Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Risk Infection
NCP Risk Infection
Uploaded by
Eni Rahmawati0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
89 views1 pageThe document outlines nursing interventions to minimize the risk of infection for an immunosuppressed child. It lists assessing the child every 2-4 hours for signs of infection, enforcing strict handwashing and infection control measures, and following immunization recommendations for immunosuppressed children. The rationales explain that frequent monitoring is needed since fever may be the only infection sign, pneumonia is a common infection, controlling the environment prevents spread of infection, and rest periods help the child regain energy.
Original Description:
ncp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines nursing interventions to minimize the risk of infection for an immunosuppressed child. It lists assessing the child every 2-4 hours for signs of infection, enforcing strict handwashing and infection control measures, and following immunization recommendations for immunosuppressed children. The rationales explain that frequent monitoring is needed since fever may be the only infection sign, pneumonia is a common infection, controlling the environment prevents spread of infection, and rest periods help the child regain energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
89 views1 pageNCP Risk Infection
NCP Risk Infection
Uploaded by
Eni RahmawatiThe document outlines nursing interventions to minimize the risk of infection for an immunosuppressed child. It lists assessing the child every 2-4 hours for signs of infection, enforcing strict handwashing and infection control measures, and following immunization recommendations for immunosuppressed children. The rationales explain that frequent monitoring is needed since fever may be the only infection sign, pneumonia is a common infection, controlling the environment prevents spread of infection, and rest periods help the child regain energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
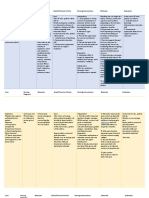
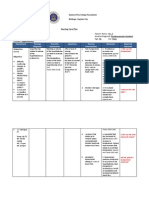
ASUHAN KEPERAWATAN
TUJUAN
INTERVENSI
RASIONAL
1. RISK FOR INFECTION RELATED TO IMMUNOSUPPRESSION
NIC Priority Intervention: Infection
Control: minimizing the acquisition
and transmission of infectious agents
Risk factor for infection
will be eliminated as
evidenced by infection
control
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Assess the child every 2-4 hour for fever;lesions in
the mouth;rednes;inflammation;soreness;and
lesions on the skin or around intravenous lines
Auscultate for changes in breath sounds every 2
hours. Perform pulmonary toilet (coughing, deep
breathing, incentive spirometry) every 24 hours.
Enforce strict handwashing. Allow no fresh
flowers, fruits, or vegetables in childs room.
Screen visitors for colds or recent exposure to
varicella. Use blood and body fluid precautions
(refer to the Skills Manual). Practice strict asepsis
for dressing changes and suctioning
Coordinate patient care assignments to avoid
exposing the child to individuals with recent
infections or immunizations
Organize patient care activities to allow for
adequate period of rest
Follow recommendations of CDC and AAP for
immunizing immunosuppressed children. Avoid
live oral polio virus vaccine and live varcella
vaccine. Perform annual TB testing.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Fever is one of the few signs of
infections in the immunoappressed
child who does not have o sufficient
number of white blood child
Pneumonia is a likely infection in
the child with AIDS
Control of environmental factors
helps prevent infection.
Planning minimizes chances for
infection.
Rest periods allow the child to
regain energy.
Special recommendations consider
the childs decreased immune
response and the danger of acquiring
disease from certain live virus
vaccines.
You might also like
- RLEFand ECSDocument3 pagesRLEFand ECSPaul JacksonNo ratings yet
- Ppe4 Reflection AssignmentDocument11 pagesPpe4 Reflection Assignmentapi-318846856100% (1)
- Case 3 Care of Client With GI, PUD, Cancer, Liver FailureDocument33 pagesCase 3 Care of Client With GI, PUD, Cancer, Liver FailureNyeam NyeamNo ratings yet
- Case CHFDocument10 pagesCase CHFAgnes Erlita Distriani Patade50% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- I.intrODUCTION Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) Is ADocument19 pagesI.intrODUCTION Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) Is Aoril04No ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAndrea Francesca SantosNo ratings yet
- Risk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPPaula AbadNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 Gerontology - WeeK 1Document38 pagesNCM 114 Gerontology - WeeK 1Jmarie Brillantes Popioco0% (1)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPErica Denice CastilloNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument17 pagesRevisionMatt RenaudNo ratings yet
- Primaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)Document2 pagesPrimaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)ENo ratings yet
- HookwormDocument4 pagesHookwormJonalyn ChewacheoNo ratings yet
- A Client With Cushing's Syndrome: Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageA Client With Cushing's Syndrome: Nursing Care PlanJulius Caesar ColladoNo ratings yet
- PeritonitisDocument6 pagesPeritonitisDiane ArgoteNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia and Risk For AspirationDocument3 pagesHyperthermia and Risk For AspirationAlmyr RimandoNo ratings yet
- Steps RationaleDocument3 pagesSteps RationaleKangMunching PotatoGamingNo ratings yet
- Spinal Anes Drug StudyDocument12 pagesSpinal Anes Drug StudyNicosia Mae FerrerNo ratings yet
- Mu CostaDocument6 pagesMu Costafarracholidia_867630No ratings yet
- Impaired Physical Mobility R/T Neuromuscular ImpairmentDocument3 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility R/T Neuromuscular ImpairmentjisooNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan Post SeizureDocument2 pagesDischarge Plan Post SeizureVecky TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Copd - NCPDocument6 pagesCopd - NCPMonique Sacherow BacherNo ratings yet
- Kabiven: (Amino Acids, Electrolytes, Dextrose and Lipid Injectable Emulsion), For Intravenous UseDocument24 pagesKabiven: (Amino Acids, Electrolytes, Dextrose and Lipid Injectable Emulsion), For Intravenous UseDivine Mercy De JulianNo ratings yet
- Bacillary DysenteryDocument32 pagesBacillary Dysenteryapi-199163990% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- HydroxyzineDocument4 pagesHydroxyzineGeorge Smith AbeledaNo ratings yet
- PYOMYOSITISDocument6 pagesPYOMYOSITISChristine CoridoNo ratings yet
- NCP CvaDocument4 pagesNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance NCPDocument1 pageIneffective Airway Clearance NCPBenz ParCoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studypopoyoio100% (2)
- 01 NGT Procedure With RationaleDocument4 pages01 NGT Procedure With RationaleAryaj SulitNo ratings yet
- Levemir Product Insert PDFDocument11 pagesLevemir Product Insert PDFDegee O. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: Tetanus DateDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: Tetanus DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Renal Fabs RefDocument61 pagesRenal Fabs RefREBECCANo ratings yet
- Problem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Document10 pagesProblem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Raidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- NCP For AsthmaDocument2 pagesNCP For AsthmawaadNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients in Emergency Situation 2Document108 pagesNursing Care of Clients in Emergency Situation 2Mary Joy FrancoNo ratings yet
- Tonsilitis NCPDocument2 pagesTonsilitis NCPFATIMA MARYAMA USMANNo ratings yet
- Tamsulosin - Drug Information - UpToDateDocument23 pagesTamsulosin - Drug Information - UpToDateGénesis GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PDFDocument7 pagesDrug Study PDFMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- RABIES Health Teaching BSN1DDocument24 pagesRABIES Health Teaching BSN1DTheother OneNo ratings yet
- Im Case Study 04Document49 pagesIm Case Study 04Shaine BalverdeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- NCP RiskDocument2 pagesNCP RiskNura ZeinNo ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- MoxifloxacinDocument16 pagesMoxifloxacinTiaraNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument3 pagesNursing DiagnosislesternNo ratings yet
- Dela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Document2 pagesDela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Atsu MiyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionTammy De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- BerodualDocument1 pageBerodualAelysa PabloNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 CabalunaDocument7 pagesNCP 2 CabalunaIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- SAS - Session-24-Research 1Document5 pagesSAS - Session-24-Research 1ella retizaNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Module 13 - Common Childhood Illnesses - UpdatedDocument32 pagesModule 13 - Common Childhood Illnesses - UpdatedDIANA ACHEAMPONGNo ratings yet
- Cough and Dyspnea Case StudyDocument4 pagesCough and Dyspnea Case StudyAbigail Balbuena100% (1)
- Group2 Diagnostic Laboratory TestDocument16 pagesGroup2 Diagnostic Laboratory TestKristle Anne Federigan - LacanlaleNo ratings yet
- Fon ModelDocument6 pagesFon ModelEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Hearing Loss Genetics II WebDocument32 pagesHearing Loss Genetics II WebEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Role of Massage Therapy On Reduction of Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia in Term and Preterm Neonates: A Review of Clinical TrialsDocument10 pagesRole of Massage Therapy On Reduction of Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia in Term and Preterm Neonates: A Review of Clinical TrialsEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Late Adulthood Cognitive Physical DevelopmentDocument51 pagesLate Adulthood Cognitive Physical DevelopmentEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & Physiology: Chris DarwinDocument24 pagesHearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & Physiology: Chris DarwinEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- NIC Velue and Belief? Prevalensi Kanker RiskesdaDocument1 pageNIC Velue and Belief? Prevalensi Kanker RiskesdaEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- BBLRDocument9 pagesBBLREni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- 10things About HearingDocument20 pages10things About HearingEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: General Medical Officer (GMO) Manual: Clinical SectionDocument3 pagesPneumonia: General Medical Officer (GMO) Manual: Clinical SectionEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Asking A Good QuestionDocument5 pagesAsking A Good QuestionEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- 1.3 FormDocument1 page1.3 FormEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Asking A Good QuestionDocument5 pagesAsking A Good QuestionEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Ads SetahunDocument1 pageJadwal Ads SetahunEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet