Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RUmus Passive Voice
RUmus Passive Voice
Uploaded by
Elma JelenatorCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ملخص شامل لدروس bac PDFDocument11 pagesملخص شامل لدروس bac PDFAnonymous wwD1u4TmGh67% (9)
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument3 pagesActive and Passive Tenses Chartrondick93% (29)
- Contribuciones de Leontief A La EconomíaDocument24 pagesContribuciones de Leontief A La EconomíaMargarita SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- InDesign and XML Tech RefDocument28 pagesInDesign and XML Tech RefMarius TNo ratings yet
- Simple Present and Simple PastDocument5 pagesSimple Present and Simple PastRaymond Sabanal BanquirigoNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument11 pagesActive and Passive Tenses ChartMarco GonzalezNo ratings yet
- The Passive Voice. Tenses ChartDocument5 pagesThe Passive Voice. Tenses Chartlondonfaidel6511No ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument4 pagesActive and Passive Tenses ChartchandraNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument5 pagesActive and Passive Tenses ChartAishhwarya PriyaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice ChartDocument15 pagesActive and Passive Voice ChartYoussef BoulaghlaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice ChartDocument3 pagesActive and Passive Voice ChartDea ZarynaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice Chart 11Document3 pagesActive and Passive Voice Chart 11Ryan Yudhistyanto PutroNo ratings yet
- Unit 7. Passives. Tenses ChartDocument0 pagesUnit 7. Passives. Tenses ChartunidienteNo ratings yet
- 8242 Active and Passive Voice ChartDocument3 pages8242 Active and Passive Voice ChartGabriela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument7 pagesActive and Passive Voiceazadali735323No ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument5 pagesActive and Passive Tenses ChartvenkteshNo ratings yet
- Grammar ChartsDocument7 pagesGrammar ChartsHashim Raza Siyal100% (2)
- Active and Passive Voice Chart 11Document3 pagesActive and Passive Voice Chart 11Inmaculada SenovillaNo ratings yet
- Passive Sentences: Ajvilches. 6/ 2009Document7 pagesPassive Sentences: Ajvilches. 6/ 2009abingvNo ratings yet
- Passive & Verb Tenses PDFDocument8 pagesPassive & Verb Tenses PDFlovely callsNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument5 pagesActive and Passive Tenses ChartManivannan SsnNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tense ChartDocument4 pagesActive and Passive Tense ChartAna Paula MedinaNo ratings yet
- Am/is/are + Being + Past Participle Q Was/were + Being + Past ParticipleDocument3 pagesAm/is/are + Being + Past Participle Q Was/were + Being + Past ParticipleBen HussaNo ratings yet
- Grammar HandoutDocument17 pagesGrammar HandoutJakir JackNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be in The PastDocument12 pagesVerb To Be in The PastAdalberto Jiménez100% (1)
- Passive VoiceDocument11 pagesPassive VoiceMtn EgnNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument3 pagesActive and Passive Tenses Chartabida jamaliNo ratings yet
- B2.1 GrammarDocument35 pagesB2.1 Grammarbarbaragarcia350No ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice Lecture 7Document38 pagesActive and Passive Voice Lecture 7maheenshaikh119No ratings yet
- Guía InglésDocument7 pagesGuía Inglésangelm.galicia.zNo ratings yet
- Review and ActivitiesDocument15 pagesReview and ActivitiesAnonymous vdUB1vlyNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice 2Document2 pagesPassive Voice 2ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesPassive VoiceCati SofiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Verbs of General UseDocument19 pagesUnit 1 Verbs of General UseRosaury Castro De Luna100% (2)
- AG1 Unit 6Document29 pagesAG1 Unit 621antonella05No ratings yet
- General Grammar ReviewDocument7 pagesGeneral Grammar ReviewKimNo ratings yet
- Modals: Going To - Might - May - Can-Could - Must - Should - Have ToDocument47 pagesModals: Going To - Might - May - Can-Could - Must - Should - Have ToghaidaNo ratings yet
- Course OneDocument120 pagesCourse OneRoberto Carlos CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Active Passive (3) YOKIBUDocument5 pagesActive Passive (3) YOKIBUsiddcric264No ratings yet
- Present Perfect-Group 3 - CompressedDocument38 pagesPresent Perfect-Group 3 - CompressedDULCE MP100% (1)
- Blue & Pink Present Tenses PresentationDocument14 pagesBlue & Pink Present Tenses PresentationGisela Cruz RiosNo ratings yet
- Types of QuestionsDocument10 pagesTypes of QuestionsSiti Hayatiwi SriwandariNo ratings yet
- Unit 9-Passives-QUDocument24 pagesUnit 9-Passives-QURw KhNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice TutorialDocument37 pagesPassive Voice TutorialmarNo ratings yet
- How Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Document24 pagesHow Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Noelia Nancy PonceNo ratings yet
- Active Passive: VoiceDocument22 pagesActive Passive: VoiceDominika ZającNo ratings yet
- English Tenses: Simple Past TenseDocument5 pagesEnglish Tenses: Simple Past TenseHasnaoui DiaNo ratings yet
- Universidad de Oriente Núcleo de AnzoáteguiDocument17 pagesUniversidad de Oriente Núcleo de AnzoáteguiHelen HernandezNo ratings yet
- Extra Review Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesExtra Review Passive VoiceBruno SenraNo ratings yet
- Voz Pasiva Worksheet SAE 22-10-4M PGDocument5 pagesVoz Pasiva Worksheet SAE 22-10-4M PGFda Correa ENo ratings yet
- 1 - Class Notes-HU 101 - (Module 1-Grammar)Document15 pages1 - Class Notes-HU 101 - (Module 1-Grammar)Sukhwinder SinghNo ratings yet
- The Passive Voice: Active I Drank Two Cups of CoffeeDocument3 pagesThe Passive Voice: Active I Drank Two Cups of Coffeeshahzeb khanNo ratings yet
- Assertive To ImperativeDocument3 pagesAssertive To ImperativeAdnanNo ratings yet
- Research Work On Exam TopicsDocument10 pagesResearch Work On Exam Topicsemely gilNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: Verb Modality Germanic LanguagesDocument8 pagesModal Verbs: Verb Modality Germanic LanguagesavdvNo ratings yet
- Ingles III - Appendixes - Unidad IIIDocument9 pagesIngles III - Appendixes - Unidad IIIJorge Schellius OrtizNo ratings yet
- Rules: So - Neither - EitherDocument3 pagesRules: So - Neither - EitherVeronica Morales MirandaNo ratings yet
- A1a2 RequirementsDocument4 pagesA1a2 Requirementsnaizabekova.a94No ratings yet
- Jose Cueva. HandbookDocument52 pagesJose Cueva. HandbookJimmi Fabricio Celi Díaz100% (2)
- Spanish for English Speakers: Dictionary English - Spanish: 700+ of the Most Important Words / Vocabulary for Beginners with Useful Phrases to Improve Learning - Level A1 - A2From EverandSpanish for English Speakers: Dictionary English - Spanish: 700+ of the Most Important Words / Vocabulary for Beginners with Useful Phrases to Improve Learning - Level A1 - A2No ratings yet
- GuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarFrom EverandGuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Bisep HSSC-A-2020 StatisticsDocument11 pagesBisep HSSC-A-2020 StatisticsArshad JehanNo ratings yet
- Decomposition of Fundamental Lamb Wave Modes in Complex Metal Structures Using COMSOLDocument8 pagesDecomposition of Fundamental Lamb Wave Modes in Complex Metal Structures Using COMSOLMohammad HarbNo ratings yet
- Com - Pg.game6327838 LogcatDocument53 pagesCom - Pg.game6327838 Logcatfordcannabis07No ratings yet
- Cornwall's Disadvantaged NeighbourhoodsDocument32 pagesCornwall's Disadvantaged NeighbourhoodsNick Wilding100% (2)
- The Iconic Influence of Queen Elizabeth IIDocument2 pagesThe Iconic Influence of Queen Elizabeth IIpatriciasusckind_574No ratings yet
- XHCC S62 enDocument60 pagesXHCC S62 enhambi1986No ratings yet
- Manual Nikon AF-S Nikkor 500mm F - 5.6E PF ED VR (Español - 2 Páginas)Document2 pagesManual Nikon AF-S Nikkor 500mm F - 5.6E PF ED VR (Español - 2 Páginas)domingo lunaNo ratings yet
- CarbonCure Whitepaper Impact of CO2 Utilization in Fresh Concrete On Corrosion of Steel ReinforcementDocument6 pagesCarbonCure Whitepaper Impact of CO2 Utilization in Fresh Concrete On Corrosion of Steel ReinforcementSakineNo ratings yet
- EXTER T150-st: Installation ManualDocument24 pagesEXTER T150-st: Installation ManualdwdawadNo ratings yet
- 3 2packetDocument6 pages3 2packetapi-327561261No ratings yet
- Chemical Technicians 10-2021Document30 pagesChemical Technicians 10-2021PRC Baguio0% (1)
- Ly Tieu Long - 1 Thoi Vang BongDocument4 pagesLy Tieu Long - 1 Thoi Vang Bonghoaitrung796969No ratings yet
- The Yoga Sutras of Patanjali PDFDocument168 pagesThe Yoga Sutras of Patanjali PDFjhonprestonNo ratings yet
- Mht-Cet Chemistry PyqDocument397 pagesMht-Cet Chemistry PyqONKAR DESHPANDE100% (2)
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 1Document20 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 1Suriati Bt A Rashid90% (10)
- Biography of Francisco ArcellanaDocument4 pagesBiography of Francisco ArcellanabooboothefoolNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem Set 4 With AnswersDocument4 pagesPractice Problem Set 4 With AnswersJoy colabNo ratings yet
- Jessica Shomphe Memo of Intro FinalDocument1 pageJessica Shomphe Memo of Intro Finalapi-583134959No ratings yet
- PerformanceDocument10 pagesPerformancecsl1600No ratings yet
- Hussain 62692Document3 pagesHussain 62692Hussain - حسينNo ratings yet
- Vector Spaces Handwritten Notes WWW - MathcityDocument58 pagesVector Spaces Handwritten Notes WWW - Mathcityatiq4pk89% (9)
- MITS01CDocument27 pagesMITS01CCherry Mae PanongNo ratings yet
- Class 3 4 KeyDocument12 pagesClass 3 4 Keyshivamsingh.fscNo ratings yet
- National Rural Health MissionDocument418 pagesNational Rural Health MissionRoy GoldenNo ratings yet
- IWS Exercise Guide UpdatedDocument85 pagesIWS Exercise Guide UpdatedLohit Ramakrishna kNo ratings yet
- Channel Allocation in Cellular SystemDocument40 pagesChannel Allocation in Cellular SystemNishant MittalNo ratings yet
- TE30 Electricity Meter Tester and Power Quality Analyzer Presentation EN PDFDocument19 pagesTE30 Electricity Meter Tester and Power Quality Analyzer Presentation EN PDFalejandroNo ratings yet
- Year 6 Mco Lesson PlanDocument25 pagesYear 6 Mco Lesson PlanVanitha ThiagarajNo ratings yet
RUmus Passive Voice
RUmus Passive Voice
Uploaded by
Elma JelenatorOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RUmus Passive Voice
RUmus Passive Voice
Uploaded by
Elma JelenatorCopyright:
Available Formats
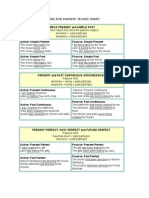
umus Passive Voice in Simple Present Tense
Berbeda dengan active voice simple present tense yang main verb-nya berupa verb-1 (pada
contoh tulisan sebelumnya: Simple Present Tense), main verb pada passive voice simple
present tense berupa past participle.
Past participle ditemani oleh auxiliary verb is/am/are disesuaikan
dengan subject pada passive voice (= object pada active voice) memenuhi subject-verb
agreement. Jika memiliki modal verb (can, should, may), past participle di dahului oleh
auxiliary verb be. Adapun agent pada passive voice merupakan subject pada active voice.
Berikut rumus passive voice dalam simple present tense:
Active Voice
Passive Voice
S (direct object) + is/am/are + past participle +/- by
S + verb-1 + direct object
(agent)
S + modal + bare infinitive + direct S (direct object) + modal + be + past participle +/- by
object
(agent)
Rumus di atas berlaku untuk transitive verb, dimana memang kata kerja tersebut yang umum
dipasifkan. Kalimat dengan intransitive verb mungkin dapat dipasifkan jika
memiliki prepositional phrase (lihat: Passive Voice pada Intransitive
Verb). Subject pada passive voice merupakan object of preposition pada active voice.
Active Voice
S + verb-1int + preposition +
object of preposition
Passive Voice
S (object of preposition) + is/am/are + past participle(V3_
+ preposition +/- by (agent)
Contoh Kalimat Passive Voice in Simple Present Tense
No.
1
2
3
4
Active Voice
Pregnant women should eat dark
chocolate regularly.
(Wanita hamil seharusnya makan coklat
hitam secara teratur.)
People make books from trees.
(Orang membuat buku dari pohon.)
My parents treat me like a baby.
(Orang tua memperlakukan saya seperti
bayi.)
You can use the photos for free.
(Kamu bisa menggunakan goto-foto
tersebut secara gratis.)
He often sleeps on the right side of the
bed.
(Dia selalu tidur di sisi kanan tempat
tidur.)
Passive Voice
Dark chocolate should be eaten regularly by
pregnant women.
(Coklat hitam seharusnya dimakan secara
teratur oleh wanita hamil.)
Books are made from trees.
(Buku dibuat dari pohon.)
I am treated like a baby by my parents .
(Saya diperlakukan seperti bayi oleh orang
tua.)
The photos can be used for free.
(Foto-foto tersebut dapat digunakan secara
gratis.)
The right side of the bed is often slept on by
him.
(Sisi kanan tempat tidur sering ditiduri
olehnya.)
Active: Did he break the window?
Passive: Was the window broken by him?
Active: Where could you find such fine art?
Passive: Where could such fine art be found?
Active: Why did you abuse your servant?
Passive: Why was your servant abused by you?
Active: Did anyone steal your purse?
Passive: Was your purse stolen by anyone?
Active: Did anyone hurt your feelings?
Passive: Were your feelings hurt by anyone?
Active: Did Alice invite you?
Passive: Were you invited by Alice?
Active: Who killed the snake?
Passive: By whom was the snake killed?
Active: Why did he punish you?
Passive: Why were you punished by him?
Active: Whom did you laugh at?
Passive: Who was laughed at by you?
Read more at http://www.englishpractice.com/improve/active-passive-voice-simpletense/#SVBDsev9SuG7xREr.99
PAST MODALS
The past passive form follows this pattern:
modal + have been + past participle
Active: SHOULD HAVE /
SHOULDN'T HAVE
The students should have
learned the verbs.
The children shouldn't have
broken the window.
Passive: SHOULD HAVE /
SHOULDN'T HAVE
The verbs should have been
learned by the students.
The window shouldn't have been
broken by the children.
Active: OUGHT TO
Passive: OUGHT TO
Students ought to have learned
The verbs ought to have been
the verbs.
learned by the students.
(negative ought to is rarely used)
Active: BE SUPPOSED TO
(past time)
I was supposed to type the
composition.
I wasn't supposed to copy the
story in the book.
Janet was supposed to clean the
living room.
She wasn't supposed to eat
candy and gum.
Frank and Jane were supposed
to make dinner.
They weren't supposed to make
dessert.
Passive: BE SUPPOSED TO
(past time)
The composition was supposed
to be typed by me.
The story in the book wasn't
supposed to be copied.
The living room was supposed to
be cleaned by Janet.
Candy and gum weren't
supposed to be eaten by her.
Dinner was supposed to be made
by them.
Dessert wasn't supposed to be
made by them.
Active: MAY / MAY NOT
That firm may have offered
Katya a new job.
The students may not have
written the paper.
MIGHT / MIGHT NOT
That firm might have offered
Katya a new job.
The students might not have
written the paper.
Passive: MAY / MAY NOT
Katya may have been offered a
new job by that firm.
The paper may not have been
written by the students.
MIGHT / MIGHT NOT
Katya might have been offered a
new job by that firm.
The paper might not have been
written by the students.
PRESENT / FUTURE MODALS
The passive form follows this pattern:
modal + be + past participle
Passive: WILL / WON'T (WILL
Active: WILL / WON'T (WILL
NOT)
NOT)
Tom will be invited to the party by
Sharon will invite Tom to the party.
Sharon.
Sharon won't invite Jeff to the party.
Jeff won't be invited to the party by
Sharon.
(Sharon will not invite Jeff to the
(Jeff will not be invited to the party
party.)
by Sharon.)
Active: CAN / CAN'T (CAN
NOT)
Mai can foretell the future.
Terry can't foretell the future.
(Terry can not foretell the future.)
Active: MAY / MAY NOT
Her company may give Katya a
new office.
The lazy students may not do the
homework.
MIGHT / MIGHT NOT
Her company might give Katya a
new office.
The lazy students might not do the
homework.
Active: SHOULD / SHOULDN'T
Students should memorize English
verbs.
Children shouldn't smoke
cigarettes.
Active: OUGHT TO
Passive: CAN / CAN'T (CAN
NOT)
The future can be foretold by Mai.
The future can't be foretold by Terry.
(The future can not be foretold by
Terry.)
Passive: MAY / MAY NOT
Katya may be given a new office by
her company.
The homework may not be done by
the lazy students.
MIGHT / MIGHT NOT
Katya might be given a new office
by her company.
The homework might not be done
by the lazy students.
Passive: SHOULD / SHOULDN'T
English verbs should be memorized
by students.
Cigarettes shouldn't be smoked by
children.
Passive: OUGHT TO
Students ought to learn English
verbs.
(negative ought to is rarely used)
English verbs ought to be
memorized by students.
Active: HAD BETTER / HAD
BETTER NOT
Students had better practice English
every day.
Children had better not drink
whiskey.
Passive: HAD BETTER / HAD
BETTER NOT
English had better be practiced
every day by students.
Whiskey had better not be drunk by
children.
Active: MUST / MUST NOT
Tourists must apply for a passport
to travel abroad.
Customers must not use that door.
Passive: MUST / MUST NOT
A passport to travel abroad must be
applied for.
That door must not be used by
customers.
Active: HAS TO / HAVE TO
She has to practice English every
day.
Sara and Miho have to wash the
dishes every day.
DOESN'T HAVE TO/ DON'T
HAVE TO
Maria doesn't have to clean her
bedroom every day.
The children don't have to clean
their bedrooms every day.
Passive: HAS TO / HAVE TO
English has to be practiced every
day.
The dishes have to be washed by
them every day.
DOESN'T HAVE TO/ DON'T
HAVE TO
Her bedroom doesn't have to be
cleaned every day.
Their bedrooms don't have to be
cleaned every day.
Active: BE SUPPOSED TO
I am supposed to type the
composition.
I am not supposed to copy the
stories in the book.
Janet is supposed to clean the living
room.
She isn't supposed to eat candy and
gum.
They are supposed to make dinner
for the family.
They aren't supposed to make
dessert.
Passive: BE SUPPOSED TO
The composition is supposed to be
typed by me.
The stories in the book are not
supposed to be copied.
The living room is supposed to be
cleaned by Janet.
Candy and gum aren't supposed to
be eaten by her.
Dinner for the family is supposed to
be made by them.
Dessert isn't supposed to be made by
them.
You might also like
- ملخص شامل لدروس bac PDFDocument11 pagesملخص شامل لدروس bac PDFAnonymous wwD1u4TmGh67% (9)
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument3 pagesActive and Passive Tenses Chartrondick93% (29)
- Contribuciones de Leontief A La EconomíaDocument24 pagesContribuciones de Leontief A La EconomíaMargarita SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- InDesign and XML Tech RefDocument28 pagesInDesign and XML Tech RefMarius TNo ratings yet
- Simple Present and Simple PastDocument5 pagesSimple Present and Simple PastRaymond Sabanal BanquirigoNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument11 pagesActive and Passive Tenses ChartMarco GonzalezNo ratings yet
- The Passive Voice. Tenses ChartDocument5 pagesThe Passive Voice. Tenses Chartlondonfaidel6511No ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument4 pagesActive and Passive Tenses ChartchandraNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument5 pagesActive and Passive Tenses ChartAishhwarya PriyaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice ChartDocument15 pagesActive and Passive Voice ChartYoussef BoulaghlaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice ChartDocument3 pagesActive and Passive Voice ChartDea ZarynaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice Chart 11Document3 pagesActive and Passive Voice Chart 11Ryan Yudhistyanto PutroNo ratings yet
- Unit 7. Passives. Tenses ChartDocument0 pagesUnit 7. Passives. Tenses ChartunidienteNo ratings yet
- 8242 Active and Passive Voice ChartDocument3 pages8242 Active and Passive Voice ChartGabriela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument7 pagesActive and Passive Voiceazadali735323No ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument5 pagesActive and Passive Tenses ChartvenkteshNo ratings yet
- Grammar ChartsDocument7 pagesGrammar ChartsHashim Raza Siyal100% (2)
- Active and Passive Voice Chart 11Document3 pagesActive and Passive Voice Chart 11Inmaculada SenovillaNo ratings yet
- Passive Sentences: Ajvilches. 6/ 2009Document7 pagesPassive Sentences: Ajvilches. 6/ 2009abingvNo ratings yet
- Passive & Verb Tenses PDFDocument8 pagesPassive & Verb Tenses PDFlovely callsNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument5 pagesActive and Passive Tenses ChartManivannan SsnNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tense ChartDocument4 pagesActive and Passive Tense ChartAna Paula MedinaNo ratings yet
- Am/is/are + Being + Past Participle Q Was/were + Being + Past ParticipleDocument3 pagesAm/is/are + Being + Past Participle Q Was/were + Being + Past ParticipleBen HussaNo ratings yet
- Grammar HandoutDocument17 pagesGrammar HandoutJakir JackNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be in The PastDocument12 pagesVerb To Be in The PastAdalberto Jiménez100% (1)
- Passive VoiceDocument11 pagesPassive VoiceMtn EgnNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument3 pagesActive and Passive Tenses Chartabida jamaliNo ratings yet
- B2.1 GrammarDocument35 pagesB2.1 Grammarbarbaragarcia350No ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice Lecture 7Document38 pagesActive and Passive Voice Lecture 7maheenshaikh119No ratings yet
- Guía InglésDocument7 pagesGuía Inglésangelm.galicia.zNo ratings yet
- Review and ActivitiesDocument15 pagesReview and ActivitiesAnonymous vdUB1vlyNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice 2Document2 pagesPassive Voice 2ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesPassive VoiceCati SofiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Verbs of General UseDocument19 pagesUnit 1 Verbs of General UseRosaury Castro De Luna100% (2)
- AG1 Unit 6Document29 pagesAG1 Unit 621antonella05No ratings yet
- General Grammar ReviewDocument7 pagesGeneral Grammar ReviewKimNo ratings yet
- Modals: Going To - Might - May - Can-Could - Must - Should - Have ToDocument47 pagesModals: Going To - Might - May - Can-Could - Must - Should - Have ToghaidaNo ratings yet
- Course OneDocument120 pagesCourse OneRoberto Carlos CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Active Passive (3) YOKIBUDocument5 pagesActive Passive (3) YOKIBUsiddcric264No ratings yet
- Present Perfect-Group 3 - CompressedDocument38 pagesPresent Perfect-Group 3 - CompressedDULCE MP100% (1)
- Blue & Pink Present Tenses PresentationDocument14 pagesBlue & Pink Present Tenses PresentationGisela Cruz RiosNo ratings yet
- Types of QuestionsDocument10 pagesTypes of QuestionsSiti Hayatiwi SriwandariNo ratings yet
- Unit 9-Passives-QUDocument24 pagesUnit 9-Passives-QURw KhNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice TutorialDocument37 pagesPassive Voice TutorialmarNo ratings yet
- How Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Document24 pagesHow Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Noelia Nancy PonceNo ratings yet
- Active Passive: VoiceDocument22 pagesActive Passive: VoiceDominika ZającNo ratings yet
- English Tenses: Simple Past TenseDocument5 pagesEnglish Tenses: Simple Past TenseHasnaoui DiaNo ratings yet
- Universidad de Oriente Núcleo de AnzoáteguiDocument17 pagesUniversidad de Oriente Núcleo de AnzoáteguiHelen HernandezNo ratings yet
- Extra Review Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesExtra Review Passive VoiceBruno SenraNo ratings yet
- Voz Pasiva Worksheet SAE 22-10-4M PGDocument5 pagesVoz Pasiva Worksheet SAE 22-10-4M PGFda Correa ENo ratings yet
- 1 - Class Notes-HU 101 - (Module 1-Grammar)Document15 pages1 - Class Notes-HU 101 - (Module 1-Grammar)Sukhwinder SinghNo ratings yet
- The Passive Voice: Active I Drank Two Cups of CoffeeDocument3 pagesThe Passive Voice: Active I Drank Two Cups of Coffeeshahzeb khanNo ratings yet
- Assertive To ImperativeDocument3 pagesAssertive To ImperativeAdnanNo ratings yet
- Research Work On Exam TopicsDocument10 pagesResearch Work On Exam Topicsemely gilNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: Verb Modality Germanic LanguagesDocument8 pagesModal Verbs: Verb Modality Germanic LanguagesavdvNo ratings yet
- Ingles III - Appendixes - Unidad IIIDocument9 pagesIngles III - Appendixes - Unidad IIIJorge Schellius OrtizNo ratings yet
- Rules: So - Neither - EitherDocument3 pagesRules: So - Neither - EitherVeronica Morales MirandaNo ratings yet
- A1a2 RequirementsDocument4 pagesA1a2 Requirementsnaizabekova.a94No ratings yet
- Jose Cueva. HandbookDocument52 pagesJose Cueva. HandbookJimmi Fabricio Celi Díaz100% (2)
- Spanish for English Speakers: Dictionary English - Spanish: 700+ of the Most Important Words / Vocabulary for Beginners with Useful Phrases to Improve Learning - Level A1 - A2From EverandSpanish for English Speakers: Dictionary English - Spanish: 700+ of the Most Important Words / Vocabulary for Beginners with Useful Phrases to Improve Learning - Level A1 - A2No ratings yet
- GuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarFrom EverandGuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Bisep HSSC-A-2020 StatisticsDocument11 pagesBisep HSSC-A-2020 StatisticsArshad JehanNo ratings yet
- Decomposition of Fundamental Lamb Wave Modes in Complex Metal Structures Using COMSOLDocument8 pagesDecomposition of Fundamental Lamb Wave Modes in Complex Metal Structures Using COMSOLMohammad HarbNo ratings yet
- Com - Pg.game6327838 LogcatDocument53 pagesCom - Pg.game6327838 Logcatfordcannabis07No ratings yet
- Cornwall's Disadvantaged NeighbourhoodsDocument32 pagesCornwall's Disadvantaged NeighbourhoodsNick Wilding100% (2)
- The Iconic Influence of Queen Elizabeth IIDocument2 pagesThe Iconic Influence of Queen Elizabeth IIpatriciasusckind_574No ratings yet
- XHCC S62 enDocument60 pagesXHCC S62 enhambi1986No ratings yet
- Manual Nikon AF-S Nikkor 500mm F - 5.6E PF ED VR (Español - 2 Páginas)Document2 pagesManual Nikon AF-S Nikkor 500mm F - 5.6E PF ED VR (Español - 2 Páginas)domingo lunaNo ratings yet
- CarbonCure Whitepaper Impact of CO2 Utilization in Fresh Concrete On Corrosion of Steel ReinforcementDocument6 pagesCarbonCure Whitepaper Impact of CO2 Utilization in Fresh Concrete On Corrosion of Steel ReinforcementSakineNo ratings yet
- EXTER T150-st: Installation ManualDocument24 pagesEXTER T150-st: Installation ManualdwdawadNo ratings yet
- 3 2packetDocument6 pages3 2packetapi-327561261No ratings yet
- Chemical Technicians 10-2021Document30 pagesChemical Technicians 10-2021PRC Baguio0% (1)
- Ly Tieu Long - 1 Thoi Vang BongDocument4 pagesLy Tieu Long - 1 Thoi Vang Bonghoaitrung796969No ratings yet
- The Yoga Sutras of Patanjali PDFDocument168 pagesThe Yoga Sutras of Patanjali PDFjhonprestonNo ratings yet
- Mht-Cet Chemistry PyqDocument397 pagesMht-Cet Chemistry PyqONKAR DESHPANDE100% (2)
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 1Document20 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 1Suriati Bt A Rashid90% (10)
- Biography of Francisco ArcellanaDocument4 pagesBiography of Francisco ArcellanabooboothefoolNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem Set 4 With AnswersDocument4 pagesPractice Problem Set 4 With AnswersJoy colabNo ratings yet
- Jessica Shomphe Memo of Intro FinalDocument1 pageJessica Shomphe Memo of Intro Finalapi-583134959No ratings yet
- PerformanceDocument10 pagesPerformancecsl1600No ratings yet
- Hussain 62692Document3 pagesHussain 62692Hussain - حسينNo ratings yet
- Vector Spaces Handwritten Notes WWW - MathcityDocument58 pagesVector Spaces Handwritten Notes WWW - Mathcityatiq4pk89% (9)
- MITS01CDocument27 pagesMITS01CCherry Mae PanongNo ratings yet
- Class 3 4 KeyDocument12 pagesClass 3 4 Keyshivamsingh.fscNo ratings yet
- National Rural Health MissionDocument418 pagesNational Rural Health MissionRoy GoldenNo ratings yet
- IWS Exercise Guide UpdatedDocument85 pagesIWS Exercise Guide UpdatedLohit Ramakrishna kNo ratings yet
- Channel Allocation in Cellular SystemDocument40 pagesChannel Allocation in Cellular SystemNishant MittalNo ratings yet
- TE30 Electricity Meter Tester and Power Quality Analyzer Presentation EN PDFDocument19 pagesTE30 Electricity Meter Tester and Power Quality Analyzer Presentation EN PDFalejandroNo ratings yet
- Year 6 Mco Lesson PlanDocument25 pagesYear 6 Mco Lesson PlanVanitha ThiagarajNo ratings yet