Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Immune System: The Defense Mechanism of The Body Dedicated To Eradicating Dangerous
The Immune System: The Defense Mechanism of The Body Dedicated To Eradicating Dangerous
Uploaded by
Lindsey0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesThe document discusses key concepts in immunology and microbiology. It defines immunity as the body's defense mechanism against pathogens. The immune system consists of immune cells that work together like a military unit to eradicate dangerous microorganisms. Vaccination has been one of immunology's greatest successes. The human body is also home to many commensal microorganisms, especially in the gut, that aid in digestion and protect against disease. However, antibiotic use can disrupt this natural balance and allow opportunistic infections. The body has multiple barriers against infection, including the skin, mucosal surfaces, mucus, cilia, and antimicrobial peptides like defensins.
Original Description:
Immunology Exam 1 study guide
Original Title
Exam 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses key concepts in immunology and microbiology. It defines immunity as the body's defense mechanism against pathogens. The immune system consists of immune cells that work together like a military unit to eradicate dangerous microorganisms. Vaccination has been one of immunology's greatest successes. The human body is also home to many commensal microorganisms, especially in the gut, that aid in digestion and protect against disease. However, antibiotic use can disrupt this natural balance and allow opportunistic infections. The body has multiple barriers against infection, including the skin, mucosal surfaces, mucus, cilia, and antimicrobial peptides like defensins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesThe Immune System: The Defense Mechanism of The Body Dedicated To Eradicating Dangerous
The Immune System: The Defense Mechanism of The Body Dedicated To Eradicating Dangerous
Uploaded by
LindseyThe document discusses key concepts in immunology and microbiology. It defines immunity as the body's defense mechanism against pathogens. The immune system consists of immune cells that work together like a military unit to eradicate dangerous microorganisms. Vaccination has been one of immunology's greatest successes. The human body is also home to many commensal microorganisms, especially in the gut, that aid in digestion and protect against disease. However, antibiotic use can disrupt this natural balance and allow opportunistic infections. The body has multiple barriers against infection, including the skin, mucosal surfaces, mucus, cilia, and antimicrobial peptides like defensins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
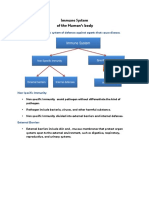
What is immunity?
In order to understand immunity, you need to understand the invading microorganism.
So, microbiology and immunology often go hand-in-hand together.
The immune system: the defense mechanism of the body dedicated to eradicating dangerous
pathogens from the body.
Immune cells: Think of the immune system like a military unit, consisting of generals and
majors and soldiers. Every immune cell plays a critical role in the immune system.
Vaccination
- The greatest triumph of immunology
- 1776: Edward Jenner made the 1st small pox vaccine from vaccinia virus
Commensal microorganisms inhabit healthy human bodies
- More than 500 microbial species live in the healthy human gut (weighs about 10 lbs)
- Commensal = eat at the same table
- Flora: the community of microbial species that inhabits a particular niche
- Commensal organisms
- enhance nutrition by digesting food and making vitamins
- protect against disease
Antibiotic treatment disrupts the natural ecology of the colon
- Clostridium difficile produces a toxin that causes severe diarrhea in pts treated with
antibiotics
Pathogens infectious organisms that cause disease
- Pathogen = any disease causing organism
- Opportunistic pathogen = usually a harmless organism that causes disease when the bodys
defenses are weakened.
- Pathogens: bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites
- Pathogens and their hosts have developed evolutionarily. Humans have a degree of built in
genetic resistance and also lifetime immunity
Barriers to infection
- Skin epithelium the bodys first defense against infection
Epithelium layers of keratinized cells that line the outer surface and inner cavities of the
body. The skin can be damaged by wounds, burns, surgical procedures
- Mucosal surfaces (mucosa) epithelia of inner cavities such as respiratory, gastrointestinal and
urogenital tracts. Mucosal surfaces are continually mathed in mucus that they secrete.
- Mucus thick fluid layer containing glycoproteins, proteoglycans and enzymes that protect
epithelial cells from damage and help to limit infection
- Cilia in the respiratory tract continually remove mucus, cleansing it of unwanted material in
Defensins antimicrobial peptides that kill bacteria, fungi and enveloped viruses
You might also like
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument25 pagesIntroduction To ImmunologySohail AhmedNo ratings yet
- PCB 3233 Chapter 1 Spring 15 73Document73 pagesPCB 3233 Chapter 1 Spring 15 73chicubs3794No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document3 pagesLecture 2Athena Thessa van VlotenNo ratings yet
- Lec # 4 Body Defence SystemsDocument31 pagesLec # 4 Body Defence SystemssamotherlianNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: The Immune System: Dr. Sanaa TorkDocument44 pagesChapter Six: The Immune System: Dr. Sanaa Torkisrar aslamNo ratings yet
- Immunity Germs, Disease and InfectionDocument4 pagesImmunity Germs, Disease and Infectionstring101No ratings yet
- Human DefensesDocument22 pagesHuman DefensesMagnaye LorenNo ratings yet
- Immunology & Serology Lecture 2Document31 pagesImmunology & Serology Lecture 2Jo Änna CampayneNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITYDocument4 pagesIMMUNITYSoni VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Richa PandeyDocument12 pagesRicha PandeyBrijesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument56 pagesImmune SystemGerome CausapinNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 2 PDFDocument33 pagesPDF Document 2 PDFKendrix FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 3rd Quarter MLG 1 PDFDocument21 pagesBiology 2 3rd Quarter MLG 1 PDFMichael John LozanoNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument36 pagesImmunologyمروه عماد عيسى100% (1)
- Basic Immunology 2017 - AmaDocument122 pagesBasic Immunology 2017 - AmaEka RizkyanaNo ratings yet
- Defence Mechanism of The BodyDocument44 pagesDefence Mechanism of The BodysayafyousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Aids To HealthDocument7 pagesAids To HealthAbhi LiteNo ratings yet
- Immunology NotesDocument18 pagesImmunology NotesSharath SNo ratings yet
- Year 10 DPP Biology Term 3 Exam RevisionDocument8 pagesYear 10 DPP Biology Term 3 Exam RevisionPoojit VenugopalaNo ratings yet
- How Animals SurviveDocument28 pagesHow Animals SurviveVirador John MichaelNo ratings yet
- Ch-10 Diseases and ImmunityDocument15 pagesCh-10 Diseases and Immunitydaveymilan36No ratings yet
- 10.0 Diseases - ImmunityDocument5 pages10.0 Diseases - ImmunityBianca Astrid AndoneNo ratings yet
- The Human Immune System: VideoDocument31 pagesThe Human Immune System: VideoCrystal Joy RebelloNo ratings yet
- Immunity ProjectDocument9 pagesImmunity ProjectAditi ShresthaNo ratings yet
- VMC 221 Coursematerials PDFDocument61 pagesVMC 221 Coursematerials PDFavenger 2100% (1)
- Innate Immune System: Fast and Broadly Effective: BacteriaDocument3 pagesInnate Immune System: Fast and Broadly Effective: BacteriaRIDANo ratings yet
- What Is Immunity?Document37 pagesWhat Is Immunity?heer100% (1)
- IMMUNITYDocument19 pagesIMMUNITYMuslimNo ratings yet
- PUBHEALTHDocument18 pagesPUBHEALTHChi Keung Langit ChanNo ratings yet
- Immunology For BSCNDocument39 pagesImmunology For BSCNHamas AliNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseasesDocument74 pagesHuman Health and Diseasessimra farooquiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Control: Michael A. Tabug, Msc. Shs-InstructorDocument19 pagesChemical Coordination and Control: Michael A. Tabug, Msc. Shs-InstructorMike TabsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunityDocument54 pagesIntroduction To ImmunityHadi Adam100% (1)
- Mutate or Die - DiseaseDocument34 pagesMutate or Die - Diseasefreddiek2004No ratings yet
- 1 Imm A What Is ImmunityDocument12 pages1 Imm A What Is ImmunityroshnayimNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOLOGYDocument26 pagesIMMUNOLOGY6r2byw6xnxNo ratings yet
- Human Health & DiseasesDocument55 pagesHuman Health & DiseasesSAGAR PADALKARNo ratings yet
- Reaction of BodDocument4 pagesReaction of BodLalit KumarNo ratings yet
- Immunesystemoffish Pptx-AutosavedDocument19 pagesImmunesystemoffish Pptx-Autosavedjaypasco79No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Immune SystemDocument13 pagesLesson 6 Immune SystemBrent PatarasNo ratings yet
- The Body's System of Defenses Against Agents That Cause DiseaseDocument9 pagesThe Body's System of Defenses Against Agents That Cause DiseasemayaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Gen Bio2 Timothy NicodemusDocument20 pagesPresentation Gen Bio2 Timothy NicodemusTim NicodemusNo ratings yet
- NCM 112: Care of Clients With Inflammatory and Immunologic Response Maricris B. Florendo/Constantino Y. Mendoza/Sandra Layne G. Luczon/Rhizza AbinsayDocument23 pagesNCM 112: Care of Clients With Inflammatory and Immunologic Response Maricris B. Florendo/Constantino Y. Mendoza/Sandra Layne G. Luczon/Rhizza AbinsayRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Defence Mechanism of The BodyDocument72 pagesDefence Mechanism of The BodyRawal Rafiq LeghariNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseaseDocument54 pagesHuman Health and DiseaseTirth TupeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Diseases & Immunity - Cecilia Benita 2Document19 pagesChapter 10 - Diseases & Immunity - Cecilia Benita 2simplyjisungNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Circulatory System in The Body's Defence MechanismDocument22 pagesThe Role of The Circulatory System in The Body's Defence MechanismSyamsamaria AzizNo ratings yet
- 1 The Immune SystemDocument25 pages1 The Immune SystemTumabangNo ratings yet
- Inflammation: InfectionDocument11 pagesInflammation: InfectionRenBautistaNo ratings yet
- The Human Immune SystemDocument24 pagesThe Human Immune Systemmilka berhaneNo ratings yet
- Defence SystemDocument33 pagesDefence Systemboneheaded9No ratings yet
- Biology - MYP 3 - 13th OctoberDocument7 pagesBiology - MYP 3 - 13th Octoberarchit.kulkarni7756No ratings yet
- The Body's System of Defenses Against Agents That Cause DiseaseDocument8 pagesThe Body's System of Defenses Against Agents That Cause Diseasemaya100% (2)
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument10 pagesIntroduction To ImmunologyArpita MishraNo ratings yet
- Communicable & Infectious DiseasesDocument3 pagesCommunicable & Infectious DiseaseshahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Immune System - Scott.k12+Document26 pagesImmune System - Scott.k12+Amit BhadhanaNo ratings yet
- Immunopharmacology - IntroductionDocument51 pagesImmunopharmacology - IntroductionIsrat Jahan Surovy 2225400672No ratings yet
- Immune System And Function, A Simple Guide And Related ConditionsFrom EverandImmune System And Function, A Simple Guide And Related ConditionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Super Immunity For Beginners: Boost Your Body's Defence, Prevent Diseases and Disorders, Live Healhier and Longer LifeFrom EverandSuper Immunity For Beginners: Boost Your Body's Defence, Prevent Diseases and Disorders, Live Healhier and Longer LifeNo ratings yet
- Barriers To InfectionDocument1 pageBarriers To InfectionLindseyNo ratings yet
- Solubility: Quantitative - by The Quantity of Solute Dissolved in The Solvent Qualitative - Terms of Approximate SolubilityDocument1 pageSolubility: Quantitative - by The Quantity of Solute Dissolved in The Solvent Qualitative - Terms of Approximate SolubilityLindseyNo ratings yet
- Pathogens - Infectious Organisms That Cause Disease - Pathogen Any Disease Causing OrganismDocument1 pagePathogens - Infectious Organisms That Cause Disease - Pathogen Any Disease Causing OrganismLindseyNo ratings yet
- The Greatest Triumph of Immunology - 1776: Edward Jenner Made The 1 Small Pox Vaccine From Vaccinia VirusDocument1 pageThe Greatest Triumph of Immunology - 1776: Edward Jenner Made The 1 Small Pox Vaccine From Vaccinia VirusLindseyNo ratings yet
- Part 6Document1 pagePart 6LindseyNo ratings yet
- Part 4Document1 pagePart 4LindseyNo ratings yet
- Pathogens From The Body.: The Immune System: The Defense Mechanism of The Body Dedicated To Eradicating DangerousDocument1 pagePathogens From The Body.: The Immune System: The Defense Mechanism of The Body Dedicated To Eradicating DangerousLindseyNo ratings yet
- Majors and Soldiers. Every Immune Cell Plays A Critical Role in The Immune SystemDocument1 pageMajors and Soldiers. Every Immune Cell Plays A Critical Role in The Immune SystemLindseyNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document1 pagePart 1LindseyNo ratings yet