Professional Documents
Culture Documents
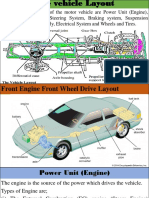
Robot Driving Mechanism
Robot Driving Mechanism
Uploaded by
salimOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Robot Driving Mechanism
Robot Driving Mechanism
Uploaded by
salimCopyright:
Available Formats
Driving Mechanism
Number of
Wheels
Mechanism
Differential
Drive
Ackerman
Steering
Omni
Directional
Drive
Three
Wheels
(Two driven
wheels and
one free
turning)
Four
Wheels
(Two for
driving,
two for
steering)
Three or
Four
wheels
Number
of Motors
Power
provided
Cost
Effective
High
Yes
Relatively
low
Yes
3 or 4
High
No
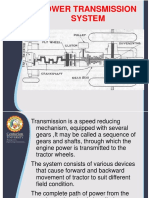
Based on the information provided by the table above, the team adopt
one of these mechanisms. First, the Differential Drive system rely on
two main driven wheels by two separate motors (one motor for each
wheel) and free turning wheel. Therefore, this system provides a high
amount of power. Furthermore, relying the structure on two motors and
three wheels maintain an inexpensive price in compare to the other
systems. Another suggested system is Ackerman Steering. This
structure is using four wheels; two driving wheels connecting to the
motor and two steering Wheels. The system provides a relatively lower
power compare to the Differential Drive mechanism. The last system is
Omni Directional Drive. The system generally uses three or four Omni
wheels, each wheel attached to a motor. The power obtained is
relatively high due to the use of three or four motors. However, the
wheels used in the structure are expensive resulting in a less costeffective system in comparison with the two other systems.
Therefore, the adopted mechanism is Differential Drive, as this system
provide a reasonable amount of power and its the most inexpensive
structure between the three mechanisms mentioned before.
The concept is simple; Velocity difference between two motors
drive the robot in any required path and direction
Since Omni wheels have smaller wheels attached perpendicular
to the circumference of another bigger wheel, they allow wheels
to move in any direction instantly
You might also like
- Tracked Vehicles Steering MechanismDocument3 pagesTracked Vehicles Steering MechanismSiva ShankerNo ratings yet
- Robotic Drive System Rebecca KyleDocument5 pagesRobotic Drive System Rebecca Kyleapi-295377491No ratings yet
- Four Cylinder Engine: Figure 1-Slider Crank Mechanism in An EngineDocument6 pagesFour Cylinder Engine: Figure 1-Slider Crank Mechanism in An EngineRamsey MejiNo ratings yet
- Power Steering Mechanism Using Cut Piece Model: Supervisor: M.R Soran Saleem Student: Shkar Hussain HamadDocument7 pagesPower Steering Mechanism Using Cut Piece Model: Supervisor: M.R Soran Saleem Student: Shkar Hussain HamadShkar GalalyNo ratings yet
- Automatic Transmissions A Short CourseDocument13 pagesAutomatic Transmissions A Short CourseMukesh Sharma100% (2)
- Transmission SystemDocument3 pagesTransmission SystemRafiNo ratings yet
- Advances in Steering Mechanisms. (First Step To Steer by Wire)Document32 pagesAdvances in Steering Mechanisms. (First Step To Steer by Wire)eizz88No ratings yet
- How A Car WorksDocument2 pagesHow A Car WorksZeroNo ratings yet
- Automatic Gear TransmissionDocument11 pagesAutomatic Gear TransmissionIntruder 47100% (1)
- Optimal Control System Based EPASDocument8 pagesOptimal Control System Based EPASNarender KumarNo ratings yet
- Projek Design Part 1Document19 pagesProjek Design Part 1Muluken TemesgenNo ratings yet
- Automatic Transmissions: A Short Course OnDocument8 pagesAutomatic Transmissions: A Short Course OnRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Drive Train SystemsDocument6 pagesDrive Train Systemsapi-296042648No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Automatic Transmission System e DDocument74 pagesLecture Notes On Automatic Transmission System e Dboafoenoch2020No ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering - UNIT 3:transmission SystemDocument19 pagesAutomobile Engineering - UNIT 3:transmission SystemSirajAyesha100% (1)
- Different Sub-Systems of Automobile: NA M E - Dittam Saha - 1 3 0 0 0 7 2 0 0 7 6Document11 pagesDifferent Sub-Systems of Automobile: NA M E - Dittam Saha - 1 3 0 0 0 7 2 0 0 7 6Dittam SahaNo ratings yet
- Automatic TransmissionDocument12 pagesAutomatic TransmissionEngine Tuning UpNo ratings yet
- Automatic Transmission5 ReportDocument17 pagesAutomatic Transmission5 ReportManhar MidhaNo ratings yet
- Power StearingDocument34 pagesPower StearingAnupamNo ratings yet
- 6th Semestermechanical Automobile Engineering Lab ManualDocument21 pages6th Semestermechanical Automobile Engineering Lab ManualSayan BiswasNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Oto Hui - Com) HybridDocument16 pages(WWW - Oto Hui - Com) Hybridperadua0% (1)
- What Is Steering SystemDocument26 pagesWhat Is Steering SystemArlyn FernandoNo ratings yet
- JLKDocument13 pagesJLKharshavardan1987No ratings yet
- Hybrid Synergy Drive (HSD)Document14 pagesHybrid Synergy Drive (HSD)Nijas MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Week 4 AIADocument2 pagesWeek 4 AIAJaya BerjayaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument31 pagesUntitledJacob BaltazarNo ratings yet
- 3.petrol Fuel SystemDocument7 pages3.petrol Fuel Systemgiriaalik55No ratings yet
- TOPIC 4 Vehicle COmponentsDocument37 pagesTOPIC 4 Vehicle COmponentsabreganaprinces30No ratings yet
- MECHANICAL LIVE PROJECTS at MECH WIND TECHNOLOGIES, HYDERABAD, PH 9542878334.Document17 pagesMECHANICAL LIVE PROJECTS at MECH WIND TECHNOLOGIES, HYDERABAD, PH 9542878334.NaniTalluriNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document21 pagesExp 3Ramanbhaman BhamanNo ratings yet
- AUTOMOTIVEpower Drive Train MODULE 2Document17 pagesAUTOMOTIVEpower Drive Train MODULE 2Selazinap LptNo ratings yet
- Fusion Between An Internal Combustion Engine and Electric MotorDocument28 pagesFusion Between An Internal Combustion Engine and Electric MotorMueed khojaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Transmission SystemDocument6 pagesAutomatic Transmission SystemjadeNo ratings yet
- Main Components of A CarDocument17 pagesMain Components of A CarSujan BanikNo ratings yet
- HOMELINK LESSON 2 - The Vehicle and Its ComponentsDocument61 pagesHOMELINK LESSON 2 - The Vehicle and Its ComponentsmharitmsNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Six: Brake SystemDocument89 pagesChapter-Six: Brake SystemMarew GetieNo ratings yet
- Technical SeminarDocument26 pagesTechnical SeminarAnish PanthathodiNo ratings yet
- Drive TrainsDocument4 pagesDrive Trainsarunaugust15No ratings yet
- Experiment No. 12: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 12: ObjectiveMoiz AamirNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Familiarization With Power Transmission System ClutchDocument10 pages2.5 Familiarization With Power Transmission System ClutchAravind RajNo ratings yet
- pr-1 ETCDocument82 pagespr-1 ETCELENo ratings yet
- Lecture 17 Notes The Braking SytemDocument22 pagesLecture 17 Notes The Braking SytemMatthew JumaNo ratings yet
- Four-Wheel Steering ReportDocument21 pagesFour-Wheel Steering ReportMuralee Dharan PillaiNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel Steering SystemDocument1 pageFour Wheel Steering SystemMatthew AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Traction SystemsDocument12 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Traction SystemsMaalmalan KeekiyyaaNo ratings yet
- Fourwheel Steering SystemDocument11 pagesFourwheel Steering SystemelangandhiNo ratings yet
- Man GN PDF 7Document30 pagesMan GN PDF 7Adrian A UPD100% (2)
- Steering SystemDocument4 pagesSteering SystemJOHN STEVEN SOYNo ratings yet
- Null 8Document27 pagesNull 8ali awadNo ratings yet
- Rack and Pinion: Sudhanshu Kashyap M-112-2K11Document20 pagesRack and Pinion: Sudhanshu Kashyap M-112-2K11YogeshGargNo ratings yet
- What Is Brake Types of Braking System Notes PDFDocument15 pagesWhat Is Brake Types of Braking System Notes PDFPun hub update vlogsNo ratings yet
- LAB Manual Automobile-EngineeringDocument34 pagesLAB Manual Automobile-EngineeringManjinderjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel Steering System Full Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesFour Wheel Steering System Full Seminar ReportYashwanth Raj50% (6)
- Latest Technology in Steering System and Epas By: Jyotirmai Sharma - A2367816029 (B.tech AME)Document5 pagesLatest Technology in Steering System and Epas By: Jyotirmai Sharma - A2367816029 (B.tech AME)Jyotirmai SharmaNo ratings yet
- AutomotiveDocument259 pagesAutomotiveNavasca RandeeNo ratings yet
- Bma4723 Vehicle Dynamics Chap 8Document36 pagesBma4723 Vehicle Dynamics Chap 8Fu HongNo ratings yet
- Usage of Tumbler Gear Mechanism in Four Wheel SteeringDocument5 pagesUsage of Tumbler Gear Mechanism in Four Wheel SteeringKitkuparbha MawrieNo ratings yet
- Gear & Gear RatioDocument4 pagesGear & Gear RatioSouvik GhatakNo ratings yet