Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aminoglycoside and Vancomycin Pharmacokinetics and Dosing Calculations
Aminoglycoside and Vancomycin Pharmacokinetics and Dosing Calculations
Uploaded by
Duy-Anh DangCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aminoglycoside and Vancomycin Pharmacokinetics and Dosing Calculations
Aminoglycoside and Vancomycin Pharmacokinetics and Dosing Calculations
Uploaded by
Duy-Anh DangCopyright:
Available Formats
CALCULATION OF AMINOGLYCOSIDE DOSE
1. Revise K and T :
1. Calculate CLcr and Aminoglycoside CL
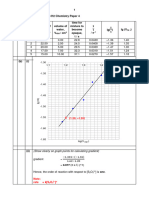
C1
C2
K=
T
ln
CLAMG(L/hr) = CLcr(ml/min) (0.06)
rd
2. Estimate Vd; (account for obesity, 3 spaced fluid)
Normal Vd(L/Kg)
Obese (>130% IBW)
Fluid overload
AMINOGLYCOSIDE REVISIONS
= 0.25 L/Kg x Wt (kg)
= 0.25 (IBW) + 0.1 (TBW IBW)
= 0.25 (Dry weight) + 1 (kg wt gain)
3. Calculate elimination rate constant (Kel) and half-life (T )
T =
0.693
K
2. Determine Model
If 6 (tin) T then use BOLUS MODEL
If 6 (tin) > T then use INFUSION MODEL
3. Revise Vd and CL
CL
Kel =
Vd
0.693 (Vd )
T =
CL
Bolus Model
Dose
C1
e kt
Vd =
1 e K
4. Choose dosing model: bolus vs. short infusion
If 6 (tin) T then use BOLUS MODEL
If 6 (tin) > T then use INFUSION MODEL
Short Infusion Model
5. Select appropriate dosing interval () (usually 4-5 T s)
(12, 24, 48) In-vivo PAE ~ 10 hours
(Craig WA, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother 1991;27(SupplC):29-40)
6. Calculate Daily Dose based on AUC target (70-100 mg h/L)
Barclay M, et al. Aust NZ J Med 1995;25:230-5
Dose (mg/24 hrs) = 70 100 (CL); [Amikacin ~ 3x higher]
Dose
C t = Vd K e Kt
1 e
t = Time from start of dose
Trough = Peak e k t
Vd =
CL
K
4. Select appropriate dosing interval () (usually 4-5 T s)
5. Calculate Daily Dose based on AUC target (70-100 mg h/L)
6. Calculate expected peak and trough concentrations
Short Infusion Model
Dose / tin
1 e K ( tin )
C1
e Kt
CL =
K
1 e
Dose (mg/24 hrs) = 70 100 (CL); [Amikacin ~ 3x higher]
7. Calculate expected peak and trough concentrations
Bolus Model
CL = (K)(Vd)
Dose / tin
1 e K (tin )
CL
Ct =
e Kt
k
1 e
t = time from end of infusion
Bolus Model
Dose
C t = Vd K e Kt
1 e
t = Time from start of dose
Trough = Peak e k t
Short Infusion Model
Dose / tin
1 e K (tin )
CL
e Kt
Ct =
k
1 e
t = time from end of infusion
CALCULATION OF VANCOMYCIN DOSE
1. Calculate CLcr and Vancomycin CL
VANCOMYCIN REVISIONS
1. Revise K, T
CLVAN(L/hr) = CLcr(ml/min) (0.06)
2. Estimate Vd
= 0.7 (L/kg) * TBW (Kg)
Normal Vd(L) = 0.17 (Age) + 0.22 (TBW)
3. Calculate elimination rate constant (Kel) and half-life (T )
Kel =
CL
Vd
T =
0.693 (Vd )
CL
4. Select appropriate dosing interval () (usually 1-2 T s)
(12, 24, 48, etc.)
5. Calculate Dose to achieve target trough (5-20 mg/L)
Rybak MJ, et al. Pharmacotherapy 1999;19:257-66
Trough (1 e k )(V )
Dose =
e k
6. Confirm trough concentration if dose rounded
Dose
Trough = Vd K e K
1 e
K=
Dose
+ Trough
Vd
ln
Trough
T =
0.693
K
CL = K [0.17 (Age) + 0.22 (TBW) + 15]
2. Select appropriate dosing interval () (usually 1-2 T s)
(12, 24, 48, etc.)
3. Calculate Dose to achieve target trough (5-20 mg/L)
Trough (1 e k )(V )
Dose =
e k
4. Confirm trough concentration if dose rounded
Dose
Trough = Vd K e K
1 e
You might also like
- Unit 2 HandoutDocument8 pagesUnit 2 HandoutAisha ShahidNo ratings yet
- 12D8Document2 pages12D8Sorrawit Tantipalakul0% (2)
- ChemLec - Module 4.1 - 4.3Document23 pagesChemLec - Module 4.1 - 4.3Jerick JasperNo ratings yet
- Note 6 - Multicomponent DistillationDocument32 pagesNote 6 - Multicomponent DistillationKaleeshNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mata Kuliah Konversi Massa BiologiDocument10 pagesTugas Mata Kuliah Konversi Massa Biologianita pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Isotonic SolutionsDocument33 pagesIsotonic SolutionsChristine Annmarie TapawanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Vitamin CDocument2 pagesDetermination of Vitamin CWalwin HareNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis of Tert-Butyl Chloride and Solvent EffectDocument7 pagesHydrolysis of Tert-Butyl Chloride and Solvent EffectangelbenavidezNo ratings yet
- Partial Molal Volumes: Department of ChemistryDocument11 pagesPartial Molal Volumes: Department of ChemistryLulua100% (1)
- Solution ManualDocument111 pagesSolution ManualRichardoNo ratings yet
- One Way or Another: Perspective in The Holy Trinity by MasaccioDocument7 pagesOne Way or Another: Perspective in The Holy Trinity by Masacciosasia12No ratings yet
- Solutions For Reactor KineticsDocument2 pagesSolutions For Reactor Kineticszy_yfNo ratings yet
- Homework Week 5: 3 Ext Ext 3 ExtDocument10 pagesHomework Week 5: 3 Ext Ext 3 ExtIsabelle SimãoNo ratings yet
- Nilai K PDFDocument6 pagesNilai K PDFRisma C. AstariniNo ratings yet
- 2018 H2 Chemistry Paper 4 (Ans)Document8 pages2018 H2 Chemistry Paper 4 (Ans)Justin GohNo ratings yet
- GLP Practical 1a Calculation 2022 BCHN213 - MEMODocument3 pagesGLP Practical 1a Calculation 2022 BCHN213 - MEMOKAGISO BRIAN MOTSHUPHINo ratings yet
- H-068 Thermo. Titr. Application Note No.: Title: Determination of Ferric Ion by Iodometric TitrationDocument3 pagesH-068 Thermo. Titr. Application Note No.: Title: Determination of Ferric Ion by Iodometric TitrationEko Setyo BudiNo ratings yet
- Unit 9.2 - Temp and Heat - Giancoli ProblemsDocument2 pagesUnit 9.2 - Temp and Heat - Giancoli Problemslucas100% (1)
- Electrochemical Study of A Commercial SoapDocument4 pagesElectrochemical Study of A Commercial Soap12jagNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document4 pagesLecture 2Peter KiptumNo ratings yet
- Applications MATH 404Document32 pagesApplications MATH 404Rocel Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- Final BFC 32403 Sem 1 2013 14 - SCHEMEDocument16 pagesFinal BFC 32403 Sem 1 2013 14 - SCHEMEtashadzureenNo ratings yet
- Example Sheet 2 (Autumn 2019-20)Document1 pageExample Sheet 2 (Autumn 2019-20)siveshNo ratings yet
- p1512 eDocument4 pagesp1512 eJavier Augusto ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process CalculationsDocument8 pagesChemical Process Calculationsbhaskar5377No ratings yet
- 18 Quantitative Aspects of Chemical ChangeDocument30 pages18 Quantitative Aspects of Chemical Changeapi-235269401No ratings yet
- Assignment Sheet-4 Submission Date: 08.11.20Document3 pagesAssignment Sheet-4 Submission Date: 08.11.20JAYDEVSINH CHAVDANo ratings yet
- Separation of Complex Cations.Document3 pagesSeparation of Complex Cations.nicolef_20100% (2)
- Thermogravimetric Analysis of Calcium OxalateDocument2 pagesThermogravimetric Analysis of Calcium Oxalateakash babelNo ratings yet
- Set6ans 10Document4 pagesSet6ans 10Natália FerreiraNo ratings yet
- 40 Micellar CatalysisDocument4 pages40 Micellar CatalysisdarkknightoneNo ratings yet
- BCHN 213 Practical Exam 1 PreprationsDocument17 pagesBCHN 213 Practical Exam 1 Preprationskamohelo tsoeuNo ratings yet
- HEat Transfer DPP 46Document46 pagesHEat Transfer DPP 46Dev PancholiNo ratings yet
- Transport Processes in The Environment 5Document23 pagesTransport Processes in The Environment 5Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- Vapour in Air DiffusionDocument4 pagesVapour in Air DiffusionAyush Shrimal100% (1)
- Determination of Vitamin C in Vitamin TabletsDocument4 pagesDetermination of Vitamin C in Vitamin TabletsIgnas ŠakuroNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Solution Isotonic Solutions: University of The Philippines-Manila Industrial Pharmacy 121Document82 pagesParenteral Solution Isotonic Solutions: University of The Philippines-Manila Industrial Pharmacy 121Bj LarracasNo ratings yet
- CRE I Assignment - 250919Document11 pagesCRE I Assignment - 250919UpanyaaNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Refrigerant ManagementDocument1 pageEnhanced Refrigerant ManagementTrần Lê Quang NgọcNo ratings yet
- Gaseous State Theory - EDocument34 pagesGaseous State Theory - Ethinkiit67% (3)
- Theory: Determination of Percentage Composition of Sugar Solution by Oswald'S ViscometerDocument5 pagesTheory: Determination of Percentage Composition of Sugar Solution by Oswald'S ViscometerSUDIPA KONERNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry First LaboratoryDocument6 pagesAnalytical Chemistry First LaboratoryMELANIE ANTOLINNo ratings yet
- Gate Chemica EngineeringDocument30 pagesGate Chemica EngineeringKapilSahuNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics PDFDocument34 pagesReaction Kinetics PDFamms9988No ratings yet
- 2008 Nov GCE A CH H2 Soln SBS PDFDocument0 pages2008 Nov GCE A CH H2 Soln SBS PDFfacistsdarkshadowNo ratings yet
- Estrogens, ConjugatedDocument10 pagesEstrogens, ConjugatedJuan PerezNo ratings yet
- Agua Superficial TAREA #2 CIENCIA Y TECNOLOGIA AMBIENTALDocument6 pagesAgua Superficial TAREA #2 CIENCIA Y TECNOLOGIA AMBIENTALMichael Villicana Aguilera100% (1)
- Assay of Tissue GlycogenDocument26 pagesAssay of Tissue GlycogenTiyah TimothyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document3 pagesAssignment 4sadaf munirNo ratings yet
- Problems SetDocument10 pagesProblems SetSajith KurianNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Determination of Ethanol inDocument6 pagesQuantitative Determination of Ethanol inAnonymous 3OFvtiNo ratings yet
- Experi Men 22Document7 pagesExperi Men 22bernardNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic Models: One Compartment ModelDocument37 pagesPharmacokinetic Models: One Compartment ModelPronoy SahaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Handout - Mass BalanceDocument39 pagesLecture 2 Handout - Mass BalancePeter SzemrajNo ratings yet
- Chptr1PrblmSolnsDocument8 pagesChptr1PrblmSolnsAsifur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Example CalculationsDocument2 pagesExample CalculationsLisajanelollyNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan KondensorDocument2 pagesPerhitungan KondensorFenny Indah JatmikoNo ratings yet
- TakeHomeR - Kimia UAS AnwarJundiy011200306Document9 pagesTakeHomeR - Kimia UAS AnwarJundiy011200306Akbar YulandraNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Problems For Zero Order Kinetics and First Order Kinetics PRDocument31 pagesToaz - Info Problems For Zero Order Kinetics and First Order Kinetics PRعبدالرحمن أبوزريدةNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document61 pagesChapter 03JohnJaye100% (7)