Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views13.2 IP - Calculating Heat of Reactions: (G) + H O (G) C H (G) + 5/2 O (G)
13.2 IP - Calculating Heat of Reactions: (G) + H O (G) C H (G) + 5/2 O (G)
Uploaded by
Nicole Morgan PancardoIndependent practice worksheet; students use Hess's Law, Standard Heats of Formation, and Bond Energies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Hess S Law: Honor S Student Resource SheetDocument3 pagesHess S Law: Honor S Student Resource SheetFarz21No ratings yet
- Hess LawDocument1 pageHess LawReniel CabunganNo ratings yet
- 6.9 Hesss Law StudentDocument3 pages6.9 Hesss Law StudentRemasa BakraibaNo ratings yet
- Calculate the ΔH for the reaction H2SO4Document2 pagesCalculate the ΔH for the reaction H2SO4Loelle RadovanNo ratings yet
- Hess Law 2023Document18 pagesHess Law 2023JELLY ANNE BAGUIONo ratings yet
- Hess Law QuestionsDocument2 pagesHess Law Questionsronnie schwiersNo ratings yet
- Name - Honors Chemistry - / - / - Hess's LawDocument4 pagesName - Honors Chemistry - / - / - Hess's LawGunjee GunjeeNo ratings yet
- Sam Hess LawDocument24 pagesSam Hess LawPromise SangoNo ratings yet
- Hesss Law WorksheetDocument3 pagesHesss Law WorksheetAtulya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law QuestionsDocument7 pagesHess's Law QuestionsFawwaaz KoodruthNo ratings yet
- 6.9 Hess LawDocument13 pages6.9 Hess Law8grvqbm7ddNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law: EQ: Why Is Hess's Law A Useful Tool in Solving For HRXN?Document16 pagesHess's Law: EQ: Why Is Hess's Law A Useful Tool in Solving For HRXN?Lealyn Alupay YagaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.5: Hess' Law of Heat of Summation: 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (G) (G) (G) 2 (G) 2 (G)Document2 pagesLesson 3.5: Hess' Law of Heat of Summation: 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (G) (G) (G) 2 (G) 2 (G)Jem SonNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy and ThermochemistryDocument12 pagesEnthalpy and ThermochemistryMollin SiwellaNo ratings yet
- Hess Law Mock Paper PDFDocument2 pagesHess Law Mock Paper PDFErwin Purnama HadiansyahNo ratings yet
- Hess Law Questions PDFDocument2 pagesHess Law Questions PDFTrond Henrichsen InstituteNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law Extra WSDocument2 pagesHess's Law Extra WSDylan OdinNo ratings yet
- WK5 - Hesss Law Hard - Ib ServerDocument4 pagesWK5 - Hesss Law Hard - Ib Serverfuzzy pillowNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law Examples With AnswersDocument1 pageHess's Law Examples With AnswersOri SeinNo ratings yet
- Hess LawDocument35 pagesHess LawMARYAM AHMED MOHAMED HAMEDNo ratings yet
- Hesss LawDocument2 pagesHesss LawBiblee ChasNo ratings yet
- Sorsogon State College: Engineering and Architecture DepartmentDocument4 pagesSorsogon State College: Engineering and Architecture DepartmentIzay Martinez CadagNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesQuiz - Chemical ThermodynamicsOliric FabiolasNo ratings yet
- Sorsogon State College: Engineering and Architecture DepartmentDocument4 pagesSorsogon State College: Engineering and Architecture DepartmentIzay Martinez CadagNo ratings yet
- 3 - 2021 Thermodynamics USTH Part 2Document13 pages3 - 2021 Thermodynamics USTH Part 2Pham Duc AnhNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Module 2 PDFDocument17 pagesGeneral Chemistry Module 2 PDFwelp100% (1)
- Chem 1-8Document43 pagesChem 1-8Cabacungan, John VinceNo ratings yet
- Aldrin Ramirez - Energy Changes in Chemical Reaction-GenChem2Document3 pagesAldrin Ramirez - Energy Changes in Chemical Reaction-GenChem2aldrinramirez20No ratings yet
- Hess's Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesHess's Law WorksheetsaadixNo ratings yet
- Do Now:: Write Equations For The Following ExpressionsDocument14 pagesDo Now:: Write Equations For The Following ExpressionsJonh MhataNo ratings yet
- First Law of Thermodynamics: Hand Out 1Document9 pagesFirst Law of Thermodynamics: Hand Out 1Maxzen SantosNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6.3a - Hesss LawDocument3 pagesExercise 6.3a - Hesss Lawsamuel.bennettNo ratings yet
- 5 2+Hess's+Law+ExamplesDocument4 pages5 2+Hess's+Law+ExamplesBrad Randel SolisNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy of Reaction and Hess' LawDocument4 pagesEnthalpy of Reaction and Hess' LawJbreNo ratings yet
- Hess's LawDocument7 pagesHess's Lawjax stykerNo ratings yet
- Hess Law Practice ProblemDocument2 pagesHess Law Practice ProblemMeryana TanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 QuestionsDocument4 pagesTutorial 2 Questionsiveco0% (1)
- Thermochemistry PracticeDocument5 pagesThermochemistry PracticemariajoticaNo ratings yet
- Lesson On Gibbs' Free EnergyDocument2 pagesLesson On Gibbs' Free EnergyJan Yeasha MendezNo ratings yet
- Hess Law Problems ChallengingDocument1 pageHess Law Problems ChallengingannaharulNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law: /K Mol)Document2 pagesHess's Law: /K Mol)Jasper DumalaogNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law EXTRADocument10 pagesHess's Law EXTRAスカイ プリンスNo ratings yet
- 7 Chemical EnergeticsDocument176 pages7 Chemical EnergeticsUng Hie HuongNo ratings yet
- Thermochem 2.0 Hesss LawDocument13 pagesThermochem 2.0 Hesss Lawprncs.5zaiNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Chemistry Questions With SolutionsDocument8 pagesThermochemistry Chemistry Questions With SolutionsHARSH RoopejaNo ratings yet
- P18 - Practice Question AnswersDocument3 pagesP18 - Practice Question AnswersdenisNo ratings yet
- 16-5Hess'sLaw CL PDFDocument1 page16-5Hess'sLaw CL PDFAlfonso0% (1)
- Hess Law YesDocument34 pagesHess Law YesAeris AkmalNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Practice Test-5/Chemistry: Thermodynamics HWT - 1Document10 pagesSolutions To Home Practice Test-5/Chemistry: Thermodynamics HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Hess's Law 2018Document2 pagesIntermediate Hess's Law 2018MasonNo ratings yet
- Thermo Problems 2Document10 pagesThermo Problems 2WhoamiNo ratings yet
- Hess PrintDocument22 pagesHess PrintAriAnggoroNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law: Start FinishDocument10 pagesHess's Law: Start FinishtausmanNo ratings yet
- Hess LawDocument24 pagesHess Lawactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- 2021-2022 - Worksheet 2 - Bonds Energy & Hess's LawDocument1 page2021-2022 - Worksheet 2 - Bonds Energy & Hess's LawTroy Christoval ThejaNo ratings yet
- Hesss Law Awesome Ib Packet Questions OnlyDocument6 pagesHesss Law Awesome Ib Packet Questions OnlyEmmanuel JoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Rev PDFDocument13 pagesChapter 17 - Rev PDFalaa al sahmaraniNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
13.2 IP - Calculating Heat of Reactions: (G) + H O (G) C H (G) + 5/2 O (G)
13.2 IP - Calculating Heat of Reactions: (G) + H O (G) C H (G) + 5/2 O (G)
Uploaded by
Nicole Morgan Pancardo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesIndependent practice worksheet; students use Hess's Law, Standard Heats of Formation, and Bond Energies.
Original Title
13.2 IP Heat of Reaction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIndependent practice worksheet; students use Hess's Law, Standard Heats of Formation, and Bond Energies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pages13.2 IP - Calculating Heat of Reactions: (G) + H O (G) C H (G) + 5/2 O (G)
13.2 IP - Calculating Heat of Reactions: (G) + H O (G) C H (G) + 5/2 O (G)
Uploaded by
Nicole Morgan PancardoIndependent practice worksheet; students use Hess's Law, Standard Heats of Formation, and Bond Energies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Name: _______________________________________
13.2 IP Calculating Heat of Reactions
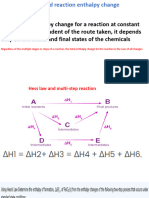
Hess Law use Hess Law to determine H for each reaction given
the step equations and their H values.
1. Reaction: 2CO2(g)+ H2O(g) C2H2(g) + 5/2 O2(g)
C2H2 (g) +2 H2 (g) C2H6 (g)
H2O (g) H2 (g) + O2 (g)
C2H6 (g) + 7/2 O2 (g) 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (g)
H = -94.5
kJ
H = 71.2
kJ
H = -283
kJ
SUM =
2. Reaction: H2SO4 (l) SO3 (g) + H2O (g)
H2S (g) + 2 O2 (g) H2SO4 (l)
H =
-235.5 kJ
H2S (g) + 2 O2 (g) SO3 (g) + H2O (l)
H = -207
kJ
H2O (l) H2O (g)
H = 44 kJ
SUM =
3. Reaction: N2 (g) + 2 O2 (g) 2 NO2 (g)
N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g)
H = -115
kJ
2 NH3 (g) + 4 H2O (l) 2 NO2 (g) + 7 H2 (g)
H =
-142.5 kJ
H2O (l) H2 (g) + O2 (g)
H = -43.7
kJ
SUM =
Name: _______________________________________
Standard EnthalpiesUse the standard enthaplies of formation to
calculate the H for each reaction.
4. NaOH(s) + HCl(g) ----> NaCl(s) + H2O(g)
5. 2 CO(g) + O2(g) ---> 2 CO2(g)
Name: _______________________________________
6. 2 H2S(g) + 3 O2(g) ---> 2 H2O(l) + 2 SO2(g)
Bond Energies Use the bond energies to determine the H of each
reaction.
7.
8.
Use bond energies to calculate the
heat of reaction
Name: _______________________________________
You might also like
- Hess S Law: Honor S Student Resource SheetDocument3 pagesHess S Law: Honor S Student Resource SheetFarz21No ratings yet
- Hess LawDocument1 pageHess LawReniel CabunganNo ratings yet
- 6.9 Hesss Law StudentDocument3 pages6.9 Hesss Law StudentRemasa BakraibaNo ratings yet
- Calculate the ΔH for the reaction H2SO4Document2 pagesCalculate the ΔH for the reaction H2SO4Loelle RadovanNo ratings yet
- Hess Law 2023Document18 pagesHess Law 2023JELLY ANNE BAGUIONo ratings yet
- Hess Law QuestionsDocument2 pagesHess Law Questionsronnie schwiersNo ratings yet
- Name - Honors Chemistry - / - / - Hess's LawDocument4 pagesName - Honors Chemistry - / - / - Hess's LawGunjee GunjeeNo ratings yet
- Sam Hess LawDocument24 pagesSam Hess LawPromise SangoNo ratings yet
- Hesss Law WorksheetDocument3 pagesHesss Law WorksheetAtulya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law QuestionsDocument7 pagesHess's Law QuestionsFawwaaz KoodruthNo ratings yet
- 6.9 Hess LawDocument13 pages6.9 Hess Law8grvqbm7ddNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law: EQ: Why Is Hess's Law A Useful Tool in Solving For HRXN?Document16 pagesHess's Law: EQ: Why Is Hess's Law A Useful Tool in Solving For HRXN?Lealyn Alupay YagaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.5: Hess' Law of Heat of Summation: 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (G) (G) (G) 2 (G) 2 (G)Document2 pagesLesson 3.5: Hess' Law of Heat of Summation: 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (G) (G) (G) 2 (G) 2 (G)Jem SonNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy and ThermochemistryDocument12 pagesEnthalpy and ThermochemistryMollin SiwellaNo ratings yet
- Hess Law Mock Paper PDFDocument2 pagesHess Law Mock Paper PDFErwin Purnama HadiansyahNo ratings yet
- Hess Law Questions PDFDocument2 pagesHess Law Questions PDFTrond Henrichsen InstituteNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law Extra WSDocument2 pagesHess's Law Extra WSDylan OdinNo ratings yet
- WK5 - Hesss Law Hard - Ib ServerDocument4 pagesWK5 - Hesss Law Hard - Ib Serverfuzzy pillowNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law Examples With AnswersDocument1 pageHess's Law Examples With AnswersOri SeinNo ratings yet
- Hess LawDocument35 pagesHess LawMARYAM AHMED MOHAMED HAMEDNo ratings yet
- Hesss LawDocument2 pagesHesss LawBiblee ChasNo ratings yet
- Sorsogon State College: Engineering and Architecture DepartmentDocument4 pagesSorsogon State College: Engineering and Architecture DepartmentIzay Martinez CadagNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesQuiz - Chemical ThermodynamicsOliric FabiolasNo ratings yet
- Sorsogon State College: Engineering and Architecture DepartmentDocument4 pagesSorsogon State College: Engineering and Architecture DepartmentIzay Martinez CadagNo ratings yet
- 3 - 2021 Thermodynamics USTH Part 2Document13 pages3 - 2021 Thermodynamics USTH Part 2Pham Duc AnhNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Module 2 PDFDocument17 pagesGeneral Chemistry Module 2 PDFwelp100% (1)
- Chem 1-8Document43 pagesChem 1-8Cabacungan, John VinceNo ratings yet
- Aldrin Ramirez - Energy Changes in Chemical Reaction-GenChem2Document3 pagesAldrin Ramirez - Energy Changes in Chemical Reaction-GenChem2aldrinramirez20No ratings yet
- Hess's Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesHess's Law WorksheetsaadixNo ratings yet
- Do Now:: Write Equations For The Following ExpressionsDocument14 pagesDo Now:: Write Equations For The Following ExpressionsJonh MhataNo ratings yet
- First Law of Thermodynamics: Hand Out 1Document9 pagesFirst Law of Thermodynamics: Hand Out 1Maxzen SantosNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6.3a - Hesss LawDocument3 pagesExercise 6.3a - Hesss Lawsamuel.bennettNo ratings yet
- 5 2+Hess's+Law+ExamplesDocument4 pages5 2+Hess's+Law+ExamplesBrad Randel SolisNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy of Reaction and Hess' LawDocument4 pagesEnthalpy of Reaction and Hess' LawJbreNo ratings yet
- Hess's LawDocument7 pagesHess's Lawjax stykerNo ratings yet
- Hess Law Practice ProblemDocument2 pagesHess Law Practice ProblemMeryana TanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 QuestionsDocument4 pagesTutorial 2 Questionsiveco0% (1)
- Thermochemistry PracticeDocument5 pagesThermochemistry PracticemariajoticaNo ratings yet
- Lesson On Gibbs' Free EnergyDocument2 pagesLesson On Gibbs' Free EnergyJan Yeasha MendezNo ratings yet
- Hess Law Problems ChallengingDocument1 pageHess Law Problems ChallengingannaharulNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law: /K Mol)Document2 pagesHess's Law: /K Mol)Jasper DumalaogNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law EXTRADocument10 pagesHess's Law EXTRAスカイ プリンスNo ratings yet
- 7 Chemical EnergeticsDocument176 pages7 Chemical EnergeticsUng Hie HuongNo ratings yet
- Thermochem 2.0 Hesss LawDocument13 pagesThermochem 2.0 Hesss Lawprncs.5zaiNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Chemistry Questions With SolutionsDocument8 pagesThermochemistry Chemistry Questions With SolutionsHARSH RoopejaNo ratings yet
- P18 - Practice Question AnswersDocument3 pagesP18 - Practice Question AnswersdenisNo ratings yet
- 16-5Hess'sLaw CL PDFDocument1 page16-5Hess'sLaw CL PDFAlfonso0% (1)
- Hess Law YesDocument34 pagesHess Law YesAeris AkmalNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Practice Test-5/Chemistry: Thermodynamics HWT - 1Document10 pagesSolutions To Home Practice Test-5/Chemistry: Thermodynamics HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Hess's Law 2018Document2 pagesIntermediate Hess's Law 2018MasonNo ratings yet
- Thermo Problems 2Document10 pagesThermo Problems 2WhoamiNo ratings yet
- Hess PrintDocument22 pagesHess PrintAriAnggoroNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law: Start FinishDocument10 pagesHess's Law: Start FinishtausmanNo ratings yet
- Hess LawDocument24 pagesHess Lawactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- 2021-2022 - Worksheet 2 - Bonds Energy & Hess's LawDocument1 page2021-2022 - Worksheet 2 - Bonds Energy & Hess's LawTroy Christoval ThejaNo ratings yet
- Hesss Law Awesome Ib Packet Questions OnlyDocument6 pagesHesss Law Awesome Ib Packet Questions OnlyEmmanuel JoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Rev PDFDocument13 pagesChapter 17 - Rev PDFalaa al sahmaraniNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet