Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sheet 10
Sheet 10
Uploaded by
AmrAliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sheet 10
Sheet 10
Uploaded by
AmrAliCopyright:
Available Formats
BENHA UNIVERSITY
BENHA FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
MECHANICAL CAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS (E1209)
2013 / 2014
SHEET No. 10
Summing Amplifiers
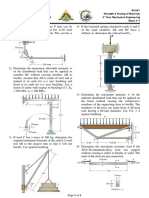
1. Determine the output voltage for each circuit in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1
2. Refer to Figure 2. Determine the following:
(a) VR1 and VR2 (b) Current through Rf
(c) VOUT
FIGURE 2
3. Find the value of Rf necessary to produce an output that is five times the
sum of the inputs in Figure 2.
4. Find the output voltage when the input voltages shown in Figure 3 are
applied to the scaling adder. What is the current through Rf?
FIGURE 3
Dr. Fawzy A. Osman
Integrators and Differentiators
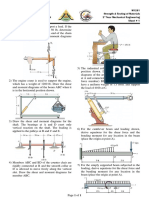
5. Determine the rate of change of the output voltage in response to the step
input to the integrator in Figure 4.
FIGURE 4
6. A triangular waveform is applied to the input of the circuit in Figure 5 as
shown. Determine what the output should be and sketch its waveform in
relation to the input.
FIGURE 5
7. A triangular waveform with a peak-to-peak voltage of 2 V and a period of 1
ms is applied to the differentiator in Figure 6(a). What is the output
voltage?
8. Beginning in position 1 in Figure 6(b), the switch is thrown into position 2
and held there for 10 ms, then back to position 1 for 10 ms, and so forth.
Sketch the resulting output waveform if its initial value is 0 V. The
saturated output levels of the op-amp are; 12 V.
FIGURE 6
Dr. Fawzy A. Osman
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Sheet (3) Chain DriveDocument1 pageSheet (3) Chain DriveAmrAliNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Chemtech Research: J.G. ManjunathaDocument11 pagesInternational Journal of Chemtech Research: J.G. ManjunathaAmrAliNo ratings yet
- SHEET6Document1 pageSHEET6AmrAliNo ratings yet
- SHEET7Document1 pageSHEET7AmrAliNo ratings yet
- Angular-Velocity 10Document1 pageAngular-Velocity 10AmrAliNo ratings yet
- Torqe - Eq 3Document1 pageTorqe - Eq 3AmrAliNo ratings yet
- XGNPR Graphene Nanoplatelets Grade M en WHMIS OSHA GHS SDS 2015-11-26Document5 pagesXGNPR Graphene Nanoplatelets Grade M en WHMIS OSHA GHS SDS 2015-11-26AmrAliNo ratings yet
- Function (W) Angular - Velocity (F) % Calculate The Angular Velocity W (2 Pi F )Document1 pageFunction (W) Angular - Velocity (F) % Calculate The Angular Velocity W (2 Pi F )AmrAliNo ratings yet
- Torqe - Eq 3Document1 pageTorqe - Eq 3AmrAliNo ratings yet
- Sheet (2) Belt Drive: Standard)Document2 pagesSheet (2) Belt Drive: Standard)AmrAliNo ratings yet
- Variables Calculatting Variable The Check On The Twist and Make It Safe The Required DiameterDocument3 pagesVariables Calculatting Variable The Check On The Twist and Make It Safe The Required DiameterAmrAliNo ratings yet
- Sheet (2) Belt Drive: Standard)Document2 pagesSheet (2) Belt Drive: Standard)AmrAliNo ratings yet
- Sheet (1) Revision: You Are Required ToDocument3 pagesSheet (1) Revision: You Are Required ToAmrAliNo ratings yet
- Impulse and MomentumDocument0 pagesImpulse and MomentumStone WangNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document1 pageSheet 1AmrAli0% (1)