Professional Documents
Culture Documents
324-8 LEC Differential
324-8 LEC Differential
Uploaded by
penihani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesThis document discusses final drives and differentials in automotive transmissions. It describes the purposes of final drives, which are to transmit and increase torque while reducing speeds, changing the direction of power flow if needed, and compensating for differences in wheel speeds. It explains the two main types of final drive gears - straight bevel and hypoid gears. Hypoid gears have advantages like silent running and ability to handle higher loads, but require special hypoid oil. The document also outlines how a differential works, including its components and how it is able to compensate for speed differences between driven wheels during turns by allowing the sun wheels to rotate slightly. It distributes torque equally to both wheels under all driving conditions.
Original Description:
nice one
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses final drives and differentials in automotive transmissions. It describes the purposes of final drives, which are to transmit and increase torque while reducing speeds, changing the direction of power flow if needed, and compensating for differences in wheel speeds. It explains the two main types of final drive gears - straight bevel and hypoid gears. Hypoid gears have advantages like silent running and ability to handle higher loads, but require special hypoid oil. The document also outlines how a differential works, including its components and how it is able to compensate for speed differences between driven wheels during turns by allowing the sun wheels to rotate slightly. It distributes torque equally to both wheels under all driving conditions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pages324-8 LEC Differential
324-8 LEC Differential
Uploaded by
penihaniThis document discusses final drives and differentials in automotive transmissions. It describes the purposes of final drives, which are to transmit and increase torque while reducing speeds, changing the direction of power flow if needed, and compensating for differences in wheel speeds. It explains the two main types of final drive gears - straight bevel and hypoid gears. Hypoid gears have advantages like silent running and ability to handle higher loads, but require special hypoid oil. The document also outlines how a differential works, including its components and how it is able to compensate for speed differences between driven wheels during turns by allowing the sun wheels to rotate slightly. It distributes torque equally to both wheels under all driving conditions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
NCTTE - Automotive Department
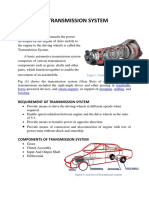
TRANSMISSION
AUT 324 - "Transmission and drive trains"
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
8. Final Drive and Differential
Duties:
- to transmit and to increase torque
- to reduce speeds
- to change direction of power flow, if required
- to compensate differences in speed of the driven wheels
- to distribute the torque equally to the driven wheels
(final drive gear)
(
"
)
(
"
)
(differential)
(
"
)
Mainly two arrangements of final
gears are known: straight bevel
pinion and hypoid bevel pinion
drives.
"Hypoid" means, that the axle of
the pinion is offset from the center
of the ring gear.
Advantages of the hypoid drive:
1. Silent running since a higher
number of teeth are in contact.
2. Higher demands (loads, forces)
possible since diameter and width
of teeth are wider.
3. Less space required since the
ring gear is with a smaller
diameter.
Propeller
shaft
arrangement can be kept down.
Disadvantage: Due to the axle
offset higher sliding motions
appear which lead to higher
pressures. Special Hypoid oil is required (API-GL-5)! Typical gear ratio of the final drive is between 3,0 and 5,0.
The position of the pinion gear
to the ring gear determines the
teeth contact and therefore the
possible torque that can be
transmitted without irregular
wear. Different ways of adjusting
are common (see LAB!),
manufacturers instructions are
to
be
followed!
Wrong
adjustment of the pinion height
leads to destruction of the
differential.
- 1 - Differential
NCTTE - Automotive Department
TRANSMISSION
AUT 324 - "Transmission and drive trains"
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
Compensation of speed differences:
During driving a curve the inner wheel passes less
distance than the outer wheel, this results in a speed
difference, which is to be compensated. Also different
frictions between wheel and ground are leading to
differences in speed.
Components: 2 planet wheels (side gears), 2 sun wheels
(spider gears), ring gear, pinion gear, 2 output shafts,
differential case (housing).
The pinion gear drives the ring gear, which is attached to the
differential case. Attached to the case (running on a small
shaft) are the two sun wheels. During equal speed on both
sides they don't move and transmit the speed equally to both
planet wheels. If there is a speed difference, the sun wheels
slightly begin to rotate and compensate this difference in
speed.
Distribution of torques:
Differentials distribute the received
torque under every driving condition
equally to both wheels. The quantity
of the transmitted torque is defined
through the tire grip of that wheel
with the worst tire grip.
Manual Differential lock:
Connecting it to the diff-case can
stop the free rotation of one of the
two output shafts. This will block the
compensation of speed differences.
- 2 - Differential
You might also like
- dct250 Powershift Rebuild ManualDocument94 pagesdct250 Powershift Rebuild ManualSanyok Ganz100% (1)
- Design of Automotive DifferentialDocument8 pagesDesign of Automotive DifferentialDeepak ChachraNo ratings yet
- HW19710 Transmission System Repair ManualDocument78 pagesHW19710 Transmission System Repair Manualsample name83% (6)
- dct250 Powershift Rebuild ManualDocument94 pagesdct250 Powershift Rebuild ManualErickson Garcia100% (5)
- Chemical Engineering Job Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesChemical Engineering Job Interview Questionschemical todi50% (2)
- Sandvik QH Blue FaultsDocument12 pagesSandvik QH Blue FaultsJuan GuzmánNo ratings yet
- 324-7 LEC Drive ShaftDocument1 page324-7 LEC Drive ShaftbernabasNo ratings yet
- 324-5 LEC Transmission 3Document1 page324-5 LEC Transmission 3penihaniNo ratings yet
- Axsm 0041Document98 pagesAxsm 0041Walter ╰⏝╯ MaonesNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Carriage Workshop LallagudaDocument28 pages1.introduction To Carriage Workshop Lallagudavenkatesh naniNo ratings yet
- 324-1+2 LEC Drivetrain (Introduction)Document1 page324-1+2 LEC Drivetrain (Introduction)penihaniNo ratings yet
- Mech 203 Term Project Automobile Differential and TransmissionDocument29 pagesMech 203 Term Project Automobile Differential and TransmissionYugi SupriatnaNo ratings yet
- DIFFERENTIALDocument4 pagesDIFFERENTIALsaffrin100% (1)
- Clutch Design PDFDocument7 pagesClutch Design PDFsreenu mNo ratings yet
- Seminar FinalDocument21 pagesSeminar FinalLOKENDRA91No ratings yet
- OCW Analisis of Gear TrainsDocument11 pagesOCW Analisis of Gear TrainsVictor SibandaNo ratings yet
- LAB Manual Automobile-EngineeringDocument34 pagesLAB Manual Automobile-EngineeringManjinderjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Gear Box Project Guide LinesDocument12 pagesGear Box Project Guide LinesteddiyfentawNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document8 pagesLab 1Mansoob BukhariNo ratings yet
- Actr Mod 2Document18 pagesActr Mod 2jithinkumar22103No ratings yet
- Differentials CompressedDocument8 pagesDifferentials CompressedMayur PanchalNo ratings yet
- Group 20 The Jugaad Crew Me322 Project ReprotDocument23 pagesGroup 20 The Jugaad Crew Me322 Project ReprotHarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 AutomobileDocument11 pagesAssignment 3 Automobilepawan sharmaNo ratings yet
- The Gearbox (Transmission) : B A A B A B B A A BDocument12 pagesThe Gearbox (Transmission) : B A A B A B B A A BVijay PanchalNo ratings yet
- 324-5 LEC Transmission 5 - Synch2Document2 pages324-5 LEC Transmission 5 - Synch2penihaniNo ratings yet
- MCT 311 Lesson 5Document16 pagesMCT 311 Lesson 5Moussa SaidNo ratings yet
- Kassahun Tadess GeerboxDocument16 pagesKassahun Tadess Geerboxabubekery61No ratings yet
- DIFFERENTIALSDocument10 pagesDIFFERENTIALSAyodeji AdeyemiNo ratings yet
- Automotive Transmission: Clutch and Gear BoxDocument28 pagesAutomotive Transmission: Clutch and Gear BoxMohan100% (1)
- Gear Boxes in Automobiles PresentationDocument24 pagesGear Boxes in Automobiles PresentationHada NanuNo ratings yet
- Differential and Driveline96zjs - 3Document34 pagesDifferential and Driveline96zjs - 3F-fatal FaxNo ratings yet
- Clutch TRNGDocument102 pagesClutch TRNGJames Scott Valderrama100% (1)
- Theory Da1Document13 pagesTheory Da1sanchit sawantNo ratings yet
- A Study On Vehicle Differential SystemDocument4 pagesA Study On Vehicle Differential SystemNguyễn Thị Minh ThuNo ratings yet
- Clutch and Manual TransmissionDocument23 pagesClutch and Manual TransmissionLatif MohdNo ratings yet
- Clutch 160919202226Document51 pagesClutch 160919202226Birjesh YaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- Geer box-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesGeer box-WPS OfficeYosef EphremNo ratings yet
- STR Drive Axle Repair ManualDocument55 pagesSTR Drive Axle Repair Manualsample nameNo ratings yet
- Tfe Module 3Document14 pagesTfe Module 3Anandhu ANo ratings yet
- Rex Techno Dotari BM 2#0703 Rex Techno enDocument10 pagesRex Techno Dotari BM 2#0703 Rex Techno enaritmeticsNo ratings yet
- Transmission System: Windmills Horse Steam Engines Pumping Milling HoistingDocument9 pagesTransmission System: Windmills Horse Steam Engines Pumping Milling Hoistingajay mauryaNo ratings yet
- Howo TransmisionDocument81 pagesHowo TransmisionMantenimiento Mecanico BiddleNo ratings yet
- Ae Unit 2Document25 pagesAe Unit 2Iyyappan SivalingamNo ratings yet
- 0B5 Etails About The SevenDocument19 pages0B5 Etails About The SevenLili100% (3)
- Exp 5 LabDocument6 pagesExp 5 LabRamesh Kavitha Sanjit 18BME0677No ratings yet
- Hotchkiss Drive RearDocument17 pagesHotchkiss Drive RearravivpsNo ratings yet
- MECH3030 04 GearDocument93 pagesMECH3030 04 GearYan NingNo ratings yet
- Power Units and TransmissionDocument42 pagesPower Units and TransmissionAmarjeet RaiNo ratings yet
- Design and Manufacturing of Differential Locking SystemDocument6 pagesDesign and Manufacturing of Differential Locking SystemShashank VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Ijme V2i6p107Document5 pagesIjme V2i6p107Atthuru ManikantaNo ratings yet
- 153698234-Summer-Training-Report-at - Jtekt .Document42 pages153698234-Summer-Training-Report-at - Jtekt .Amit AryaNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering Lab (ME-314-F) List of ExperimentsDocument48 pagesAutomobile Engineering Lab (ME-314-F) List of ExperimentsTapas Kumar SahooNo ratings yet
- Gear Box ReportDocument39 pagesGear Box ReportNisar HussainNo ratings yet
- 6th Semestermechanical Automobile Engineering Lab ManualDocument21 pages6th Semestermechanical Automobile Engineering Lab ManualSayan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Construction of A Constant Mesh Gear BoxDocument21 pagesConstruction of A Constant Mesh Gear BoxAmare Eshetie0% (1)
- AckermanDocument11 pagesAckermanVansh JainNo ratings yet
- 950K Diferencial LSDDocument7 pages950K Diferencial LSDJoseph Maury Pàrraga100% (1)
- Noncircular GearsDocument6 pagesNoncircular GearsRăzvan NicolaeNo ratings yet
- Essential Scooter Maintenance for the Absolute BeginnerFrom EverandEssential Scooter Maintenance for the Absolute BeginnerNo ratings yet
- Mercedes Benz & Dodge Sprinter CDI 2000-2006 Owners Workshop ManualFrom EverandMercedes Benz & Dodge Sprinter CDI 2000-2006 Owners Workshop ManualRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Group Members 1. Bernabas Solomon 2. Firew Teferi 3. Fitsum Hailu 4. Gizealew NiggussieDocument3 pagesGroup Members 1. Bernabas Solomon 2. Firew Teferi 3. Fitsum Hailu 4. Gizealew NiggussiepenihaniNo ratings yet
- Power PointDocument3 pagesPower PointpenihaniNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Science and Technolog1 (Autorecovered) (Autorecovered)Document70 pagesAddis Ababa Science and Technolog1 (Autorecovered) (Autorecovered)penihaniNo ratings yet
- DellDocument2 pagesDellpenihaniNo ratings yet
- ThenodynamicsDocument2 pagesThenodynamicspenihaniNo ratings yet
- Power PointDocument3 pagesPower PointpenihaniNo ratings yet
- God's PowerDocument2 pagesGod's PowerpenihaniNo ratings yet
- DellDocument2 pagesDellpenihaniNo ratings yet
- Who Is GodDocument2 pagesWho Is GodpenihaniNo ratings yet
- By BernabasDocument2 pagesBy BernabaspenihaniNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Science and Technolog1Document9 pagesAddis Ababa Science and Technolog1penihaniNo ratings yet
- Belay AyalewDocument48 pagesBelay Ayalewpenihani50% (2)
- Gizachew EndaleDocument51 pagesGizachew EndalepenihaniNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument45 pagesInternship Reportbernabas100% (3)
- ThenodynamicsDocument2 pagesThenodynamicspenihaniNo ratings yet
- ElseDocument19 pagesElsepenihaniNo ratings yet
- Toyota Yaris 2006 Model PDFDocument7 pagesToyota Yaris 2006 Model PDFpenihaniNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Science and TechnologyDocument13 pagesAddis Ababa Science and TechnologypenihaniNo ratings yet
- Toyota Yaris 2006 Model (Yaris Compact) : Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering (Automotive Engineering)Document9 pagesToyota Yaris 2006 Model (Yaris Compact) : Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering (Automotive Engineering)penihaniNo ratings yet
- Main Slide For CATS Training For BeginnersDocument416 pagesMain Slide For CATS Training For Beginnerspenihani83% (6)
- Outline For Internship ProjectDocument2 pagesOutline For Internship ProjectpenihaniNo ratings yet
- List Down Some of The Benefits Obtained From Implementing A Good Material Handling SystemDocument11 pagesList Down Some of The Benefits Obtained From Implementing A Good Material Handling SystempenihaniNo ratings yet
- Magenatic Belt Conveyer Design: 1.0 BackgroundDocument20 pagesMagenatic Belt Conveyer Design: 1.0 BackgroundpenihaniNo ratings yet
- Gear Box TypesDocument4 pagesGear Box TypespenihaniNo ratings yet
- 80ZV 80C4 5001 93309 00134 - UsaDocument604 pages80ZV 80C4 5001 93309 00134 - UsaДенис Сухарев100% (3)
- Presentation On Moment Area Method To FindDocument26 pagesPresentation On Moment Area Method To FindMuhammad Fahad AliNo ratings yet
- CH # 2 Vectors and EquilibriumDocument14 pagesCH # 2 Vectors and EquilibriumMehak MuradaniNo ratings yet
- Doosan Gas TurbinesDocument20 pagesDoosan Gas TurbinesUhrin Imre100% (1)
- MCD 00001Document10 pagesMCD 00001ariyaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: A/Prof Mehdi Khiadani Office: 23.203 Phone: 6304 5825 Email: M.khiadani@ecu - Edu.auDocument43 pagesFluid Mechanics: A/Prof Mehdi Khiadani Office: 23.203 Phone: 6304 5825 Email: M.khiadani@ecu - Edu.aunalinaNo ratings yet
- Expanding Fire Tube Boiler Tubes - Elliott ToolDocument3 pagesExpanding Fire Tube Boiler Tubes - Elliott ToolAVINASH ANAND RAONo ratings yet
- 1 Well Completions PDFDocument43 pages1 Well Completions PDFMurali Daren100% (1)
- Rotary Drilling Rig ComponentsDocument130 pagesRotary Drilling Rig Componentsgarry_dirak100% (22)
- 2008 - 2 - Tube & PipeDocument7 pages2008 - 2 - Tube & PipecanettijNo ratings yet
- User Instructions: Installation Operation MaintenanceDocument44 pagesUser Instructions: Installation Operation MaintenancePhi MacNo ratings yet
- Welder-456A-EN-TS Skill LevelDocument6 pagesWelder-456A-EN-TS Skill LevelAnilNo ratings yet
- 1-Bridge Design Manual 2010-MoWT, UgandaDocument169 pages1-Bridge Design Manual 2010-MoWT, UgandaSolomon Balemezi100% (3)
- Noc19 Me10 Assignment5Document4 pagesNoc19 Me10 Assignment5averify53No ratings yet
- Polaris Ranger Owners ManualDocument110 pagesPolaris Ranger Owners ManualIvan RochfordNo ratings yet
- Ijesrt: International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research TechnologyDocument16 pagesIjesrt: International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research TechnologySai Krishna SKNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning & Refrigeration Systems 1 PDFDocument129 pagesAir Conditioning & Refrigeration Systems 1 PDFMinita ManeNo ratings yet
- SC8.T2 5TH Doc En1998-1-2Document356 pagesSC8.T2 5TH Doc En1998-1-2d_i_z_zNo ratings yet
- Piping Design Codes and StandardDocument30 pagesPiping Design Codes and StandardHashim Ali100% (1)
- ProblemsDocument24 pagesProblemsRichardManuel100% (1)
- Gear Pump (Hoist and Rear Brake Cooling) Efficiency - Test: Pruebas y AjustesDocument3 pagesGear Pump (Hoist and Rear Brake Cooling) Efficiency - Test: Pruebas y AjustesLENIN JHAIR VALDERRAMA SEGURANo ratings yet
- Racorduri Inel TaietorDocument113 pagesRacorduri Inel TaietorgcbitziNo ratings yet
- Library BooksDocument3 pagesLibrary BooksSunil Yadav33% (3)
- FXFQ-PVE Cassette Round FlowDocument16 pagesFXFQ-PVE Cassette Round Flowame004No ratings yet
- Theories of Failure PDFDocument18 pagesTheories of Failure PDFSatish Raja Dhulipala0% (1)
- Composite Construction MethodsDocument4 pagesComposite Construction Methodskimobar34No ratings yet
- MMPX 403 Tech Data - PmiDocument1 pageMMPX 403 Tech Data - PmiMizan SarkarNo ratings yet
- Crash Tests Are Used To Measure The Safety of New Car Designs. in One Type of Test, A CarDocument2 pagesCrash Tests Are Used To Measure The Safety of New Car Designs. in One Type of Test, A CarYu SunNo ratings yet