Professional Documents
Culture Documents
November 22, 2016
November 22, 2016
Uploaded by
ashley goodmanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
November 22, 2016
November 22, 2016
Uploaded by
ashley goodmanCopyright:
Available Formats
November 22, 2016
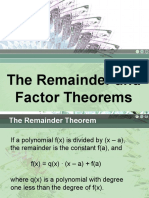
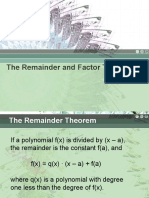
f(x)/g(x)=q(x)+r(x)/g(x)
example f(x)=x^2+ x -12= (x-3)(x+4)
f(3)=0
f(-4)=0
example f(x)=x^3-4x^2+2x-5 check if x-3 is a factor
f(3)=-8
f(x)=(x-c)q(x)+R
1. Factor Theorem: Let f be a polynomial function. Then x-c is a factor of f(x) if
and only if f(c)=0
2. What is the max number of zeros possible???????
Answer: the degree of the polynomial
3. Decartes' Rule of Signs:
the number of positive real zeros of f either equals the number of variations in
sign of the nonzero coefficients of f(x) or two less.
5x^4+2x^2-6x-5
Answer: 1 possible positive zero
the number of negative real zeros of f either equals the number of variations
in the sign of nonzero coefficients of f(-x) or two less
f(-x)= 5x^4+2x^2 +6x-5
Answer: 1 possible negative zero
4. How to figure out the possible zeros or factors????
Look at the coefficient in front of the variable with the highest degree
q=factors of ^^^ 1, 5
Look at the constant
p=factors of ^^^^^ 1, 5
All the possible factors of f(x)=+ p/q = + 5/1, + 5/5, + 1/5, + 1/1
HW page 261 1-45 (odd)
1-10 Use the Factor theorem to determine whether x-c is a factor of f(x)
2. f(x) = -4x^3+5x^2+ 8
; x+3
f(-3)=161 NO NOT A FACTOR BECAUSE WE HAVE A NUMBER AND NOT
0 THIS MEANS THE REMAINDER IS 161
11-22, tell the maximum number of zeros that each polynomial function may
have. Then, use Decartes' rule of signs to determine how many positive and
how many negative zeros each polynomial may have.
f(x)= -3x^5+4x^4+2
Maximum possible zeros: 5
Positive zeros: 1
Negative zeros: 0 possible negative zeros
f(-x)= 3x^5 + 4x^4+ 2
23-34 List the potential rational zeros of each polynomial function. Do not
attempt to find the zeros.
f(x)=-4x^3+x^2+x+6
p=Factors of 6 = 1, 2, 3, 6
q= factors of 4 = 1, 2, 4
p/q= + 1/1, 2/1, 3/1, 6/1, 1/2, 2/2, 3/2, 6/2, 1/4, 2/4, 3/4, 6/4
= +1,+ 2, +3, +6, +1/2, +3/2, +1/4, +3/4
35-46 Use Descartes' Rule of Signs AND the rational zeros theorem to find
all the real zeros of each polynomial function. Use the zeros to FACTOR.
example above: 1 possible positive zero,
either 2 possible negative zeros or 0 negative zeros
f(p/q) to check if it equals 0. If it does equal 0 then use that p/q value to factor
using synthetic division. Page 261 1-45(odd)
You might also like
- Polynomials ProjectDocument21 pagesPolynomials ProjectDhananjay57% (7)
- L8 Polynomial FunctionsDocument23 pagesL8 Polynomial FunctionsFlorence FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Chapter 8Document31 pagesAlgebra 2 Chapter 8Nguyễn TrâmNo ratings yet
- Section 2.5 Zeros of Polynomial FunctionsDocument22 pagesSection 2.5 Zeros of Polynomial FunctionsdavogezuNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Real Zeros of PolynomialDocument35 pages2.3 Real Zeros of PolynomialYukiC123No ratings yet
- Polynomials: Nur Liyana BT Za'Im Siti Izzati Dyanah BT Zainal Wan Izzah KamilahDocument39 pagesPolynomials: Nur Liyana BT Za'Im Siti Izzati Dyanah BT Zainal Wan Izzah KamilahLiyana Za'imNo ratings yet
- The Remainder, Zeroes & Factor TheoremsDocument27 pagesThe Remainder, Zeroes & Factor TheoremsKirtikamalarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Algeb ProjectDocument17 pagesAdvanced Algeb ProjectdiomNo ratings yet
- Zeros of Polynomial FunctionDocument27 pagesZeros of Polynomial FunctionJulianneNo ratings yet
- Zeros of Polynomial FunctionDocument27 pagesZeros of Polynomial FunctionJulianneNo ratings yet
- Polynomials 2Document21 pagesPolynomials 2Akash MahalikNo ratings yet
- Math 10.3Document14 pagesMath 10.3bea sailNo ratings yet
- SsDocument3 pagesSscristinejoydalag3No ratings yet
- Spcg6e PPT 4 1Document63 pagesSpcg6e PPT 4 1api-334707195No ratings yet
- Remainder and Factor TheoremDocument17 pagesRemainder and Factor Theorembruhwhatdoievenwritenaymore123No ratings yet
- Submitted By:-Archit Matta of Class XDocument18 pagesSubmitted By:-Archit Matta of Class XLovish MattaNo ratings yet
- The Zeros of A PolynomialDocument21 pagesThe Zeros of A PolynomialutpNo ratings yet
- Remainderfactortheorem PPT Math-10Document17 pagesRemainderfactortheorem PPT Math-10Reply NoreplyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10Document4 pagesMathematics 10Lance Akizha PrintshopNo ratings yet
- The Remainder and Factor TheoremsDocument17 pagesThe Remainder and Factor TheoremsLenny Rose MoritoNo ratings yet
- Homework 5.4-5.5 Factoring and Long Division WSDocument2 pagesHomework 5.4-5.5 Factoring and Long Division WSstephanie karminiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Polynomial FunctionsDocument29 pagesModule 1 - Polynomial FunctionsHazel Clemente Carreon100% (1)
- Remainder and Factor TheoremDocument16 pagesRemainder and Factor TheoremNestor Bong Bordaje NemeñoNo ratings yet
- Part 3 The Rational Root TheoremDocument7 pagesPart 3 The Rational Root TheoremJimmy AbalosNo ratings yet
- Descartes' Rule of SignsDocument21 pagesDescartes' Rule of SignsChona ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Remainderfactortheorem PPT Alg2Document15 pagesRemainderfactortheorem PPT Alg2Jane OlescoNo ratings yet
- PC Polynomial ZerosDocument15 pagesPC Polynomial ZerosHector R.100% (1)
- The Remainder and Factor TheoremsDocument15 pagesThe Remainder and Factor TheoremsKristine HensonNo ratings yet
- 2GP Mathematics - November - Peer Tutoring MaterialDocument40 pages2GP Mathematics - November - Peer Tutoring MaterialCedrick Nicolas ValeraNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Polynomials 8.3 Partial FractionsDocument71 pages8.1 Polynomials 8.3 Partial FractionsZakiah Tuan MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Patricia Tomboc (Module 7-Week 7 Answer Sheet)Document8 pagesPatricia Tomboc (Module 7-Week 7 Answer Sheet)Patricia TombocNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Factoring PolynomialsDocument13 pagesMathematics: Factoring PolynomialsPrecious Elaine RosalesNo ratings yet
- Polynomials & Linear Equations MLDocument21 pagesPolynomials & Linear Equations MLmedhansh.sinha151107No ratings yet
- Basics of Polynomials: Coefficients, Degree, and Leading TermsDocument6 pagesBasics of Polynomials: Coefficients, Degree, and Leading Termsr1u2No ratings yet
- Descartes Rule of SignsDocument4 pagesDescartes Rule of Signsfrancel floresNo ratings yet
- ch12 PDFDocument53 pagesch12 PDFcathy100% (1)
- Lecture 1 of 7Document29 pagesLecture 1 of 7Joey Chow C ANo ratings yet
- Random Variables 2019Document25 pagesRandom Variables 2019Clarence Jester CustorioNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 PT 3 Factor PolynomialsDocument9 pagesUnit 3 PT 3 Factor Polynomialssprinklesdb16No ratings yet
- Polynomial Function: PX Ax Ax Ax AxaDocument15 pagesPolynomial Function: PX Ax Ax Ax AxautpNo ratings yet
- ConfidentialDocument8 pagesConfidentialhannahjoymachucateberioNo ratings yet
- Calg t3 4Document23 pagesCalg t3 4api-261379705No ratings yet
- 2 Differentiation 1 SlidesDocument102 pages2 Differentiation 1 Slidesmseconroy84No ratings yet
- Upper and Lower BoundsDocument12 pagesUpper and Lower BoundsJonard G. TrajanoNo ratings yet
- Descartes Rule of SignsDocument1 pageDescartes Rule of SignsArindam GaraiNo ratings yet
- Module 11 (Polynomial Equations) : Learning Activity Sheet in Mathematics 10Document2 pagesModule 11 (Polynomial Equations) : Learning Activity Sheet in Mathematics 10Jeanie PeNo ratings yet
- Roots & Zeros of PolynomialsDocument31 pagesRoots & Zeros of PolynomialsMohamed RafatNo ratings yet
- Solving Polynomial SystemsDocument164 pagesSolving Polynomial SystemsChristophe LauwerysNo ratings yet
- Graphing Polynomial FunctionsDocument19 pagesGraphing Polynomial Functionshcnè dynnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Four PolynomialsDocument3 pagesLesson Four PolynomialsT-girlNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Remainder and Factor TheoremDocument7 pagesLesson 5 - Remainder and Factor TheoremAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Remainder TheoremDocument21 pagesRemainder TheoremReinabelle Marfil MarquezNo ratings yet
- MAT097 CHP - 1 - POLYNOMIALS (Without - Solution)Document12 pagesMAT097 CHP - 1 - POLYNOMIALS (Without - Solution)Anis BuxNo ratings yet
- Factor Theorem Grade 10Document9 pagesFactor Theorem Grade 10Asif SoomroNo ratings yet
- B1 G. Factor Theorem, Remainder Theorem, Binomial TheoremDocument15 pagesB1 G. Factor Theorem, Remainder Theorem, Binomial TheoremMarianne Lou PalomarNo ratings yet
- Shapiro Inequality PDFDocument13 pagesShapiro Inequality PDFPippo MiriNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet