Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 viewsBond Dissociation Energy
Bond Dissociation Energy
Uploaded by
Grace Llorente PatricioBond-dissociation energy is a measure of bond strength defined as the standard enthalpy change required to break a bond. There are two types of bond cleavage: homolysis, where the bond breaks symmetrically into two radicals, and heterolysis, where the bond breaks asymmetrically into an ion pair. Bond-dissociation energy values are provided for many different bonds and compounds. The bond energy of a molecule is the average bond-dissociation energy of all its bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- ATP-3.2.1 Land TacticsDocument273 pagesATP-3.2.1 Land Tacticsian R100% (16)
- Chapter 6 Chemical EnergeticsDocument42 pagesChapter 6 Chemical Energeticsgajenrao100% (1)
- ks5 - Haloalkanes - Chemistry-Of-Haloalkanes - StudentDocument33 pagesks5 - Haloalkanes - Chemistry-Of-Haloalkanes - Studentapi-504683923No ratings yet
- Decision Tables ExercisesDocument3 pagesDecision Tables ExercisesmubasherNo ratings yet
- SB10 Chapter 8 AnswersDocument16 pagesSB10 Chapter 8 Answersanna jones20% (5)
- Bond-Dissociation Energy - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesBond-Dissociation Energy - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSatyendra Nath PandeyNo ratings yet
- Making and Breaking Bonds: Bond EnthalpyDocument4 pagesMaking and Breaking Bonds: Bond EnthalpyEdvards GrīgsNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 - Physical Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesChapter - 1 - Physical Organic ChemistryAcidri Abdulkarim100% (1)
- Alkanes 2 PDFDocument14 pagesAlkanes 2 PDFmartin mulengaNo ratings yet
- Bond Enthalpy (Bond Energy)Document6 pagesBond Enthalpy (Bond Energy)Khyzer HayyatNo ratings yet
- Bond Energies NotesDocument3 pagesBond Energies NotesKarthi100% (1)
- Bonds Forming and Bonds BreakingDocument3 pagesBonds Forming and Bonds Breakingareejhussaini26No ratings yet
- A Energetics Notes Chem Unit 1 - (New)Document8 pagesA Energetics Notes Chem Unit 1 - (New)Khaila SimmondNo ratings yet
- 08-Bond Energies and Enthalpy ChangesDocument3 pages08-Bond Energies and Enthalpy ChangesNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Bond Enthalpy: IB SL Chemistry Mrs. Page 2015-2016Document26 pages5.3 Bond Enthalpy: IB SL Chemistry Mrs. Page 2015-2016Patrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- Topic R 1.2 1Document26 pagesTopic R 1.2 1lmasadehNo ratings yet
- Bond EnthalpyDocument10 pagesBond EnthalpyPartha SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Bond Dissociation EnergiesDocument5 pagesBond Dissociation Energiesjean ruNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law As Chem Tutorial 2 KajanaDocument6 pagesHess's Law As Chem Tutorial 2 KajanaKajana Sivarasa ShenthanNo ratings yet
- 12.6: Intermolecular Forces: Dispersion, Dipole-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-DipoleDocument11 pages12.6: Intermolecular Forces: Dispersion, Dipole-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-DipoleGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Energetics - CN - STDT5Document2 pagesEnergetics - CN - STDT5NkemziNo ratings yet
- C7-1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument24 pagesC7-1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsUYÊN NGUYỄN NGỌC QUỲNHNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument9 pagesThermochemistryZuhura RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Bond EnthalpyDocument12 pagesBond EnthalpynivineNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energy PDFDocument12 pagesChemical Energy PDFfarsxdchgNo ratings yet
- CHM122 - Bonding PART CDocument52 pagesCHM122 - Bonding PART COyem DavidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics PDFDocument11 pagesChemical Energetics PDFJoanne75% (4)
- Energetics by Abhishek JaguessarDocument10 pagesEnergetics by Abhishek Jaguessarreedoye21No ratings yet
- Estimating Enthalpy Using Bond EnergyDocument3 pagesEstimating Enthalpy Using Bond EnergyEmille IlmansyahNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Intermolecular ForcesDocument10 pages11.2 Intermolecular ForcesethanNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Energy ChangesDocument34 pages4.2 Energy ChangesMala CharlesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Chemical EnergeticsDocument15 pagesChapter 5 - Chemical EnergeticsAdam BeyNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy ChangesDocument17 pagesEnthalpy ChangesDoc_Croc100% (1)
- Enthalpy AsDocument9 pagesEnthalpy AsA LEVEL TOPNo ratings yet
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 5: Chemical EnergeticsDocument7 pagesCIE Chemistry A Level: 5: Chemical EnergeticsahumanbeinginearthNo ratings yet
- Physics-Third Law of ThermodynamicsDocument17 pagesPhysics-Third Law of ThermodynamicsShubham JainNo ratings yet
- Honors 8.7-8.8Document14 pagesHonors 8.7-8.8Kristine I-ReeseNo ratings yet
- Ib Enthalpy KHDocument39 pagesIb Enthalpy KHSamer EhabNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergyDocument12 pagesChemical EnergyMathews ZimbaNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergyDocument12 pagesChemical EnergyFaiza RizwanNo ratings yet
- 04 EnergeticsDocument14 pages04 EnergeticsafshinNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces, Liquid and SolidsDocument64 pagesIntermolecular Forces, Liquid and Solidsmdnishathasan141No ratings yet
- Thermochem HbyiuhbiuDocument16 pagesThermochem HbyiuhbiudanielleanastaciaoscarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Chemical EnergeticsDocument51 pagesModule 5 - Chemical Energeticspoopoodotcom23No ratings yet
- Reactions of AlkanesDocument44 pagesReactions of AlkanesKunjalNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy 093302Document22 pagesEnthalpy 093302Mikhoy RiveralNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThirteenDocument19 pagesChapter ThirteenFarah AttallahNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Study of C AH Bond Dissociation Energies of HC (@X) R (X O, S, Se R H, CH, CL, NH)Document7 pagesTheoretical Study of C AH Bond Dissociation Energies of HC (@X) R (X O, S, Se R H, CH, CL, NH)Tyler HermanNo ratings yet
- Bonding EnergiesDocument9 pagesBonding EnergiesAdam RasheedNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Lecture 4Document36 pagesMolecular Biology Lecture 4Anton IrvingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5a (AS-Level) : Chemical EnergeticsDocument12 pagesChapter 5a (AS-Level) : Chemical EnergeticsMohamed AkkashNo ratings yet
- Energy ChangeDocument10 pagesEnergy ChangeIntelligence EmpireNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (Structure and Bonding) AnswersDocument3 pagesTutorial (Structure and Bonding) Answersoh khang chiangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 ThermochemistryDocument8 pagesLesson 4 Thermochemistryaloysius limNo ratings yet
- Bond EnergyDocument13 pagesBond EnergyreddygrNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Lecturer Final 2003Document52 pagesTopic 3 Lecturer Final 2003ibel1eveNo ratings yet
- L3 MOD 4 IQ2 HESS'S LAW and Bond EnergyDocument22 pagesL3 MOD 4 IQ2 HESS'S LAW and Bond EnergylEENo ratings yet
- downloadChemistryA LevelNotesOCR A3 Periodic Table and EnergyDetailed3.2.20PhysicalDocument17 pagesdownloadChemistryA LevelNotesOCR A3 Periodic Table and EnergyDetailed3.2.20Physicalz akterNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry,: Lecture OutlineDocument64 pagesOrganic Chemistry,: Lecture Outlinedhanaa_132254No ratings yet
- Topic 4 Notes (New)Document12 pagesTopic 4 Notes (New)amenaNo ratings yet
- The Happy PrinceDocument3 pagesThe Happy PrinceLaurence UyNo ratings yet
- 6 Settlement Response of A Multi-Story BuildingDocument4 pages6 Settlement Response of A Multi-Story BuildingmazNo ratings yet
- TDS BLR 896 EN ScreenDocument1 pageTDS BLR 896 EN ScreenLuis Angel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Vibracord. Vibration Meter Summary Sheet (Graphic) : Record Time: 4 SDocument1 pageVibracord. Vibration Meter Summary Sheet (Graphic) : Record Time: 4 SSadettin BağdatlıNo ratings yet
- Delta Function and So OnDocument20 pagesDelta Function and So OnLionel TopperNo ratings yet
- MTCR - Missile Technology Control RegimeDocument11 pagesMTCR - Missile Technology Control Regimefernandocwrocha-1No ratings yet
- Fall 2023 MATH 39100 Final Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesFall 2023 MATH 39100 Final Exam ReviewSimranjit SinghNo ratings yet
- United States v. Gerard Valmore Brown, A/K/A Blackie, A/K/A Gerald Kennedy, United States of America v. Melvin Sanders, A/K/A Pops, United States of America v. Andre Simpson, 76 F.3d 376, 4th Cir. (1996)Document5 pagesUnited States v. Gerard Valmore Brown, A/K/A Blackie, A/K/A Gerald Kennedy, United States of America v. Melvin Sanders, A/K/A Pops, United States of America v. Andre Simpson, 76 F.3d 376, 4th Cir. (1996)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- English Essay Bros Before HosDocument5 pagesEnglish Essay Bros Before HosAndrés I. Rivera33% (3)
- Ignou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19Document7 pagesIgnou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19NEW THINK CLASSES100% (1)
- Carbo GelDocument2 pagesCarbo Gelyehia sayedNo ratings yet
- Matlab: 'HZ Sine Wave To 20Hz Square Wave ConversionDocument10 pagesMatlab: 'HZ Sine Wave To 20Hz Square Wave ConversionSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- Flogocid Cream - Google SearchDocument1 pageFlogocid Cream - Google SearchAyesha SohailNo ratings yet
- Data SufficiencyDocument7 pagesData SufficiencySaurav BhasinNo ratings yet
- Mental Health InventoryDocument7 pagesMental Health InventoryALi Sarmad100% (1)
- Bhopal Disaster: Too LongDocument5 pagesBhopal Disaster: Too LongrevathisudhaNo ratings yet
- Ud 6 Naturales 2º - Tools and MachinesDocument27 pagesUd 6 Naturales 2º - Tools and MachinesLola FrancoNo ratings yet
- ACP1withsolution 16303 16301873391Document23 pagesACP1withsolution 16303 16301873391Arman DehuriNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan-Badminton Jenna Maceachen: Subject Area Grade Level Topic Length of Unit (Days)Document8 pagesUnit Plan-Badminton Jenna Maceachen: Subject Area Grade Level Topic Length of Unit (Days)api-507324305No ratings yet
- Concept NoteDocument4 pagesConcept NoteAfanie Mae Romero EstepaNo ratings yet
- Secrets of A Millionaire Magician DeluxeDocument480 pagesSecrets of A Millionaire Magician DeluxelautaroNo ratings yet
- Sexual Orientation Sexuality Wiki Fandom PDFDocument1 pageSexual Orientation Sexuality Wiki Fandom PDFAngus FieldingNo ratings yet
- Ipc 2581BDocument9 pagesIpc 2581BlaxenovNo ratings yet
- Appserver Job - LogDocument1,225 pagesAppserver Job - LogThiago Ximenes LopesNo ratings yet
- Notes in Criminal SociologyDocument8 pagesNotes in Criminal SociologyWevinneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 ReviewDocument10 pagesChapter 23 ReviewThanat MilinthachindaNo ratings yet
- Module IDocument14 pagesModule IDianna Rose BelenNo ratings yet
Bond Dissociation Energy
Bond Dissociation Energy
Uploaded by
Grace Llorente Patricio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views2 pagesBond-dissociation energy is a measure of bond strength defined as the standard enthalpy change required to break a bond. There are two types of bond cleavage: homolysis, where the bond breaks symmetrically into two radicals, and heterolysis, where the bond breaks asymmetrically into an ion pair. Bond-dissociation energy values are provided for many different bonds and compounds. The bond energy of a molecule is the average bond-dissociation energy of all its bonds.
Original Description:
Bond Dissociation Energy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBond-dissociation energy is a measure of bond strength defined as the standard enthalpy change required to break a bond. There are two types of bond cleavage: homolysis, where the bond breaks symmetrically into two radicals, and heterolysis, where the bond breaks asymmetrically into an ion pair. Bond-dissociation energy values are provided for many different bonds and compounds. The bond energy of a molecule is the average bond-dissociation energy of all its bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views2 pagesBond Dissociation Energy
Bond Dissociation Energy
Uploaded by
Grace Llorente PatricioBond-dissociation energy is a measure of bond strength defined as the standard enthalpy change required to break a bond. There are two types of bond cleavage: homolysis, where the bond breaks symmetrically into two radicals, and heterolysis, where the bond breaks asymmetrically into an ion pair. Bond-dissociation energy values are provided for many different bonds and compounds. The bond energy of a molecule is the average bond-dissociation energy of all its bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Bond-dissociation energy
1.2 Homolytic versus heterolytic dissociation
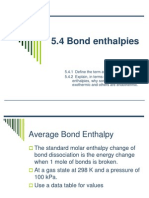
In chemistry, bond-dissociation energy (BDE) or D0 ,
is one measure of the strength in a chemical bond. It is
dened as the standard enthalpy change when a bond is
cleaved by homolysis,[1] with reactants and products of
the homolysis reaction at 0 K (absolute zero). For instance, the bond-dissociation energy for one of the CH
bonds in ethane (C2 H6 ) is dened by the process:
Bonds can be broken symmetrically or asymmetrically.
The former is called homolysis and is the basis of the
usual BDEs. Asymmetrical scission of a bond is called
heterolysis. For molecular hydrogen, the alternatives are:
CH3 CH2 H CH3 CH2 + H
H2 2 H G = 102 kcal/mol (see table below)
D0 = H = 101.1 kcal/mol = 423.0 kJ/mol = 4.40 eV
(per bond)
H2 H+ + H G = 66 kcal/mol (in water)
|69r>bromocarbons are often labile and are useful re retardants
Denitions of BDE and related
parameters
The data tabulated above shows how bond strengths vary
over the periodic table. There is great interest, especially
The bond-dissociation energy is sometime also called the in organic chemistry, concerning bond strengths of bonds
bond-dissociation enthalpy (or bond enthalpy), but these within a given group of compounds.[2]
terms are not strictly equivalent, as they refer to the above
reaction enthalpy at standard conditions, and dier from
D0 by about 1.5 kcal/mol (6 kJ/mol) in the case of a bond
2 See also
to hydrogen in a large organic molecule.[2]
Bond strength
1.1
BDE versus bond energy
Bond energy
Except in the case of diatomic molecules, the bonddissociation energy is dierent from the bond energy,
which is an average calculated from the sum of the bonddissociation energies of all bonds in a molecule.[3]
Binding energy
For example, an HOH bond of a water molecule (H
OH) has 493.4 kJ/mol of bond-dissociation energy, and
424.4 kJ/mol is needed to cleave the remaining OH
bond. The bond energy of the covalent OH bonds in
water is 458.9 kJ/mol, which is the average of the values.
Hydrogen bond-dissociation energy in water is about 23
kJ/mol.[4]
3 References
Chemical bond
[1] IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed.
(the Gold Book) (1997). Online corrected version:
(1994) "Bond dissociation energy".
[2] Blanksby, S. J.; Ellison, G. B.; (2003). Bond Dissociation Energies of Organic Molecules. Acc. Chem.
Res. 36 (4): 255263. doi:10.1021/ar020230d. PMID
12693923.
In the same way for removing successive hydrogen atoms
from methane the bond-dissociating energies are 104
kcal/mol (435 kJ/mol) for D(CH3 H), 106 kcal/mol (444
kJ/mol) for D(CH2 H), 106 kcal/mol (444 kJ/mol) for
D(CHH) and nally 81 kcal/mol (339 kJ/mol) for D(C
H). The bond energy is, thus, 99 kcal/mol or 414 kJ/mol
(the average of the bond-dissociation energies). Notice
that none of the C-H BDEs is 99 kcal/mol.
[3] Morrison & Boyd Organic Chemistry 4th Ed. ISBN 0205-05838-8
[4] Principles of biochemistry by Albert L. Lehninger, David
Lee Nelson, Michael M. Cox; edition 4, page 48
Following dissociation if new bonds are formed at lower
enthalpy there is a net loss of energy, and thus an overall
exothermic process.
1
4 TEXT AND IMAGE SOURCES, CONTRIBUTORS, AND LICENSES
Text and image sources, contributors, and licenses
4.1
Text
Bond-dissociation energy Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bond-dissociation_energy?oldid=673835136 Contributors: Taxman,
Blainster, Karol Langner, Kwamikagami, Tomgally, Kjkolb, Ripero, Yougi, Gene Nygaard, The Wordsmith, V8rik, Az7997, Tony1, Itub,
SmackBot, Bluebot, GregRM, Smokefoot, Drphilharmonic, John, Christian75, Thijs!bot, Leyo, Bombhead, 28bytes, SieBot, BlueDevil,
Addbot, Wickey-nl, Choij, Citation bot, Esmu Igors, Citation bot 1, Nirmos, Xook1kai Choa6aur, EmausBot, Francisco Quiumento,
ZroBot, Wakebrdkid, Rmashhadi, NotWith, EagerToddler39, Petece19, Bananasoldier, Crystallizedcarbon and Anonymous: 28
4.2
Images
4.3
Content license
Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0
You might also like
- ATP-3.2.1 Land TacticsDocument273 pagesATP-3.2.1 Land Tacticsian R100% (16)
- Chapter 6 Chemical EnergeticsDocument42 pagesChapter 6 Chemical Energeticsgajenrao100% (1)
- ks5 - Haloalkanes - Chemistry-Of-Haloalkanes - StudentDocument33 pagesks5 - Haloalkanes - Chemistry-Of-Haloalkanes - Studentapi-504683923No ratings yet
- Decision Tables ExercisesDocument3 pagesDecision Tables ExercisesmubasherNo ratings yet
- SB10 Chapter 8 AnswersDocument16 pagesSB10 Chapter 8 Answersanna jones20% (5)
- Bond-Dissociation Energy - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesBond-Dissociation Energy - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSatyendra Nath PandeyNo ratings yet
- Making and Breaking Bonds: Bond EnthalpyDocument4 pagesMaking and Breaking Bonds: Bond EnthalpyEdvards GrīgsNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 - Physical Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesChapter - 1 - Physical Organic ChemistryAcidri Abdulkarim100% (1)
- Alkanes 2 PDFDocument14 pagesAlkanes 2 PDFmartin mulengaNo ratings yet
- Bond Enthalpy (Bond Energy)Document6 pagesBond Enthalpy (Bond Energy)Khyzer HayyatNo ratings yet
- Bond Energies NotesDocument3 pagesBond Energies NotesKarthi100% (1)
- Bonds Forming and Bonds BreakingDocument3 pagesBonds Forming and Bonds Breakingareejhussaini26No ratings yet
- A Energetics Notes Chem Unit 1 - (New)Document8 pagesA Energetics Notes Chem Unit 1 - (New)Khaila SimmondNo ratings yet
- 08-Bond Energies and Enthalpy ChangesDocument3 pages08-Bond Energies and Enthalpy ChangesNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Bond Enthalpy: IB SL Chemistry Mrs. Page 2015-2016Document26 pages5.3 Bond Enthalpy: IB SL Chemistry Mrs. Page 2015-2016Patrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- Topic R 1.2 1Document26 pagesTopic R 1.2 1lmasadehNo ratings yet
- Bond EnthalpyDocument10 pagesBond EnthalpyPartha SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Bond Dissociation EnergiesDocument5 pagesBond Dissociation Energiesjean ruNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law As Chem Tutorial 2 KajanaDocument6 pagesHess's Law As Chem Tutorial 2 KajanaKajana Sivarasa ShenthanNo ratings yet
- 12.6: Intermolecular Forces: Dispersion, Dipole-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-DipoleDocument11 pages12.6: Intermolecular Forces: Dispersion, Dipole-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-DipoleGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Energetics - CN - STDT5Document2 pagesEnergetics - CN - STDT5NkemziNo ratings yet
- C7-1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument24 pagesC7-1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsUYÊN NGUYỄN NGỌC QUỲNHNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument9 pagesThermochemistryZuhura RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Bond EnthalpyDocument12 pagesBond EnthalpynivineNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energy PDFDocument12 pagesChemical Energy PDFfarsxdchgNo ratings yet
- CHM122 - Bonding PART CDocument52 pagesCHM122 - Bonding PART COyem DavidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics PDFDocument11 pagesChemical Energetics PDFJoanne75% (4)
- Energetics by Abhishek JaguessarDocument10 pagesEnergetics by Abhishek Jaguessarreedoye21No ratings yet
- Estimating Enthalpy Using Bond EnergyDocument3 pagesEstimating Enthalpy Using Bond EnergyEmille IlmansyahNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Intermolecular ForcesDocument10 pages11.2 Intermolecular ForcesethanNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Energy ChangesDocument34 pages4.2 Energy ChangesMala CharlesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Chemical EnergeticsDocument15 pagesChapter 5 - Chemical EnergeticsAdam BeyNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy ChangesDocument17 pagesEnthalpy ChangesDoc_Croc100% (1)
- Enthalpy AsDocument9 pagesEnthalpy AsA LEVEL TOPNo ratings yet
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 5: Chemical EnergeticsDocument7 pagesCIE Chemistry A Level: 5: Chemical EnergeticsahumanbeinginearthNo ratings yet
- Physics-Third Law of ThermodynamicsDocument17 pagesPhysics-Third Law of ThermodynamicsShubham JainNo ratings yet
- Honors 8.7-8.8Document14 pagesHonors 8.7-8.8Kristine I-ReeseNo ratings yet
- Ib Enthalpy KHDocument39 pagesIb Enthalpy KHSamer EhabNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergyDocument12 pagesChemical EnergyMathews ZimbaNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergyDocument12 pagesChemical EnergyFaiza RizwanNo ratings yet
- 04 EnergeticsDocument14 pages04 EnergeticsafshinNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces, Liquid and SolidsDocument64 pagesIntermolecular Forces, Liquid and Solidsmdnishathasan141No ratings yet
- Thermochem HbyiuhbiuDocument16 pagesThermochem HbyiuhbiudanielleanastaciaoscarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Chemical EnergeticsDocument51 pagesModule 5 - Chemical Energeticspoopoodotcom23No ratings yet
- Reactions of AlkanesDocument44 pagesReactions of AlkanesKunjalNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy 093302Document22 pagesEnthalpy 093302Mikhoy RiveralNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThirteenDocument19 pagesChapter ThirteenFarah AttallahNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Study of C AH Bond Dissociation Energies of HC (@X) R (X O, S, Se R H, CH, CL, NH)Document7 pagesTheoretical Study of C AH Bond Dissociation Energies of HC (@X) R (X O, S, Se R H, CH, CL, NH)Tyler HermanNo ratings yet
- Bonding EnergiesDocument9 pagesBonding EnergiesAdam RasheedNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Lecture 4Document36 pagesMolecular Biology Lecture 4Anton IrvingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5a (AS-Level) : Chemical EnergeticsDocument12 pagesChapter 5a (AS-Level) : Chemical EnergeticsMohamed AkkashNo ratings yet
- Energy ChangeDocument10 pagesEnergy ChangeIntelligence EmpireNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (Structure and Bonding) AnswersDocument3 pagesTutorial (Structure and Bonding) Answersoh khang chiangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 ThermochemistryDocument8 pagesLesson 4 Thermochemistryaloysius limNo ratings yet
- Bond EnergyDocument13 pagesBond EnergyreddygrNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Lecturer Final 2003Document52 pagesTopic 3 Lecturer Final 2003ibel1eveNo ratings yet
- L3 MOD 4 IQ2 HESS'S LAW and Bond EnergyDocument22 pagesL3 MOD 4 IQ2 HESS'S LAW and Bond EnergylEENo ratings yet
- downloadChemistryA LevelNotesOCR A3 Periodic Table and EnergyDetailed3.2.20PhysicalDocument17 pagesdownloadChemistryA LevelNotesOCR A3 Periodic Table and EnergyDetailed3.2.20Physicalz akterNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry,: Lecture OutlineDocument64 pagesOrganic Chemistry,: Lecture Outlinedhanaa_132254No ratings yet
- Topic 4 Notes (New)Document12 pagesTopic 4 Notes (New)amenaNo ratings yet
- The Happy PrinceDocument3 pagesThe Happy PrinceLaurence UyNo ratings yet
- 6 Settlement Response of A Multi-Story BuildingDocument4 pages6 Settlement Response of A Multi-Story BuildingmazNo ratings yet
- TDS BLR 896 EN ScreenDocument1 pageTDS BLR 896 EN ScreenLuis Angel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Vibracord. Vibration Meter Summary Sheet (Graphic) : Record Time: 4 SDocument1 pageVibracord. Vibration Meter Summary Sheet (Graphic) : Record Time: 4 SSadettin BağdatlıNo ratings yet
- Delta Function and So OnDocument20 pagesDelta Function and So OnLionel TopperNo ratings yet
- MTCR - Missile Technology Control RegimeDocument11 pagesMTCR - Missile Technology Control Regimefernandocwrocha-1No ratings yet
- Fall 2023 MATH 39100 Final Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesFall 2023 MATH 39100 Final Exam ReviewSimranjit SinghNo ratings yet
- United States v. Gerard Valmore Brown, A/K/A Blackie, A/K/A Gerald Kennedy, United States of America v. Melvin Sanders, A/K/A Pops, United States of America v. Andre Simpson, 76 F.3d 376, 4th Cir. (1996)Document5 pagesUnited States v. Gerard Valmore Brown, A/K/A Blackie, A/K/A Gerald Kennedy, United States of America v. Melvin Sanders, A/K/A Pops, United States of America v. Andre Simpson, 76 F.3d 376, 4th Cir. (1996)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- English Essay Bros Before HosDocument5 pagesEnglish Essay Bros Before HosAndrés I. Rivera33% (3)
- Ignou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19Document7 pagesIgnou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19NEW THINK CLASSES100% (1)
- Carbo GelDocument2 pagesCarbo Gelyehia sayedNo ratings yet
- Matlab: 'HZ Sine Wave To 20Hz Square Wave ConversionDocument10 pagesMatlab: 'HZ Sine Wave To 20Hz Square Wave ConversionSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- Flogocid Cream - Google SearchDocument1 pageFlogocid Cream - Google SearchAyesha SohailNo ratings yet
- Data SufficiencyDocument7 pagesData SufficiencySaurav BhasinNo ratings yet
- Mental Health InventoryDocument7 pagesMental Health InventoryALi Sarmad100% (1)
- Bhopal Disaster: Too LongDocument5 pagesBhopal Disaster: Too LongrevathisudhaNo ratings yet
- Ud 6 Naturales 2º - Tools and MachinesDocument27 pagesUd 6 Naturales 2º - Tools and MachinesLola FrancoNo ratings yet
- ACP1withsolution 16303 16301873391Document23 pagesACP1withsolution 16303 16301873391Arman DehuriNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan-Badminton Jenna Maceachen: Subject Area Grade Level Topic Length of Unit (Days)Document8 pagesUnit Plan-Badminton Jenna Maceachen: Subject Area Grade Level Topic Length of Unit (Days)api-507324305No ratings yet
- Concept NoteDocument4 pagesConcept NoteAfanie Mae Romero EstepaNo ratings yet
- Secrets of A Millionaire Magician DeluxeDocument480 pagesSecrets of A Millionaire Magician DeluxelautaroNo ratings yet
- Sexual Orientation Sexuality Wiki Fandom PDFDocument1 pageSexual Orientation Sexuality Wiki Fandom PDFAngus FieldingNo ratings yet
- Ipc 2581BDocument9 pagesIpc 2581BlaxenovNo ratings yet
- Appserver Job - LogDocument1,225 pagesAppserver Job - LogThiago Ximenes LopesNo ratings yet
- Notes in Criminal SociologyDocument8 pagesNotes in Criminal SociologyWevinneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 ReviewDocument10 pagesChapter 23 ReviewThanat MilinthachindaNo ratings yet
- Module IDocument14 pagesModule IDianna Rose BelenNo ratings yet