Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 viewsBiological Booster
Biological Booster
Uploaded by
api-308625760The document describes the nervous system and its components:
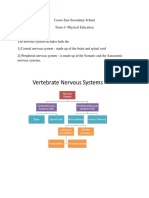
1. The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord.
2. The peripheral nervous system is divided into the somatic nervous system, which is involved in voluntary movement, and the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary functions.
3. The autonomic nervous system has two divisions - the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems - which generally work in opposition to maintain homeostasis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Neurofunctional Blueprints Transcripts For Tempe, January 2015 PDFDocument82 pagesNeurofunctional Blueprints Transcripts For Tempe, January 2015 PDFAnonymous oCjRxyBP100% (3)
- Medical Surgical Nursing NotesDocument66 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Notessimon92% (12)
- Medical Surgical Nursing PinoyDocument85 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing PinoyrosebaseNo ratings yet
- Sociology Activities BankDocument8 pagesSociology Activities Bankapi-308625760No ratings yet
- Biopsychology Topic Worksheet Year 1 SampleDocument17 pagesBiopsychology Topic Worksheet Year 1 SamplebasiaNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesCentral Nervous SystemJaybelle MadolariaNo ratings yet
- Case Pres MeningitisDocument25 pagesCase Pres MeningitisDrew CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Titip Tugas 1Document5 pagesTitip Tugas 1Listia NingsihNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Lecture BorromeoDocument6 pagesNeurologic Lecture BorromeoKriztian BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System1Document43 pagesNervous System1human anatomy100% (1)
- 179 Anatomy Nervous System 1Document55 pages179 Anatomy Nervous System 1Ralph NilloNo ratings yet
- BONADocument4 pagesBONATucho YadetaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Physiology (Nervous System)Document44 pagesUnit 2 Physiology (Nervous System)Laisa RarugalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - The Nervous Systemxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Week 1b Term 2 The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesGrade 10 Week 1b Term 2 The Nervous SystemEsther KissoonNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemsDocument37 pagesNervous SystemsHannah CabritoNo ratings yet
- 14.1 The Nervous SystemDocument15 pages14.1 The Nervous SystemNathan TeferaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PDFDocument20 pagesModule 3 PDFSuiluj Omatsodlab100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document7 pagesChapter 3Azzem JenalNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - QuizDocument65 pagesNervous System - Quizrmmms100% (1)
- NIOT-UnitII-The Nervous System-AnnotationsDocument9 pagesNIOT-UnitII-The Nervous System-Annotationsrt.cseNo ratings yet
- Asynch NotesDocument18 pagesAsynch NotesEricka Mae BruanNo ratings yet
- File 1476322561Document31 pagesFile 1476322561Maria Tricia Desiree ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Psychology Notes Midterm 1Document24 pagesPsychology Notes Midterm 1AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Organisation of The Nervous System: Form 5 Biology Chapter 3 Body Coordination (A)Document24 pagesOrganisation of The Nervous System: Form 5 Biology Chapter 3 Body Coordination (A)Mei QiiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Notes - Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Notes - Biological Bases of BehaviorMarina QuaveNo ratings yet
- Bio LabW5Document8 pagesBio LabW5iloveacuandtuinaNo ratings yet
- 23.1 Gen Bio ReportingDocument39 pages23.1 Gen Bio ReportingKruk KrukNo ratings yet
- Unit III Nervous System and ElectromyographyDocument101 pagesUnit III Nervous System and ElectromyographyakshayNo ratings yet
- Corticospinal Tract Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesCorticospinal Tract Practice QuestionsAlexaNo ratings yet
- Wa0041Document161 pagesWa0041SULDAANUL CAASHIQIINNo ratings yet
- Theory: History of EEGDocument7 pagesTheory: History of EEGdipakNo ratings yet
- Biology of MindOK1Document120 pagesBiology of MindOK16130019037 FATCHUR RIZQI HAMZAHNo ratings yet
- Molina, Zciedie FDocument2 pagesMolina, Zciedie FZeny Ann MolinaNo ratings yet
- CH 7 The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesCH 7 The Nervous Systemapi-267543553No ratings yet
- Week 004 Animal-Nervous-SystemDocument8 pagesWeek 004 Animal-Nervous-SystemMark Lorens StaanaNo ratings yet
- Lect 12Document70 pagesLect 12fatima shahNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Two Major DivisionsDocument33 pagesNervous System: Two Major DivisionsRudi ArfiansyahNo ratings yet
- Brain and BehaviourDocument9 pagesBrain and BehaviourKenya BaileyNo ratings yet
- MARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesMARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemAlmira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Shri PracticleDocument74 pagesShri PracticleshrishivankarNo ratings yet
- MARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesMARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemAlmira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Nervous Systemzainab umerNo ratings yet
- CH 3 (Biology and Behavior) NotesDocument12 pagesCH 3 (Biology and Behavior) NotesMelanieShiNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument51 pagesThe Nervous SystemCho NaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous SystemSatrioNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System 1Document57 pagesThe Nervous System 1seno.kirzvhan.bmlsNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Organization of Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesIntroduction and Organization of Nervous Systemzaraali2405No ratings yet
- CNS and PNSDocument4 pagesCNS and PNSDeepshikhaNo ratings yet
- Neural TissueDocument9 pagesNeural TissueJeff ParkNo ratings yet
- Nervous and Endocrine System Test ChecklistDocument4 pagesNervous and Endocrine System Test Checklistbhoumik.malipeddiNo ratings yet
- 5 BMCDocument18 pages5 BMCRPh FarhatainNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - IDocument38 pagesNervous System - IHa Thuc TienNo ratings yet
- HA Lecture MIDTERM (Neuro)Document31 pagesHA Lecture MIDTERM (Neuro)knowamai567No ratings yet
- Form 5 Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesForm 5 Nervous SystemJeanMichael VincentNo ratings yet
- Group 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Document24 pagesGroup 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Tara DolotaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesNervous SystemPhoebe dane M PandayNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument4 pagesClass Notesdaniel holmesNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesThe Nervous SystemmalakbasahalNo ratings yet
- Review of Peripheral Nervous System: Dr. Syed Atif AbbasDocument31 pagesReview of Peripheral Nervous System: Dr. Syed Atif AbbasAfif HalimNo ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyNo ratings yet
- ApproachesDocument3 pagesApproachesapi-308625760No ratings yet
- Growth Mindset ConversationDocument1 pageGrowth Mindset Conversationapi-308625760No ratings yet
- BiopsychologyDocument29 pagesBiopsychologyapi-308625760No ratings yet
- Research Methods Booklet 1Document5 pagesResearch Methods Booklet 1api-308625760No ratings yet
- Is Psychology A ScienceDocument17 pagesIs Psychology A Scienceapi-308625760No ratings yet
- Research Methods - Report WritingDocument11 pagesResearch Methods - Report Writingapi-308625760No ratings yet
- Psychopathology WorksheetDocument9 pagesPsychopathology Worksheetapi-308625760No ratings yet
- The Sign Test - WorksheetDocument6 pagesThe Sign Test - Worksheetapi-308625760No ratings yet
- Eye Witness TestimonyDocument32 pagesEye Witness Testimonyapi-308625760No ratings yet
Biological Booster
Biological Booster
Uploaded by
api-3086257600 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views3 pagesThe document describes the nervous system and its components:
1. The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord.
2. The peripheral nervous system is divided into the somatic nervous system, which is involved in voluntary movement, and the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary functions.
3. The autonomic nervous system has two divisions - the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems - which generally work in opposition to maintain homeostasis.
Original Description:
Original Title
biological booster
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the nervous system and its components:
1. The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord.
2. The peripheral nervous system is divided into the somatic nervous system, which is involved in voluntary movement, and the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary functions.
3. The autonomic nervous system has two divisions - the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems - which generally work in opposition to maintain homeostasis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views3 pagesBiological Booster
Biological Booster
Uploaded by
api-308625760The document describes the nervous system and its components:
1. The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord.
2. The peripheral nervous system is divided into the somatic nervous system, which is involved in voluntary movement, and the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary functions.
3. The autonomic nervous system has two divisions - the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems - which generally work in opposition to maintain homeostasis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Instructio
ns: Match
the letter
label with
the
description
s and write
in the
missing
Nervous
System (A)
Peripheral
Nervous
System (B)
Somatic
Nervous
System (F)
Central
Nervous
Sytem (C)
Auntonomic
Nervous
System (G)
Sympathetic
Nervous
System (H)
Brain (D)
Spinal Cord
(E)
Parasympath
etic Nervous
System (I)
Transmits information
to and from internal
organs to sustain life
processes.
Provides the biological
basis of psychological
experience.
H
Concerned with all life
functions and
psychological
processes.
Maintains life, involved in
higher functions and
psychological processes.
Transmits information
to and from the
central nervous
system.
Generally maintains or
decreases bodily
activities
The synapse is a specialised gap between neurons
with the electrical impulse from the neuron is
transmitted chemically. The gap between one neuron
and the next is called the synaptic cleft.
Synaptic transmission is the process for transmitting
messages from neuron to neuron.
To start with the electrical nerve impulse travels down
the neuron and prompts the release of
neurotransmitters at the pre-synaptic terminal.
Firing of inhibitory synapses instructs the neuron not to
send an impulse.
The membrane that lies before the cleft is the presynaptic membrane and the one that lies after is the
post-synaptic membrane.
On the post-synaptic membrane are receptor
molecules, these can open or close holes called ion
channels in the membrane.
The adjacent neuron must then quickly take up the
neurotransmitter from the fluid and convert them to an
electrical impulse to travel down the neuron to the
next pre-synaptic terminal.
Synapses can also be excitatory or inhibitory, firing of
excitatory synapses gives the instruction that the
receiving neuron should send an impulse along its
axon.
Number the stages 1-9- and what
stage is missing?
Motor
Sensory
Neuron
Relay
Neuron
These neurons tell the rest of
the brain about the external
and internal environment by
processing information taken
from one of the five senses.
These neurons carry
messages from one part of
the CNS to another. They
connect the other two
neurons.
These neurons carry
signals from the CNS
which helps both organs,
including glands and
muscles function.
You might also like
- Neurofunctional Blueprints Transcripts For Tempe, January 2015 PDFDocument82 pagesNeurofunctional Blueprints Transcripts For Tempe, January 2015 PDFAnonymous oCjRxyBP100% (3)
- Medical Surgical Nursing NotesDocument66 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Notessimon92% (12)
- Medical Surgical Nursing PinoyDocument85 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing PinoyrosebaseNo ratings yet
- Sociology Activities BankDocument8 pagesSociology Activities Bankapi-308625760No ratings yet
- Biopsychology Topic Worksheet Year 1 SampleDocument17 pagesBiopsychology Topic Worksheet Year 1 SamplebasiaNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesCentral Nervous SystemJaybelle MadolariaNo ratings yet
- Case Pres MeningitisDocument25 pagesCase Pres MeningitisDrew CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Titip Tugas 1Document5 pagesTitip Tugas 1Listia NingsihNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Lecture BorromeoDocument6 pagesNeurologic Lecture BorromeoKriztian BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System1Document43 pagesNervous System1human anatomy100% (1)
- 179 Anatomy Nervous System 1Document55 pages179 Anatomy Nervous System 1Ralph NilloNo ratings yet
- BONADocument4 pagesBONATucho YadetaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Physiology (Nervous System)Document44 pagesUnit 2 Physiology (Nervous System)Laisa RarugalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - The Nervous Systemxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Week 1b Term 2 The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesGrade 10 Week 1b Term 2 The Nervous SystemEsther KissoonNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemsDocument37 pagesNervous SystemsHannah CabritoNo ratings yet
- 14.1 The Nervous SystemDocument15 pages14.1 The Nervous SystemNathan TeferaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PDFDocument20 pagesModule 3 PDFSuiluj Omatsodlab100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document7 pagesChapter 3Azzem JenalNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - QuizDocument65 pagesNervous System - Quizrmmms100% (1)
- NIOT-UnitII-The Nervous System-AnnotationsDocument9 pagesNIOT-UnitII-The Nervous System-Annotationsrt.cseNo ratings yet
- Asynch NotesDocument18 pagesAsynch NotesEricka Mae BruanNo ratings yet
- File 1476322561Document31 pagesFile 1476322561Maria Tricia Desiree ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Psychology Notes Midterm 1Document24 pagesPsychology Notes Midterm 1AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Organisation of The Nervous System: Form 5 Biology Chapter 3 Body Coordination (A)Document24 pagesOrganisation of The Nervous System: Form 5 Biology Chapter 3 Body Coordination (A)Mei QiiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Notes - Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Notes - Biological Bases of BehaviorMarina QuaveNo ratings yet
- Bio LabW5Document8 pagesBio LabW5iloveacuandtuinaNo ratings yet
- 23.1 Gen Bio ReportingDocument39 pages23.1 Gen Bio ReportingKruk KrukNo ratings yet
- Unit III Nervous System and ElectromyographyDocument101 pagesUnit III Nervous System and ElectromyographyakshayNo ratings yet
- Corticospinal Tract Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesCorticospinal Tract Practice QuestionsAlexaNo ratings yet
- Wa0041Document161 pagesWa0041SULDAANUL CAASHIQIINNo ratings yet
- Theory: History of EEGDocument7 pagesTheory: History of EEGdipakNo ratings yet
- Biology of MindOK1Document120 pagesBiology of MindOK16130019037 FATCHUR RIZQI HAMZAHNo ratings yet
- Molina, Zciedie FDocument2 pagesMolina, Zciedie FZeny Ann MolinaNo ratings yet
- CH 7 The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesCH 7 The Nervous Systemapi-267543553No ratings yet
- Week 004 Animal-Nervous-SystemDocument8 pagesWeek 004 Animal-Nervous-SystemMark Lorens StaanaNo ratings yet
- Lect 12Document70 pagesLect 12fatima shahNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Two Major DivisionsDocument33 pagesNervous System: Two Major DivisionsRudi ArfiansyahNo ratings yet
- Brain and BehaviourDocument9 pagesBrain and BehaviourKenya BaileyNo ratings yet
- MARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesMARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemAlmira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Shri PracticleDocument74 pagesShri PracticleshrishivankarNo ratings yet
- MARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesMARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemAlmira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Nervous Systemzainab umerNo ratings yet
- CH 3 (Biology and Behavior) NotesDocument12 pagesCH 3 (Biology and Behavior) NotesMelanieShiNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument51 pagesThe Nervous SystemCho NaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous SystemSatrioNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System 1Document57 pagesThe Nervous System 1seno.kirzvhan.bmlsNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Organization of Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesIntroduction and Organization of Nervous Systemzaraali2405No ratings yet
- CNS and PNSDocument4 pagesCNS and PNSDeepshikhaNo ratings yet
- Neural TissueDocument9 pagesNeural TissueJeff ParkNo ratings yet
- Nervous and Endocrine System Test ChecklistDocument4 pagesNervous and Endocrine System Test Checklistbhoumik.malipeddiNo ratings yet
- 5 BMCDocument18 pages5 BMCRPh FarhatainNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - IDocument38 pagesNervous System - IHa Thuc TienNo ratings yet
- HA Lecture MIDTERM (Neuro)Document31 pagesHA Lecture MIDTERM (Neuro)knowamai567No ratings yet
- Form 5 Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesForm 5 Nervous SystemJeanMichael VincentNo ratings yet
- Group 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Document24 pagesGroup 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Tara DolotaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesNervous SystemPhoebe dane M PandayNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument4 pagesClass Notesdaniel holmesNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesThe Nervous SystemmalakbasahalNo ratings yet
- Review of Peripheral Nervous System: Dr. Syed Atif AbbasDocument31 pagesReview of Peripheral Nervous System: Dr. Syed Atif AbbasAfif HalimNo ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyNo ratings yet
- ApproachesDocument3 pagesApproachesapi-308625760No ratings yet
- Growth Mindset ConversationDocument1 pageGrowth Mindset Conversationapi-308625760No ratings yet
- BiopsychologyDocument29 pagesBiopsychologyapi-308625760No ratings yet
- Research Methods Booklet 1Document5 pagesResearch Methods Booklet 1api-308625760No ratings yet
- Is Psychology A ScienceDocument17 pagesIs Psychology A Scienceapi-308625760No ratings yet
- Research Methods - Report WritingDocument11 pagesResearch Methods - Report Writingapi-308625760No ratings yet
- Psychopathology WorksheetDocument9 pagesPsychopathology Worksheetapi-308625760No ratings yet
- The Sign Test - WorksheetDocument6 pagesThe Sign Test - Worksheetapi-308625760No ratings yet
- Eye Witness TestimonyDocument32 pagesEye Witness Testimonyapi-308625760No ratings yet