Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Judicial Committee of The Privy Council 2. Privy Council of Jamaica
Judicial Committee of The Privy Council 2. Privy Council of Jamaica
Uploaded by
Reshima GayleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Judicial Committee of The Privy Council 2. Privy Council of Jamaica
Judicial Committee of The Privy Council 2. Privy Council of Jamaica
Uploaded by
Reshima GayleCopyright:
Available Formats
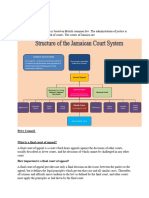
Page 1- Appeals Level
3. JUDICIAL COMMITTEE OF THE PRIVY COUNCIL
2. PRIVY COUNCIL OF JAMAICA
Statute: Judicature (Appellate Jurisdiction Act) Constitution of Jamaica S.110
Jurisdiction:
a. Appeals:
Section 110 Constitution of Jamaica
Section 35 Judicature (Appellate Jurisdiction Act)
Statute: Constitution of Jamaica
Jurisdiction:
a. Prerogative of Mercy
Section 90 -91 Constitution of Jamaica
1. COURT OF APPEAL
Statutes: Judicature (Appellate Jurisdiction Act)
Constitution of Jamaica (Section 103-109)
Jurisdiction:
a. Civil and Criminal Appeals from:
Supreme Court (1b)
Revenue Court (1b)
Gun Court (1b)
Resident Magistrates Court (1a)
Family and Childrens Court (1a)
Traffic Court (1a)
Coroners Court (1a)
Office of the Special Coroners (1a)
Tribunals and Administrative Bodies
Court of Appeal is constituted of a President and six (6)
Judges of Appeal
One (1) President appointed by Governor General on
the recommendation of the Judicial Services
Commission.
The Chief Justice as head of the Judiciary sits but only
when there are at least four (4) other Judges and on
the invitation of the President.
Six (6) Judges of Appeal appointed by the Governor
General on the recommendation of the Judicial
Services Commission.
Qualification required for Judges of Appeal is a minimum of
ten (10) years at the Bar or one who has held office as a
Judge of unlimited Jurisdiction in the Commonwealth.
Privy Council of Jamaica is
constituted of six (6) members
appointed by the Governor
General after consultation with
Prime Minister by instrument
under Board Seal.
Page 2- High Court Level
1b.REVENUE COURT
Statutes: Judicature Revenue Court Act
Jurisdiction:
a. Appeal Cause or Matter
Customs Act
Excise Duty Act
Valuation Act
Income Tax Act
Land Valuation Act
Land Development Act
Transfer Tax Act
Bauxite Production Levy Act
The Revenue Court is presided over
by a Puisne Judge.
Puisne Judges are appointed by the
Governor General on
recommendation of the Judicial
Services Commission.
1b. SUPREME COURT
Statutes: Judicature (Supreme Court) Act
Constitution of Jamaica (Section 97-102)
Jurisdiction:
b. Criminal Division
a. Civil Division
Home Circuit and
High Court Civil
Rural Circuit
Matrimonial
Probate and
Gun Court (Circuit
Administration
Court Division) Judge
Commercial
Sitting with a Jury
Process:
Criminal - Indictment
Civil - Pleadings
Motions
The Supreme Court is presided over by The Chief
Justice who is appointed by the Governor General on
the recommendation of the Prime Minister after
consultation with the Leader of the Opposition.
Also presiding is one (1) Senior Puisne Judge and
thirty-two (32) Puisne Judges all appointed by the
Governor General on recommendation of the Judicial
Services Commission.
There are also up to four (4) Masters in Chambers.
Two (2) Registrars and five (5) Deputy Registrars
1c.CARIBBEAN COURT OF JUSTICE
Statute: Revised Treaty of Chaguaramas
Original Jurisdiction: Hears first instance cases - Interprets and
applies the Revised Treaty of Chagaramus.
NB: Does not have appellate jurisdiction
1b. GUN COURT
Statutes: The Gun Court Act
Jurisdiction: High Court Division - Judge sitting
without a jury
The Gun Court is presided over by a
Puisne Judge.
Puisne Judges are appointed by the
Governor General on
recommendation of the Judicial
Services Commission.
Page 3- First level of Judicature
1a.RESIDENT MAGISTRATES COURT
1a.FAMILY COURT
Statutes: Judicature Family Court Act
Jurisdiction:
Affiliation Act
Childrens (Adoption) Act
Children (Guardianship) Act
Education Act
Child Care and Protection Act
Maintenance Act
Married Womens Property Act
Maintenance Order (Facilities For
Enforcement) Act
The Family Court is presided over by
a Resident Magistrate. Referred to in
this Court as a Judge of the Family
Court.
Resident Magistrates are appointed
by the Governor General on
recommendation of the Judicial
Services Commission.
They are assigned to a parish by the
Chief Justice and report to the Chief
Justice.
The minimum qualification for the
Resident Magistrate is five (5) years
at the Bar.
1a. TRAFFIC COURT
1a.CORONERS COURT
1a.OFFICE OF THE
SPECIAL CORONER
Statutes: The Coroners Act
Statutes: The Traffic Court Act
Statutes: Judicature (Resident Magistrates) Act
Jurisdiction:
Statutes: The Corners Act
a. 1 Parish + 1 mile beyond boundary line of
Parish
b. Summary
Criminal 3 years imprisonment
Process:
The Resident Magistrates Court, Traffic Court, Drug Court, Coroners Court and Office
Information
of the Special Coroner are presided over by a Resident Magistrate.
Indictment
Arrest/ Warrant
Civil- J$3,000,000
Process:
Plaint and statement of claim. The
Resident Magistrates Court is a Court of
evidence and not a Court of pleadings.
1a. DRUG COURT
Statutes: Drug Court (Treatment and
Rehabilitation of Offenders) Act
The Drug court is held under special sitting of
the Resident Magistrates Court
Two (2) Justices of the Peace of which one (1)
must be a woman may preside over the Drug
Court in place of the Resident Magistrate.
Resident Magistrates are appointed by the Governor General on recommendation of
the Judicial Services Commission.
They are assigned to a parish by the Chief Justice and report to the Chief Justice.
The minimum qualification for the Resident Magistrate is five (5) years at the Bar.
Page 4 Petty Sessions / Lay Magistrates Court
PETTY SESSIONS OR LAY MAGISTRATES COURT
Statutes: Justices of the Peace Jurisdiction Act
Jurisdiction:
a. Parish in which the Court sits
b. Summary Criminal or Minor Offences
Maximum Term- 3 months
Maximum fine - J$2000.00
Penalty determined by statute creating offence
Process:
Summons on information
1. The Petty Sessions Court is Presided Over by Two (2) or three (3) Justices of the
Peace. One (1) Resident Magistrate sitting exercises the power of two (2) Justices.
2. Justices of the Peace are appointed by the Governor General on the recommendation
of the Minister if Justice.
3. They are appointed by commission and appointed to the Petty Sessions panel by the
Custos of the Parish.
4. They report to the Custos in relation to conduct. The tenure of their office depends
on good behaviour.
5. The functions of the Justice of the Peace include:
Petty Sessions Duty
Attest Legal Documents
Witness making of statements under caution
Attend Identification Parades
Attend Spirit Licence Sessions
Consider applications for bail
You might also like
- Ebook PDF We The People Full Twelfth Edition 12th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF We The People Full Twelfth Edition 12th Edition PDFdale.brinkman835100% (40)
- Adheen Vyas Bar Vocational Course Civil Procedure PDFDocument100 pagesAdheen Vyas Bar Vocational Course Civil Procedure PDFVikash Beesoon100% (1)
- Introduction To South African LawDocument45 pagesIntroduction To South African LawZakiyyah Parker100% (1)
- Business Law Notes UCTDocument86 pagesBusiness Law Notes UCTLouisNo ratings yet
- Criminal Procedure Notes - KucDocument159 pagesCriminal Procedure Notes - KucDickson Tk Chuma Jr.100% (3)
- Assignment BA in Communication Studies, Media and Journalism Media Law and EthicsDocument12 pagesAssignment BA in Communication Studies, Media and Journalism Media Law and Ethicsvimal coosnaNo ratings yet
- Administrative Law in Tanzania. A Digest of CasesFrom EverandAdministrative Law in Tanzania. A Digest of CasesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Form U Abstract of The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972 (English Version)Document2 pagesForm U Abstract of The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972 (English Version)chirag bhojak0% (1)
- Lecture 3 - The Hierarchy of Courts Hierarchy of Courts in JamaicaDocument4 pagesLecture 3 - The Hierarchy of Courts Hierarchy of Courts in JamaicaCrisNo ratings yet
- Branches of Philippine GovernmentDocument15 pagesBranches of Philippine Governmentgab sapkiNo ratings yet
- The Judicial System in CameroonDocument8 pagesThe Judicial System in CameroonKïdd bkwNo ratings yet
- Structure EgyptDocument22 pagesStructure EgyptEgyptian proudNo ratings yet
- THE-JUDICIAL-DEPARTMENTDocument2 pagesTHE-JUDICIAL-DEPARTMENTMikaella LorañaNo ratings yet
- Jesus Loves You: Law Notes, Past Questions and Answers atDocument40 pagesJesus Loves You: Law Notes, Past Questions and Answers atVite Researchers75% (4)
- The British Judiciary: Unit 4Document76 pagesThe British Judiciary: Unit 4anemajaNo ratings yet
- British Judiciary 11Document72 pagesBritish Judiciary 11medusaqueenNo ratings yet
- Machinery of JusticeDocument38 pagesMachinery of JusticeSam HarrisonNo ratings yet
- CLJ1 Lesson Part 4Document3 pagesCLJ1 Lesson Part 4DE GUZMAN VONNo ratings yet
- Court: The Third Pillar of PCJSDocument23 pagesCourt: The Third Pillar of PCJSMariel AlcazarNo ratings yet
- Court of Tax Appeals (RA1125 As Amended by RA 9503 and RA 9282)Document2 pagesCourt of Tax Appeals (RA1125 As Amended by RA 9503 and RA 9282)G23 Roniza Mae RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Judiciary Arm of Goverment Evening School 2024Document13 pagesJudiciary Arm of Goverment Evening School 2024lamarmendez254No ratings yet
- MTC Prac Court Written ReportDocument6 pagesMTC Prac Court Written ReportMak FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 4 - Caselaw - Efundi - 2024 - 5Document54 pagesStudy Unit 4 - Caselaw - Efundi - 2024 - 5mpolosigusbaNo ratings yet
- Court StructureDocument3 pagesCourt StructureCasandraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Law and The Jamaican Legal SystemDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Law and The Jamaican Legal Systemnishaura100% (2)
- Hierarchy of Court AuthorityDocument6 pagesHierarchy of Court AuthorityYwani Ayowe KasilaNo ratings yet
- Court SystemDocument20 pagesCourt SystemEcoboy MimiNo ratings yet
- The Judicial System of CameroonDocument3 pagesThe Judicial System of CameroonPASTOR STARNo ratings yet
- Bruce ch2Document6 pagesBruce ch2Khristian DanielNo ratings yet
- Lpr105d Chapter 5Document17 pagesLpr105d Chapter 5savory-clouts-0yNo ratings yet
- Revision NoteDocument18 pagesRevision NoteNipuni PereraNo ratings yet
- The Hierachy of CourtsDocument2 pagesThe Hierachy of CourtsAnnelly WanderaNo ratings yet
- The Romanian Judiciary - Overview - A. The Romanian JudiciaryDocument4 pagesThe Romanian Judiciary - Overview - A. The Romanian JudiciaryBabeanu GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Summary Article 8Document10 pagesSummary Article 8Rhoda Beth VergaraNo ratings yet
- The Court System in The UkDocument29 pagesThe Court System in The UkMiron XescuNo ratings yet
- Cape Law Courts StructuresDocument7 pagesCape Law Courts StructuresJustin GrahamNo ratings yet
- Criminal Procedure LLB 2 LECTURESDocument47 pagesCriminal Procedure LLB 2 LECTURESABDOULIENo ratings yet
- Judicial Power: Kinds of OffensesDocument2 pagesJudicial Power: Kinds of OffensesCharmane MaeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document29 pagesLecture 4James MakauNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document48 pagesChapter 4Celyn Anne Jati EkongNo ratings yet
- Good Morning UsaDocument4 pagesGood Morning UsamvanishcNo ratings yet
- Article Viii: Judicial DepartmentDocument62 pagesArticle Viii: Judicial DepartmentShalene Mesina QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- 3) Courts in MalaysiaDocument50 pages3) Courts in MalaysiaAisyah MohamadNo ratings yet
- Philippine Judicial System: Historical BackgroundDocument34 pagesPhilippine Judicial System: Historical BackgroundRinelky Agacid DandasanNo ratings yet
- Structure, Power, and Functions of JudiciaryDocument8 pagesStructure, Power, and Functions of JudiciarySubhodip MalakarNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document15 pagesTopic 1Ocaka RonnieNo ratings yet
- Civil Court: Presented byDocument33 pagesCivil Court: Presented byZeesahnNo ratings yet
- Topic 2b - MALAYSIA LEGAL SYSTEMDocument25 pagesTopic 2b - MALAYSIA LEGAL SYSTEMLuqman NHNo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and GovernanceDocument5 pagesPhilippine Politics and GovernanceAndrea MacatangayNo ratings yet
- 3 Judiciary BranchDocument13 pages3 Judiciary BranchBianca RomeroNo ratings yet
- Business Law 1 NotesDocument80 pagesBusiness Law 1 Notestnrkyl001100% (2)
- What Is The Relationship of The 3 Branches of The Philippine Government As Shown in The Graphic Organizer?Document57 pagesWhat Is The Relationship of The 3 Branches of The Philippine Government As Shown in The Graphic Organizer?Dexter Balisi Bacani100% (2)
- Sep 23 ELSDocument7 pagesSep 23 ELSAreesha RahatNo ratings yet
- Article Viii - Judicial Department Section 1-8Document21 pagesArticle Viii - Judicial Department Section 1-8Noel IV T. BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Criminal Process: Appeals LA1Document9 pagesCriminal Process: Appeals LA1TobyOsinowoNo ratings yet
- LAW416 (LECTURE WEEK 2) (MLS - LEGISLATIVE PROCESS AND THE COURT SYSTEM) (No Recording)Document16 pagesLAW416 (LECTURE WEEK 2) (MLS - LEGISLATIVE PROCESS AND THE COURT SYSTEM) (No Recording)Tengku HafiyNo ratings yet
- Criminal Procedure LecturesDocument28 pagesCriminal Procedure LecturesAngela MalesiNo ratings yet
- LRDocument6 pagesLRMae EspellargaNo ratings yet
- R.A. 296 PDFDocument20 pagesR.A. 296 PDFavisibleNo ratings yet
- Article Viii - Judicial Department Section 1-8Document21 pagesArticle Viii - Judicial Department Section 1-8Arnel M. MapaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Court StructureDocument5 pagesChapter 1 The Court Structureqeylazatiey93_598514No ratings yet
- The Jurisprudence on Regional and International Tribunals DigestFrom EverandThe Jurisprudence on Regional and International Tribunals DigestNo ratings yet
- Com StudiesDocument3 pagesCom StudiesReshima GayleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Law and Legal Systems in The Commonwealth CaribbeanDocument140 pagesIntroduction To Law and Legal Systems in The Commonwealth CaribbeanReshima GayleNo ratings yet
- NaturalDocument8 pagesNaturalReshima GayleNo ratings yet
- J SDocument9 pagesJ SReshima GayleNo ratings yet
- Constitution: Source of LawDocument13 pagesConstitution: Source of LawReshima GayleNo ratings yet
- Sources of Law Unit 1Document12 pagesSources of Law Unit 1Reshima GayleNo ratings yet
- DR Nadeem Shafiq Malik PDFDocument4 pagesDR Nadeem Shafiq Malik PDFRitu Raj RamanNo ratings yet
- PosterDocument1 pagePosterIndustrial LinkagesNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals Tenth CircuitDocument5 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals Tenth CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Jones2000 - CHEP History GovtDocument14 pagesJones2000 - CHEP History GovtAravind VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- The Great DegenerationDocument2 pagesThe Great DegenerationFaris Ahmad FadzilNo ratings yet
- Rizal NotesDocument4 pagesRizal NotesTifanny Araneta DalisayNo ratings yet
- Turkish-U.S. Relations: The Way ForwardDocument4 pagesTurkish-U.S. Relations: The Way ForwardGerman Marshall Fund of the United StatesNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced SC/ST Certificate FormatDocument1 pageJEE Advanced SC/ST Certificate FormatNishit kumar100% (1)
- Shantanu Upadhyay - Sec C - Eco - Roll No 132Document17 pagesShantanu Upadhyay - Sec C - Eco - Roll No 132Abhishek TiwariNo ratings yet
- Kanlungan Convention PaperDocument4 pagesKanlungan Convention PaperAi Vhee100% (1)
- Aiza A. Cabrera, RSW: Planning Officer Policy and Planning DivisionDocument7 pagesAiza A. Cabrera, RSW: Planning Officer Policy and Planning DivisionMhay Khaeyl Badajos AndohuYhanNo ratings yet
- Graeme B. Robertson-The Politics of Protest in Hybrid Regimes - Managing Dissent in Post-Communist Russia-Cambridge University Press (2010)Document303 pagesGraeme B. Robertson-The Politics of Protest in Hybrid Regimes - Managing Dissent in Post-Communist Russia-Cambridge University Press (2010)wagmart18No ratings yet
- Supreme Court: Guevara v. COMELEC G.R. No. L-12596Document4 pagesSupreme Court: Guevara v. COMELEC G.R. No. L-12596Jopan SJNo ratings yet
- Lessons From The TurnaroundDocument25 pagesLessons From The TurnaroundAlistair DeakinNo ratings yet
- Stereotyping of Muslim Converts: A Preliminary Study On Chinese MuallafDocument12 pagesStereotyping of Muslim Converts: A Preliminary Study On Chinese MuallafRazaleigh MuhamatNo ratings yet
- Handbook On The Construction and Interpretation of The LawDocument1 pageHandbook On The Construction and Interpretation of The Lawlicopodicum7670No ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in - Telephone Directory SL Name Designation Office e Directory English14052019pdfDocument27 pagesFdocuments - in - Telephone Directory SL Name Designation Office e Directory English14052019pdfShubham TyagiNo ratings yet
- Spouses Galang v. Spouses ReyesDocument9 pagesSpouses Galang v. Spouses ReyesRostum AgapitoNo ratings yet
- Toring J. Final ExamDocument5 pagesToring J. Final ExamJessa Dela Rosa ToringNo ratings yet
- Political ScienceDocument62 pagesPolitical ScienceUmayr AzamNo ratings yet
- Minutes of Lisbon Meeting - 2010Document10 pagesMinutes of Lisbon Meeting - 2010Branko BrkicNo ratings yet
- Office of The Ministry of The Attorney GeneralDocument4 pagesOffice of The Ministry of The Attorney GeneralFredNo ratings yet
- Annex 4C Affidavit of UndertakingDocument2 pagesAnnex 4C Affidavit of UndertakingSometimes goodNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow: Administrative LAW - Separation OF PowersDocument20 pagesDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow: Administrative LAW - Separation OF PowersAnonymous LXbdzsgKigNo ratings yet
- Hospital Hotline Number'sDocument2 pagesHospital Hotline Number'sJZ CaraveoNo ratings yet
- Preporuke Za Sigurnosnu Politiku EU Temeljem Iskustva Drzava JUDocument138 pagesPreporuke Za Sigurnosnu Politiku EU Temeljem Iskustva Drzava JUMargoMargo90No ratings yet
- E0363 PDFDocument29 pagesE0363 PDFAnjali KilledarNo ratings yet
- Nonhegemonic International Relations: A Preliminary ConceptualizationDocument22 pagesNonhegemonic International Relations: A Preliminary ConceptualizationPriya NaikNo ratings yet