagesGS Bronchial Asthma Bronchiectasis EmphysemaBibika MallaNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Airway DiseasesDocument46 pagesObstructive Airway DiseasesSobia HaleemNo ratings yet
- The Importance of A Healthy Respiratory System: Name: Tan Li Ying Class:3k2 Teacher: Cik Raja ShahrinaDocument24 pagesThe Importance of A Healthy Respiratory System: Name: Tan Li Ying Class:3k2 Teacher: Cik Raja ShahrinaRaja InaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio Cases Ch.7Document2 pagesPathophysio Cases Ch.7heidee1No ratings yet
- Emphysema 1Document7 pagesEmphysema 1ironNo ratings yet
- Gas ExchangeDocument20 pagesGas ExchangeAmi AnubhabNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document13 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Dua ZaheerNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument73 pagesCOPDBroken Oreos100% (1)
- COPD PTDocument49 pagesCOPD PTSathish RathnamNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Disorders: Dr. Suman SherazDocument45 pagesObstructive Disorders: Dr. Suman SherazSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of COPDDocument8 pagesPa Tho Physiology of COPDDaniel NgNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument3 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseJessica Corona - MarianoNo ratings yet
- P ATHODocument2 pagesP ATHOValentino Andres Y AntonioNo ratings yet
- Respiration CH 43.Dr SarahDocument59 pagesRespiration CH 43.Dr Sarahaiman siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument93 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseArleen MatincaNo ratings yet
- Copd PathoDocument1 pageCopd PathoHenry Roque TagalagNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease .: Swathi Swaroopa. BDocument29 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease .: Swathi Swaroopa. BKavya sriNo ratings yet
- CopdDocument73 pagesCopdbuttmahnoor851No ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis: Citadel B. Rabanes, MD First Year JRRMMC-Department of RadiologyDocument34 pagesBronchiectasis: Citadel B. Rabanes, MD First Year JRRMMC-Department of Radiologyadhik_deepak100% (1)
- COPDDocument3 pagesCOPDGloTesoreroNo ratings yet
- Scenario 5: Group 6Document51 pagesScenario 5: Group 6Gd SuarantaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Illnesses (Grade 10 High School Biology)Document10 pagesRespiratory System Illnesses (Grade 10 High School Biology)Lemie ChumaNo ratings yet
- Onchi & CopdDocument8 pagesOnchi & CopdAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- 呼吸系统英文实习Document109 pages呼吸系统英文实习nqhtw4wgn9No ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument17 pagesChronic BronchitisAhamad MansurNo ratings yet
- Emphysema Chronic Bronchitis BronchiectasisDocument7 pagesEmphysema Chronic Bronchitis BronchiectasisFortin BerryNo ratings yet
- Substances Harmful To The Respiratory SystemDocument25 pagesSubstances Harmful To The Respiratory SystemKar Wai67% (3)
- Gas Exchange 4 1Document2 pagesGas Exchange 4 1jody.muller.metiasNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument6 pagesCOPDAubrey PerezNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Copd)Document11 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Copd)Dave Michael GeliNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument15 pagesCOPDlouirufi3003No ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Lung DiseaseDocument31 pagesChronic Obstructive Lung DiseaseKrizdan PaguioNo ratings yet
- Respi PathophysioDocument31 pagesRespi PathophysioIsmael JaaniNo ratings yet
- Chronic LaryngitisDocument20 pagesChronic LaryngitisameliaNo ratings yet
- COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease REVISEDDocument37 pagesCOPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease REVISEDSonny AgultoNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis, COPD, BA 2020Document31 pagesBronchitis, COPD, BA 2020Aditi JainNo ratings yet
- Acute & Chronic Bronchitis & COPDDocument49 pagesAcute & Chronic Bronchitis & COPDHendraDarmawanNo ratings yet
- Air and Your Health: Clean Air Is Vital to Your HealthFrom EverandAir and Your Health: Clean Air Is Vital to Your HealthRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 2 - Nurse Managers As Transformational and Transactional LeadersDocument7 pages2 - Nurse Managers As Transformational and Transactional LeadersNicole FelicianoNo ratings yet
- 1 - Nurses Motivation and Its Relationship To The Characteristic of Patient Care Delivery SystemDocument9 pages1 - Nurses Motivation and Its Relationship To The Characteristic of Patient Care Delivery SystemNicole FelicianoNo ratings yet
- C 6 Memb KartilyaDocument6 pagesC 6 Memb KartilyaNicole FelicianoNo ratings yet
- E 7 Ej GomburzaDocument3 pagesE 7 Ej GomburzaNicole FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Del Bibliofilo Filipino, Vol. III (Madrid:: Source: Dimas Alan, "Pahayag"Document4 pagesDel Bibliofilo Filipino, Vol. III (Madrid:: Source: Dimas Alan, "Pahayag"Nicole FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Meal Plan2 Sheet1Document2 pagesMeal Plan2 Sheet1Nicole FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Meal Plan2 Sheet1Document2 pagesMeal Plan2 Sheet1Nicole FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Question and AnswerDocument2 pagesQuestion and AnswerNicole FelicianoNo ratings yet