Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quiz 3: 1 2 Crit
Quiz 3: 1 2 Crit
Uploaded by
cab0oseOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quiz 3: 1 2 Crit
Quiz 3: 1 2 Crit
Uploaded by
cab0oseCopyright:
Available Formats
Quiz 3
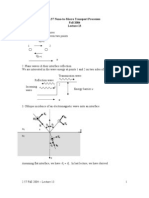
Q1. Total internal reflection
In lectures, we saw that total reflection of EM waves occurs at the boundary between two dielectrics for the case of
grazing incidence. Similarly, total internal reflection can occur for EM waves in a dielectric surrounded by a medium
with a lower refractive index (i.e. n1 > n2 ). In this case, there is a critical incidence angle crit above which the
transmission angle becomes imaginary and EM waves will be completely reflected.
(a) Write down an expression for crit and calculate its value for the following two cases: 1. n1 = 1.6, n2 = 1.5 (typical
refractive indices for the core and cladding of optical fibres); 2. n1 = 2.6 and n2 = 1 (diamond surrounded by air).
Answer crit = sin 1 (n2 /n1 ).
crit = 69.6 (or 1.22 radians) for optical fibre.
crit = 22.6 (or 0.395 radians) for diamond.
(b) Assuming a standard monochromatic complex plane wave solution for the transmitted wave of the form
T = E0T exp i
E
where
= kT r
!t +
explain in your own words why no transmitted wave can penetrate medium 2. (Hint: assume the plane of incidence
is the x z plane and consider the phase of the complex wavefunction.)
T is attenuated in the z-direction and is directed parallel to the interface,
Answer By Snells law, cos T is imaginary, so E
in the x-direction. Thus, no EM wave can penetrate into medium 2 and no energy is propagated there (this is an
evanescent wave).
Q2. Gauge transformations
Which of the following potentials are in the Coulomb gauge, the Lorenz gauge, both or neither:
(a)
V =0
A(x, t) =
(0 k/4c)(ct
0
|x|)2 z
,
,
Answer dV /dt = 0, r A = 0 =) BOTH
(b)
V =0
Answer dV /dt = 0, r A =
(qt/0 ) 3 (r) 6=
A(r, t) =
1 qt
r
40 r2
0 0 dV /dt =) NEITHER
(c)
V =0
Answer dV /dt = 0, r A = 0 =) BOTH
A(x, t) = A0 sin(kx
!t)
y
|x| < ct
|x| > ct
You might also like
- Dielectric WaveguideDocument9 pagesDielectric Waveguide曾令睿No ratings yet
- Problem3 Slab WaveguideDocument3 pagesProblem3 Slab WaveguideMijael StNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document9 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ae Be CeDocument7 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ae Be CecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Optical Waveguides Write-UpDocument7 pagesOptical Waveguides Write-UpgowdamandaviNo ratings yet
- Waves in Media: Ashcroft and Mermin, Solid State Physics (Saunders College, 1976, Page 553)Document42 pagesWaves in Media: Ashcroft and Mermin, Solid State Physics (Saunders College, 1976, Page 553)Amina lbrahimNo ratings yet
- 1 Bragg Scattering in A Periodic Medium: 1.138J/2.062J/18.376J, WAVE PROPAGATIONDocument15 pages1 Bragg Scattering in A Periodic Medium: 1.138J/2.062J/18.376J, WAVE PROPAGATIONwenceslaoflorezNo ratings yet
- Optical Waveguide TheoryDocument17 pagesOptical Waveguide Theory23213mNo ratings yet
- Optical FibreDocument19 pagesOptical FibreAbdul Qadir Mohamed AbdiNo ratings yet
- CH 13Document19 pagesCH 13Eufemio MorenoNo ratings yet
- Optics of Metals - PlasmonsDocument18 pagesOptics of Metals - PlasmonsyvvictorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Quantum & Atomic StructureDocument41 pagesLecture 1 - Quantum & Atomic Structurejasumin91No ratings yet
- Wave EquationDocument14 pagesWave EquationbigouzypolNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document60 pagesCH 7Paul ArcillaNo ratings yet
- J. R. Herring Et Al - Statistical and Dynamical Questions in Strati Ed TurbulenceDocument23 pagesJ. R. Herring Et Al - Statistical and Dynamical Questions in Strati Ed TurbulenceWhiteLighteNo ratings yet
- Topic 10.quantumDocument34 pagesTopic 10.quantumNOR AZAM BIN ENDOT / FSNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Tunneling & Harmonic OscillatorDocument33 pagesQuantum Mechanics Tunneling & Harmonic Oscillatorvivek patelNo ratings yet
- TUPMN038Document3 pagesTUPMN038Particle Beam Physics LabNo ratings yet
- 2023 Fall Optics (I) Homework #2, Due 10/26: 0 R I R 0 I 0 - 1Document1 page2023 Fall Optics (I) Homework #2, Due 10/26: 0 R I R 0 I 0 - 1藍博懷No ratings yet
- 604 BookDocument82 pages604 BooknewzadNo ratings yet
- Free VibrationDocument5 pagesFree VibrationLokesh DandgavalNo ratings yet
- P2214 Homework 14 Solutions - Spring 2011Document7 pagesP2214 Homework 14 Solutions - Spring 2011calcyeeNo ratings yet
- MIT OCW Wave Propagation Lecture Part 5Document22 pagesMIT OCW Wave Propagation Lecture Part 5Mohan NayakaNo ratings yet
- ELEC06I03 AnexDocument36 pagesELEC06I03 Anexangel_hunNo ratings yet
- Solution - Assignment 1 PoolDocument7 pagesSolution - Assignment 1 Poolf20230405No ratings yet
- EM Waves in Material Media: 1 Wave PropagationDocument8 pagesEM Waves in Material Media: 1 Wave PropagationDinesh RamuNo ratings yet
- HW 7Document6 pagesHW 7Diana UrizaNo ratings yet
- PCV - Ch1Document27 pagesPCV - Ch1Yathin gowda 8971095275No ratings yet
- Electron-Phonon Interaction: 2.1 Phonons and Lattice DynamicsDocument14 pagesElectron-Phonon Interaction: 2.1 Phonons and Lattice DynamicsYeong Gyu KimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 24 Oblique Incidence On DielectricsDocument19 pagesLecture 24 Oblique Incidence On Dielectricsvaldesc_tolNo ratings yet
- Classical Electromagnetism and OpticsDocument159 pagesClassical Electromagnetism and OpticsRodrigo PaludoNo ratings yet
- Phys511 PS06Document5 pagesPhys511 PS06Mac LNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: E HN MDocument10 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: E HN McaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Lecture 08 - Reflection and Transmission of WavesDocument38 pagesLecture 08 - Reflection and Transmission of WavesJitendraBehera50% (2)
- Physical Optics Lecture MaterialsDocument22 pagesPhysical Optics Lecture Materialsaryan kumarNo ratings yet
- Atoms: Testing Quantum Coherence in Stochastic Electrodynamics With Squeezed Schrödinger Cat StatesDocument9 pagesAtoms: Testing Quantum Coherence in Stochastic Electrodynamics With Squeezed Schrödinger Cat StatesSimon SavittNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations and Light WavesDocument24 pagesMaxwell's Equations and Light WavesFarizalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument72 pagesLecture 2 Electronic Structure of AtomsKEMPNo ratings yet
- Classical & Quantum Harmonic OscillatorsDocument4 pagesClassical & Quantum Harmonic OscillatorsFredrick MutungaNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of The Equation Sheet Interference & DiffractionDocument6 pagesMaking Sense of The Equation Sheet Interference & DiffractionAkash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Determination of Wave Length of Laser Radiation by Interference. Jung MethodDocument12 pagesDetermination of Wave Length of Laser Radiation by Interference. Jung MethodMəhəmmədəliNo ratings yet
- Formulas Optica Ondulatoria (By Carrascal)Document9 pagesFormulas Optica Ondulatoria (By Carrascal)Iñaki0% (1)
- Física Moderna e Óptica - QualifyingDocument128 pagesFísica Moderna e Óptica - QualifyingDaniel PaixãoNo ratings yet
- Modern and Nonlinear OpticsDocument181 pagesModern and Nonlinear Opticssoma_venuNo ratings yet
- Emission and Absorption of Light Shape of The Emission BandDocument17 pagesEmission and Absorption of Light Shape of The Emission BandSemakalu AntonioNo ratings yet
- Surface Plasmon Resonance in A Thin Metal Film: 1 BackgroundDocument10 pagesSurface Plasmon Resonance in A Thin Metal Film: 1 BackgroundPoonam Pratap KadamNo ratings yet
- EC 232 Tutorial 2Document3 pagesEC 232 Tutorial 2RUSHIL MOTWANINo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: I T KXDocument8 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: I T KXcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Part 1Document23 pagesChapter 2 Part 1tariku fkaduNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document8 pagesLecture 14captainhassNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and Quantum MechanicsDocument28 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Quantum MechanicsHardeepSinghNo ratings yet
- Tesla Scalar WavesDocument9 pagesTesla Scalar WavesMike D.100% (2)
- Lecture21 Electromagnetic WavesDocument39 pagesLecture21 Electromagnetic WavesTaqi ShahNo ratings yet
- MIT2 57S12 Lec Notes 2004 PDFDocument177 pagesMIT2 57S12 Lec Notes 2004 PDFGerman ToledoNo ratings yet
- Rosenzweig 1998 0154Document19 pagesRosenzweig 1998 0154Particle Beam Physics LabNo ratings yet
- Wopho Problems PDFDocument17 pagesWopho Problems PDFIonel ChiosaNo ratings yet
- Advances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenFrom EverandAdvances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenR. BrillNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- CarbonationDocument79 pagesCarbonationAzeem Abbas100% (1)
- Chroma Notes 2Document8 pagesChroma Notes 2Marielle GuevaraNo ratings yet
- MSY GT Aircon BrochureDocument2 pagesMSY GT Aircon BrochureMichael AngeloNo ratings yet
- Fw001-Olive Facial WashDocument1 pageFw001-Olive Facial WashSanggari MogarajaNo ratings yet
- Dewi Kurnia 60400118035 - Jurnal JFT Difraksi LaserDocument9 pagesDewi Kurnia 60400118035 - Jurnal JFT Difraksi LaserDewi KurniaNo ratings yet
- DPP-01 Chemical KineticsDocument1 pageDPP-01 Chemical Kineticsprathmfed100% (1)
- CPM3700 Acid Gas Removal PlantsDocument32 pagesCPM3700 Acid Gas Removal PlantsFawaz AlsaifNo ratings yet
- 03 - Nozzle Thermodynamics and Isentropic Relations v1Document37 pages03 - Nozzle Thermodynamics and Isentropic Relations v1Ervin IsabellaNo ratings yet
- Paramagnetism Spin One HalfDocument42 pagesParamagnetism Spin One Halfpesta0% (1)
- Previous Hse Questions and Answers of The Chapter "Hydrocarbons"Document10 pagesPrevious Hse Questions and Answers of The Chapter "Hydrocarbons"Muhammed SadiqNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Water Wetting in Oil Water Two Phase Flow - JCaiDocument11 pagesExperimental Study of Water Wetting in Oil Water Two Phase Flow - JCaiSyafiqah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Brittle Vs Sloughing ShaleDocument9 pagesBrittle Vs Sloughing ShaleJoseph BimoNo ratings yet
- Science Fair ProjectDocument5 pagesScience Fair Project•Ale Garcia•No ratings yet
- Lelm108 Pages 8Document1 pageLelm108 Pages 8ABCNo ratings yet
- Polymer Testing: W. Stark, M. JaunichDocument7 pagesPolymer Testing: W. Stark, M. JaunichJohnSmithNo ratings yet
- Enve 208 Experiment 2.1 SonDocument10 pagesEnve 208 Experiment 2.1 Sonmihrican302No ratings yet
- OTC-26068-MS Wettability Alteration of Heavy-Oil/Bitumen Containing Carbonates Using Solvents, High PH Solutions and Nano/Ionic LiquidsDocument18 pagesOTC-26068-MS Wettability Alteration of Heavy-Oil/Bitumen Containing Carbonates Using Solvents, High PH Solutions and Nano/Ionic Liquidsjose floresNo ratings yet
- Final Jee-Main Examination - July, 2022: Chemistry Test Paper With SolutionDocument6 pagesFinal Jee-Main Examination - July, 2022: Chemistry Test Paper With SolutionYogy YNo ratings yet
- Chemicals Zetag DATA Powder Zetag 7650 - 0410Document2 pagesChemicals Zetag DATA Powder Zetag 7650 - 0410PromagEnviro.comNo ratings yet
- New Correlation Equationsfor Finned Tube HeatexchangersDocument12 pagesNew Correlation Equationsfor Finned Tube HeatexchangerssergioteroNo ratings yet
- 9 - PH WorksheetDocument2 pages9 - PH WorksheetAntoneaNo ratings yet
- Chapt2 PDFDocument4 pagesChapt2 PDFDrjasmeet KaurNo ratings yet
- HPLC 2015Document102 pagesHPLC 2015Ojan FauzanNo ratings yet
- Transport Fall 2021 PS 2 2Document9 pagesTransport Fall 2021 PS 2 2Jocelyn Grisel García GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Colgate-Emery ProcessDocument6 pagesColgate-Emery ProcessEvans Azka FNo ratings yet
- 560-Article Text-1223-2-10-20211220Document16 pages560-Article Text-1223-2-10-20211220jenan h.albayatiiNo ratings yet
- Electrospun Nanofiber - Emerging Reinforcing Filler in Polymer MatrixDocument35 pagesElectrospun Nanofiber - Emerging Reinforcing Filler in Polymer MatrixsaadnaumanNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument5 pagesPhotoelectric EffectUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- FlowDocument150 pagesFlowMohamed KilanyNo ratings yet
- Lecture on Cavitation: Npsh = p γ v − p γDocument16 pagesLecture on Cavitation: Npsh = p γ v − p γAriel Gamboa100% (1)