Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsRoots
Roots
Uploaded by
Ellah GutierrezRoots have several important functions including anchoring the plant, absorbing water and nutrients from the soil, storing starch and water, and producing hormones. There are two main types of roots - taproots and adventitious roots. Taproots have a main root with smaller branch roots and are better for anchorage, while adventitious roots can form from other plant organs.
The internal structure of roots consists of several zones. The root tip contains the root cap which covers and protects the underlying meristematic tissue. Behind this is the root apical meristem where cell division occurs. In the zone of cell elongation, cells expand through water uptake into their vacuoles. Further back is the zone of cell maturation where cells differentiate and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- LeavesDocument3 pagesLeavesEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument30 pagesPlantsRanin, Manilac Melissa SNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.the Anatomical Regions of A Plant BodyDocument7 pagesLesson 2.the Anatomical Regions of A Plant BodyMark Allen L. VicenteNo ratings yet
- Botany RootsDocument6 pagesBotany RootsKrianne Chris DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Andamun Tle106 ReportDocument34 pagesAndamun Tle106 ReportNaharia RangirisNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document10 pagesGeneral Biology 2kristineNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Week 1 2 q4Document12 pagesReviewer Week 1 2 q4Jayce BanesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pagesChapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)FITRINESSA IBOLNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions in Plants: Roots, Stems, and LeavesDocument32 pagesStructures and Functions in Plants: Roots, Stems, and LeavesDanielle AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- Plant Form and FunctionDocument32 pagesPlant Form and FunctionPaula SanicoNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions in PlantsDocument32 pagesStructures and Functions in PlantsAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Lecture NotesDocument24 pagesSupplementary Lecture NotesAntonette OngNo ratings yet
- Topic 2a Agr3101Document40 pagesTopic 2a Agr3101Sleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Discussion IIDocument64 pagesPost Lab Discussion IIJeli Mae Ysabel PerezNo ratings yet
- Plant Propagation by Adam PDFDocument99 pagesPlant Propagation by Adam PDFHusna Fatima EprilianNo ratings yet
- Roots: Functions, Forms, and RegionsDocument17 pagesRoots: Functions, Forms, and RegionsJoe marie BotioNo ratings yet
- 2 General Biology 2 - Parts of The Plants HDocument57 pages2 General Biology 2 - Parts of The Plants HBLESSIE MARIE ACADEMIANo ratings yet
- 528211336-2-General-Biology-2-Part PlantsDocument58 pages528211336-2-General-Biology-2-Part PlantsPeter MascarenhasNo ratings yet
- Bio - LT2 Reviewer (Plant Leaf)Document2 pagesBio - LT2 Reviewer (Plant Leaf)AnnaV2493No ratings yet
- 1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pages1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Guru temp id-04 for Sekolah-8252 Moe100% (1)
- Plants MorphologyDocument3 pagesPlants MorphologyNovilyn VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsJigyansa DashNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Botany Lab - FINALS 1Document18 pagesReviewer Botany Lab - FINALS 1Ordinary GuitaristNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument12 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsTamal NayakNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument26 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsfidhavfathimaNo ratings yet
- BASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 2Document7 pagesBASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 2Polee SheaNo ratings yet
- Botany RootsDocument49 pagesBotany RootsCudal, Estephanie RoseNo ratings yet
- Vegetative Structures and Their Functions: RootsDocument5 pagesVegetative Structures and Their Functions: RootsJohn Francis FernandezNo ratings yet
- The Stem and LeavesDocument2 pagesThe Stem and LeavesMaria Vanessa SagarioNo ratings yet
- 5-Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument15 pages5-Morphology of Flowering PlantsVasant Kumar VarmaNo ratings yet
- Roots: Members: Albert Escober Ervin Joseph Flores Aldrin ErminoDocument16 pagesRoots: Members: Albert Escober Ervin Joseph Flores Aldrin ErminoJnll JstnNo ratings yet
- Roots Basic BotanyDocument25 pagesRoots Basic BotanyManjunath Ajanal100% (1)
- Morphology of PlantsDocument58 pagesMorphology of PlantsRishikesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Science BotanyDocument6 pagesScience BotanybalagbaganjoymargaretNo ratings yet
- Plant PropagationDocument4 pagesPlant PropagationChryselleNo ratings yet
- SN Chapter 3Document90 pagesSN Chapter 3Mohd Razin F2025No ratings yet
- How The Plant SurviveDocument16 pagesHow The Plant SurvivedhonaNo ratings yet
- Root Meristem, Root Cap, and RootDocument23 pagesRoot Meristem, Root Cap, and RootJulian ManongdoNo ratings yet
- Botany 101Document7 pagesBotany 101Gladdin ChloeNo ratings yet
- L4-Stem MorphologyDocument57 pagesL4-Stem MorphologySleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Propagação de Plantas (Inglês)Document99 pagesPropagação de Plantas (Inglês)Geremias AraujoNo ratings yet
- Botany StemDocument36 pagesBotany Stemartadiel28No ratings yet
- 1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi) (2) Black and WhiteDocument96 pages1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi) (2) Black and Whiterivera hutchNo ratings yet
- Muntinlupa National High School Tunasan AnnexDocument6 pagesMuntinlupa National High School Tunasan AnnexShaine DelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants: The RootDocument14 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants: The RootbOKALNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy and MorphologyDocument85 pagesPlant Anatomy and MorphologyHarinder Kaur100% (1)
- Main Function of LeavesDocument3 pagesMain Function of LeavesAndrea AnoverNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and GrowthDocument3 pagesPlant Structure and GrowthCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Translocation in PlantsDocument39 pagesAbsorption and Translocation in PlantsChelsie Fae SantosNo ratings yet
- P3 SC NotesDocument3 pagesP3 SC NotesTollerNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Vegetative Organs of A Seed Plant: Root, Stem and LeavesDocument13 pagesStructure and Functions of The Vegetative Organs of A Seed Plant: Root, Stem and Leaveskarl riveraNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants: 1. Root 2. Stem 3. Leaf 4. Flower 5. Fruit 6. SeedDocument52 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants: 1. Root 2. Stem 3. Leaf 4. Flower 5. Fruit 6. SeedPrasanth Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Structure: Plant Form and FunctionDocument12 pagesStructure: Plant Form and FunctionPhilippines QatarNo ratings yet
- Topic 2B Agr3101Document52 pagesTopic 2B Agr3101Sleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Chapter III. The Nature and Composition of PlantsDocument70 pagesChapter III. The Nature and Composition of PlantsJhunell Juan100% (3)
- Project PlantsDocument21 pagesProject Plantsapi-239496035No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument52 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Tissue FruitsDocument78 pagesTissue FruitsAbegail SerenoNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 GenBio2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet 1 GenBio2Sean MatuguinasNo ratings yet
- LeavesDocument3 pagesLeavesEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Regional Trial Court: Menor, Rose Anne GDocument8 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Regional Trial Court: Menor, Rose Anne GEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Movement-Rigid Strong Bones Is Well Suited ForDocument7 pagesMovement-Rigid Strong Bones Is Well Suited ForEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Physiology & Anatomy Nervous System: MuscleDocument2 pagesPhysiology & Anatomy Nervous System: MuscleEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
Roots
Roots
Uploaded by
Ellah Gutierrez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesRoots have several important functions including anchoring the plant, absorbing water and nutrients from the soil, storing starch and water, and producing hormones. There are two main types of roots - taproots and adventitious roots. Taproots have a main root with smaller branch roots and are better for anchorage, while adventitious roots can form from other plant organs.
The internal structure of roots consists of several zones. The root tip contains the root cap which covers and protects the underlying meristematic tissue. Behind this is the root apical meristem where cell division occurs. In the zone of cell elongation, cells expand through water uptake into their vacuoles. Further back is the zone of cell maturation where cells differentiate and
Original Description:
botany
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRoots have several important functions including anchoring the plant, absorbing water and nutrients from the soil, storing starch and water, and producing hormones. There are two main types of roots - taproots and adventitious roots. Taproots have a main root with smaller branch roots and are better for anchorage, while adventitious roots can form from other plant organs.
The internal structure of roots consists of several zones. The root tip contains the root cap which covers and protects the underlying meristematic tissue. Behind this is the root apical meristem where cell division occurs. In the zone of cell elongation, cells expand through water uptake into their vacuoles. Further back is the zone of cell maturation where cells differentiate and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesRoots
Roots
Uploaded by
Ellah GutierrezRoots have several important functions including anchoring the plant, absorbing water and nutrients from the soil, storing starch and water, and producing hormones. There are two main types of roots - taproots and adventitious roots. Taproots have a main root with smaller branch roots and are better for anchorage, while adventitious roots can form from other plant organs.
The internal structure of roots consists of several zones. The root tip contains the root cap which covers and protects the underlying meristematic tissue. Behind this is the root apical meristem where cell division occurs. In the zone of cell elongation, cells expand through water uptake into their vacuoles. Further back is the zone of cell maturation where cells differentiate and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
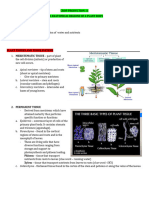
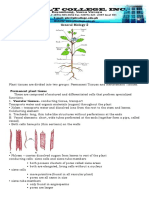
ROOTS
Root- descending axis, usually
underground.
TYPES OF ROOTS
TAPROOT- with main root and smaller
branch roots. Control usually the
growth & development of roots and
better for ANCHORAGE.
Dicots& conifers
Store starch and water
same sized massive roots and
extensive
For absorption
Soil binder
ADVENTITIOUS forms on many
organ of the plant, may grow from the
seed or from nodes.
PROP ROOTS- on branches
BRACE ROOTS- on main stem
BUTTRESS ROOTS- base of
the trunk
CLINGING ROOTS- on the
surface of stems
PRIMARY FUNCTION OF THE
ROOTS
Anchorage
Storage
Absorption
Conduction
Produce hormones
gibberellins, cytokinins
INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE
ROOT
A. ROOTS TIP- cells at the tip
of the root.
a. Root cap- covers the
root & meristematic.
b. Columella- columnar
cells ,5-30 amylopast
responsive to gravity,
SENSE LIGHT AND
PRESSURE by soil
particle.
c. Peripheral cellmeristematic , push the
columella to the side.
d. Secrete MUCIGELpolysaccharides, organic
acid, sugars, vitamins,
enzymes.
a) Protection
b) Lubrication
c) Water absorption
d) Nutrient
absorption
carboxy better ion
intake.
e) Establish
symbiosis
B. ROOT APICAL MERISTEM
a. Quiescent center
behind root cap 500
-1000 inactive cells.
Reservoir to replace
damage cells. Organize
pattern of primary
growth in roots
b. Zone of Divisiondense cytoplasm.
Meristematic, apical
meristem here is sub
terminal due to root cap.
c. Zone of Cellular
Elongation- 4- 10mm
behind the root apical
meristem. Cells
elongated by filling their
vacuole with water. Cells
are quite permeable
deep into roots by
appoplast diffusion.
d. Zone of Cellular
Maturation- 1-5 cm
behind the root tip. Cell
differentiate. Elongated
by filling their vacuole
water.
Behind zone of
nmutation. Consist
1 cell rick no cutin,
covers root expect
root cap from the
protodeerm Sob of
maturation.
You might also like
- LeavesDocument3 pagesLeavesEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument30 pagesPlantsRanin, Manilac Melissa SNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.the Anatomical Regions of A Plant BodyDocument7 pagesLesson 2.the Anatomical Regions of A Plant BodyMark Allen L. VicenteNo ratings yet
- Botany RootsDocument6 pagesBotany RootsKrianne Chris DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Andamun Tle106 ReportDocument34 pagesAndamun Tle106 ReportNaharia RangirisNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document10 pagesGeneral Biology 2kristineNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Week 1 2 q4Document12 pagesReviewer Week 1 2 q4Jayce BanesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pagesChapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)FITRINESSA IBOLNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions in Plants: Roots, Stems, and LeavesDocument32 pagesStructures and Functions in Plants: Roots, Stems, and LeavesDanielle AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- Plant Form and FunctionDocument32 pagesPlant Form and FunctionPaula SanicoNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions in PlantsDocument32 pagesStructures and Functions in PlantsAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Lecture NotesDocument24 pagesSupplementary Lecture NotesAntonette OngNo ratings yet
- Topic 2a Agr3101Document40 pagesTopic 2a Agr3101Sleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Discussion IIDocument64 pagesPost Lab Discussion IIJeli Mae Ysabel PerezNo ratings yet
- Plant Propagation by Adam PDFDocument99 pagesPlant Propagation by Adam PDFHusna Fatima EprilianNo ratings yet
- Roots: Functions, Forms, and RegionsDocument17 pagesRoots: Functions, Forms, and RegionsJoe marie BotioNo ratings yet
- 2 General Biology 2 - Parts of The Plants HDocument57 pages2 General Biology 2 - Parts of The Plants HBLESSIE MARIE ACADEMIANo ratings yet
- 528211336-2-General-Biology-2-Part PlantsDocument58 pages528211336-2-General-Biology-2-Part PlantsPeter MascarenhasNo ratings yet
- Bio - LT2 Reviewer (Plant Leaf)Document2 pagesBio - LT2 Reviewer (Plant Leaf)AnnaV2493No ratings yet
- 1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pages1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Guru temp id-04 for Sekolah-8252 Moe100% (1)
- Plants MorphologyDocument3 pagesPlants MorphologyNovilyn VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsJigyansa DashNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Botany Lab - FINALS 1Document18 pagesReviewer Botany Lab - FINALS 1Ordinary GuitaristNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument12 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsTamal NayakNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument26 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsfidhavfathimaNo ratings yet
- BASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 2Document7 pagesBASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 2Polee SheaNo ratings yet
- Botany RootsDocument49 pagesBotany RootsCudal, Estephanie RoseNo ratings yet
- Vegetative Structures and Their Functions: RootsDocument5 pagesVegetative Structures and Their Functions: RootsJohn Francis FernandezNo ratings yet
- The Stem and LeavesDocument2 pagesThe Stem and LeavesMaria Vanessa SagarioNo ratings yet
- 5-Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument15 pages5-Morphology of Flowering PlantsVasant Kumar VarmaNo ratings yet
- Roots: Members: Albert Escober Ervin Joseph Flores Aldrin ErminoDocument16 pagesRoots: Members: Albert Escober Ervin Joseph Flores Aldrin ErminoJnll JstnNo ratings yet
- Roots Basic BotanyDocument25 pagesRoots Basic BotanyManjunath Ajanal100% (1)
- Morphology of PlantsDocument58 pagesMorphology of PlantsRishikesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Science BotanyDocument6 pagesScience BotanybalagbaganjoymargaretNo ratings yet
- Plant PropagationDocument4 pagesPlant PropagationChryselleNo ratings yet
- SN Chapter 3Document90 pagesSN Chapter 3Mohd Razin F2025No ratings yet
- How The Plant SurviveDocument16 pagesHow The Plant SurvivedhonaNo ratings yet
- Root Meristem, Root Cap, and RootDocument23 pagesRoot Meristem, Root Cap, and RootJulian ManongdoNo ratings yet
- Botany 101Document7 pagesBotany 101Gladdin ChloeNo ratings yet
- L4-Stem MorphologyDocument57 pagesL4-Stem MorphologySleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Propagação de Plantas (Inglês)Document99 pagesPropagação de Plantas (Inglês)Geremias AraujoNo ratings yet
- Botany StemDocument36 pagesBotany Stemartadiel28No ratings yet
- 1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi) (2) Black and WhiteDocument96 pages1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi) (2) Black and Whiterivera hutchNo ratings yet
- Muntinlupa National High School Tunasan AnnexDocument6 pagesMuntinlupa National High School Tunasan AnnexShaine DelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants: The RootDocument14 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants: The RootbOKALNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy and MorphologyDocument85 pagesPlant Anatomy and MorphologyHarinder Kaur100% (1)
- Main Function of LeavesDocument3 pagesMain Function of LeavesAndrea AnoverNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and GrowthDocument3 pagesPlant Structure and GrowthCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Translocation in PlantsDocument39 pagesAbsorption and Translocation in PlantsChelsie Fae SantosNo ratings yet
- P3 SC NotesDocument3 pagesP3 SC NotesTollerNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Vegetative Organs of A Seed Plant: Root, Stem and LeavesDocument13 pagesStructure and Functions of The Vegetative Organs of A Seed Plant: Root, Stem and Leaveskarl riveraNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants: 1. Root 2. Stem 3. Leaf 4. Flower 5. Fruit 6. SeedDocument52 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants: 1. Root 2. Stem 3. Leaf 4. Flower 5. Fruit 6. SeedPrasanth Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Structure: Plant Form and FunctionDocument12 pagesStructure: Plant Form and FunctionPhilippines QatarNo ratings yet
- Topic 2B Agr3101Document52 pagesTopic 2B Agr3101Sleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Chapter III. The Nature and Composition of PlantsDocument70 pagesChapter III. The Nature and Composition of PlantsJhunell Juan100% (3)
- Project PlantsDocument21 pagesProject Plantsapi-239496035No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument52 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Tissue FruitsDocument78 pagesTissue FruitsAbegail SerenoNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 GenBio2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet 1 GenBio2Sean MatuguinasNo ratings yet
- LeavesDocument3 pagesLeavesEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Regional Trial Court: Menor, Rose Anne GDocument8 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Regional Trial Court: Menor, Rose Anne GEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Movement-Rigid Strong Bones Is Well Suited ForDocument7 pagesMovement-Rigid Strong Bones Is Well Suited ForEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Physiology & Anatomy Nervous System: MuscleDocument2 pagesPhysiology & Anatomy Nervous System: MuscleEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet