Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Warfarin Drug Study
Warfarin Drug Study
Uploaded by
Cheezy Bread100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views3 pagesWarfarin is an oral anticoagulant used to treat and prevent blood clots. It works by interfering with vitamin K dependent clotting factors. It has many drug interactions and requires careful monitoring due to risk of bleeding. Nursing considerations include monitoring PT/INR regularly to adjust dosage, evaluating the patient for signs of bleeding, maintaining therapeutic levels based on indication, being aware of many drug interactions, and arranging for frequent follow-up and testing.
Original Description:
Warfarin Drug Study
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWarfarin is an oral anticoagulant used to treat and prevent blood clots. It works by interfering with vitamin K dependent clotting factors. It has many drug interactions and requires careful monitoring due to risk of bleeding. Nursing considerations include monitoring PT/INR regularly to adjust dosage, evaluating the patient for signs of bleeding, maintaining therapeutic levels based on indication, being aware of many drug interactions, and arranging for frequent follow-up and testing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views3 pagesWarfarin Drug Study
Warfarin Drug Study
Uploaded by
Cheezy BreadWarfarin is an oral anticoagulant used to treat and prevent blood clots. It works by interfering with vitamin K dependent clotting factors. It has many drug interactions and requires careful monitoring due to risk of bleeding. Nursing considerations include monitoring PT/INR regularly to adjust dosage, evaluating the patient for signs of bleeding, maintaining therapeutic levels based on indication, being aware of many drug interactions, and arranging for frequent follow-up and testing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
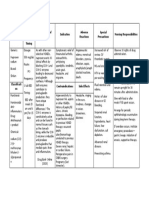
Warfarin Drug Study
In making a Drug Study, the following elements must be present:
Generic Name and the Brand name (not all brands, just the brand
used by the patient), Action, Indication, Pregnancy Category, Drug
Classification, and Contraindication, Adverse Effect, Drug
interaction and Nursing Consideration/Intervention. Most clinical
instructors preferred this to be in a long bond paper in printed or
handwritten with paper in landscape.
Warfarin sodium
Brand Name: Coumadin, Warfilone (CAN)
Pregnancy Category X
Drug classes: Oral anticoagulant, Coumarin derivative
Therapeutic actions
Interferes with the hepatic synthesis of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors
(factors II-prothrombin, VII, IX, and X), resulting in their eventual depletion
and prolongation of clotting times.
Indications
Venous thrombosis and its extension, treatment, and prophylaxis
Treatment of thromboembolic complications of atrial fibrillation with
embolization, and cardiac valve replacement
Pulmonary embolism, treatment, and prophylaxis
Prophylaxis of systemic embolization after acute MI
Unlabeld uses: prevention of recurrent TIAs, prevention of recurrent MI,
adjunct to therapy in small-cell carcinoma of the lung
Contraindications
Contraindicated with allergy to warfarin; SBE; hemorrhagic disorders; TB;
hepatic diseases; GI ulcers; renal disease; indwelling catheters, spinal
puncture; aneurysm; diabetes; visceral carcinoma; uncontrolled
hypertension; severe trauma (including recent or contemplated CNS, eye
surgery; recent placement of IUD); threatened abortion, menometrorrhagia;
pregnancy (fetal damage and death); lactation (suggest using heparin if
anticoagulation is required).
Adverse effects
Hemorrhage; GI or urinary tract bleeding (hematuria, dark stools; paralytic
ileus, intestinal obstruction from hemorrhage into GI tract); petechiae and
purpura, bleeding from mucous membranes; hemorrhagic infarction,
vasculitis, skin necrosis of female breast; adrenal hemorrhage and resultant
adrenal insufficiency; compressive neuropathy secondary to hemorrhage
near a nerve, Alopecia, urticaria, dermatitis, Nausea, vomiting, anorexia,
abdominal cramping, diarrhea, retroperitoneal hematoma, hepatitis,
jaundice, mouth ulcers, Priapism, nephropathy, red-orange urine,
Granulocytosis, leukopenia, eosinophilia, Fever, "purple toes" syndrome
Drug Interactions:
Increased bleeding tendencies with salicylates, chloral hydrate,
phenylbutazone, clofibrate, disulfiram, chloramphenicol, metronidazole,
cimetidine, ranitidine, co-trimoxazole, sulfinpyrazone, quinidine, quinine,
oxyphenbutazone, thyroid drugs, glucagon, danazol, erythromycin,
androgens, amiodarone, cefamandole, cefoperazone, cefotetan, moxalactam,
cefazolin, cefoxitin, ceftriaxone, meclofenamate, mefenamic acid,
famotidine, nizatidine, nalidixic acid
Decreased anticoagulation effect may occur with barbiturates, griseofulvin,
rifampin, phenytoin, glutethimide, carbamazepine, vitamin K, vitamin E,
cholestyramine, aminoglutethimide, ethchlorvynol
Altered effects with methimazole, propylthiouracil
Increased activity and toxicity of phenytoin when taken with oral
anticoagulants
Nursing considerations
Do not use drug if patient is pregnant (heparin is anticoagulant of choice);
advise patient to use contraceptives.
Monitor PT ratio or INR regularly to adjust dosage.
Administer IV form to patients stabilized on Coumadin who are not able to
take oral drug. Dosages are the same. Return to oral form as soon as
feasible.
Do not change brand names once stabilized; bioavailability problems exist.
Evaluate patient regularly for signs of blood loss (petechiae, bleeding gums,
bruises, dark stools, dark urine). Maintain PT ratio of 1.31.5, 1.52 with
mechanical prosthetic valves or recurrent systemic embolism; INR ratio of 2
3, 34.5 with mechanical prosthetic valves or recurrent systemic emboli.
Do not give patient any IM injections.
Double check all drugs ordered for potential drugdrug interaction; dosage
of both drugs may need to be adjusted.
Use caution when discontinuing other medications; warfarin dosage may
need to be adjusted; carefully monitor PT values.
Maintain vitamin K on standby in case of overdose.
Arrange for frequent follow-up, including blood tests to evaluate drug
effects.
Evaluate for therapeutic effects: PT 1.52.5 times the control value; PT
ratio, INR within therapeutic range.
You might also like
- Penicillin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPenicillin Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Phenobarbital Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPhenobarbital Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Risperidone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesRisperidone Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Lovenox (Enoxaparin)Document1 pageLovenox (Enoxaparin)E100% (5)
- XareltoDocument2 pagesXareltoMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- Drug LisinoprilDocument1 pageDrug LisinoprilSrkocherNo ratings yet
- DemerolDocument1 pageDemerolCassie100% (1)
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Ranitidine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesRanitidine Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPrednisone Drug StudyCheezy Bread67% (3)
- Diltiazem CardizemDocument2 pagesDiltiazem CardizemLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- WarfarinDocument10 pagesWarfarinMar Ordanza100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAnn Therese C. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Warfarin SodiumDocument3 pagesWarfarin SodiumAndrea Huecas TriaNo ratings yet
- DRug Study PhenytoinDocument1 pageDRug Study Phenytoinmichelle marquezNo ratings yet
- SpironolactoneDocument2 pagesSpironolactoneKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- NebivololDocument1 pageNebivololshaeNo ratings yet
- Naproxen Sodium Drug StudyDocument1 pageNaproxen Sodium Drug StudyKarl Lourenz Deysolong100% (1)
- HeparinDocument4 pagesHeparinTri Purma SariNo ratings yet
- THEOPHYLLINE - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTHEOPHYLLINE - Drug Studyeric macabiogNo ratings yet
- PropranololDocument6 pagesPropranololanon_678895677No ratings yet
- Nalbuphine (Nubain)Document2 pagesNalbuphine (Nubain)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- LABETALOL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLABETALOL Drug StudyLeoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Drug Actions Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ConsideartionsDocument1 pageDrug Study: Drug Actions Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ConsideartionsRoxas Cedrick100% (1)
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: ClassificationsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Route: Frequency: Before:: AE: HemorrhageDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Route: Frequency: Before:: AE: HemorrhageKim SunooNo ratings yet
- EsmololDocument2 pagesEsmololtherock316_995149No ratings yet
- MEROPENEMDocument1 pageMEROPENEMJust now0% (1)
- DRUG STUDY: Metoprolol - BetalocDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY: Metoprolol - BetalocYum C100% (1)
- Ditropan Drug CardDocument2 pagesDitropan Drug CardBenNo ratings yet
- Darbepoetin AlfaDocument3 pagesDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Heparin MedicationDocument1 pageHeparin Medicationtriagestation100% (2)
- Drug Study of FurosemideDocument5 pagesDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Document4 pagesChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliNo ratings yet
- Mycophenolate MofetilDocument1 pageMycophenolate MofetilAndyPua100% (1)
- Drug Study - KetoprofenDocument3 pagesDrug Study - KetoprofenThalia UyNo ratings yet
- Benazepril Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Document3 pagesBenazepril Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Drug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Delivery RoomDocument7 pagesDrug Study Delivery RoomkhleeoNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oDocument5 pagesFerrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oLelanie Japitana100% (1)
- IsoketDocument2 pagesIsoketJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument4 pagesAmiodaroneTri Purma SariNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - DobutamineDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY - DobutamineAjon Veloso75% (4)
- Patient M. G Drug 1 - Ob MaxDocument5 pagesPatient M. G Drug 1 - Ob MaxGrace MellaineNo ratings yet
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- Verapamil HCL Drug StudyDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCL Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Brand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris IncludingDocument3 pagesBrand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris Includingianecunar0% (1)
- Codeine Phosphate (Drug Study)Document2 pagesCodeine Phosphate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (2)
- Ramipril Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- MetoprololDocument1 pageMetoprololjchowking100% (1)
- Fluimucil Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFluimucil Drug StudyDenzel Ivan A. TadusNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate)Document13 pagesDrug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate)Flauros Ryu Jabien50% (2)
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Med 3 Drug StudyDocument12 pagesMed 3 Drug StudyJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- Lyks - Part 7 Drug StudyDocument6 pagesLyks - Part 7 Drug StudyLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Simvastatin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSimvastatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Simvastatin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSimvastatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- WarfarinDocument5 pagesWarfarinboddarambabuNo ratings yet
- ABX Common Effects of Antibiotics On Other Drugs MMDocument3 pagesABX Common Effects of Antibiotics On Other Drugs MMmicheal1960No ratings yet
- List of Top Ten Drug Interactions in Long-Term CareDocument8 pagesList of Top Ten Drug Interactions in Long-Term Careanon_511980284No ratings yet
- Drug Interaction Report PDFDocument111 pagesDrug Interaction Report PDFbaerbaNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant DrugsDocument7 pagesAnticoagulant DrugsNadia MohammadNo ratings yet
- Phenytoin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPhenytoin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Nitroglycerine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNitroglycerine Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Nifedepine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNifedepine Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Nystatin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNystatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Benadryl Drug StudyDocument3 pagesBenadryl Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Diazepam Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDiazepam Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Lansoprazole Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLansoprazole Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Simvastatin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSimvastatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Potassium Salts Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPotassium Salts Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Ramipril Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- Benicar Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBenicar Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Phenytoin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPhenytoin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Tetracycline HCL Drug StudyDocument4 pagesTetracycline HCL Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Simvastatin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSimvastatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Theophylline Drug StudyDocument3 pagesTheophylline Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (5)
- Verapamil HCL Drug StudyDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCL Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Tramadol HCL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTramadol HCL Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Warfarin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesWarfarin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (2)
- Losartan Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLosartan Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)