Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pseudocode Examples
Pseudocode Examples
Uploaded by
Trixdhy X'sCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pseudocode Examples
Pseudocode Examples
Uploaded by
Trixdhy X'sCopyright:
Available Formats
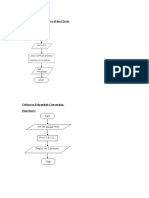
Introductory Examples of Flowcharts and Pseudocode
Sum of 2 Numbers - sequence
Chapter 3
Start
Calculate Pay - sequence
Start
input hours
input x
input y
Begin
input hours
input rate
pay = hours * rate
print pay
End
Begin
input x, y
sum = x + y
print sum
End
sum = x + y
input rate
output sum
pay = hours * rate
End
print pay
End
Average of 3 Numbers - sequence
Start
input x
input y
input z
Calculate Pay with Overtime - selection
Begin
input x
input y
input z
sum = x + y + z
avg = sum / 3.0
print avg
End
input hours, rate
sum = x + y + z
avg = sum / 3.0
hours 40
T
print avg
pay = hours * rate
pay = 40 * rate +
(hours - 40) * 1.5 * rate
End
print pay
Begin
input hours, rate
if hours 40 then
pay = hours * rate
else
pay = 40 * rate + (hours 40) * rate * 1.5
print pay
End
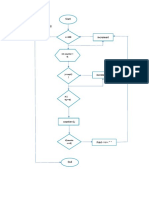
Average of 10 Numbers iteration with a while loop
Average of 10 Numbers iteration with a for loop
i = 0
sum = 0
Begin
sum = 0
for i = 1 to 10
input x
sum = sum + x
avg = sum / 10.0
print avg
End
sum = 0
while i < 10
i
1
10
F
1
T
input x
avg = sum / 10.0
input x
sum = x + sum
increment i
print avg
sum = x + sum
Begin
i = 0
sum = 0
while i < 10
input x
sum = sum + x
++i
avg = sum / 10.0
print avg
End
Begin
i = 0
sum = 0
a: if i 10 goto b
input x
sum = sum + x
++i
goto a
b: avg = sum / 10.0
print avg
End
avg = sum / 10.0
print avg
Comment Strictly speaking, the above flowchart corresponds more to the
pseudocode on the right hand side. However, as you can see, gotos make
code less modular and more unreadable.
5
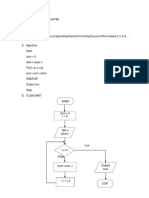
Flowchart for Function or Subroutine Module
Begin
print input 3 numbers
input a, b, c
Begin
print Input 3 numbers:
input a, b, c
avg = average(a, b, c)
print Average is , avg
End
Average
print average is, avg
input a, b, c
End
Average
sum = a + b + c
avg = sum / 3
Begin Average(a, b, c)
sum = a + b + c
avg = sum / 3.0
return avg
End
Exit
You might also like
- Number SystemsDocument12 pagesNumber Systemsabdul.azeezNo ratings yet
- Math Reviewer LETDocument12 pagesMath Reviewer LETMarizel B PopuliNo ratings yet
- HW 11 N°2Document23 pagesHW 11 N°2Christian David WillNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AlgorithmDocument46 pagesChapter 1 AlgorithmrahulNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument22 pagesFlowchartRaji Krishnamoorthy100% (1)
- HCIDocument22 pagesHCIHimanshu ThakurNo ratings yet
- JAVA and Python - ArraysDocument24 pagesJAVA and Python - ArraysJoe KierNo ratings yet
- 05 Arduino Sensors, Motors and External InterruptsDocument20 pages05 Arduino Sensors, Motors and External InterruptsMalik Adil Farooq100% (2)
- Computer Graphics and Animation - 09 TransformationsDocument35 pagesComputer Graphics and Animation - 09 TransformationsmisteryfollowNo ratings yet
- Writing PsuedoCodeDocument31 pagesWriting PsuedoCodeapi-3814408100% (3)
- Course-Outline - Introduction To ComputingDocument4 pagesCourse-Outline - Introduction To ComputingMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Fy2021 Air Force UplDocument3 pagesFy2021 Air Force UplBreakingDefense100% (1)
- Binary Numbers and Computer ArithmeticDocument24 pagesBinary Numbers and Computer ArithmeticyezidNo ratings yet
- 18Csc203J:Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument56 pages18Csc203J:Computer Organization and ArchitectureSENTHIL RNo ratings yet
- Course Hero - Take Home AssignmentDocument2 pagesCourse Hero - Take Home AssignmentfdfdfddNo ratings yet
- Flowchart - ProgrammingDocument6 pagesFlowchart - Programmingminhthuanit100% (23)
- Lab 16 - PointersDocument8 pagesLab 16 - PointersDavid VillaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis On CLOUD COMPUTING by Prashant GuptaDocument6 pagesSynopsis On CLOUD COMPUTING by Prashant GuptaPrashant GuptaNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Lecture 5 Board Based Embedded SystemDocument79 pagesEmbedded Systems Lecture 5 Board Based Embedded SystemElihu GetachewNo ratings yet
- Discipline Electrical Engineering Computer Science Computer HardwareDocument8 pagesDiscipline Electrical Engineering Computer Science Computer HardwareYewJiHui0% (1)
- C++ Lab PracticeDocument10 pagesC++ Lab PracticeDevendra patidar0% (1)
- C++ Programms TaskDocument2 pagesC++ Programms TaskNabh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- CS2405 Computer Graphics Lab ManualDocument60 pagesCS2405 Computer Graphics Lab ManualSonia DudleyNo ratings yet
- Hedi 10Document12 pagesHedi 10hedizarayane9No ratings yet
- Programming Sec 2Document24 pagesProgramming Sec 2BADR ESLAMNo ratings yet
- Karl Andrea CDocument5 pagesKarl Andrea CKarl AndasanNo ratings yet
- C. Flowchart. (Prime Numbers) : StartDocument13 pagesC. Flowchart. (Prime Numbers) : Startbong bongNo ratings yet
- Seatwork 4Document4 pagesSeatwork 4Keana IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Test 2 - Problem Solving and Design - MemoDocument7 pagesTest 2 - Problem Solving and Design - MemodkandpalNo ratings yet
- Algorithm - Pseudo Code Problem SolvingDocument14 pagesAlgorithm - Pseudo Code Problem SolvingHamza NiazNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Problem Solving (Powerpoint Exercise) PDFDocument11 pagesTopic 2 Problem Solving (Powerpoint Exercise) PDFSaraPhetcharathNo ratings yet
- FuntionsDocument22 pagesFuntionsFaheem AwaisNo ratings yet
- David Putra Simanjuntak. 42290059. Tugas AlgortmaDocument5 pagesDavid Putra Simanjuntak. 42290059. Tugas AlgortmaYossy ImeldaaNo ratings yet
- Invoice Form: Products Price Quantity TotalDocument1 pageInvoice Form: Products Price Quantity TotalTecnoinfanteNo ratings yet
- IntroductionToProgramming L02Document16 pagesIntroductionToProgramming L02Falguni IyerNo ratings yet
- Meron BirhanuDocument12 pagesMeron BirhanuMeronNo ratings yet
- Asmaa Waleed AlnabhanDocument8 pagesAsmaa Waleed AlnabhanLOZ SAMANo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Faculty of Electronic Engineering EGN 2712: Applied ProgrammingDocument4 pagesAssignment 1: Faculty of Electronic Engineering EGN 2712: Applied ProgrammingKhawla AlameriNo ratings yet
- C++ AssignmentDocument18 pagesC++ Assignmentheaven letaNo ratings yet
- Flowchart BasicsDocument20 pagesFlowchart BasicsBilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Design & Analysis of Algorithms: Practical FileDocument34 pagesDesign & Analysis of Algorithms: Practical FileaatmashrisanyalNo ratings yet
- PPC AlgorithmDocument4 pagesPPC Algorithm2023isjsuhasbNo ratings yet
- Compound Interest NotesDocument19 pagesCompound Interest NotesINTENSENo ratings yet
- Flowchart BasicsDocument20 pagesFlowchart BasicspanamasmasNo ratings yet
- Title of The Project:-: Introduction To Programing Using CDocument7 pagesTitle of The Project:-: Introduction To Programing Using CSHAIK UMAR FAROOQNo ratings yet
- Note 29 Apr 2024Document1 pageNote 29 Apr 2024CryptazNo ratings yet
- Terminator: Start/Begin Stop/EndDocument13 pagesTerminator: Start/Begin Stop/EndNan Moe Sandar ChoNo ratings yet
- Group 6 FlowchartDocument4 pagesGroup 6 FlowchartIcaro SantanaNo ratings yet
- Programming and Data Structures: Control Flow: LoopingDocument55 pagesProgramming and Data Structures: Control Flow: LoopingKSHITIJ SONI 19PE10041No ratings yet
- Homepage For Staf: Enter 1 Salary Enter 2 Service Enter 3 Stock Enter 4 ReportDocument5 pagesHomepage For Staf: Enter 1 Salary Enter 2 Service Enter 3 Stock Enter 4 Reportمحمد ازواديNo ratings yet
- Python Fundamentals IIDocument4 pagesPython Fundamentals IIاشفاق احمدNo ratings yet
- Assignment SolutionDocument6 pagesAssignment SolutionODAA TUBENo ratings yet
- Assignment SolutionDocument6 pagesAssignment SolutionODAA TUBENo ratings yet
- Assignment SolutionDocument6 pagesAssignment SolutionODAA TUBENo ratings yet
- Control Structure-Repetition: FOR LoopDocument15 pagesControl Structure-Repetition: FOR LoopSky FireNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merge1dDocument19 pagesIlovepdf Merge1dghufran.201kNo ratings yet
- CF TutoDocument6 pagesCF Tutonashida hikariNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument1 pageFlowchartAnupama BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Flow ChartsDocument3 pagesFlow ChartsTaonaishe Hastings MuzavaziNo ratings yet
- Java To FlowchartDocument1 pageJava To FlowchartYahya Di SiniNo ratings yet
- Annuity and Perpetuity HandoutsDocument3 pagesAnnuity and Perpetuity HandoutsKen AguilaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHYSICS 1 - Module 3 - Week 2Document15 pagesGENERAL PHYSICS 1 - Module 3 - Week 2Jaylanie EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- AMS StyleGuide PrintDocument176 pagesAMS StyleGuide PrintmemfilmatNo ratings yet
- Lec 0813Document10 pagesLec 0813Chevy TeoNo ratings yet
- Modified Gauss Elimination MethodDocument3 pagesModified Gauss Elimination MethodIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- DM GTU Study Material Presentations Unit-2 17032021053028AMDocument60 pagesDM GTU Study Material Presentations Unit-2 17032021053028AMmuhammad Shoaib janjuaNo ratings yet
- Eulers de Serie Lambertina Translated From Latin To English WitDocument22 pagesEulers de Serie Lambertina Translated From Latin To English WitГульнара ЖанбакиеваNo ratings yet
- LimitesDocument45 pagesLimitesRubenNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transforms of Special FunctionsDocument47 pagesFourier Transforms of Special FunctionsAntigoniBarouniNo ratings yet
- Q1 PengramDocument46 pagesQ1 PengramermiasNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 3: Least Common MultipleDocument29 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 3: Least Common MultipleEmman Fernandez100% (1)
- Nokbo Ak AnayDocument6 pagesNokbo Ak Anaydave lucasNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Cheat Sheet For Data Science - LondonSchoolofEconomicsDocument9 pagesMATLAB Cheat Sheet For Data Science - LondonSchoolofEconomicsFAISAL ALOTAIBINo ratings yet
- Đề Sở Vĩnh Phúc + Đáp ÁnDocument6 pagesĐề Sở Vĩnh Phúc + Đáp ÁnChâu Bảo HânNo ratings yet
- Common Technical Definition: QuantificationDocument2 pagesCommon Technical Definition: QuantificationNidaNo ratings yet
- Kriging 1 - 3Document23 pagesKriging 1 - 3Sunil DuwalNo ratings yet
- Mathchapter 2Document12 pagesMathchapter 2gcu974No ratings yet
- Bihar Board Solutions: Bihar Board 12th Maths Objective Answers Chapter 13 ProbabilityDocument22 pagesBihar Board Solutions: Bihar Board 12th Maths Objective Answers Chapter 13 ProbabilitySanjayNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 CirclesDocument3 pagesQuiz 2 Circlesvictorli cionNo ratings yet
- Exploration On The ParabolaDocument12 pagesExploration On The ParabolaEllen Rodríguez pedersenNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Code For Structural Analysis of 2-D Structures Subjected To Static and Self-Weight Loading ConditionsDocument9 pagesMATLAB Code For Structural Analysis of 2-D Structures Subjected To Static and Self-Weight Loading ConditionsAnax SouzaNo ratings yet
- Eigenvalue SMMHDocument10 pagesEigenvalue SMMH2050-Ramisa FarihaNo ratings yet
- Computational HydraulicsDocument130 pagesComputational HydraulicsPeter Riad100% (3)
- GMath2Q3Week7Day1 4Document15 pagesGMath2Q3Week7Day1 4Jerick JohnNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods NotesDocument553 pagesNumerical Methods Notesfuwad84100% (1)
- Maths Deleted SyllabusDocument7 pagesMaths Deleted SyllabusHazardicNo ratings yet
- Circles PDFDocument9 pagesCircles PDFbansallove2008No ratings yet
- Awers Af34125Document1 pageAwers Af34125kingofpaladinsNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Design and Manufacturing of Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) - A Review - CompressedDocument27 pagesIntelligent Design and Manufacturing of Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) - A Review - CompressedGian Fraga MoreiraNo ratings yet