Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GCSE More Higher Algebra
GCSE More Higher Algebra
Uploaded by
Nana Asare0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pages1. The simultaneous equations are y=x+2 and y^2=3x. You must show your working and not use trial and improvement to solve.
2. Given a cuboid with square base x cm and volume V cm^3, write an expression for x in terms of V and height h.
3. Calculate the value of y if two shapes, a rectangle and L-shape, have equal areas and dimensions given in cm.
Original Description:
Some Gcse algebra questions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The simultaneous equations are y=x+2 and y^2=3x. You must show your working and not use trial and improvement to solve.
2. Given a cuboid with square base x cm and volume V cm^3, write an expression for x in terms of V and height h.
3. Calculate the value of y if two shapes, a rectangle and L-shape, have equal areas and dimensions given in cm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesGCSE More Higher Algebra
GCSE More Higher Algebra
Uploaded by
Nana Asare1. The simultaneous equations are y=x+2 and y^2=3x. You must show your working and not use trial and improvement to solve.
2. Given a cuboid with square base x cm and volume V cm^3, write an expression for x in terms of V and height h.
3. Calculate the value of y if two shapes, a rectangle and L-shape, have equal areas and dimensions given in cm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
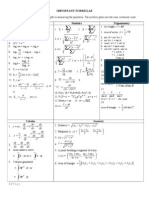
Algebra A A*
1.
Solve the simultaneous equations
y=x+2
2
y = 3x
You must show your working.
Do not use trial and improvement.
(5)
h cm
2.
A cuboid has a square base of side x cm.
3
The volume of the cuboid is V cm and the height is h cm.
x cm
x cm
Write down an expression for x in terms of V and h.
(3)
3.
The diagrams show a rectangle and an L shape
All the angles are right angles.
All lengths are in centimetres.
The shapes are equal in area.
D ia g ra m s n o t to s c a le
x
3x + 2
3x
x + 1
y
5
Calculate the value of y.
(6)
4.
Simplify
GCSE Mathematics Higher Assignment 1
5 x 2 14 x 3
x2 9
(4)
2
2
x 6x + 13 = (x a) + b
5.
(a)
Find the values of a and b.
(3)
(b)
2
Hence find the minimum value of x 6x + 13.
(1)
6.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through the point (0, 5) which is perpendicular
to the line
y=
2
3
x+3
(2)
7.
Solve the simultaneous equations.
y=x+7
2
2
x + y = 25
YOU must show your working.
Do not use trial and improvement.
(7)
GCSE Mathematics Higher Assignment 1
8.
A rectangle has length (x + 5) cm and width (x 2) cm.
A triangle has base (x + 8) cm and height x cm.
N o t to s c a le
(x 2 ) c m
x cm
(x + 5 ) cm
(x + 8 ) c m
The area of the rectangle is equal to the area of the triangle.
2
Show that x 2x 20 = 0
(You are not required to solve this equation.)
(4)
9.
The base of a triangle is 7 cm longer than its height.
2
The area of the triangle is 32 cm .
(a)
Taking the height to be h cm, show that
2
h + 7h 64 = 0
(3)
(b)
Solve this equation to find the height of the triangle.
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
(3)
10.
Make r the subject of the formula
r 3 = (t 2r)
(4)
11.
Simplify fully
x 2 16
3x 10 x 8
2
(4)
GCSE Mathematics Higher Assignment 1
12.
Cylinder A has diameter 2 cm and height (x + 6) cm.
Cylinder B has diameter 2x cm and height 5 cm.
2 cm
2x cm
(x + 6 ) c m
5 cm
N o t to s c a le
The volumes of A and B are equal.
(a)
2
Show that 5x x 6 = 0.
(2)
(b)
Solve the equation 5x x 6 = 0.
(3)
GCSE Mathematics Higher Assignment 1
You might also like
- Mathematics Form 2 RevisionDocument10 pagesMathematics Form 2 RevisionAustin Phua Yun Hock86% (69)
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- JHS 1Document9 pagesJHS 1solomonNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Revision ExerciseDocument10 pagesForm 2 Revision Exerciseramsun2129100% (2)
- CBSE Board Class IX MathematicsDocument19 pagesCBSE Board Class IX MathematicsMintu KhanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Cbse Maths 2010 Sample Paper Model 2Document25 pagesClass 10 Cbse Maths 2010 Sample Paper Model 2Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Somaiya - STD 7 (2021-22) - Sem 2 (Revision Paper) (S&A)Document16 pagesSomaiya - STD 7 (2021-22) - Sem 2 (Revision Paper) (S&A)Hardik ViraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Year 12 Trial HSC ExaminationDocument17 pagesMathematics: Year 12 Trial HSC ExaminationJessie LeungNo ratings yet
- 2 Unit Year 11 Yearly 2010Document10 pages2 Unit Year 11 Yearly 2010carinaa_truongNo ratings yet
- Which Real Numbers Are Equal To Their CubesDocument12 pagesWhich Real Numbers Are Equal To Their Cubesdanini1234No ratings yet
- Peperiksaan 4 2013 Add Math P2 F5Document9 pagesPeperiksaan 4 2013 Add Math P2 F5hpchen9407No ratings yet
- Form 2 Revision ExercisesDocument10 pagesForm 2 Revision ExercisesAmrik DussoyeNo ratings yet
- 3na Quadratic Equations 1Document3 pages3na Quadratic Equations 1John GohNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Sample Test Paper Class IxDocument3 pagesMathematics Sample Test Paper Class Ixapi-243565143No ratings yet
- 1 Stmathsbnew 2012Document3 pages1 Stmathsbnew 2012api-142567765No ratings yet
- SS2 Math QuestionsDocument8 pagesSS2 Math QuestionsPolukayNo ratings yet
- Quiz qr9Document4 pagesQuiz qr9LalaNo ratings yet
- IntoMath Grade 10 Practice 2Document13 pagesIntoMath Grade 10 Practice 2Jay el CuadraNo ratings yet
- C1 Mock Paper Exam PaperDocument22 pagesC1 Mock Paper Exam PaperNesreen Kamel Al-SayeedNo ratings yet
- Math 9Document2 pagesMath 9smritipublicschool26No ratings yet
- Honors - AP Physics Algebra Review Problem SheetDocument12 pagesHonors - AP Physics Algebra Review Problem SheetjtpmlNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument2 pagesFinal Examramezkhur480No ratings yet
- 3RD Term Pointers For Review in MathDocument6 pages3RD Term Pointers For Review in MathEnzo AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Maths QuestionsDocument25 pagesMaths QuestionsSha YosiNo ratings yet
- STPM Mathematics T Past Year Question P1 P2 P3Document19 pagesSTPM Mathematics T Past Year Question P1 P2 P3Sou Voyage0% (3)
- Sample Question Paper - Class - X Mathematics: General InstructionsDocument4 pagesSample Question Paper - Class - X Mathematics: General InstructionsCafaso IniyanNo ratings yet
- Class - 11 (Maths) MCQ'S: Write X (1, 4, 9, 16, 25, ) in Set Builder FormDocument9 pagesClass - 11 (Maths) MCQ'S: Write X (1, 4, 9, 16, 25, ) in Set Builder FormNationFirst IndianNo ratings yet
- Elmwood Press C1 Paper ADocument4 pagesElmwood Press C1 Paper Aiabdi1No ratings yet
- 2012 HSC Exam MathsDocument20 pages2012 HSC Exam MathsDavidNo ratings yet
- SPM Additional Mathematics Examination: Name: Class: I/Cno: Angka GiliranDocument14 pagesSPM Additional Mathematics Examination: Name: Class: I/Cno: Angka GiliranSilvaraj DavidNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Foundation Studies-Science, Technology and Engineering 2014/2015 SAMPLE Maths ExaminationDocument6 pagesDiploma in Foundation Studies-Science, Technology and Engineering 2014/2015 SAMPLE Maths ExaminationIñaki AlonsoNo ratings yet
- First Term SS 2 Maths ExamDocument3 pagesFirst Term SS 2 Maths ExamjonahorjiNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument4 pagesMathematicsFashola AbdulhamidNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: ७०८ सदाशिव पेठ, कुमठेकर मार्ग, पुणे ४११०३० संपकग क्रमांक (020) 2447 6938 E-mailDocument31 pagesQuestion Bank: ७०८ सदाशिव पेठ, कुमठेकर मार्ग, पुणे ४११०३० संपकग क्रमांक (020) 2447 6938 E-mailPrayasNo ratings yet
- Math First Periodical ReviewerDocument3 pagesMath First Periodical Reviewerluluhbelle cruzNo ratings yet
- Part A: 2 Sin X 2 +Document6 pagesPart A: 2 Sin X 2 +Jason BoustanyNo ratings yet
- Somaiya - STD 7 (2021-22) - Sem 2 (Revision Paper) (Q)Document7 pagesSomaiya - STD 7 (2021-22) - Sem 2 (Revision Paper) (Q)Hardik ViraNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper - 1: Section - ADocument21 pagesModel Question Paper - 1: Section - AgcrajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Islamia English School, Abu Dhabi.: Grade 9 Graphs Revision Chapter - 5Document2 pagesIslamia English School, Abu Dhabi.: Grade 9 Graphs Revision Chapter - 5attooNo ratings yet
- Quadratics Worksheet Sept 2017 QDocument8 pagesQuadratics Worksheet Sept 2017 QnatalieNo ratings yet
- Math Practice Test QuestionDocument27 pagesMath Practice Test QuestionKhin Khin ThanNo ratings yet
- Final Term Revision 1Document2 pagesFinal Term Revision 1dulya tharindiNo ratings yet
- Q1: (2+2+2 Marks) Evaluate The Following LimitsDocument7 pagesQ1: (2+2+2 Marks) Evaluate The Following LimitsAbdelrahmanJamalNo ratings yet
- AT-4e Chapter 1 FormsDocument27 pagesAT-4e Chapter 1 FormsmgestaNo ratings yet
- College Level Math Practice TestDocument17 pagesCollege Level Math Practice TestHarsha Kasaragod100% (1)
- Polynomials ws2Document1 pagePolynomials ws2Chetan AnandNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW - Maa.ac - indocumentsquestionbank10engMathsPart I Eng 10th PDFDocument31 pagesHTTPSWWW - Maa.ac - indocumentsquestionbank10engMathsPart I Eng 10th PDFmital chauhanNo ratings yet
- Choose The Correct Option To The Following.: Fill in The BlanksDocument3 pagesChoose The Correct Option To The Following.: Fill in The BlanksHarsh AnmolNo ratings yet
- Add MathsDocument40 pagesAdd MathsJoseph TingNo ratings yet
- Problem Set For Quarter 2 2023 2024Document4 pagesProblem Set For Quarter 2 2023 2024roxyquidepNo ratings yet
- ACS Exercise 2Document2 pagesACS Exercise 2RanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Holiday HomeworkDocument13 pagesMathematics Holiday Homeworkdashrath guptaNo ratings yet
- 2015 James Ruse Agricultural HS Ext 2Document26 pages2015 James Ruse Agricultural HS Ext 2omhreemaimhreemNo ratings yet
- Core 1 Revision PackDocument28 pagesCore 1 Revision PackSunny AfgNo ratings yet
- ISI Sample Question 2015 For B.stat & B.mathDocument9 pagesISI Sample Question 2015 For B.stat & B.mathMota Chashma100% (1)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet