Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hepatic Metabolism. Oxidation, Hydroxylation, Conjufation W/ Glucoronic Acid (Exc. Lore and Oxa)
Hepatic Metabolism. Oxidation, Hydroxylation, Conjufation W/ Glucoronic Acid (Exc. Lore and Oxa)
Uploaded by
Mohammad Ali Ismail0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageBenzodiazepines work by binding to GABA receptors in the brain, increasing chloride ion flow and neural inhibition. They are highly lipid soluble, can cross the blood-brain barrier and placenta, and are secreted in breast milk. They are metabolized in the liver. Common side effects include drowsiness, ataxia, cognitive impairment, and withdrawal symptoms like anxiety and insomnia. They can cause physical dependence with long-term use. Short and intermediate-acting benzodiazepines include oxazepam and lorazepam. Flumazepam is an antagonist used to reverse benzodiazepine overdoses. Azapirones like buspirone are anxi
Original Description:
pharm drugs
Original Title
Pharm Drugs Block 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBenzodiazepines work by binding to GABA receptors in the brain, increasing chloride ion flow and neural inhibition. They are highly lipid soluble, can cross the blood-brain barrier and placenta, and are secreted in breast milk. They are metabolized in the liver. Common side effects include drowsiness, ataxia, cognitive impairment, and withdrawal symptoms like anxiety and insomnia. They can cause physical dependence with long-term use. Short and intermediate-acting benzodiazepines include oxazepam and lorazepam. Flumazepam is an antagonist used to reverse benzodiazepine overdoses. Azapirones like buspirone are anxi
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageHepatic Metabolism. Oxidation, Hydroxylation, Conjufation W/ Glucoronic Acid (Exc. Lore and Oxa)
Hepatic Metabolism. Oxidation, Hydroxylation, Conjufation W/ Glucoronic Acid (Exc. Lore and Oxa)
Uploaded by
Mohammad Ali IsmailBenzodiazepines work by binding to GABA receptors in the brain, increasing chloride ion flow and neural inhibition. They are highly lipid soluble, can cross the blood-brain barrier and placenta, and are secreted in breast milk. They are metabolized in the liver. Common side effects include drowsiness, ataxia, cognitive impairment, and withdrawal symptoms like anxiety and insomnia. They can cause physical dependence with long-term use. Short and intermediate-acting benzodiazepines include oxazepam and lorazepam. Flumazepam is an antagonist used to reverse benzodiazepine overdoses. Azapirones like buspirone are anxi
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
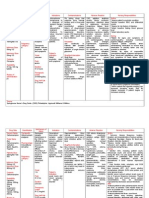
Benzodiazepines: allosteric binding site
that binds to a site adjacent to the GABA
receptor to increase the influx of Cl- ions
resulting in hyperpolarization =
inhibition of neural stimulus. Highly lipid
soluble cross barriers easily. Cross
placenta secreted in breast milk. Hepatic
metabolism. Oxidation, hydroxylation,
conjufation w/ glucoronic acid (exc. Lore
and oxa). Drowsiness and confusion,
ataxia if high doses, cognitive
impairment, potentiate alcohol and other
CNS depresents. Withdrawl can occur:
anxiety, insomnia, irritability, muscle
weakness. Longer halflife= lower
symptoms. Use titration to wean them
off the drug. Decreased responsiveness
after continuous exposure. Cause
dependence if given long term.
Short Acting: OXAZEPAM: use for elderly,
hepatic disease, no metab.
Intermediate Acting:
Lorazepam: use for elderly, hepatic
disease, no metab.
Alprazolam:
Long Acting:
Chlordiazepoxide:
Diazepam:
Clorazepate: dont use in liver disease
ANTAGONIST: Flumazenil: comp
antagonizes BDZs. BDZ overdose,
reversal of sedative effects produced by
BDZs. Anesthesia, diagnostic,
therapeutic procedures
Azapirones: Buspirone: mediated by
serotonin receptors 5HT1a>autoreceptors coupled to G proteins
regulating K+ membrane channels.
Increase opening causes
hyperpolarization. Partial agonist.
Selevtive anxiolytic effect. Adv: NO:
physical dependence, withdrawl,
potentiation of CNS dep and alcohol,
cross tolerance with BDZs, muscle
relaxation or anticonvulsant. Low SE
(headache, dizzy), Use long term
therapy. Disadv: slow OA, 2wks.
SSRI: inhibit serotonin reuptake at
trasporter by blocking major NT removal.
Adv: same as above. Disadv. Same as
above. Highly protein bound. Met. In
liver (cimetidine may increase t1/2). CNS:
Insomnia, tremor. CV: palpitations,
postural hypotension, vasodilation GI:
anorexia, N.V.D GU: loss of libido, sexual
dysfunction. Monoamine Oxidase
Inhibitors: can be fatal, wait 14 day
intervals in between two drugs>hyperthermia, muscle rigidity,
myoclonus and rapid mental changes
(increase in tricyclic antidepressents due
to met inhibition). Tryptophan: serotonin
precursor. Warfarin: increased bleeding.
Paroxetine: social anxiety disorder.
Sertraline: PTSD-(kids too)
Escitalopram
SNRI: blocks both serotonin and NE
reuptake. General anxiety disorder.
Similar to SSRI, may cause HTN. Slowly
You might also like
- Action: Indications:: Drug: Oxygen Class of Medication: Oxidizing Agent (Gas)Document6 pagesAction: Indications:: Drug: Oxygen Class of Medication: Oxidizing Agent (Gas)Andreas100% (2)
- Sullam Munawariq EnglishDocument13 pagesSullam Munawariq EnglishMohammad Ali IsmailNo ratings yet
- Sedation of Patients in ICUDocument9 pagesSedation of Patients in ICUAlfrin AntonyNo ratings yet
- English Mohammad The Last Prophet A Model For All TimeDocument216 pagesEnglish Mohammad The Last Prophet A Model For All TimeMohammad Ali IsmailNo ratings yet
- Barbiturates: of Action of GABA. Independent of GABADocument10 pagesBarbiturates: of Action of GABA. Independent of GABAAvi WerdesheimNo ratings yet
- Doctor's Order Levodopa +carbidopa 250mg/25mg 1 Tab BIDDocument25 pagesDoctor's Order Levodopa +carbidopa 250mg/25mg 1 Tab BIDspain michaelisNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument6 pagesDiazepamF - TOMELDAN, CERESNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument11 pagesPharmaGohar KamranNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument2 pagesGeneric NameJhennyvie Dueñas ArcoirezNo ratings yet
- PhharmaDocument21 pagesPhharmaVelado Alessandra Loraine B.No ratings yet
- Final PharmaDocument22 pagesFinal PharmaVelado Alessandra Loraine B.No ratings yet
- Lorazepam (Drug Monograph)Document1 pageLorazepam (Drug Monograph)Muhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Coronary Ward IIDocument7 pagesDrugs Coronary Ward IITimothy Joy VercelesNo ratings yet
- ZonisamideDocument2 pagesZonisamideRo-anne AkuNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Part 2Document24 pagesEpilepsy Part 2Sara AbbasNo ratings yet
- Benzodiazepine Poisoning PDFDocument18 pagesBenzodiazepine Poisoning PDFNeicu Marius-RăzvanNo ratings yet
- BENZODIAZEPINESDocument20 pagesBENZODIAZEPINESHamza DossaNo ratings yet
- Secret Pharmacology Step 1 Study Guide: Pharm"Document29 pagesSecret Pharmacology Step 1 Study Guide: Pharm"Fahd Abdullah Al-refaiNo ratings yet
- AnxiolyticsDocument23 pagesAnxiolyticsNalafNo ratings yet
- Drugs CoroDocument2 pagesDrugs CoroKim RodriguezNo ratings yet
- NPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesDocument83 pagesNPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesValeria AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptics PD 501Document27 pagesAntiepileptics PD 501SidraNo ratings yet
- Drug PresentationDocument32 pagesDrug PresentationManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument7 pagesDrugs Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationPrincess Jenelly CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Mood Stabilisers: PsychopharmacologyDocument50 pagesMood Stabilisers: Psychopharmacologymeno321No ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- Pharm 2 TESTDocument26 pagesPharm 2 TESTRachel MackeyNo ratings yet
- Alcohols: Pharmacological ActionDocument5 pagesAlcohols: Pharmacological ActionMuhammad AbbasNo ratings yet
- Furosemide HaloperidolDocument6 pagesFurosemide HaloperidolLady Lou ArmadaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Parkinsonism: Functional Circuitry Between The Cortex, Basal Ganglia, and ThalamusDocument5 pagesDrugs Used in Parkinsonism: Functional Circuitry Between The Cortex, Basal Ganglia, and ThalamusHamad AlshabiNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonismDocument18 pagesParkinsonismShivsharanNo ratings yet
- OxcarbazepineDocument4 pagesOxcarbazepineahmad_makhtarNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System Pharmacology: Elly Nurus SakinahDocument64 pagesCentral Nervous System Pharmacology: Elly Nurus Sakinahkareem92No ratings yet
- Of Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart FailureDocument31 pagesOf Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart Failurenaikram420No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateTempoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyMeraflor BahonsuaNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol Drug StudyDocument3 pagesHaloperidol Drug StudyAysaaa DCNo ratings yet
- 7 - Drugs Used in ParkinsonDocument47 pages7 - Drugs Used in ParkinsonSara AbbasNo ratings yet
- Benzodiazepines ToxicityDocument19 pagesBenzodiazepines ToxicityNagendra NayakNo ratings yet
- Drugs That Cause and Drugs That Alleviate Parkinsonism: BY Prof. Mbah A.UDocument24 pagesDrugs That Cause and Drugs That Alleviate Parkinsonism: BY Prof. Mbah A.UtemitopeNo ratings yet
- FDCDocument10 pagesFDCAnkit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Leaflet For Dd1 AssgmntDocument2 pagesLeaflet For Dd1 AssgmntayuNo ratings yet
- Alcohol 2Document18 pagesAlcohol 2Halima AtikuNo ratings yet
- Xanax Drug CardDocument3 pagesXanax Drug Cardnasir khanNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinson Drugs FinallDocument36 pagesAnti Parkinson Drugs FinallandrapradeshsseNo ratings yet
- Dear Reader, These Papers Were Meant To Be As An Extremely Quick Review and Ultra-Short Summary ofDocument9 pagesDear Reader, These Papers Were Meant To Be As An Extremely Quick Review and Ultra-Short Summary ofHazel D. Venus100% (2)
- 2020 Feb Answer KeyDocument27 pages2020 Feb Answer KeyAjitha boopathiNo ratings yet
- LEXOTANIL Bromazepam MeppoDocument4 pagesLEXOTANIL Bromazepam MeppoTkt Sheik AbdullahNo ratings yet
- c32d9117 1591958900298Document39 pagesc32d9117 1591958900298Marzi MdvNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPao HinojosaNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationDocument4 pagesBrand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationApril Joy MangsatNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- BazetolDocument18 pagesBazetolpabitraNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment of EpilepsyDocument81 pagesDrug Treatment of EpilepsyAnifowose SamsonNo ratings yet
- Ativan CIV Tablets: R OnlyDocument8 pagesAtivan CIV Tablets: R OnlyP KasikrishnarajaNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Aksi DiazepamDocument4 pagesMekanisme Aksi DiazepamWijaya Kusuma MaheruNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Reporting-1Document32 pagesPharmacology Reporting-1Mj TalentNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14A Pituitary Adenomas and CraniopharyngiomasDocument8 pagesChapter 14A Pituitary Adenomas and CraniopharyngiomasMohammad Ali IsmailNo ratings yet
- Historic Judgement On Interest Delivered in The Supreme Court of Pakistan PDFDocument133 pagesHistoric Judgement On Interest Delivered in The Supreme Court of Pakistan PDFMohammad Ali IsmailNo ratings yet
- Job Shadowing PolicyDocument6 pagesJob Shadowing PolicyMohammad Ali IsmailNo ratings yet
- Mashaikh Naqshband Final 03022015Document244 pagesMashaikh Naqshband Final 03022015Mohammad Ali IsmailNo ratings yet
- ACOFP 2016 PT Education Handout Zajac Breast Cancer Screening Recommendations (002) FINAL REVDocument1 pageACOFP 2016 PT Education Handout Zajac Breast Cancer Screening Recommendations (002) FINAL REVMohammad Ali IsmailNo ratings yet
- 1-Purification of The HeartDocument236 pages1-Purification of The HeartMohammad Ali IsmailNo ratings yet
- Readanki 109246Document1 pageReadanki 109246Mohammad Ali IsmailNo ratings yet
- Arabic Vocabulary Bank: (Madinah Book 1 Chapter 1-23)Document29 pagesArabic Vocabulary Bank: (Madinah Book 1 Chapter 1-23)mazad1985No ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument760 pages1 PDFMohammad Ali Ismail100% (1)
- DailyQuietTimeGuide2011 12803Document3 pagesDailyQuietTimeGuide2011 12803Mohammad Ali IsmailNo ratings yet