Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notebook 8
Notebook 8
Uploaded by
api-3407319000 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesThe document discusses different types of x-ray machine power supplies:
Single phase is the least efficient with 100% power loss and 60 pulses per second. Full wave rectification is more efficient at 100% power loss and uses both halves of the AC cycle for 120 pulses per second. Three phase 6-pulse has 4% power loss and 87-90% of x-rays at peak voltage, while three phase 12-pulse has <1% power loss and 96.5-100% of x-rays at peak voltage. High frequency supplies have <1% power loss, 1000 pulses per second using AC and DC, and are more efficient, less costly and smaller than 60 Hz generators.
Original Description:
Original Title
notebook 8
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of x-ray machine power supplies:
Single phase is the least efficient with 100% power loss and 60 pulses per second. Full wave rectification is more efficient at 100% power loss and uses both halves of the AC cycle for 120 pulses per second. Three phase 6-pulse has 4% power loss and 87-90% of x-rays at peak voltage, while three phase 12-pulse has <1% power loss and 96.5-100% of x-rays at peak voltage. High frequency supplies have <1% power loss, 1000 pulses per second using AC and DC, and are more efficient, less costly and smaller than 60 Hz generators.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesNotebook 8
Notebook 8
Uploaded by
api-340731900The document discusses different types of x-ray machine power supplies:
Single phase is the least efficient with 100% power loss and 60 pulses per second. Full wave rectification is more efficient at 100% power loss and uses both halves of the AC cycle for 120 pulses per second. Three phase 6-pulse has 4% power loss and 87-90% of x-rays at peak voltage, while three phase 12-pulse has <1% power loss and 96.5-100% of x-rays at peak voltage. High frequency supplies have <1% power loss, 1000 pulses per second using AC and DC, and are more efficient, less costly and smaller than 60 Hz generators.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
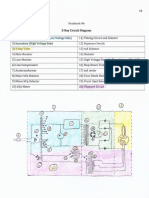
Notebook #8 Revisions
20
Notebook #B
Single Phase:
End #phrrtont extrp bub.q
S
Lar+
c,Q
d^eNnssxrt ir5
tttb|
trd of,+,&e
+l^
t:
Crrce rl'k
g+h 't-rh
llltllitlt
t&h
^+h
1t+z--+l
:
(J
o. I second,
[(rHz)
Tirne
Half WaVe:
Least efficient with 100%o power loss/ripple. X-ray output is
pulsating at 60 x-ray pulses/second. The downsides are it wastes half the power
supply and requires twice the exposure time of full wave rectification.
FUll WaVl
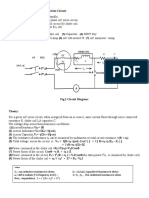
input enerry more efficientlywith 10070 power loss/ripple.
Uses the full AC rycle with a minimum of 4 rectifiers placed into the circuit. The 1$
part uses the positive part of AC cycle and 2"d pair uses the negative part of AC
rycle. It flips the negative half to the positive side. It sends an entire electric
wave/current through the x-ray tube. Exposure time is halved with 120 pulses/sec.
7/3 of beam is not useful.
Uses
2L
Notebook #8 Revisions
Three Phase 6-pulse:
1,4orb
power loss/ripple with 87-7000/6 of x-rays produced are at kV peak Has at least 6
Three Phase l2-pulse:
power loss/ripple with 96.5-L00o/o of x-rays produced are at peak kV. Has at least 12
rectifi ers. 720 pulses/second.
4o/o
High Frequency:
use AC and DC power
<Lo/opower loss/ripple with 1000 pulses/second, Creates a pulsed DC currentwith slight
power. Advantages are t}tat it is more efficient than 60 Hz generators, it is less costly, and
smaller.
You might also like
- Lab-Report On DC Power Supply PDFDocument4 pagesLab-Report On DC Power Supply PDFakongo gordon80% (5)
- Square Wave GeneratorDocument6 pagesSquare Wave GeneratorRahul KunduNo ratings yet
- Half-Wave Rectifier: Programme: Subject Group MembersDocument22 pagesHalf-Wave Rectifier: Programme: Subject Group MembersBhagyalaxmi patilNo ratings yet
- Lab Session: 3: Demonstrate The Behavior of A Silicon Diode in Half Wave RectifierDocument7 pagesLab Session: 3: Demonstrate The Behavior of A Silicon Diode in Half Wave RectifierFatima AmjadNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab: (Experiment No:1)Document9 pagesElectronics Lab: (Experiment No:1)satyaki kunduNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument8 pagesBasic Electronicsengineer.chiranjitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9.Pptx FEEDocument9 pagesChapter 9.Pptx FEEk tine23No ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier Circuits Part (1-A) : Experiment: DiodeDocument13 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier Circuits Part (1-A) : Experiment: DiodeCatalina ZelayaNo ratings yet
- PoEC 18 RLC Circuits and ResonanceDocument52 pagesPoEC 18 RLC Circuits and ResonanceKrishnaveni Subramani SNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Power SuppliesDocument7 pagesCalculation of Power SuppliesAnonymous DjWqKpZ1No ratings yet
- FE Exam Review2011Document53 pagesFE Exam Review2011Juan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Tugas Ke 3 Elka TelkomDocument5 pagesTugas Ke 3 Elka TelkomAzHar HrNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Class C Amplifier PDFDocument2 pagesLab 1 Class C Amplifier PDFআব্দুল্লাহ আল ইমরান100% (1)
- Chilewa Exp No. 06Document21 pagesChilewa Exp No. 06frank samndomiNo ratings yet
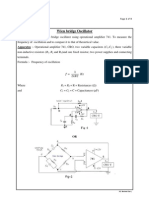
- Operational Amplifier 741 As Wein Bridge Oscillator 1Document4 pagesOperational Amplifier 741 As Wein Bridge Oscillator 1Deepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Eee 04Document10 pagesEee 04farah.hoque.cseNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document40 pagesUnit 3Venkat ChadalavadaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Power System Analysis and Design Si Edition 6Th Edition Glover Overbye Sarma 130563618X 9781305636187 Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesTest Bank For Power System Analysis and Design Si Edition 6Th Edition Glover Overbye Sarma 130563618X 9781305636187 Full Chapter PDFthomas.pelosi630100% (10)
- Power System Analysis and Design SI Edition 6th Edition Glover Overbye Sarma 130563618X Test BankDocument14 pagesPower System Analysis and Design SI Edition 6th Edition Glover Overbye Sarma 130563618X Test Bankwanda100% (30)
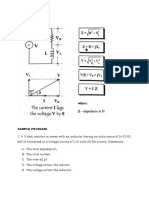
- LCR Circuits: Learning Objectives of This Experiment Is That Students Will Be Able ToDocument6 pagesLCR Circuits: Learning Objectives of This Experiment Is That Students Will Be Able ToAryan sahuNo ratings yet
- Exp 9Document6 pagesExp 9abdelmalekhadiakNo ratings yet
- Wein Bridge OscillatorDocument11 pagesWein Bridge OscillatorDimas RioNo ratings yet
- Astable MultivibratorDocument4 pagesAstable MultivibratorWaldo PulancoNo ratings yet
- Mulvaney Graham 352 Lab 1Document6 pagesMulvaney Graham 352 Lab 1api-125239608No ratings yet
- Rectifiers and FiltersDocument13 pagesRectifiers and FiltersAko si GianNo ratings yet
- Eee DepartmentDocument11 pagesEee DepartmentAriston EtormaNo ratings yet
- CT SizingDocument62 pagesCT SizingNoli OtebaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report of Analogue ElectronicDocument8 pagesLab Report of Analogue ElectronicKing EverestNo ratings yet
- EDC QB With AnswersDocument119 pagesEDC QB With Answersharshavardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Exp3 (Ac Series)Document2 pagesExp3 (Ac Series)Deepankar Synthesizer Playist DspNo ratings yet
- 44968911-Exp-1 PSIMDocument35 pages44968911-Exp-1 PSIMJorge CasaliniNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Operation PDFDocument11 pagesRectifier Operation PDFaliNo ratings yet
- Antenna 2Document14 pagesAntenna 2xbahoaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Power of Power System Analysis and Design 6Th Edition Glover Overbye Sarma 1305632133 9781305632134 Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesTest Bank For Power of Power System Analysis and Design 6Th Edition Glover Overbye Sarma 1305632133 9781305632134 Full Chapter PDFthomas.pelosi630100% (12)
- Practical Transformer Sample ProblemDocument40 pagesPractical Transformer Sample ProblemJosua Bretania100% (1)
- UNIT 1-DC Power SupplyDocument30 pagesUNIT 1-DC Power SupplyMuizz ZainolNo ratings yet
- Analog Communications Lab ManualDocument61 pagesAnalog Communications Lab ManualSriLakshmi RaheemNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document6 pagesExperiment 5VHIMBER GALLUTANNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Rectifier Circuits: Chapter 3. Diodes and RectifiersDocument16 pages3.4 Rectifier Circuits: Chapter 3. Diodes and RectifiersAlan PakarNo ratings yet
- Analysis, Design and Implementation of An Active Clamp Flyback Converter PDFDocument6 pagesAnalysis, Design and Implementation of An Active Clamp Flyback Converter PDFDeniz UzelNo ratings yet
- Multivibrator Circuit Types: Ray MarstonDocument21 pagesMultivibrator Circuit Types: Ray MarstonBóza GyörgyNo ratings yet
- ADE - Exp 1Document15 pagesADE - Exp 1Dhruv pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Lab Title:: A Full Wave Rectifier Using Controlled and Uncontrolled DiodesDocument6 pagesLab Title:: A Full Wave Rectifier Using Controlled and Uncontrolled DiodesSAEED ULLAHNo ratings yet
- Half-Wave and Full-Wave RectDocument11 pagesHalf-Wave and Full-Wave RectSunghoonie KangNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Lab ReportDocument21 pagesExperiment 1 Lab ReportOisin MaguireNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectification: EE241 (Active Device I) Third Laboratory ExperimentDocument8 pagesFull Wave Rectification: EE241 (Active Device I) Third Laboratory ExperimentNasser DjeradaNo ratings yet
- Linear & Switching Voltage Regulator HandbookDocument6 pagesLinear & Switching Voltage Regulator HandbookSanti RuasNo ratings yet
- EDI LAb ManualDocument33 pagesEDI LAb ManualMadangle JungleNo ratings yet
- RL Series and RC Series CircuitDocument6 pagesRL Series and RC Series CircuitJomari Carl Rafal MansuetoNo ratings yet
- Basic Rectifier CircuitsDocument8 pagesBasic Rectifier CircuitssensitivesensesNo ratings yet
- CT SizingDocument62 pagesCT SizingMohamed TalebNo ratings yet
- Rectifying CircuitsDocument13 pagesRectifying Circuitssina981No ratings yet
- ECE334 Lab3Document5 pagesECE334 Lab3star89690% (1)
- Diode Voltage DoublerDocument2 pagesDiode Voltage DoublerPrashant GuptaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Experiment 4Document13 pagesElectronic Devices Experiment 4ArvinALNo ratings yet
- EDCM2Document19 pagesEDCM2yanith kumarNo ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument34 pagesFormulaedineshvhavalNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)No ratings yet
- Notebook 10Document12 pagesNotebook 10api-340731900No ratings yet
- Notebook 12Document3 pagesNotebook 12api-340731900No ratings yet
- Notebook 9Document4 pagesNotebook 9api-340731900No ratings yet
- Notebook 7Document5 pagesNotebook 7api-340731900No ratings yet
- Notebook 1Document3 pagesNotebook 1api-340731900No ratings yet
- Notebook 6Document5 pagesNotebook 6api-340731900No ratings yet
- Notebook 14Document2 pagesNotebook 14api-340731900No ratings yet
- Notebook 13Document3 pagesNotebook 13api-340731900No ratings yet
- Notebook 11Document2 pagesNotebook 11api-340731900No ratings yet
- Notebook 6Document1 pageNotebook 6api-340731900100% (1)
- Notebook 9Document1 pageNotebook 9api-340731900No ratings yet
- Notebook 3Document2 pagesNotebook 3api-340731900No ratings yet