Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dka Patho Diagram
Dka Patho Diagram
Uploaded by
Grae TaclobCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sitel Resignation LetterDocument1 pageSitel Resignation LetterGrae Taclob50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document4 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2jo_annamae4413100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of DM IIDocument6 pagesPathophysiology of DM IIJulie SimaurioNo ratings yet
- Sitel Resignation LetterDocument1 pageSitel Resignation LetterGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisDocument4 pagesPathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisCyrus Ortalla RobinNo ratings yet
- Colon Rectal CancerDocument6 pagesColon Rectal Cancerbryantmaroney811No ratings yet
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesHypertension PathophysiologyJems60% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseKeij AranetaNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Records - AdultsDocument2 pagesVaccination Records - AdultsverumluxNo ratings yet
- Vivek Jain COMMED Prepladder PDFDocument116 pagesVivek Jain COMMED Prepladder PDFswastik100% (3)
- Pathology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Romeo Rivera Jr.Document1 pagePathology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Romeo Rivera Jr.romeo riveraNo ratings yet
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyDocument3 pages"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisSuzette PipoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of DMRgn Mckl100% (3)
- Liver Cirrhosis: A Case Study OnDocument31 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: A Case Study OnCharmaine del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Pancreatitis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Document7 pagesPancreatitis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Jorie Roco0% (1)
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CHFPerry Oliver AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Concept MapDocument2 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Concept MapIzhra Margate100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Liver Cirrhosisgaelty100% (4)
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS)Document8 pagesHyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS)amiraNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument12 pagesUlcerative ColitisSanthu SuNo ratings yet
- Patof DMDocument1 pagePatof DMxerwaneNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Breast Cancerpauline mangadaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DiabetesDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of DiabetesJeffrey Ramos GironNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument8 pagesHypertensiongilma100% (3)
- Case Study - Septic ShockDocument16 pagesCase Study - Septic ShockIrene Mae Villanueva Ariola100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisHelcon John Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyNo ratings yet
- CHOLANGITISDocument1 pageCHOLANGITISKirk Torregosa PañaresNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusJerene67% (3)
- Case Study: Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument66 pagesCase Study: Diabetic Ketoacidosisllaychin100% (2)
- Patho of DM-2, Case PresentationDocument5 pagesPatho of DM-2, Case PresentationLouella Mae CoraldeNo ratings yet
- DkaDocument29 pagesDkaShadowSpectre0No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document1 pagePathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2faula rocamora100% (3)
- Case Study CholelithiasisDocument14 pagesCase Study Cholelithiasisb_faye20No ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis CaseDocument8 pagesLiver Cirrhosis Casemarlx5No ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument12 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosispolaris_027No ratings yet
- Path o PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersNo ratings yet
- Case Study DM TYPE IIDocument16 pagesCase Study DM TYPE IIrose_avy200975% (4)
- Diabetis MellitusDocument25 pagesDiabetis Mellituscdamasco18No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisKush KhannaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisGeevine CansinoNo ratings yet
- HypopituitarismDocument2 pagesHypopituitarismAnne de VeraNo ratings yet
- CKD PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCKD Pathophysiologylloyd_santino67% (3)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Case PresentationDocument37 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Case PresentationNathan Vince Cruz100% (2)
- Diagram of Pathophysiology CancerDocument5 pagesDiagram of Pathophysiology CancerKristaMaeC.Lazo0% (3)
- Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument3 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Bleedingplayaz_dan2100% (1)
- PathoDocument7 pagesPathoAnonymous 87fNoO2fhVNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument3 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisJanna FavilaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1CajRofuli100% (2)
- HCVD KoDocument10 pagesHCVD KoMarianne BaquilalaNo ratings yet
- Final CVADocument76 pagesFinal CVAGabriel Apalisok100% (1)
- Liver Cirrhosis: Review HepatologyDocument71 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: Review HepatologyAstri Arri FebriantiNo ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationsDocument37 pagesCellular AberrationsJess NinaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Breast CancerChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument3 pagesCholelithiasisMIlanSagittarius0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Adenocarcinoma, Moderately DifferentiatedDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Adenocarcinoma, Moderately Differentiatedmacel sibayan33% (3)
- HCVD Cad Cva InfarctionDocument2 pagesHCVD Cad Cva InfarctionMiguel Carlos Tacderan100% (1)
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Patho 1Document1 pagePatho 1ricciNo ratings yet
- Concept Map AtekharlssDocument3 pagesConcept Map AtekharlssAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Chart - DM MedsDocument7 pagesEndocrine Chart - DM MedsrhondaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYGerome ManantanNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On LeiomyomasDocument4 pagesA Case Study On LeiomyomasGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- NCP 3Document3 pagesNCP 3Grae TaclobNo ratings yet
- Simple Study Was Done Through Survey Using Questionnaire Among Selected Individuals From Cebu, Leyte, Cagayan de Oro, Manila, Doha and United KingdomDocument1 pageSimple Study Was Done Through Survey Using Questionnaire Among Selected Individuals From Cebu, Leyte, Cagayan de Oro, Manila, Doha and United KingdomGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- Scope and LimitationDocument1 pageScope and LimitationGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- A. General Appearance: Pale Palpable ConjunctivaeDocument3 pagesA. General Appearance: Pale Palpable ConjunctivaeGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- She Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andDocument1 pageShe Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- How Many of You Feel As Though You Make Better Decisions When You Have Information? Reminder About Using Index Cards For Anonymous QuestionsDocument6 pagesHow Many of You Feel As Though You Make Better Decisions When You Have Information? Reminder About Using Index Cards For Anonymous QuestionsGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- She Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andDocument1 pageShe Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- LabsDocument1 pageLabsGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- 2 LettersDocument1 page2 LettersGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- She Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andDocument1 pageShe Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- She Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andDocument1 pageShe Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- Ventilator Acquired Pneumonia BundleDocument8 pagesVentilator Acquired Pneumonia BundleGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- Basic Hara Diagnosis An Introduction To Kiiko Style The Avi Way"Document90 pagesBasic Hara Diagnosis An Introduction To Kiiko Style The Avi Way"sillypolo100% (1)
- Synergistic Effect of Lantana CamaraDocument5 pagesSynergistic Effect of Lantana CamaraMarlon Sta. CatalinaNo ratings yet
- Maharani Vashtichandra Shamaradewi UAS B.ingDocument4 pagesMaharani Vashtichandra Shamaradewi UAS B.ingMaharani ShamaradewiNo ratings yet
- Cementum in Disease - PerioDocument50 pagesCementum in Disease - PerioPoojan ThakoreNo ratings yet
- Parotid EctomyDocument33 pagesParotid EctomyAgung Anom Arie WiradanaNo ratings yet
- Mudras and BenefitsDocument15 pagesMudras and BenefitsRangarajan PeramburNo ratings yet
- Correlation of Pericoronitis and The Status of Eruption of Mandibular Third Molar A Clinicoradiographic StudyDocument4 pagesCorrelation of Pericoronitis and The Status of Eruption of Mandibular Third Molar A Clinicoradiographic StudyNa_filaNo ratings yet
- Adverse Effects of Blood TransfusionsDocument3 pagesAdverse Effects of Blood Transfusionsay254No ratings yet
- The Truth Behind The Vaccine Cover-Up, Russell Blaylock Neurosurgeon 2004Document28 pagesThe Truth Behind The Vaccine Cover-Up, Russell Blaylock Neurosurgeon 2004karatekla100% (1)
- BronchiolitisDocument12 pagesBronchiolitisEz BallNo ratings yet
- James W.D., Elston D.M., 2011. Andrews' Diseases of The Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 11th Ed. Saunders/Elsevier London, UK: P. 126Document4 pagesJames W.D., Elston D.M., 2011. Andrews' Diseases of The Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 11th Ed. Saunders/Elsevier London, UK: P. 126FranditaNo ratings yet
- How To Reduce PollutionDocument3 pagesHow To Reduce Pollutionalyaa_haziraNo ratings yet
- EnterobakterDocument36 pagesEnterobakterUttari DalemNo ratings yet
- Donning and DoffingDocument54 pagesDonning and Doffingsasa100% (1)
- Corrected Risk Assessment For Ems SracoDocument7 pagesCorrected Risk Assessment For Ems SracoZeb KhanNo ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology of LabyrinthitisDocument2 pagesThe Pathophysiology of LabyrinthitisSurya Michael ChanceNo ratings yet
- Disadvantages of Fast FoodDocument8 pagesDisadvantages of Fast FoodAhmad SaeedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Health EducationDocument43 pagesChapter 1 - Health EducationKHURT MICHAEL ANGELO TIU100% (2)
- 2013 MedicalsDocument5 pages2013 MedicalsSebastia Felipe SolisNo ratings yet
- Bovine Theileriosis: A Case Study Survey at Chitwan, NepalDocument28 pagesBovine Theileriosis: A Case Study Survey at Chitwan, NepalJibachha ShahNo ratings yet
- Natural Mineral Water and Bottled Drinking Water: P. MadarasingheDocument6 pagesNatural Mineral Water and Bottled Drinking Water: P. MadarasinghekrisshawkNo ratings yet
- Synergistic Antibacterial Activity of Amoxicillin and Bakhaw (Rhizophora Mucronata) Bark Crude Methanolic and Aqueous Extracts Against Staphylococcus Aureus andDocument22 pagesSynergistic Antibacterial Activity of Amoxicillin and Bakhaw (Rhizophora Mucronata) Bark Crude Methanolic and Aqueous Extracts Against Staphylococcus Aureus andGenessa Agustin BuenafeNo ratings yet
- The First AmendmentDocument9 pagesThe First AmendmentJakobi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Infection Control Standard Precautions in Health Care: Aide-MemoireDocument2 pagesInfection Control Standard Precautions in Health Care: Aide-MemoireDaryll Gil Cordova TorregosaNo ratings yet
- Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)Document91 pagesBenign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)UjjawalShriwastavNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Immunization FormDocument1 pageCertificate of Immunization FormPrecilla Janet RosarioNo ratings yet
- 100 MCQsDocument35 pages100 MCQsBader AlMajedNo ratings yet
- Plasmodium Ovale: Phylum Subphylum Class Subclass Family Genes Species:Plasmodium OvaleDocument36 pagesPlasmodium Ovale: Phylum Subphylum Class Subclass Family Genes Species:Plasmodium OvaleAditya MuchayatsyahNo ratings yet
Dka Patho Diagram
Dka Patho Diagram
Uploaded by
Grae TaclobOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dka Patho Diagram
Dka Patho Diagram
Uploaded by
Grae TaclobCopyright:
Available Formats
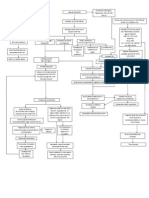
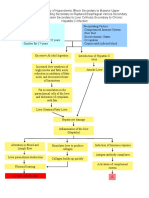
Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
NONMODIFIABLE RISK FACTOR MODIFIABLE RISK FACTOR
Insulin from Pancreas
- (+) FAMILY HISTORY OF PANCREATITIS, - DIET, EXERCISE, LIFESTYLE
DM TYPE 1, MI , STROKE, + - ACUTE INFECTION
& other Hereditary illness - TRAUMA
Glucagon Excess
- SICKNESS, STRESS
- DECREASED OR MISSED INSULIN
- INSULIN DOES NOT MEET PHYSIOLOGIC STRESS
Release of Glucose
From Liver
Glucose cannot
Be used by cell w/o
insulin
Use of fat as source
of energy instead
of glucose
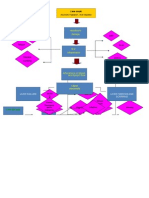
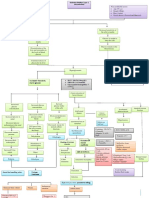
Regular IV insulin 5 units/hr Check BS q hr
Monitor signs BS
Fruity Breath
odor blood Ketones blood glucose
Polyphagia, Polydypsia
(acetone) 300-800 mg/dL
Blood Vessel Injury
vomiting
Draw LABS: Acidosis
Osmotic Diuresis
Lactate/ Urine Output Urinalysis
Lactic Acid S&Sx: Oxygen in body (Polyuria) Urine specific gravity
0.4-2.0 mg/dL
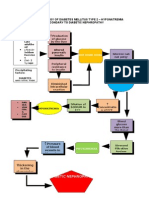
- Hypotension
- Tachycardia Cellular
ABG
Dysfunction
- Nausea
- Vomiting Fluid & electrolyte
- Abdominal pain depletion
- RR
-Kussmaul respiration
Dehydration HR, PR, RR, BP
-Confusion Dry mucous membranes
Shock
-LOC Sodium (Na) Potassium (K+)
Fluid volume deficit
-headache 135-145mEq/L 3.5-5 mEq/L
-drowsiness
-Coma
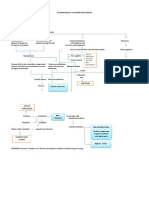
Cerebral Mgmt: Mgmt: IV Fluid
Edema K+ replacement 1L of 0.9% NaCl per hr for 2-3hrs Assess CVP q 30min
Then,
D5W or D51/2 NSS
Seizure Precaution
Check K+ level q
LOC
2-4 hrs
EKG 2-4 hrs
If unmanaged: MODS
Multiorgan Dysfunction Syndrome
THYROID
LIVER
GLAND
= DISEASE PROCESS
= DIAGNOSTIC TESTS ; LABORATORY
= SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
= MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
= NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
New Section 1 Page 1
You might also like
- Sitel Resignation LetterDocument1 pageSitel Resignation LetterGrae Taclob50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document4 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2jo_annamae4413100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of DM IIDocument6 pagesPathophysiology of DM IIJulie SimaurioNo ratings yet
- Sitel Resignation LetterDocument1 pageSitel Resignation LetterGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisDocument4 pagesPathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisCyrus Ortalla RobinNo ratings yet
- Colon Rectal CancerDocument6 pagesColon Rectal Cancerbryantmaroney811No ratings yet
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesHypertension PathophysiologyJems60% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseKeij AranetaNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Records - AdultsDocument2 pagesVaccination Records - AdultsverumluxNo ratings yet
- Vivek Jain COMMED Prepladder PDFDocument116 pagesVivek Jain COMMED Prepladder PDFswastik100% (3)
- Pathology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Romeo Rivera Jr.Document1 pagePathology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Romeo Rivera Jr.romeo riveraNo ratings yet
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyDocument3 pages"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisSuzette PipoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of DMRgn Mckl100% (3)
- Liver Cirrhosis: A Case Study OnDocument31 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: A Case Study OnCharmaine del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Pancreatitis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Document7 pagesPancreatitis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Jorie Roco0% (1)
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CHFPerry Oliver AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Concept MapDocument2 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Concept MapIzhra Margate100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Liver Cirrhosisgaelty100% (4)
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS)Document8 pagesHyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS)amiraNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument12 pagesUlcerative ColitisSanthu SuNo ratings yet
- Patof DMDocument1 pagePatof DMxerwaneNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Breast Cancerpauline mangadaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DiabetesDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of DiabetesJeffrey Ramos GironNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument8 pagesHypertensiongilma100% (3)
- Case Study - Septic ShockDocument16 pagesCase Study - Septic ShockIrene Mae Villanueva Ariola100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisHelcon John Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyNo ratings yet
- CHOLANGITISDocument1 pageCHOLANGITISKirk Torregosa PañaresNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusJerene67% (3)
- Case Study: Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument66 pagesCase Study: Diabetic Ketoacidosisllaychin100% (2)
- Patho of DM-2, Case PresentationDocument5 pagesPatho of DM-2, Case PresentationLouella Mae CoraldeNo ratings yet
- DkaDocument29 pagesDkaShadowSpectre0No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document1 pagePathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2faula rocamora100% (3)
- Case Study CholelithiasisDocument14 pagesCase Study Cholelithiasisb_faye20No ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis CaseDocument8 pagesLiver Cirrhosis Casemarlx5No ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument12 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosispolaris_027No ratings yet
- Path o PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersNo ratings yet
- Case Study DM TYPE IIDocument16 pagesCase Study DM TYPE IIrose_avy200975% (4)
- Diabetis MellitusDocument25 pagesDiabetis Mellituscdamasco18No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisKush KhannaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisGeevine CansinoNo ratings yet
- HypopituitarismDocument2 pagesHypopituitarismAnne de VeraNo ratings yet
- CKD PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCKD Pathophysiologylloyd_santino67% (3)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Case PresentationDocument37 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Case PresentationNathan Vince Cruz100% (2)
- Diagram of Pathophysiology CancerDocument5 pagesDiagram of Pathophysiology CancerKristaMaeC.Lazo0% (3)
- Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument3 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Bleedingplayaz_dan2100% (1)
- PathoDocument7 pagesPathoAnonymous 87fNoO2fhVNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument3 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisJanna FavilaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1CajRofuli100% (2)
- HCVD KoDocument10 pagesHCVD KoMarianne BaquilalaNo ratings yet
- Final CVADocument76 pagesFinal CVAGabriel Apalisok100% (1)
- Liver Cirrhosis: Review HepatologyDocument71 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: Review HepatologyAstri Arri FebriantiNo ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationsDocument37 pagesCellular AberrationsJess NinaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Breast CancerChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument3 pagesCholelithiasisMIlanSagittarius0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Adenocarcinoma, Moderately DifferentiatedDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Adenocarcinoma, Moderately Differentiatedmacel sibayan33% (3)
- HCVD Cad Cva InfarctionDocument2 pagesHCVD Cad Cva InfarctionMiguel Carlos Tacderan100% (1)
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Patho 1Document1 pagePatho 1ricciNo ratings yet
- Concept Map AtekharlssDocument3 pagesConcept Map AtekharlssAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Chart - DM MedsDocument7 pagesEndocrine Chart - DM MedsrhondaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYGerome ManantanNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On LeiomyomasDocument4 pagesA Case Study On LeiomyomasGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- NCP 3Document3 pagesNCP 3Grae TaclobNo ratings yet
- Simple Study Was Done Through Survey Using Questionnaire Among Selected Individuals From Cebu, Leyte, Cagayan de Oro, Manila, Doha and United KingdomDocument1 pageSimple Study Was Done Through Survey Using Questionnaire Among Selected Individuals From Cebu, Leyte, Cagayan de Oro, Manila, Doha and United KingdomGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- Scope and LimitationDocument1 pageScope and LimitationGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- A. General Appearance: Pale Palpable ConjunctivaeDocument3 pagesA. General Appearance: Pale Palpable ConjunctivaeGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- She Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andDocument1 pageShe Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- How Many of You Feel As Though You Make Better Decisions When You Have Information? Reminder About Using Index Cards For Anonymous QuestionsDocument6 pagesHow Many of You Feel As Though You Make Better Decisions When You Have Information? Reminder About Using Index Cards For Anonymous QuestionsGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- She Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andDocument1 pageShe Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- LabsDocument1 pageLabsGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- 2 LettersDocument1 page2 LettersGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- She Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andDocument1 pageShe Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- She Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andDocument1 pageShe Has Been Working in Our Hospital Since April 7, 2014 andGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- Ventilator Acquired Pneumonia BundleDocument8 pagesVentilator Acquired Pneumonia BundleGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- Basic Hara Diagnosis An Introduction To Kiiko Style The Avi Way"Document90 pagesBasic Hara Diagnosis An Introduction To Kiiko Style The Avi Way"sillypolo100% (1)
- Synergistic Effect of Lantana CamaraDocument5 pagesSynergistic Effect of Lantana CamaraMarlon Sta. CatalinaNo ratings yet
- Maharani Vashtichandra Shamaradewi UAS B.ingDocument4 pagesMaharani Vashtichandra Shamaradewi UAS B.ingMaharani ShamaradewiNo ratings yet
- Cementum in Disease - PerioDocument50 pagesCementum in Disease - PerioPoojan ThakoreNo ratings yet
- Parotid EctomyDocument33 pagesParotid EctomyAgung Anom Arie WiradanaNo ratings yet
- Mudras and BenefitsDocument15 pagesMudras and BenefitsRangarajan PeramburNo ratings yet
- Correlation of Pericoronitis and The Status of Eruption of Mandibular Third Molar A Clinicoradiographic StudyDocument4 pagesCorrelation of Pericoronitis and The Status of Eruption of Mandibular Third Molar A Clinicoradiographic StudyNa_filaNo ratings yet
- Adverse Effects of Blood TransfusionsDocument3 pagesAdverse Effects of Blood Transfusionsay254No ratings yet
- The Truth Behind The Vaccine Cover-Up, Russell Blaylock Neurosurgeon 2004Document28 pagesThe Truth Behind The Vaccine Cover-Up, Russell Blaylock Neurosurgeon 2004karatekla100% (1)
- BronchiolitisDocument12 pagesBronchiolitisEz BallNo ratings yet
- James W.D., Elston D.M., 2011. Andrews' Diseases of The Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 11th Ed. Saunders/Elsevier London, UK: P. 126Document4 pagesJames W.D., Elston D.M., 2011. Andrews' Diseases of The Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 11th Ed. Saunders/Elsevier London, UK: P. 126FranditaNo ratings yet
- How To Reduce PollutionDocument3 pagesHow To Reduce Pollutionalyaa_haziraNo ratings yet
- EnterobakterDocument36 pagesEnterobakterUttari DalemNo ratings yet
- Donning and DoffingDocument54 pagesDonning and Doffingsasa100% (1)
- Corrected Risk Assessment For Ems SracoDocument7 pagesCorrected Risk Assessment For Ems SracoZeb KhanNo ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology of LabyrinthitisDocument2 pagesThe Pathophysiology of LabyrinthitisSurya Michael ChanceNo ratings yet
- Disadvantages of Fast FoodDocument8 pagesDisadvantages of Fast FoodAhmad SaeedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Health EducationDocument43 pagesChapter 1 - Health EducationKHURT MICHAEL ANGELO TIU100% (2)
- 2013 MedicalsDocument5 pages2013 MedicalsSebastia Felipe SolisNo ratings yet
- Bovine Theileriosis: A Case Study Survey at Chitwan, NepalDocument28 pagesBovine Theileriosis: A Case Study Survey at Chitwan, NepalJibachha ShahNo ratings yet
- Natural Mineral Water and Bottled Drinking Water: P. MadarasingheDocument6 pagesNatural Mineral Water and Bottled Drinking Water: P. MadarasinghekrisshawkNo ratings yet
- Synergistic Antibacterial Activity of Amoxicillin and Bakhaw (Rhizophora Mucronata) Bark Crude Methanolic and Aqueous Extracts Against Staphylococcus Aureus andDocument22 pagesSynergistic Antibacterial Activity of Amoxicillin and Bakhaw (Rhizophora Mucronata) Bark Crude Methanolic and Aqueous Extracts Against Staphylococcus Aureus andGenessa Agustin BuenafeNo ratings yet
- The First AmendmentDocument9 pagesThe First AmendmentJakobi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Infection Control Standard Precautions in Health Care: Aide-MemoireDocument2 pagesInfection Control Standard Precautions in Health Care: Aide-MemoireDaryll Gil Cordova TorregosaNo ratings yet
- Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)Document91 pagesBenign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)UjjawalShriwastavNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Immunization FormDocument1 pageCertificate of Immunization FormPrecilla Janet RosarioNo ratings yet
- 100 MCQsDocument35 pages100 MCQsBader AlMajedNo ratings yet
- Plasmodium Ovale: Phylum Subphylum Class Subclass Family Genes Species:Plasmodium OvaleDocument36 pagesPlasmodium Ovale: Phylum Subphylum Class Subclass Family Genes Species:Plasmodium OvaleAditya MuchayatsyahNo ratings yet