Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 3 Question
Tutorial 3 Question
Uploaded by
Jackson TeohOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 3 Question
Tutorial 3 Question
Uploaded by
Jackson TeohCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particles: Work & Energy (b)
Tutorial 2
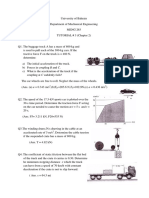
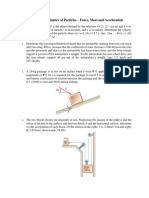
1. The material hoist and the load have a total mass of 800 kg and the counterweight C
has a mass of 150 kg. At a given instant, the hoist has an upward velocity of 2 m/s
and an acceleration of 1.5 m/s 2 . Determine the power generated by the motor M at
this instant if it operates with an efficiency of 0.8 .
(19.5 kW)
Figure Q1
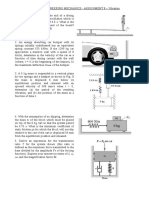
2. The block has a mass of 150 kg and rests on a surface for which the coefficients of
static and kinetic friction are s 0.5 and k 0.4 , respectively. If a force
F 60t 2 N where t is in seconds, is applied to the cable, determine the power
developed by the force when t 5 s . Hint: First determine the time needed for the
force to cause motion.
(58.1 kW)
Figure Q2
3. The roller coaster car having a mass m is released from rest at point A. If the track is
to be designed so that the car does not leave it at B, determine the required height h.
Also, find the speed of the car when it reaches point C. Neglect friction.
(h = 23.75 m, vc = 21.6 m/s)
Figure Q3
Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particles: Work & Energy (b)
Tutorial 2
4. The vertical guide is smooth and the 5-kg collar is released from rest at A. Determine
the speed of the collar when it is at position C. The spring has an unstretched length of
300 mm.
(vC = 2.09 m/s)
Figure Q4
5. The Raptor is an outside loop roller coaster in which riders are belted into seats
resembling ski-lift chairs. If the cars travel at v0 4 m/s when they are at the top of
the hill, determine their speed when they are at the top of the loop and the reaction
force of the 70-kg passenger on his seat at this instant. The car has a mass of 50 kg.
Take h = 12 m, 5 m . Neglect friction and the size of the car and passenger.
(v1 = 7.432 m/s, N = 86.7 N
Figure Q5
Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particles: Impulse and Momentum
Tutorial 2
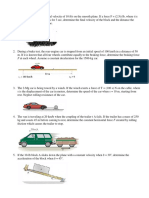
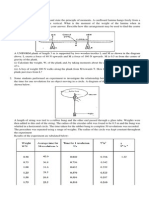
1. If it takes 35 s for the 50-Mg tugboat to increase its speed uniformly to 25 km/h
starting from rest, determine the force of the rope on the tugboat. The propeller
provides the propulsion force F which gives the tugboat forward motion, whereas the
barge moves freely. Also, determine F acting on the tugboat. The barge has a mass of
75 Mg.
(F = 24.8 kN, T = 14.9 kN)
Figure Q1
2. The crate B and cylinder A have a mass of 200 kg and 75 kg, respectively. If the
system is released from rest, determine the speed of the crate and cylinder when
t 3 s . Neglect the mass of the pulleys.
(8.41 m/s)
Figure Q2
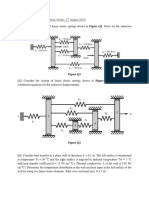
3. The 30-Mg freight car A and 15-Mg freight car B are moving towards each other with
the velocities shown. Determine the maximum compression of the spring mounted on
car A. Neglect rolling resistance.
(481 mm)
Figure Q3
Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particles: Impulse and Momentum
Tutorial 2
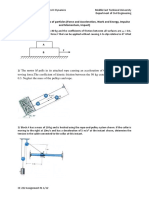
4. The 5-Mg truck and 2-Mg car are traveling with the free rolling velocities shown just
before they collide. After the collision, the car moves with a velocity of 15 km/h to
the right relative to the truck. Determine the coefficient of restitution between the
truck and car and the loss of energy due to the collision.
(e = 0.75, E 9.65 kJ )
Figure Q4
5. Block A has a mass of 3 kg and is sliding on a rough horizontal surface with a velocity
vA 1 5 m/s when it makes a direct collision with block B, which has a mass of 2 kg
and is originally at rest. If the collision is perfectly elastic determine the velocity of
each block just after collision and the distance between the blocks when they stop
sliding. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the blocks and the plane is
k 0.3 .
(vA, 2 = 0.4 m/s, vB, 2 = 2.4 m/s, d = 0.951 m)
Figure Q5
6. At the instant r 1.5 m , the 5-kg disk is given a speed of v 5 m/s , perpendicular to
the elastic cord. Determine the speed of the disk and the rate of shortening of the
elastic cord at the instant r 1.2 m . The disk slides on the smooth horizontal plane.
Neglect its size. The cord has an unstretched length of 0.5 m.
(v2 = 6.732 m/s, v2, r = 2.52 m/s)
Figure Q6
You might also like
- Tutorial 12 Scheduling 2017-18Document4 pagesTutorial 12 Scheduling 2017-18Jackson TeohNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Unit 2 QuizDocument11 pagesAP Physics Unit 2 QuizReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- SMK Bandar Sungai Petani 2021 Yearly Planner (Mapping Table) For English Language Form 5Document3 pagesSMK Bandar Sungai Petani 2021 Yearly Planner (Mapping Table) For English Language Form 5Siti Rohana Darus100% (1)
- Ee2233 - Tutorial 01Document3 pagesEe2233 - Tutorial 01Aneel NaickerNo ratings yet
- CO-4 Assignment QuestionsDocument7 pagesCO-4 Assignment QuestionsrajeswariNo ratings yet
- Examples MomentumDocument9 pagesExamples Momentumettypasewang0% (1)
- DinmjgDocument10 pagesDinmjghaker linkisNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetDocument12 pagesWork Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetAnonymous LZmFaXc100% (2)
- Pisiks 71 Prob SetsDocument8 pagesPisiks 71 Prob SetsAndroNo ratings yet
- John Carroll University Magazine Spring 2012Document54 pagesJohn Carroll University Magazine Spring 2012johncarrolluniversityNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document4 pagesTutorial 2Chong Sing0% (2)
- Dynamics Tutorial Sheet 4 - Particle KineticsDocument6 pagesDynamics Tutorial Sheet 4 - Particle KineticsmahirNo ratings yet
- MecDocument2 pagesMecsiddharth yadavNo ratings yet
- Mechanics TutorialDocument23 pagesMechanics TutorialDipesh PanditNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 6: (A 1.547 m/s2, T 60 N) 4Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 6: (A 1.547 m/s2, T 60 N) 4Aashish BhandariNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document3 pagesTutorial 3Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- Tutorial W12 Kinetics of A Particle Force & AccelerationDocument3 pagesTutorial W12 Kinetics of A Particle Force & AccelerationSek Chin JiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 8Document3 pagesTutorial 7 8Zahida ParnisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2Lhey Anne Dipasupil EstiloNo ratings yet
- F at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarDocument12 pagesF at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarAndre BocoNo ratings yet
- CE222 Problem Set 2Document12 pagesCE222 Problem Set 2Mehmet ArasNo ratings yet
- Dinamik Final Örnek Sorular PDFDocument3 pagesDinamik Final Örnek Sorular PDFgedikoNo ratings yet
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Document5 pagesUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- The Tow Truck With Attached 1200Document18 pagesThe Tow Truck With Attached 1200david caraballoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 & 4Document13 pagesUnit 3 & 4Ram Chandra0% (1)
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledObiedaNo ratings yet
- Semester 2 2013/2014: Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringDocument7 pagesSemester 2 2013/2014: Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringBong Kuek KongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Dynamics-Kinematics-KineticsDocument36 pagesChapter 6-Dynamics-Kinematics-Kineticsعمر صرانNo ratings yet
- Assignment #2Document3 pagesAssignment #2Eileen WongNo ratings yet
- Es 221 - Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: I. Kinetics of A Particle (Force & Acceleration)Document4 pagesEs 221 - Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: I. Kinetics of A Particle (Force & Acceleration)Jerard BalalaNo ratings yet
- M1 Chap-5 Supporting MaterialDocument19 pagesM1 Chap-5 Supporting MaterialRocketNo ratings yet
- 1st Yr Hy 09Document4 pages1st Yr Hy 09Grezzju CauchiNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of A Particle-ExDocument20 pagesKinetics of A Particle-ExDerrick Maatla MoadiNo ratings yet
- QuestionafdaDocument11 pagesQuestionafdadinovekNo ratings yet
- AMME 2500 Assig 4 2014Document4 pagesAMME 2500 Assig 4 2014divaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Force and MotionDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Force and MotionJerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- Dynamics RevisionDocument14 pagesDynamics Revision地雷0% (1)
- Tutorial TwoDocument5 pagesTutorial TwoParas gurungNo ratings yet
- Oscillation SDocument2 pagesOscillation SSpammerNo ratings yet
- Unit V - Unid End Questions - EMDocument6 pagesUnit V - Unid End Questions - EMNaresh JonnaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 WEDocument5 pagesTutorial 3 WE2B Dai Ko DUPLICATENo ratings yet
- CHP 1 HOIST 2019Document22 pagesCHP 1 HOIST 2019Max LuxNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 24Document2 pagesAssignment 1 24Laurens KwofieNo ratings yet
- Tute Sheet # 2 (Conventional DC and Ac Traction) : Uee841 Industrial ElectronicsDocument1 pageTute Sheet # 2 (Conventional DC and Ac Traction) : Uee841 Industrial Electronicsalisha27No ratings yet
- Section A and B MechanicsDocument7 pagesSection A and B MechanicsJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations - Sample TestDocument4 pagesMechanical Vibrations - Sample TestTurin TurambarNo ratings yet
- Model Questiones For Engineering Mechanics 1 Year All BranchesDocument10 pagesModel Questiones For Engineering Mechanics 1 Year All BranchesFeolo Riel TarayNo ratings yet
- Applied Dynamics QuestionsDocument5 pagesApplied Dynamics QuestionsKritamMaharjanNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document5 pagesModule 6John Kennedy EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- WIRE ROPE HAULAGE WordDocument16 pagesWIRE ROPE HAULAGE WordAnshul yadavNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument8 pagesMomentumPraphul Malol0% (1)
- Solve Rectilinear MotionDocument4 pagesSolve Rectilinear Motionصادق سلام محمود شوطNo ratings yet
- T2 Force - AccelerationDocument4 pagesT2 Force - AccelerationDipesh PanditNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 NewtonsDocument4 pagesTutorial 2 Newtons2B Dai Ko DUPLICATENo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNNo ratings yet
- M1 Supporting Material 3 - Connected Particles Types I - IXDocument9 pagesM1 Supporting Material 3 - Connected Particles Types I - IXTanvir IslamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6: Me 313: Dynamics of Machinery Tutorial ProblemsDocument4 pagesTutorial 6: Me 313: Dynamics of Machinery Tutorial Problemsdab111No ratings yet
- Applied MechanicsDocument3 pagesApplied MechanicssushilNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document4 pagesCH 07Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- 3.1 External Forced Convection PDFDocument32 pages3.1 External Forced Convection PDFJackson TeohNo ratings yet
- Ehm 3066 Engineer and Soceity TRIMESTER 3 2017/2018 Chapter 2 TutorialDocument1 pageEhm 3066 Engineer and Soceity TRIMESTER 3 2017/2018 Chapter 2 TutorialJackson TeohNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Jackson TeohNo ratings yet
- Before 4pm, Friday, 2 August 2019) : Figure Q1Document3 pagesBefore 4pm, Friday, 2 August 2019) : Figure Q1Jackson TeohNo ratings yet
- 3.1 External Forced ConvectionDocument32 pages3.1 External Forced ConvectionJackson TeohNo ratings yet
- Supply-ChainDocument61 pagesSupply-ChainJackson TeohNo ratings yet
- Internal Forced Internal Forced Internal Forced Internal Forced Convection Convection Convection ConvectionDocument9 pagesInternal Forced Internal Forced Internal Forced Internal Forced Convection Convection Convection ConvectionJackson TeohNo ratings yet
- MTS MOM 1730 TutorialDocument3 pagesMTS MOM 1730 TutorialJackson TeohNo ratings yet
- Lean SystemDocument33 pagesLean SystemJackson TeohNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Method in Control - Root Locus MethodDocument41 pagesChapter 5: Method in Control - Root Locus MethodJackson TeohNo ratings yet
- EME 1066 Strength of Materials 2016/2017/02: Tutorial Solution 1Document7 pagesEME 1066 Strength of Materials 2016/2017/02: Tutorial Solution 1Jackson TeohNo ratings yet
- Availability Analysis: Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesAvailability Analysis: Tutorial QuestionsJackson TeohNo ratings yet
- EME 1066 Strength of Materials 2015/2016/02: Tutorial Solution 4Document13 pagesEME 1066 Strength of Materials 2015/2016/02: Tutorial Solution 4Jackson TeohNo ratings yet
- Ay"+ By' + Cy : (A) Basic Rule Term in Choice For 2eDocument4 pagesAy"+ By' + Cy : (A) Basic Rule Term in Choice For 2eJackson TeohNo ratings yet
- 3 - Module 2 Masonry WorksDocument20 pages3 - Module 2 Masonry WorksallankatenguddoNo ratings yet
- Systematic Review On Success of Narrow ImplantsDocument31 pagesSystematic Review On Success of Narrow Implantsjosue_eNo ratings yet
- MKT Marunda Center ProfileDocument47 pagesMKT Marunda Center ProfileMuhammad AbidinNo ratings yet
- GIS Data ModelDocument46 pagesGIS Data ModelFAizal AbdillahNo ratings yet
- Korean WaveDocument12 pagesKorean WaveJm PogiNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 10 02443Document19 pagesSustainability 10 02443mercyella prasetyaNo ratings yet
- Oops FinalDocument47 pagesOops Finaludaya57No ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX - Toyota 8fg45n Forklift Service Repair Manual 1608089928 PDFDocument23 pagesVdocuments - MX - Toyota 8fg45n Forklift Service Repair Manual 1608089928 PDFGUILHERME SANTOSNo ratings yet
- SG250HX User+Manual V15 20201106Document78 pagesSG250HX User+Manual V15 20201106specopbookieNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Coulomb's Law Sample ProblemsDocument7 pages7.2 Coulomb's Law Sample ProblemsMeeriya NewtonNo ratings yet
- Personal Report Rajiv Patil: Focus StylesDocument3 pagesPersonal Report Rajiv Patil: Focus Stylesrajivpatil11No ratings yet
- Bestcom-Considerate ComputingDocument8 pagesBestcom-Considerate ComputingĐức Nguyễn TuấnNo ratings yet
- Setting Goals: Throughout This Course You Have Gone Through The Process of Education and Career/Life PlanningDocument4 pagesSetting Goals: Throughout This Course You Have Gone Through The Process of Education and Career/Life PlanningMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- LVL 0 - Practical - 2 Contouring Cut and Fill For EarthworksDocument4 pagesLVL 0 - Practical - 2 Contouring Cut and Fill For Earthworksnuraina aqilahNo ratings yet
- Mini Proj RCT 222 PDFDocument34 pagesMini Proj RCT 222 PDF4073 kolakaluru mounishaNo ratings yet
- 624-DEFLECTOR PLATE CHANGING of CSR#3Document4 pages624-DEFLECTOR PLATE CHANGING of CSR#3Buddy HartNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 - Sequence 1.mdiDocument7 pagesUNIT 1 - Sequence 1.mdi,arcisNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Book PDFDocument4 pagesMicroprocessor Book PDFJagan Eashwar0% (4)
- Estonian Foreign Intelligence Service Annual Report - 2020Document82 pagesEstonian Foreign Intelligence Service Annual Report - 2020Silviu TanaseNo ratings yet
- AnimejsDocument27 pagesAnimejsJesus RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 5.5 CBM Waste Skip Open Top - POWER BearDocument1 page5.5 CBM Waste Skip Open Top - POWER Bearqtia71133No ratings yet
- Siemes (SAMA Standard)Document6 pagesSiemes (SAMA Standard)Cristian RomeroNo ratings yet
- Purpose and Objectives of Starting Up A Project ProcessDocument2 pagesPurpose and Objectives of Starting Up A Project ProcessSocrates KontosNo ratings yet
- Environmental Conservation in Bhutan: Organization and PolicyDocument21 pagesEnvironmental Conservation in Bhutan: Organization and PolicyApriele Rose Gaudicos HermogenesNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics: Dr. Arun Kumar Dr. Arun Kumar Assistant Professor ABV-IIITM, GwaliorDocument11 pagesManagerial Economics: Dr. Arun Kumar Dr. Arun Kumar Assistant Professor ABV-IIITM, GwaliorAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Radiator - Assemble: Previous ScreenDocument8 pagesRadiator - Assemble: Previous ScreenKusuma JayaNo ratings yet
- PS GrammarDocument3 pagesPS GrammarMastermind SunnyNo ratings yet
- Technical Guidelines: Physical Properties of Refrigerants R-410ADocument2 pagesTechnical Guidelines: Physical Properties of Refrigerants R-410AYaxmine Edward StylesNo ratings yet