Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem 221 Bruice Chapter 4 Answers To Problems in The Coursepack
Chem 221 Bruice Chapter 4 Answers To Problems in The Coursepack
Uploaded by
Parham ElahiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by HartDocument30 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by HartLaura Eraso100% (36)
- CH 8 Test BankDocument14 pagesCH 8 Test BankVanessa James100% (2)
- Organic Nitrogen Compounds Tutorial SolutionsDocument8 pagesOrganic Nitrogen Compounds Tutorial SolutionsDomNo ratings yet
- Org Chem 3Document37 pagesOrg Chem 3tyron9520100% (1)
- ch13 ProblemsDocument84 pagesch13 Problemsbrownhazel67% (6)
- Organic Chemistry: Nucleophilic Substitution at Saturated CarbonDocument107 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Nucleophilic Substitution at Saturated CarbonMafalda FernandesNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by HartDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by HartJesus Carter100% (39)
- Reaction IntermediateDocument18 pagesReaction IntermediateManaswini P100% (1)
- 12thchemistrysamplepaper1 291223044313Document9 pages12thchemistrysamplepaper1 291223044313aditikharb2020No ratings yet
- Chem PreboardDocument13 pagesChem Preboardvirender.pinghalNo ratings yet
- CHM101Document44 pagesCHM101YunusNo ratings yet
- XII Chemistry Sample Question Paper - FinalDocument65 pagesXII Chemistry Sample Question Paper - Finalkrishnapradhani091No ratings yet
- Chemistry - 2 Page EditDocument11 pagesChemistry - 2 Page EditNorish SamdaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SQP 2Document11 pagesChemistry SQP 2ACHAL PATILNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SQPDocument11 pagesChemistry SQPMohd Zaid KhanNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII Chemistry-SQP 22-23Document16 pagesCLASS XII Chemistry-SQP 22-23Yug GandhiNo ratings yet
- Sample PapersDocument65 pagesSample PapersKatara BittuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 243 Mid-Term Test Answers and Comments: Class PerformanceDocument5 pagesChemistry 243 Mid-Term Test Answers and Comments: Class Performancemasruri123No ratings yet
- Chemistry SQPDocument11 pagesChemistry SQPSariska MehraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document32 pagesChapter 03hussainNo ratings yet
- KOT121 Answer Sem1 2008 2009Document6 pagesKOT121 Answer Sem1 2008 2009Ren Liew Jia QingNo ratings yet
- Rearrangement ReactionsDocument5 pagesRearrangement Reactionsblue_l1100% (1)
- Practise Paper - Chemistry - Class XI 2023-24Document6 pagesPractise Paper - Chemistry - Class XI 2023-24mysixthidisNo ratings yet
- Dec 2018Document70 pagesDec 2018sridharR hahahaNo ratings yet
- Aromaticity ProblemDocument13 pagesAromaticity ProblemSagar ThakreNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper, XII, 2023-24, PDFDocument8 pagesSample Paper, XII, 2023-24, PDFfareehafatima18No ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of Test Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by Hart All ChapterDocument53 pagesFull Download PDF of Test Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by Hart All Chaptermasartfrohn100% (8)
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question BankDocument16 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Question BankBrown HustlerNo ratings yet
- L6S Final Examination Students)Document12 pagesL6S Final Examination Students)Fazliawati MahayuddinNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions On HydrocarbonsDocument10 pagesJEE Advanced Previous Year Questions On Hydrocarbonsananyashri30No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Bank 1690183665Document26 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Bank 1690183665Pratibaa LNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Answer KeyDocument7 pagesHydrocarbon Answer KeyVK CREATIONNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 203/2/2017: General Chemistry 1BDocument18 pagesTutorial Letter 203/2/2017: General Chemistry 1BLeigh MakanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Theory (043) MM: 70 Time: 3hours: A) B) C) D)Document9 pagesChemistry Theory (043) MM: 70 Time: 3hours: A) B) C) D)Arun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions Answers CHEMDocument16 pagesSample Questions Answers CHEMlal0% (1)
- CHM112 CBT Ca (Merit)Document4 pagesCHM112 CBT Ca (Merit)teamtruth50No ratings yet
- USM XI ChemistryDocument7 pagesUSM XI ChemistryPriyanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 MCQs Questions With AnswersDocument10 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 MCQs Questions With AnswersMohammed Shadab KhanNo ratings yet
- Question PAPERDocument6 pagesQuestion PAPERharsh.mahori09No ratings yet
- Chap 2Document47 pagesChap 2h2300147No ratings yet
- Essential Organic Chemistry 2nd Edition Bruice Test BankDocument21 pagesEssential Organic Chemistry 2nd Edition Bruice Test Bankmarykirbyifsartwckp100% (15)
- Sample Paper Gr11Document3 pagesSample Paper Gr11Enoca AJNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2023 QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2023 QuestionnaireJD6 Agarb100% (1)
- Full Download PDF of Organic Chemistry Brown 7th Edition Test Bank All ChapterDocument47 pagesFull Download PDF of Organic Chemistry Brown 7th Edition Test Bank All Chapteringvilsabael100% (4)
- Exam Class XIDocument5 pagesExam Class XIFIITJEE DPSNo ratings yet
- 12TH ChemistryDocument11 pages12TH ChemistryAkshatNo ratings yet
- Entry Test Chemistry Answer KeyDocument4 pagesEntry Test Chemistry Answer KeyMudassir HussainNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam Review Chemistry For Engineers FinalDocument102 pagesPrelim Exam Review Chemistry For Engineers Finalkat rinaNo ratings yet
- Chem SQP2023-24Document9 pagesChem SQP2023-24anshulchauhan94595No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument20 pagesCHEMISTRYdishugirdhar08No ratings yet
- Halo Alkanes Sample PaperDocument6 pagesHalo Alkanes Sample PapervasuNo ratings yet
- MCQ Questions For Class 10 Science Carbon and Its Compounds With AnswersDocument30 pagesMCQ Questions For Class 10 Science Carbon and Its Compounds With AnswersAymen WaelNo ratings yet
- 6 - QP and MS - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument9 pages6 - QP and MS - Haloalkanes and Haloareneskrish dabhi0% (1)
- Final 11 Chemistry (Answersheet)Document11 pagesFinal 11 Chemistry (Answersheet)Kedar GuravNo ratings yet
- Chem 132 2019 Tutorial QuestionsDocument3 pagesChem 132 2019 Tutorial QuestionsYusuf Zaynab100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Brown 7th Edition Test BankDocument24 pagesOrganic Chemistry Brown 7th Edition Test Bankeganfarrerkv8x2No ratings yet
- Chem Sample Paper 1 PersonalDocument10 pagesChem Sample Paper 1 Personalsiddharthplays2010No ratings yet
- II PUCmid Term 23Document4 pagesII PUCmid Term 23Varun. B. CNo ratings yet
- 11-Chemistry-A1-Annual Exam 2023-24Document8 pages11-Chemistry-A1-Annual Exam 2023-24harshitsharmasportsNo ratings yet
- Che102 Likely Qs and AnsDocument13 pagesChe102 Likely Qs and AnsAlexander GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Hult2007 Enzyme Promiscuity Mechanism and ApplicationsDocument8 pagesHult2007 Enzyme Promiscuity Mechanism and ApplicationsRoshiio Espinoza100% (1)
- Bs Alkal 2018 11 001Document117 pagesBs Alkal 2018 11 001Shar KhanNo ratings yet
- Temkin 100 YearsDocument30 pagesTemkin 100 YearsMarina ShestakovaNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL KINETICS FinalDocument6 pagesCHEMICAL KINETICS FinalBOTHRA CLASSESNo ratings yet
- Chapter7elimination Ans SubstnDocument22 pagesChapter7elimination Ans Substnjagabandhu_patraNo ratings yet
- Borrowing HydrogenDocument7 pagesBorrowing HydrogenVinayak KhairnarNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Substituted Benzenes: 6 Edition Paula Yurkanis BruiceDocument72 pagesReactions of Substituted Benzenes: 6 Edition Paula Yurkanis BruiceyulliarperezNo ratings yet
- Base HydrolysisDocument8 pagesBase Hydrolysissaud100% (1)
- Organic Reaction MechanismsDocument14 pagesOrganic Reaction MechanismstylerNo ratings yet
- WahyudiDocument5 pagesWahyudimeNo ratings yet
- Module - Organic Advanced - Reaction MechanismDocument33 pagesModule - Organic Advanced - Reaction Mechanismkaransharma690No ratings yet
- 3 Catalyst De-Poisoning by HydrogenationDocument9 pages3 Catalyst De-Poisoning by HydrogenationChuka OmeneNo ratings yet
- Meerwein Ponndorf Verley - ReductionDocument6 pagesMeerwein Ponndorf Verley - ReductionAndey HemanthNo ratings yet
- 10 ch05.2.1 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives 29Document29 pages10 ch05.2.1 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives 29NH Khánh NhiiNo ratings yet
- CHEM 20273 F23 Problem-Solving Set 8Document4 pagesCHEM 20273 F23 Problem-Solving Set 8Nitin PNo ratings yet
- Answer KDocument5 pagesAnswer KJerome MosadaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument44 pagesChemical KineticsShania ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Reaction MechanismDocument19 pagesReaction Mechanismtapas kunduNo ratings yet
- PW-049a-Limiting Reagents-01Document5 pagesPW-049a-Limiting Reagents-01JoHan Xyth RizaldoNo ratings yet
- Adv Retrosynthesis PDFDocument29 pagesAdv Retrosynthesis PDFericaNo ratings yet
- Kinetics IntroductionDocument55 pagesKinetics IntroductionAgano juma mwakasendoNo ratings yet
- ch9 AlkynesDocument7 pagesch9 AlkynesApichat JunsodNo ratings yet
- The Kinetics of The Acid-Catalyzed Formation of Peracetic Acid FromDocument4 pagesThe Kinetics of The Acid-Catalyzed Formation of Peracetic Acid FromDaniella DenleschiNo ratings yet
- 50 6th Sem-C13-Kinetics Oct Substitution - Dr. Sunirban DasDocument10 pages50 6th Sem-C13-Kinetics Oct Substitution - Dr. Sunirban DasSIMARAN JAISWAL 41 M3SNo ratings yet
- O-Mercaptoacylphenones: Facile Preparation of 3-Substituted Benzisothiazoles FromDocument3 pagesO-Mercaptoacylphenones: Facile Preparation of 3-Substituted Benzisothiazoles Frompaula salamancaNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Reactions of EthersDocument54 pagesPreparation and Reactions of EthersEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab#2 Hydrolysis RateDocument4 pagesBiology Lab#2 Hydrolysis RateTyler EdwardsNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemical Equilibrium SolutionDocument25 pages11 Chemical Equilibrium SolutionRajNo ratings yet
- Molecules: Diazocarbonyl and Related Compounds in The Synthesis of AzolesDocument70 pagesMolecules: Diazocarbonyl and Related Compounds in The Synthesis of Azolespopescu vasilicaNo ratings yet
Chem 221 Bruice Chapter 4 Answers To Problems in The Coursepack
Chem 221 Bruice Chapter 4 Answers To Problems in The Coursepack
Uploaded by
Parham ElahiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chem 221 Bruice Chapter 4 Answers To Problems in The Coursepack
Chem 221 Bruice Chapter 4 Answers To Problems in The Coursepack
Uploaded by
Parham ElahiCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEM
221
Bruice Chapter 4
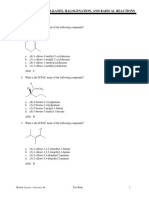
4.37 a)
b)
Answers to problems in the coursepack
c)
d)
nucleophile
electophile
CH3CHCH3
CH3CH=CH2
nucleophile
4.38a)
H-Br
electophile
b)
4.39 a)
c)
h)
i)
d)
f)
j)
k)
g)
m)
4.41 a)
CHEM 221
Bruice Chapter 4
Answers to problems in the coursepack
B is a tetrasubstituted alkene, A is a trisubstituted alkene and C is a disubstituted alkene. The more
substituted the alkene is the more stable it is. Hence 2,3-dimethyl(B) is the most stable, 3,4-dimethyl
(A) is the second most stable and 4,5-dimethyl (C) is the least stable.
b) B it is the most stable, the lowest in energy and it will give the smallest amount of energy upon
hydrogenation. Since the reaction is exothermic, it will be negative and the highest value. It will be the
least negative of the three.
c)C it is the least stable, the highest in energy and it will give the largest amount of energy upon
hydrogenation. Since the reaction is exothermic, it will be negative and the smallest value. It will be the
most negative of the three.
H+
H2O
1)Hg(OAc)2
2) NaBH4
1) BH3 THF
2) NaOH, H2O2
4.42
CHEM 221
Bruice Chapter 4
Answers to problems in the coursepack
4.43
The
first
step
involves
protonation
of
the
double
bond.
It
can
produce
two
carbocation
A,
with
1
electrondonating
group
i.e.
primary
and
B,
with
two
electrondonating
groups
i.e.
secondary.
Electrondonating
groups
stabilize
the
electrondeficient
carbocation
by
donating
electrons.
B
is
more
stable
than
A
because
it
has
more
electrondonating
groups.
It
is
the
major
intermediate
formed
in
the
first
step.
Whence
B
is
formed
it
could
react
with
the
bromide
ion
to
form
2-bromo-3-methylbutane.
B
could
also
rearrange
to
form
C.
The
migration
of
a
hydride
H-
forms
a
new
carbocation
C
which
is
tertiary
i.e.
it
has
three
electrondonating
groups.
It
is
more
stable
than
B
and
can
further
react
with
Br-
to
give
2-bromo-2-methylbutane.
4.44
a)
See
structures
in
3.37
L
is
the
most
stable
because
it
is
the
most
substituted.
It
is
the
only
one
that
has
four
alkyl
substituents.
Each
alkyl
groups
increases
the
number
of
C-sp2-Csp3
bonds
which
are
most stable thanCsp3-sp3 bonds.
b)Among all possibilities, A is the only that has only one alkyl group on the double bond. With the
A
fewest
number
of
alkyl
groups,
it
is
the
least
stable
alkene.
CHEM 221
Bruice Chapter 4
Answers to problems in the coursepack
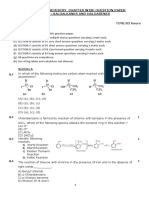
4.46
1)BH3THF
2) NaOH, H2O2
H2
Br2
THF
Pd/C
HBr
H+
H2O
Br2
H2O
4.47a)
d)
e)
f)
h)
CHEM 221
Bruice Chapter 4
Answers to problems in the coursepack
H2
HCl
Pd/C
4.48
a)
THF c)
b)
1)BH3THF
2) NaOH, H2O2
Br2
H2O e)
d)
H+
H2O
4.49
4.50 a)first one is tertiary, second one is secondary; first one is more stable. B)second one is more stable
because
the
chlorine
can
stabilize
the
carbocation
by
forming
a
chlorinium
ion
c)first
one
is
a
trisubtituted
alkene
and
the
second
one
is
disusbtituted.
First
one
is
more
stable.
d)
Same
argument
as
c)
,
but
second
compound
is
more
stable.
4.57
a)
There
are
five
alkenes.
H2
Pt
A
CHEM 221
Bruice Chapter 4
Answers to problems in the coursepack
b)B
is
the
most
stable
because
it
is
the
most
substituted
alkene
with
three
alkyl
groups.
All
other
ones
have
two
alkyl
groups.
4.58
a)
b)The
initially
formed
carbocation
is
B.
A
is
not
formed
because
it
is
primary,
1EDG.
B
is
tertiary
with
3
EDG
and
is
more
stable
than
A.
c)
The
first
rearranged
carbocation,
C,
is
secondary.
The
second
rearranged
carbocation,
D,
is
tertiary.
d)
The
first
rearrangement
from
B
to
C
produces
a
secondary
carbocation(C),
less
stable
than
a
tertiary
carbocation(B).
Ring
strain
should
also
be
considered.
C
is
a
five-membered
ring
whereas
B
is
a
four-
membered
ring.
C,
although
it
is
secondary
is
more
stable
than
B
because
it
has
less
ring
strain.
This
is
the
driving
force
for
the
first
rearrangement.
The
second
rearrangement
from
C
to
D
is
standard.
The
rearranged
carbocation
is
tertiary
i.e.
more
stable
than
C
(secondary).
Both
are
five-membered
rings.
Ring
strain
is
not
an
issue.
CHEM 221
Bruice Chapter 4
Answers to problems in the coursepack
4.60
For
this
problem,
the
rearrangement
from
B
to
C
is
also
favored
due
to
ring
strain
relief.
Six-membered
ring
has
less
ring
strain
than
five-membered
ring.
The
rearrangement
is
also
favored
due
to
the
fact
that
C
is
tertiary
whereas
B
is
secondary.
You might also like
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by HartDocument30 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by HartLaura Eraso100% (36)
- CH 8 Test BankDocument14 pagesCH 8 Test BankVanessa James100% (2)
- Organic Nitrogen Compounds Tutorial SolutionsDocument8 pagesOrganic Nitrogen Compounds Tutorial SolutionsDomNo ratings yet
- Org Chem 3Document37 pagesOrg Chem 3tyron9520100% (1)
- ch13 ProblemsDocument84 pagesch13 Problemsbrownhazel67% (6)
- Organic Chemistry: Nucleophilic Substitution at Saturated CarbonDocument107 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Nucleophilic Substitution at Saturated CarbonMafalda FernandesNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by HartDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by HartJesus Carter100% (39)
- Reaction IntermediateDocument18 pagesReaction IntermediateManaswini P100% (1)
- 12thchemistrysamplepaper1 291223044313Document9 pages12thchemistrysamplepaper1 291223044313aditikharb2020No ratings yet
- Chem PreboardDocument13 pagesChem Preboardvirender.pinghalNo ratings yet
- CHM101Document44 pagesCHM101YunusNo ratings yet
- XII Chemistry Sample Question Paper - FinalDocument65 pagesXII Chemistry Sample Question Paper - Finalkrishnapradhani091No ratings yet
- Chemistry - 2 Page EditDocument11 pagesChemistry - 2 Page EditNorish SamdaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SQP 2Document11 pagesChemistry SQP 2ACHAL PATILNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SQPDocument11 pagesChemistry SQPMohd Zaid KhanNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII Chemistry-SQP 22-23Document16 pagesCLASS XII Chemistry-SQP 22-23Yug GandhiNo ratings yet
- Sample PapersDocument65 pagesSample PapersKatara BittuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 243 Mid-Term Test Answers and Comments: Class PerformanceDocument5 pagesChemistry 243 Mid-Term Test Answers and Comments: Class Performancemasruri123No ratings yet
- Chemistry SQPDocument11 pagesChemistry SQPSariska MehraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document32 pagesChapter 03hussainNo ratings yet
- KOT121 Answer Sem1 2008 2009Document6 pagesKOT121 Answer Sem1 2008 2009Ren Liew Jia QingNo ratings yet
- Rearrangement ReactionsDocument5 pagesRearrangement Reactionsblue_l1100% (1)
- Practise Paper - Chemistry - Class XI 2023-24Document6 pagesPractise Paper - Chemistry - Class XI 2023-24mysixthidisNo ratings yet
- Dec 2018Document70 pagesDec 2018sridharR hahahaNo ratings yet
- Aromaticity ProblemDocument13 pagesAromaticity ProblemSagar ThakreNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper, XII, 2023-24, PDFDocument8 pagesSample Paper, XII, 2023-24, PDFfareehafatima18No ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of Test Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by Hart All ChapterDocument53 pagesFull Download PDF of Test Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by Hart All Chaptermasartfrohn100% (8)
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question BankDocument16 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Question BankBrown HustlerNo ratings yet
- L6S Final Examination Students)Document12 pagesL6S Final Examination Students)Fazliawati MahayuddinNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions On HydrocarbonsDocument10 pagesJEE Advanced Previous Year Questions On Hydrocarbonsananyashri30No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Bank 1690183665Document26 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Bank 1690183665Pratibaa LNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Answer KeyDocument7 pagesHydrocarbon Answer KeyVK CREATIONNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 203/2/2017: General Chemistry 1BDocument18 pagesTutorial Letter 203/2/2017: General Chemistry 1BLeigh MakanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Theory (043) MM: 70 Time: 3hours: A) B) C) D)Document9 pagesChemistry Theory (043) MM: 70 Time: 3hours: A) B) C) D)Arun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions Answers CHEMDocument16 pagesSample Questions Answers CHEMlal0% (1)
- CHM112 CBT Ca (Merit)Document4 pagesCHM112 CBT Ca (Merit)teamtruth50No ratings yet
- USM XI ChemistryDocument7 pagesUSM XI ChemistryPriyanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 MCQs Questions With AnswersDocument10 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 MCQs Questions With AnswersMohammed Shadab KhanNo ratings yet
- Question PAPERDocument6 pagesQuestion PAPERharsh.mahori09No ratings yet
- Chap 2Document47 pagesChap 2h2300147No ratings yet
- Essential Organic Chemistry 2nd Edition Bruice Test BankDocument21 pagesEssential Organic Chemistry 2nd Edition Bruice Test Bankmarykirbyifsartwckp100% (15)
- Sample Paper Gr11Document3 pagesSample Paper Gr11Enoca AJNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2023 QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2023 QuestionnaireJD6 Agarb100% (1)
- Full Download PDF of Organic Chemistry Brown 7th Edition Test Bank All ChapterDocument47 pagesFull Download PDF of Organic Chemistry Brown 7th Edition Test Bank All Chapteringvilsabael100% (4)
- Exam Class XIDocument5 pagesExam Class XIFIITJEE DPSNo ratings yet
- 12TH ChemistryDocument11 pages12TH ChemistryAkshatNo ratings yet
- Entry Test Chemistry Answer KeyDocument4 pagesEntry Test Chemistry Answer KeyMudassir HussainNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam Review Chemistry For Engineers FinalDocument102 pagesPrelim Exam Review Chemistry For Engineers Finalkat rinaNo ratings yet
- Chem SQP2023-24Document9 pagesChem SQP2023-24anshulchauhan94595No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument20 pagesCHEMISTRYdishugirdhar08No ratings yet
- Halo Alkanes Sample PaperDocument6 pagesHalo Alkanes Sample PapervasuNo ratings yet
- MCQ Questions For Class 10 Science Carbon and Its Compounds With AnswersDocument30 pagesMCQ Questions For Class 10 Science Carbon and Its Compounds With AnswersAymen WaelNo ratings yet
- 6 - QP and MS - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument9 pages6 - QP and MS - Haloalkanes and Haloareneskrish dabhi0% (1)
- Final 11 Chemistry (Answersheet)Document11 pagesFinal 11 Chemistry (Answersheet)Kedar GuravNo ratings yet
- Chem 132 2019 Tutorial QuestionsDocument3 pagesChem 132 2019 Tutorial QuestionsYusuf Zaynab100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Brown 7th Edition Test BankDocument24 pagesOrganic Chemistry Brown 7th Edition Test Bankeganfarrerkv8x2No ratings yet
- Chem Sample Paper 1 PersonalDocument10 pagesChem Sample Paper 1 Personalsiddharthplays2010No ratings yet
- II PUCmid Term 23Document4 pagesII PUCmid Term 23Varun. B. CNo ratings yet
- 11-Chemistry-A1-Annual Exam 2023-24Document8 pages11-Chemistry-A1-Annual Exam 2023-24harshitsharmasportsNo ratings yet
- Che102 Likely Qs and AnsDocument13 pagesChe102 Likely Qs and AnsAlexander GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Hult2007 Enzyme Promiscuity Mechanism and ApplicationsDocument8 pagesHult2007 Enzyme Promiscuity Mechanism and ApplicationsRoshiio Espinoza100% (1)
- Bs Alkal 2018 11 001Document117 pagesBs Alkal 2018 11 001Shar KhanNo ratings yet
- Temkin 100 YearsDocument30 pagesTemkin 100 YearsMarina ShestakovaNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL KINETICS FinalDocument6 pagesCHEMICAL KINETICS FinalBOTHRA CLASSESNo ratings yet
- Chapter7elimination Ans SubstnDocument22 pagesChapter7elimination Ans Substnjagabandhu_patraNo ratings yet
- Borrowing HydrogenDocument7 pagesBorrowing HydrogenVinayak KhairnarNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Substituted Benzenes: 6 Edition Paula Yurkanis BruiceDocument72 pagesReactions of Substituted Benzenes: 6 Edition Paula Yurkanis BruiceyulliarperezNo ratings yet
- Base HydrolysisDocument8 pagesBase Hydrolysissaud100% (1)
- Organic Reaction MechanismsDocument14 pagesOrganic Reaction MechanismstylerNo ratings yet
- WahyudiDocument5 pagesWahyudimeNo ratings yet
- Module - Organic Advanced - Reaction MechanismDocument33 pagesModule - Organic Advanced - Reaction Mechanismkaransharma690No ratings yet
- 3 Catalyst De-Poisoning by HydrogenationDocument9 pages3 Catalyst De-Poisoning by HydrogenationChuka OmeneNo ratings yet
- Meerwein Ponndorf Verley - ReductionDocument6 pagesMeerwein Ponndorf Verley - ReductionAndey HemanthNo ratings yet
- 10 ch05.2.1 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives 29Document29 pages10 ch05.2.1 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives 29NH Khánh NhiiNo ratings yet
- CHEM 20273 F23 Problem-Solving Set 8Document4 pagesCHEM 20273 F23 Problem-Solving Set 8Nitin PNo ratings yet
- Answer KDocument5 pagesAnswer KJerome MosadaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument44 pagesChemical KineticsShania ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Reaction MechanismDocument19 pagesReaction Mechanismtapas kunduNo ratings yet
- PW-049a-Limiting Reagents-01Document5 pagesPW-049a-Limiting Reagents-01JoHan Xyth RizaldoNo ratings yet
- Adv Retrosynthesis PDFDocument29 pagesAdv Retrosynthesis PDFericaNo ratings yet
- Kinetics IntroductionDocument55 pagesKinetics IntroductionAgano juma mwakasendoNo ratings yet
- ch9 AlkynesDocument7 pagesch9 AlkynesApichat JunsodNo ratings yet
- The Kinetics of The Acid-Catalyzed Formation of Peracetic Acid FromDocument4 pagesThe Kinetics of The Acid-Catalyzed Formation of Peracetic Acid FromDaniella DenleschiNo ratings yet
- 50 6th Sem-C13-Kinetics Oct Substitution - Dr. Sunirban DasDocument10 pages50 6th Sem-C13-Kinetics Oct Substitution - Dr. Sunirban DasSIMARAN JAISWAL 41 M3SNo ratings yet
- O-Mercaptoacylphenones: Facile Preparation of 3-Substituted Benzisothiazoles FromDocument3 pagesO-Mercaptoacylphenones: Facile Preparation of 3-Substituted Benzisothiazoles Frompaula salamancaNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Reactions of EthersDocument54 pagesPreparation and Reactions of EthersEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab#2 Hydrolysis RateDocument4 pagesBiology Lab#2 Hydrolysis RateTyler EdwardsNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemical Equilibrium SolutionDocument25 pages11 Chemical Equilibrium SolutionRajNo ratings yet
- Molecules: Diazocarbonyl and Related Compounds in The Synthesis of AzolesDocument70 pagesMolecules: Diazocarbonyl and Related Compounds in The Synthesis of Azolespopescu vasilicaNo ratings yet