Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 viewsMIS
MIS
Uploaded by
Vaibhav JainFramework of MIS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- RgoDocument17 pagesRgoGabriella Mae Magpayo ValentinNo ratings yet
- The Muppets: Peter Linz (Born June 28, 1967) Is AnDocument1 pageThe Muppets: Peter Linz (Born June 28, 1967) Is AnVaibhav JainNo ratings yet
- Use Case DiagramDocument35 pagesUse Case DiagramVaibhav Jain100% (1)
- Race Car: Need For Speed: UndergroundDocument2 pagesRace Car: Need For Speed: UndergroundVaibhav JainNo ratings yet
- Game Modes: Counter-Strike: Global Offensive Added New Weapons and Equipment Not Seen inDocument3 pagesGame Modes: Counter-Strike: Global Offensive Added New Weapons and Equipment Not Seen inVaibhav JainNo ratings yet
- International School of Asia and The PacificDocument5 pagesInternational School of Asia and The Pacificmary ann corpuzNo ratings yet
- BI206 Week1 Lab ResponsesDocument4 pagesBI206 Week1 Lab ResponsesJaelen KnollaNo ratings yet
- Globalization Debate Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesGlobalization Debate Lesson Planapi-375601641No ratings yet
- Ahmad Sherniza EssayDocument1 pageAhmad Sherniza EssaySherniza AhmadNo ratings yet
- DLL World Religion wk1Document3 pagesDLL World Religion wk1Verna Santos Garchitorena50% (2)
- Mathematics Panel MeetingDocument4 pagesMathematics Panel MeetingRahimah Amat RosmanNo ratings yet
- Wes Kline Resume 2019-2020Document2 pagesWes Kline Resume 2019-2020api-213445283No ratings yet
- Knowledge Management Concept (KPMG Case)Document14 pagesKnowledge Management Concept (KPMG Case)Hieu Dinh LeNo ratings yet
- Gerasimos Terrorism StudyDocument6 pagesGerasimos Terrorism StudyGerasimos TrakakisNo ratings yet
- Ppt-G10-Bartolome - M1.1 Use of Information From Text Read Listened ToDocument42 pagesPpt-G10-Bartolome - M1.1 Use of Information From Text Read Listened ToJohn Paul C. BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide On Article AnalysisDocument12 pagesComplete Guide On Article AnalysisRazzOzzNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of EducationDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of EducationYvetteNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 1 Learning Task 1Document19 pagesStudy Guide 1 Learning Task 1Andrenet OrlandaNo ratings yet
- Rita DeMaria - Veronica Haggerty - Briana Bogue - The Attachment-Based Focused Genogram Workbook - Expanding The Realms of Attachment Theory-Routledge (2019) PDFDocument176 pagesRita DeMaria - Veronica Haggerty - Briana Bogue - The Attachment-Based Focused Genogram Workbook - Expanding The Realms of Attachment Theory-Routledge (2019) PDFAndrew Connor100% (7)
- Virtual Internship - 2020 PDFDocument3 pagesVirtual Internship - 2020 PDFMAYANK KANHAIYALAL JAISWALNo ratings yet
- ADUSEI OWUSU MEd TR01 03 PDFDocument185 pagesADUSEI OWUSU MEd TR01 03 PDFseptian_bbyNo ratings yet
- Child Support Worker Cover LetterDocument4 pagesChild Support Worker Cover Letterkylopuluwob2100% (2)
- HR Management Strategy and PerformanceDocument19 pagesHR Management Strategy and Performanceihab awwadNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 4 - Q2 - W6Document3 pagesDLL - Mathematics 4 - Q2 - W6Moharah JaneNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Leadership and Followership 2022 - PDF FriendlyDocument24 pagesWeek 5 - Leadership and Followership 2022 - PDF FriendlyKimberly Antonella Perez RoncalNo ratings yet
- SLSA Draft Program 2022Document19 pagesSLSA Draft Program 2022Mickey ValleeNo ratings yet
- Welcome To 1119: Mohamad Razif Bin DisaDocument23 pagesWelcome To 1119: Mohamad Razif Bin DisaTiramisu PutihNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Q3 COTDocument6 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics V Q3 COTBRENDA SUBAANNo ratings yet
- Mother Tongue-Based Multilingual Educati PDFDocument75 pagesMother Tongue-Based Multilingual Educati PDFMerlyn Thoennette Etoc ArevaloNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument4 pagesScriptPrincess Fatima De JuanNo ratings yet
- Zhang 2023 ArxivDocument11 pagesZhang 2023 ArxivYan AecNo ratings yet
- Proforma For Call For Book ChaptersDocument2 pagesProforma For Call For Book Chaptersnitin jainNo ratings yet
- Oracle Fusion Talent ManagementDocument25 pagesOracle Fusion Talent ManagementmadhulikaNo ratings yet
- A Naturalistic Model of in Service Education and Training PDFDocument13 pagesA Naturalistic Model of in Service Education and Training PDFAlexandra PodoleanuNo ratings yet
MIS
MIS
Uploaded by
Vaibhav Jain0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesFramework of MIS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFramework of MIS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesMIS
MIS
Uploaded by
Vaibhav JainFramework of MIS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Framework of MIS
In order to understand the importance of MIS one must understand
and appreciate the role that MIS plays in an organization. An
organization may be conceived in a lot of ways. One can visualize an
organization as a balance sheet or a function of financial
statements, i.e., as a financial entity or as an organization chart
delineating the decision-making hierarchy levels and formal
communication channels. While both views are correct, the latter
view is more appropriate for understanding an organization's MIS.
Anthony in his seminal work elaborated (R.A. Anthony 1965) on this
view of an organization as its hierarchy of decision-making. He
focused on the managerial aspects of an organization and classified
the management process into three distinct levels.
Strategic Planning
This requires focusing on the objectives and goals of the
organization, on changes in the objectives, on the resource
requirements to fulfill the objectives and on the guiding principles
and policies that will govern the acquisition, use and disposal of
resources to attain the objectives. In short, this role is the most
important role in the management hierarchy and the decisions taken
by managers in this role have a far-reaching impact on the
organization. Managers in this role set the direction in which the
organization will travel. In terms of hierarchy, this lies at the top.
Managerial Control
This requires that resources are acquired and used effectively and
efficiently to attain the objectives of the organization. This is a
middle management role. Managers in this role take guidance from
the strategic planning hierarchy and control the activities of the
organization such that the goals set by the higher level are attained
in an efficient and effective manner. The impact of the decisions of
the managers in this role is medium term and degree.
Operational Control
This requires that directives as set by the immediate higher
hierarchy is followed and that specific task/s are carried out
effectively and efficiently. The decisions at this level have very little
impact on the organization. The organization behaves in a routine
nature where the parameters of the decision-making process are
well laid and certain.
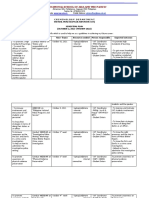
As is clear, it is a three-level pyramid with very distinct levels. Each
level has its own set of tasks and decisions to take which have a
varying impact on the organization as a whole.
Organizations
Management
Function
Planning
Strategic
Planning
Long-range,
high impact
Management
Levels
in
Management
Control
Operational
Control
Medium range, Short range,
medium
impact
low
impact
Organizing
Staffing
Directing
General
framework
Key
people
Departmental
level
Small unit level
senior Medium
level, Operational level
tactical level
General
long range
and Tactics
Routine activities
directives
Controlling
Aggregate level
Periodic control Regular
and
continuous
controlling
exceptions
and
supervision
For example, if we want to classify the decisions of a manufacturing
firm, the strategic planning will encompass the annual production
planning, annual budgeting, setting up of new plants and/or
installation of new machinery to upgrade the production process and
other such activities. Management control activities would include
monthly production planning, maintenance planning and scheduling.
Operational control on the other will deal with routine daily tasks of
managing and supervising shifts to exercise control over the process
so that the monthly plans and schedules as made by the
management control level managers are met.
Operational Control
concerned with carrying out the tasks necessary and that need
to be performed
lower level of the organizational hierarchy
performed by supervisors of small work units
Management Control
concerned with the utilization and management of resources to
achieve organizational objectives.
concerned with effective and efficient performance.
performed by middle managers
Strategic Planning
focuses on decisions on the objectives for the organization as a
whole and also on the way to achieving them
typically involves a small number of high level people
carried out by top corporate executives and corporate boards
responsible for setting and monitoring long-term directions for
the organization three or more years into the future
Target audience
The target audience for the management information system would
be:
Schools - This is because they use SIMS.
NHS - This is because they need to keep track on records.
Businesses - This is so they can make secure decisions and keep
track on how they are doing.
Supermarkets - This is so they can keep track on how many
products are sold in one day.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- RgoDocument17 pagesRgoGabriella Mae Magpayo ValentinNo ratings yet
- The Muppets: Peter Linz (Born June 28, 1967) Is AnDocument1 pageThe Muppets: Peter Linz (Born June 28, 1967) Is AnVaibhav JainNo ratings yet
- Use Case DiagramDocument35 pagesUse Case DiagramVaibhav Jain100% (1)
- Race Car: Need For Speed: UndergroundDocument2 pagesRace Car: Need For Speed: UndergroundVaibhav JainNo ratings yet
- Game Modes: Counter-Strike: Global Offensive Added New Weapons and Equipment Not Seen inDocument3 pagesGame Modes: Counter-Strike: Global Offensive Added New Weapons and Equipment Not Seen inVaibhav JainNo ratings yet
- International School of Asia and The PacificDocument5 pagesInternational School of Asia and The Pacificmary ann corpuzNo ratings yet
- BI206 Week1 Lab ResponsesDocument4 pagesBI206 Week1 Lab ResponsesJaelen KnollaNo ratings yet
- Globalization Debate Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesGlobalization Debate Lesson Planapi-375601641No ratings yet
- Ahmad Sherniza EssayDocument1 pageAhmad Sherniza EssaySherniza AhmadNo ratings yet
- DLL World Religion wk1Document3 pagesDLL World Religion wk1Verna Santos Garchitorena50% (2)
- Mathematics Panel MeetingDocument4 pagesMathematics Panel MeetingRahimah Amat RosmanNo ratings yet
- Wes Kline Resume 2019-2020Document2 pagesWes Kline Resume 2019-2020api-213445283No ratings yet
- Knowledge Management Concept (KPMG Case)Document14 pagesKnowledge Management Concept (KPMG Case)Hieu Dinh LeNo ratings yet
- Gerasimos Terrorism StudyDocument6 pagesGerasimos Terrorism StudyGerasimos TrakakisNo ratings yet
- Ppt-G10-Bartolome - M1.1 Use of Information From Text Read Listened ToDocument42 pagesPpt-G10-Bartolome - M1.1 Use of Information From Text Read Listened ToJohn Paul C. BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide On Article AnalysisDocument12 pagesComplete Guide On Article AnalysisRazzOzzNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of EducationDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of EducationYvetteNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 1 Learning Task 1Document19 pagesStudy Guide 1 Learning Task 1Andrenet OrlandaNo ratings yet
- Rita DeMaria - Veronica Haggerty - Briana Bogue - The Attachment-Based Focused Genogram Workbook - Expanding The Realms of Attachment Theory-Routledge (2019) PDFDocument176 pagesRita DeMaria - Veronica Haggerty - Briana Bogue - The Attachment-Based Focused Genogram Workbook - Expanding The Realms of Attachment Theory-Routledge (2019) PDFAndrew Connor100% (7)
- Virtual Internship - 2020 PDFDocument3 pagesVirtual Internship - 2020 PDFMAYANK KANHAIYALAL JAISWALNo ratings yet
- ADUSEI OWUSU MEd TR01 03 PDFDocument185 pagesADUSEI OWUSU MEd TR01 03 PDFseptian_bbyNo ratings yet
- Child Support Worker Cover LetterDocument4 pagesChild Support Worker Cover Letterkylopuluwob2100% (2)
- HR Management Strategy and PerformanceDocument19 pagesHR Management Strategy and Performanceihab awwadNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 4 - Q2 - W6Document3 pagesDLL - Mathematics 4 - Q2 - W6Moharah JaneNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Leadership and Followership 2022 - PDF FriendlyDocument24 pagesWeek 5 - Leadership and Followership 2022 - PDF FriendlyKimberly Antonella Perez RoncalNo ratings yet
- SLSA Draft Program 2022Document19 pagesSLSA Draft Program 2022Mickey ValleeNo ratings yet
- Welcome To 1119: Mohamad Razif Bin DisaDocument23 pagesWelcome To 1119: Mohamad Razif Bin DisaTiramisu PutihNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Q3 COTDocument6 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics V Q3 COTBRENDA SUBAANNo ratings yet
- Mother Tongue-Based Multilingual Educati PDFDocument75 pagesMother Tongue-Based Multilingual Educati PDFMerlyn Thoennette Etoc ArevaloNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument4 pagesScriptPrincess Fatima De JuanNo ratings yet
- Zhang 2023 ArxivDocument11 pagesZhang 2023 ArxivYan AecNo ratings yet
- Proforma For Call For Book ChaptersDocument2 pagesProforma For Call For Book Chaptersnitin jainNo ratings yet
- Oracle Fusion Talent ManagementDocument25 pagesOracle Fusion Talent ManagementmadhulikaNo ratings yet
- A Naturalistic Model of in Service Education and Training PDFDocument13 pagesA Naturalistic Model of in Service Education and Training PDFAlexandra PodoleanuNo ratings yet