Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Screw Conveyor PDF
Screw Conveyor PDF
Uploaded by
Taufik 'opics' AkbarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Screw Conveyor PDF
Screw Conveyor PDF
Uploaded by
Taufik 'opics' AkbarCopyright:
Available Formats
SCREW CONVEYOR.
Mechanical Engineering Department
Carlos III University
SCREW CONVEYOR.
TRANSPORTATION
SCREW CONVEYOR.
SCREW CONVEYOR
Transport of material along a tube by means of a
screw
Advantages:
They are compact
Modular design: easy installation
Simple supports
High temperatures
Easily hermetic
Extremely versatile:
Dose
Mixer
Distance up to 50 m
Several loading and unloading
points
SCREW CONVEYOR.
SCREW CONVEYOR
Drawbacks:
No big sizes
No fragile or delicate materials
Non abrasive materials
Bigger power requirements
Material pollution
Low material volume
SCREW CONVEYOR.
COMPONENTS
Hanger
Covers and clamps
Bearing
Shaft
Job rated components,
jig-drilled couplings,
Tem-U-Lac self locking
coupling bolts
Screw
Blades
Conveyor housing
Trough ends
Supporting feet and saddles
Feed and discharge spouts
SCREW CONVEYOR.
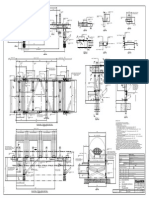
SCREW
It consists of a several of blades of helix shape welded
to a pipe or shaft. It moves the material.
Flight outside diameter, type of blades, spacing between the
blades, thickness of the external diameter and interior shaft
and rotation direction.
Shaft length
Pitch
Flight outside
diameter
Thickness
Shaft outside diameter
SCREW CONVEYOR.
SCREW
Classification:
Spiral screw conveyor (or flight).
Sectional screw conveyor.
Single cut flight.
Ribbon flight.
Standard pitch with paddles.
Screw cut and folded flight.
Single flight short pitch.
Van paddle conveyor.
Single tapered flight standard pitch.
Step flight.
Single flight variable pitch.
Single flight large pitch.
Double flight standard pitch.
SCREW CONVEYOR.
MATERIAL FLUX CALCULATION
Conveyor housing filled area
(m2)
s=
D2
Type of load
Heavy and abrasive
0,125
Heavy and a little
abrasive
0,25
Light and a little
abrasive
0,32
Fill coefficient of the section
(lower than unity)
Light not abrasive
0,4
Screw rotating speed (rpm)
Screw pitch (m)
Travelling speed (m/s)
v=
t n
60
SCREW CONVEYOR.
MATERIAL FLUX CALCULATION
Screw pitch:
Between 0,5 and 1 times its diameter
Bigger for a lighter load
Screw diameter:
12 times bigger than the diameter of the material particles being
transported (homogeneous material)
4 times bigger than the bigger diameter of the material particles
being transported (heterogeneous material)
Screw speed:
Inversely proportional to:
Heavy materials n 50 rpm
Lighter materials n < 150 rpm
Weight of the bulk material
Abrasive materials
Screw diameter
SCREW CONVEYOR.
MATERIAL FLUX CALCULATION
Flux material
decrement coefficient
Material density (t/m3)
Transported
material flux (t/h)
Q = 3600 s v k
s=
D2
v=
Q = 3600
D 2 t n
4
60
t n
60
k
Conveyor housing
inclination
10
15
20
0,9
0,8
0,7
0,6
SCREW CONVEYOR.
POWER
P = PH + PN + PSt
PH is the required power to move the material horizontally
PN is the required power to operate an unloaded screw
PSt is the required power for an inclined screw conveyor
SCREW CONVEYOR.
POWER
Material travelling
Installation length
PH (kW ) = c0
QLg
QL
= c0
3600
367
Material resistance
coefficient
Material
c0 Empiric
Flour, sawdust, granular
1,2
Peat fibre, soda, coal dust
1,6
Anthracite, coal, rock salt
2,5
Gypsum, dry clay, fine soil, cement, lime, sand
SCREW CONVEYOR.
POWER
Unloaded operated screw
PN (kW ) =
DL
20
It is much lower than the power required to move the material
SCREW CONVEYOR.
POWER
Inclined screw conveyor
QH
PSt (kW ) =
367
Installation height
Required power
P=
Q(c0 L + H ) DL
+
367
20
You might also like
- Coiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!From EverandCoiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Screw Conveyor Calculation - Rev. 1Document19 pagesScrew Conveyor Calculation - Rev. 1octatheweelNo ratings yet
- Impact Crusher PDFDocument45 pagesImpact Crusher PDFMusheer BashaNo ratings yet
- WWW Mechanicalengineeringblog Com 2Document6 pagesWWW Mechanicalengineeringblog Com 2Mashudi FikriNo ratings yet
- Screw Conveyor CatalogueDocument100 pagesScrew Conveyor CatalogueAhmedManamaNo ratings yet
- SCREW CONVEYOR Design Speed CalculatorDocument1 pageSCREW CONVEYOR Design Speed Calculatorozzy22No ratings yet
- Pulley CatalogDocument36 pagesPulley CatalogTito FuentesNo ratings yet
- The Selection and Sizing of Bins, Hopper Outlets and FeedersDocument13 pagesThe Selection and Sizing of Bins, Hopper Outlets and FeedersJean Pool Alarcon VilaNo ratings yet
- DTS - Belt Bucket Elevator - DatasheetDocument3 pagesDTS - Belt Bucket Elevator - DatasheetBRUNA NASCIMENTONo ratings yet
- Screw Conveyor CalculationDocument14 pagesScrew Conveyor Calculationvvijaybhan100% (2)
- CP6 Chain FeederDocument119 pagesCP6 Chain Feederdeddy ariyantoNo ratings yet
- Bucket Elevators Catalogue: Gambarotta GschwendtDocument64 pagesBucket Elevators Catalogue: Gambarotta GschwendtRICARDOALEXBORGESNo ratings yet
- Chain Conveyor PT MagmaDocument22 pagesChain Conveyor PT MagmaendriaberNo ratings yet
- Apron Feeder Data SheetDocument1 pageApron Feeder Data SheetPat AuffretNo ratings yet
- Bucket Elevator CatalogDocument43 pagesBucket Elevator Catalogsunyahnil67% (3)
- Screw Conveyor and Bucket Elevator Engineering GuideDocument32 pagesScrew Conveyor and Bucket Elevator Engineering GuideJorge Cronwell Montaño VásquezNo ratings yet
- BELT CONVEYOR - Discharge TrajectoryDocument1 pageBELT CONVEYOR - Discharge TrajectoryEslam FaroukNo ratings yet
- Conveyor Pulley Failure Analysis PDFDocument3 pagesConveyor Pulley Failure Analysis PDFriysallNo ratings yet
- Coal Feeder Catalog (Color)Document10 pagesCoal Feeder Catalog (Color)suparnabhoseNo ratings yet
- Screw ConveyorDocument7 pagesScrew ConveyorTots HolaresNo ratings yet
- SC Calculation Screw Conveyor-Horsepower PDFDocument4 pagesSC Calculation Screw Conveyor-Horsepower PDFQuality Tech AccessoriesNo ratings yet
- I Feeder Application Design CalculationsDocument2 pagesI Feeder Application Design Calculationsarsaniose100% (1)
- Design and Sizing of Screw FeedersDocument8 pagesDesign and Sizing of Screw FeedersPooja PillaiNo ratings yet
- Bucket Elevator ChainDocument4 pagesBucket Elevator Chainluisreng100% (1)
- 7155 - 5 Apron Conveyors Apron FeedersDocument5 pages7155 - 5 Apron Conveyors Apron FeedersMann GurpreetNo ratings yet
- Diemme 2500x2500Document8 pagesDiemme 2500x2500Cristian Mena HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Screw Conveyor CatalogDocument88 pagesScrew Conveyor Catalogmortensen5100% (4)
- T7111-DAS-1053-A-IFA-Baghouse Datasheet - 20170930 PDFDocument4 pagesT7111-DAS-1053-A-IFA-Baghouse Datasheet - 20170930 PDFtiantaufikNo ratings yet
- 830 CB 120 M07 - Rev0Document1 page830 CB 120 M07 - Rev0EDUARDONo ratings yet
- 2010 - Telescopic ChuteDocument29 pages2010 - Telescopic ChutesteelageNo ratings yet
- Rational Design of Conveyor ChutesDocument7 pagesRational Design of Conveyor ChutesarsanioseNo ratings yet
- CEMA Idlers 2008Document72 pagesCEMA Idlers 2008rimarima2barNo ratings yet
- 185-170-5-300-M44-0058 RevDDocument1 page185-170-5-300-M44-0058 RevDVashish RamrechaNo ratings yet
- Vertical Screw Elevators PDFDocument10 pagesVertical Screw Elevators PDFtamil vaananNo ratings yet
- Shaftless Screw ConveyorsDocument2 pagesShaftless Screw Conveyorshenker21No ratings yet
- Bins & Feeders in Cement IndustryDocument29 pagesBins & Feeders in Cement IndustryNaelNo ratings yet
- Screw Conveyor.: C:/Documents and Settings/Damir/Desktop/ Kalkulacija Spirale Transportera - Screw - Conveyor PDFDocument7 pagesScrew Conveyor.: C:/Documents and Settings/Damir/Desktop/ Kalkulacija Spirale Transportera - Screw - Conveyor PDF022freeNo ratings yet
- ConveyorsDocument48 pagesConveyorsAd Man GeTigNo ratings yet
- H02 Processing of Municipal Solid WasteDocument6 pagesH02 Processing of Municipal Solid WasteforuzzNo ratings yet
- Bucket ElevatorDocument9 pagesBucket Elevatorkoripella_prasadNo ratings yet
- Material Handling SC 3.3.2019Document43 pagesMaterial Handling SC 3.3.2019Manoy BermeoNo ratings yet
- Belt Conveyors - RBLDocument141 pagesBelt Conveyors - RBLMigue Migue Salgado ZequedaNo ratings yet
- Extrusion 2012Document100 pagesExtrusion 2012Fernando Lotero100% (4)
- The Capacity of A Screw Conveyor Depends On The Screw DiameterDocument4 pagesThe Capacity of A Screw Conveyor Depends On The Screw Diameterprajesh_bilvaNo ratings yet
- Conveyer Belt DesignDocument21 pagesConveyer Belt DesignAvinnash Vemula96% (25)
- Screw Conveyor DesignDocument5 pagesScrew Conveyor DesignSaron Yayneshet100% (4)
- Chapter Four Storage and Transportation of Solids in Bulk: Chemical Engineering DepartmentDocument30 pagesChapter Four Storage and Transportation of Solids in Bulk: Chemical Engineering DepartmentYohannes EndaleNo ratings yet
- WWW Mechanicalengineeringblog ComDocument4 pagesWWW Mechanicalengineeringblog ComMashudi FikriNo ratings yet
- Materials HandlingDocument27 pagesMaterials HandlingPatricia de LeonNo ratings yet
- EBUYDocument51 pagesEBUYebuy100% (1)
- Chain ConveyorsDocument11 pagesChain Conveyorssgupta_61579683% (6)
- Belt ConveyorsDocument62 pagesBelt Conveyorsjayaraman3100% (1)
- Presentación Equipo 2Document62 pagesPresentación Equipo 2Ruben Lopez RicoNo ratings yet
- Eng A43-A52Document10 pagesEng A43-A52Catherine ExcondeNo ratings yet
- Design Efficient FeedersDocument0 pagesDesign Efficient FeedersRajaram JayaramanNo ratings yet
- Chapter III Solid Handling PDFDocument44 pagesChapter III Solid Handling PDFnahom100% (1)
- Beltconveyor PDFDocument24 pagesBeltconveyor PDFrao159951No ratings yet
- Beltconveyor 170407133414Document24 pagesBeltconveyor 170407133414Ganesh Sakhalkar GSNo ratings yet
- Chap 3MHDocument43 pagesChap 3MHAnonymous HzaFK17Kb100% (1)
- Welcome: Advanced Bulk Material Conveying Technologies in Cement IndustryDocument15 pagesWelcome: Advanced Bulk Material Conveying Technologies in Cement Industry1977julNo ratings yet