Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Faraday'S Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Faraday'S Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Uploaded by
bahia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageFaraday's law of electromagnetic induction states that a voltage is induced in a conductor when the magnetic flux through a loop of the conductor changes over time. The induced voltage is proportional to the rate of change of flux. Specifically, a voltage of 1 volt is induced when the flux changes by 1 weber per second. This fundamental relationship led to practical applications like transformers, generators, and AC motors. Generators and motors work by moving a coil within a magnetic field, causing the flux through the coil to change and induce a voltage according to Faraday's law.
Original Description:
:
Original Title
Faraday
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFaraday's law of electromagnetic induction states that a voltage is induced in a conductor when the magnetic flux through a loop of the conductor changes over time. The induced voltage is proportional to the rate of change of flux. Specifically, a voltage of 1 volt is induced when the flux changes by 1 weber per second. This fundamental relationship led to practical applications like transformers, generators, and AC motors. Generators and motors work by moving a coil within a magnetic field, causing the flux through the coil to change and induce a voltage according to Faraday's law.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageFaraday'S Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Faraday'S Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Uploaded by
bahiaFaraday's law of electromagnetic induction states that a voltage is induced in a conductor when the magnetic flux through a loop of the conductor changes over time. The induced voltage is proportional to the rate of change of flux. Specifically, a voltage of 1 volt is induced when the flux changes by 1 weber per second. This fundamental relationship led to practical applications like transformers, generators, and AC motors. Generators and motors work by moving a coil within a magnetic field, causing the flux through the coil to change and induce a voltage according to Faraday's law.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Universit Kasdi Merbah Ouargla Module : Anglais 2me
anne LMD : Contrle et Automatique, tlcommunication
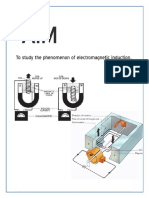
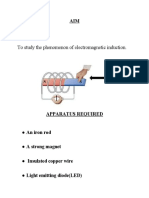
FARADAYS LAW OF ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
In 1831, where pursuing his experiment, Joseph faraday made
one of the most important discoveries in electromagnetism, know is
known as faradays law of electromagnetic induction, It revealed a
fundamental relationship between the voltage and flux in a circuit.
Faradays law states that:
1-If the flux linking a loop (or turn) varies as function of time; a
voltage is induced between its terminals.
2-The value of the induced voltage is proportional to the rate of
change of flux.
By definition, and according to the system of units, when the flux
inside a loop varies at rate of 1 Weber per second, a voltage of 1V is
induced between its terminals, consequently, if a flux varies inside a coil
of N turns, the voltage induced is given by: faradays law of
electromagnetic induction opens the door to a host of practical
applications and establishes the basis of operation of transformers,
generators and alternating current motors.
In many motors and generators, the coils move with respect to a
constant flux.
The relative motion produces a change in the flux linking the coils and
consequently, a voltage is induced, according to faradays 1aw.
However, in this special case, it is easier to calculate the induced
voltage with reference to a conductor, rather than with reference the coil
itself. In effect, whenever a conductor cuts a magnetic field voltage is
induced across its terminals. The value the induced voltage is given by:
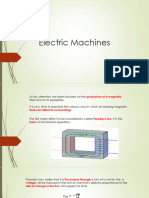
VOLTAGE INDUCED IN A RECTANGULAR CONDUCTOR
Following the discovery of Faradays law of electromagnetic
induction scientists and technicians of the 19 th century did not wait long
to invent and build all kinds of mechanical machines to generate
electricity. The operating principal of these machines is always based
upon the relative motion of a rectangular coil with respect to a
magnetic. Consider a permanent magnet SN revolving at constant
speed inside a stationary iron ring. The ring reduces the reluctance of
the magnetic circuit; consequently, the flux density in the air gap is
greater than if the ring were absent. A rectangular conductor ABCD is
mounted inside the ring, but insulated from it.
Anne universitaire 2016/2017
You might also like
- Emi Class 12 ProjectDocument18 pagesEmi Class 12 ProjectAnsuman Panigrahi71% (7)
- Electromagnetic Induction (Emi) (Phy)Document23 pagesElectromagnetic Induction (Emi) (Phy)Mayank MirchandaniNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectVINIT MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek C 38661023Document19 pagesTinywow Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek C 38661023hackerhack2021centuryNo ratings yet
- PDF Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class XiiDocument19 pagesPDF Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class Xiinandish gupta100% (1)
- KN Phy Project 12Document13 pagesKN Phy Project 12Mariappan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Name - Tirth Joshi Class - Xii Roll No. - 2019-2020Document19 pagesName - Tirth Joshi Class - Xii Roll No. - 2019-2020TIRTH JOSHINo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument8 pagesProjectRaV anNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysics Projectnandish guptaNo ratings yet
- Physics Investogatory Project 2023Document17 pagesPhysics Investogatory Project 2023revNo ratings yet
- Phy-EMI-Shreya ProjectDocument20 pagesPhy-EMI-Shreya Projectshreyaaa1104No ratings yet
- Investigatory Project of PhysicsDocument19 pagesInvestigatory Project of Physicsshubham singhNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek CDocument17 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Abhishek CMr. JANGDANo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectLalit KediaNo ratings yet
- Wa0002.Document21 pagesWa0002.arghyabhai685No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class Xii20190809 5001 1yrh7h0Document19 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class Xii20190809 5001 1yrh7h0Ankita Singh TanwarNo ratings yet
- Physics Faraday ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics Faraday ProjectAlviya Rizwan100% (1)
- Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class Xii PDFDocument19 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class Xii PDFRahulNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction (P) 3Document9 pagesElectromagnetic Induction (P) 3seliyanvalNo ratings yet
- Physics AbhinavDocument22 pagesPhysics AbhinavabhinavNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument20 pagesProjectHIMANSHU GOELNo ratings yet
- Phy104 Electricity and Magnetism 5Document12 pagesPhy104 Electricity and Magnetism 5kadebiyiojoNo ratings yet
- Physics Sample ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysics Sample ProjectRishi Kumar AryaNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class XiiDocument19 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class XiiSai SaranNo ratings yet
- Dheeraj 1Document16 pagesDheeraj 1dheeraj singhrajputNo ratings yet
- EerieDocument19 pagesEerieOmkar GhatageNo ratings yet
- Physics PPT InductDocument19 pagesPhysics PPT InductShrestha Kumar Mishra' XA'No ratings yet
- Phy ProjectDocument18 pagesPhy ProjectRohit rajaNo ratings yet
- AC Generator 2Document18 pagesAC Generator 2sheikhiyad60No ratings yet
- AC GeneratorDocument16 pagesAC Generatorsheikhiyad60No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectSnejjwNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction Ravindra KumarDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic Induction Ravindra KumarDakshya Chandra100% (2)
- Physics Project: Reliance Foundation School KoparkhairaneDocument18 pagesPhysics Project: Reliance Foundation School KoparkhairanePrerana PorechaNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical File 12THDocument18 pagesPhysics Practical File 12THDevayush Enterprise'sNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument18 pagesElectromagnetismShubhojeet BiswasNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Manisha Pal CDocument19 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Manisha Pal CKhushi YadavNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Abhay Class Xii PDFDocument19 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Abhay Class Xii PDFnishra keshavNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument20 pagesPhysics Projectblah68194No ratings yet
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction Project (Ca) (Xii)Document13 pagesPhysics Electromagnetic Induction Project (Ca) (Xii)Asmit UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Chittaranjan Dutta FinalDocument19 pagesChittaranjan Dutta Finalchitta5828No ratings yet
- ISC12 Physics Project668Document19 pagesISC12 Physics Project668Ruhi BhattNo ratings yet
- Kheerthna 12 SapDocument19 pagesKheerthna 12 SapKheerthna GNo ratings yet
- MansiDocument18 pagesMansiOmkar GhatageNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: Name - Kunal Agrawal Roll No. - 20Document22 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Name - Kunal Agrawal Roll No. - 20Kunal AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 06Document17 pagesLecture 06muhammadarsalank01No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction ArmanDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic Induction ArmanMalikNo ratings yet
- Aniruddh RaghuwanshiDocument15 pagesAniruddh Raghuwanshiatharvsolanki.11No ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in Physics Investigatory Project Class XiiDocument21 pagesFdocuments - in Physics Investigatory Project Class XiiEntertainment with IndianNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sector 47 Chandigarh: Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument20 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sector 47 Chandigarh: Physics Investigatory ProjectvinyasNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument49 pagesElectromagnetic InductionalexandrearebucasNo ratings yet
- Electro MagnetDocument18 pagesElectro Magnetshikharvashishtha1729No ratings yet
- Faraday's LawDocument5 pagesFaraday's LawSyeda Rutab AzizNo ratings yet
- Transformer Basic Details4Document2 pagesTransformer Basic Details4amulya sNo ratings yet
- PDF Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class XiiDocument19 pagesPDF Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class XiiDev Tinker100% (1)
- FinalDocument20 pagesFinalKheerthna GNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: Physics Project Report Submitted For Class XIIDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Physics Project Report Submitted For Class XIIsenthil kumarNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project RohiniDocument20 pagesInvestigatory Project RohiniStudy StuffNo ratings yet
- Project On EMIDocument19 pagesProject On EMIPranav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument3 pagesPhysics Investigatory Projectsivansh shuklaNo ratings yet