Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsSuprarenal Glands Clint
Suprarenal Glands Clint
Uploaded by
Bianca WatanabeThe suprarenal glands, also known as adrenal glands, are located above the kidneys. Each gland has a yellow outer cortex that secretes hormones involved in fluid balance, metabolism, and sex development. The inner medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine. The right gland is pyramid-shaped above the kidney while the left is crescent-shaped along the kidney. Blood supply comes from the inferior phrenic, aorta and renal arteries, while veins drain into the inferior vena cava on the right and renal vein on the left. Lymph drains to lateral aortic nodes and the glands receive nerve fibers from the splanchnic nerves.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 3 - Adrenal Glands (386-389, 184-187, 215-217)Document18 pages3 - Adrenal Glands (386-389, 184-187, 215-217)Osama adel Mohamed SmadiNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Renal System: by DR Amber IlyasDocument51 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Renal System: by DR Amber IlyasAlexah BanuagNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument15 pagesAdrenal GlandSivanandan Ramar100% (1)
- Urinary Organs - MahasiswaDocument43 pagesUrinary Organs - MahasiswaJendral Andi Wijaya KusumaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland-1Document2 pagesAdrenal Gland-1Nnanyelugo AdaobiNo ratings yet
- 1 - Anatomy of KidneysDocument22 pages1 - Anatomy of KidneysAHMAD YUNUSA GARBANo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary Tract BaruDocument68 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Tract BaruAdya ArradikhaNo ratings yet
- 8th Seminar TopoDocument36 pages8th Seminar TopoKarthick RajaNo ratings yet
- Ureter and Suprarenal GlandDocument9 pagesUreter and Suprarenal GlandOnwumerechimdikepreciousNo ratings yet
- Suprarenal GlandDocument13 pagesSuprarenal GlandAaa JjjjNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Shakar Mudrik Omer Asma Ibrahem Ismahel Supervisor: DR - Younis ZandyDocument24 pagesPrepared By: Shakar Mudrik Omer Asma Ibrahem Ismahel Supervisor: DR - Younis Zandyزيد مسعودNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.3 Adrenal GlandDocument15 pagesAnatomy Lec.3 Adrenal Glandزينب فؤاد موسىNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Suprarenal Glands f2f-s1b2-23Document17 pages7.2 Suprarenal Glands f2f-s1b2-23shlokNo ratings yet
- The Kidneys IDocument8 pagesThe Kidneys Ior1da2sa3No ratings yet
- Sistem Perkemihan - Hendriyan Sh. B.InggrisDocument13 pagesSistem Perkemihan - Hendriyan Sh. B.InggrisHaniyyahNo ratings yet
- UrinaryDocument18 pagesUrinaryaliofficial12355No ratings yet
- N Ephron 1111Document9 pagesN Ephron 1111Syed Sakline HossainNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Adrenal GlandsDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Adrenal GlandsAnastazia AdeelaNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument40 pagesKidneyOlaifa victorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology-KIDNEYSDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-KIDNEYSnessie dianne c. cuevasNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of The Retroperitoneum, Kidneys, and UretersDocument46 pagesSurgical Anatomy of The Retroperitoneum, Kidneys, and UretersDiana MarcusNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 2023-2024Document16 pagesEndocrine System 2023-2024michaelsoncole410No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The KidneyDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Kidneycatherine kate gulengNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology 1 1aDocument88 pagesRenal Physiology 1 1afentaw melkieNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Visceral OrgansDocument5 pagesAbdominal Visceral OrgansYudi Kelsi KaharapNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument2 pagesPancreasSam TagardaNo ratings yet
- UT AnatomyDocument35 pagesUT AnatomyAngel SaraNo ratings yet
- Lapsus InvaginasiDocument41 pagesLapsus InvaginasiHanda YaniNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesUrinary SystemAubrey Yu JaneaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Endocrine Glands: HypothalamusDocument10 pagesAnatomy of The Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamusgashbin latifNo ratings yet
- L1 - KidneyDocument27 pagesL1 - KidneyKhadeja JayashNo ratings yet
- Kerala University of Health Sciences (Kuhs) Expected Questions On First Year BSC Nursing Degree Examinations 2021Document5 pagesKerala University of Health Sciences (Kuhs) Expected Questions On First Year BSC Nursing Degree Examinations 2021ashna anilNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Kidney - ForDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Kidney - ForKristelle ModalesNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Kidney PDFDocument14 pagesThe Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Kidney PDFredderdatNo ratings yet
- The Adrenal Gland: Anatomy, Embryology & PhysiologyDocument29 pagesThe Adrenal Gland: Anatomy, Embryology & PhysiologyrajarshikNo ratings yet
- Location and External Anatomy of The KidneysDocument15 pagesLocation and External Anatomy of The KidneysKyla Malapit GarvidaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - de Jesus MDDocument3 pagesEndocrine System - de Jesus MDKerenTabuenaNo ratings yet
- The Adrenal Glands - Location - Structure - TeachMeAnatomy PDFDocument4 pagesThe Adrenal Glands - Location - Structure - TeachMeAnatomy PDFUsama KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Endokrin Mei 2019Document64 pagesAnatomi Endokrin Mei 2019insiya insiyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of PancreasDocument6 pagesAnatomy of PancreasNariska CooperNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocument43 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Systemandrea titus100% (1)
- Kidney and Kidneys Function 1Document5 pagesKidney and Kidneys Function 1nogakojasmrdiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy RCR1 RenalDocument3 pagesAnatomy RCR1 RenaleamcrawleyNo ratings yet
- Iii. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesIii. Anatomy and Physiologytedy_berNo ratings yet
- The KidneysDocument11 pagesThe KidneysJordan MosesNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland: Nani Murniat Departemen AnatomiDocument43 pagesAdrenal Gland: Nani Murniat Departemen Anatomisintia saputraNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocument41 pagesThe Urinary System: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin Universityraynhard b. fandresNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Ingles MédicoDocument14 pagesVocabulary Ingles MédicoMayra LandoNo ratings yet
- Kidney AnatomyDocument55 pagesKidney AnatomyMohammad zreadNo ratings yet
- 2 2018 04 12!08 19 02 PM PDFDocument61 pages2 2018 04 12!08 19 02 PM PDFMohammed ZewduNo ratings yet
- 9 The Endocrine SystemDocument10 pages9 The Endocrine SystemSenthereng MoaisiNo ratings yet
- Lect 4 Urinary SystemDocument42 pagesLect 4 Urinary Systemnightter4No ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument24 pagesUrinary Systemmahdia18No ratings yet
- Document 2Document6 pagesDocument 2nasaiyumi5No ratings yet
- Physio Renal Physiology Notes 1Document10 pagesPhysio Renal Physiology Notes 1Jeeson MichaelNo ratings yet
- DR Laxman Khanal Bpkihs 07-06-2013Document86 pagesDR Laxman Khanal Bpkihs 07-06-2013Bilal YimamNo ratings yet
- Seminar Cs 15 NovDocument24 pagesSeminar Cs 15 Novzeenatn1995No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy,: Renal /urinary SystemDocument62 pagesHuman Anatomy,: Renal /urinary Systemsapana shresthaNo ratings yet
- Kidneys and Suprarenal Glands - DR Nto, Nto JDocument34 pagesKidneys and Suprarenal Glands - DR Nto, Nto JMary-precious EgboNo ratings yet
Suprarenal Glands Clint
Suprarenal Glands Clint
Uploaded by
Bianca Watanabe0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageThe suprarenal glands, also known as adrenal glands, are located above the kidneys. Each gland has a yellow outer cortex that secretes hormones involved in fluid balance, metabolism, and sex development. The inner medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine. The right gland is pyramid-shaped above the kidney while the left is crescent-shaped along the kidney. Blood supply comes from the inferior phrenic, aorta and renal arteries, while veins drain into the inferior vena cava on the right and renal vein on the left. Lymph drains to lateral aortic nodes and the glands receive nerve fibers from the splanchnic nerves.
Original Description:
Supraprenal Glands Anatomy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe suprarenal glands, also known as adrenal glands, are located above the kidneys. Each gland has a yellow outer cortex that secretes hormones involved in fluid balance, metabolism, and sex development. The inner medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine. The right gland is pyramid-shaped above the kidney while the left is crescent-shaped along the kidney. Blood supply comes from the inferior phrenic, aorta and renal arteries, while veins drain into the inferior vena cava on the right and renal vein on the left. Lymph drains to lateral aortic nodes and the glands receive nerve fibers from the splanchnic nerves.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageSuprarenal Glands Clint
Suprarenal Glands Clint
Uploaded by
Bianca WatanabeThe suprarenal glands, also known as adrenal glands, are located above the kidneys. Each gland has a yellow outer cortex that secretes hormones involved in fluid balance, metabolism, and sex development. The inner medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine. The right gland is pyramid-shaped above the kidney while the left is crescent-shaped along the kidney. Blood supply comes from the inferior phrenic, aorta and renal arteries, while veins drain into the inferior vena cava on the right and renal vein on the left. Lymph drains to lateral aortic nodes and the glands receive nerve fibers from the splanchnic nerves.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Suprarenal Glands
Location and Description
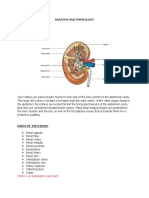
yellowish retroperitoneal organs that lie on the upper poles of the kidneys
surrounded by renal fascia (but are separated from the kidneys by the perirenal fat)
Each gland has a yellow cortex and a dark brown medulla
The cortex of the suprarenal glands secretes hormones that include mineral corticoids, which are
concerned with the control of fluid and electrolyte balance; glucocorticoids, which are concerned with
the control of the metabolism of carbohydrates,fats, and proteins; and small amounts of sex hormones,
which probably play a role in the prepubertal development of the sex organs. The medulla of the
suprarenal glands secretes the catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Right suprarenal gland
pyramid shaped and caps the upper pole of the right kidney (Figure). It lies behind the right lobe
of the liver and extends medially behind the inferior vena cava. It rests posteriorly on the
diaphragm.
Left suprarenal gland
crescentic in shape and extends along the medial border of the left kidney from the upper pole to
the hilus (Figure). It lies behind the pancreas, the lesser sac, and the stomach and rests
posteriorly on the diaphragm.
Blood Supply
Arteries
The arteries supplying each gland are three in number: inferior phrenic artery, aorta, and renal artery.
Veins
A single vein emerges from the hilum of each gland and drains into the inferior vena cava on the right and into the
renal vein on the left.
Lymph Drainage
The lymph drains into the lateral aortic nodes.
Nerve Supply
Preganglionic sympathetic fibers derived from the splanchnic nerves supply the glands. Most of the nerves end in
the medulla of the gland.
You might also like
- 3 - Adrenal Glands (386-389, 184-187, 215-217)Document18 pages3 - Adrenal Glands (386-389, 184-187, 215-217)Osama adel Mohamed SmadiNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Renal System: by DR Amber IlyasDocument51 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Renal System: by DR Amber IlyasAlexah BanuagNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument15 pagesAdrenal GlandSivanandan Ramar100% (1)
- Urinary Organs - MahasiswaDocument43 pagesUrinary Organs - MahasiswaJendral Andi Wijaya KusumaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland-1Document2 pagesAdrenal Gland-1Nnanyelugo AdaobiNo ratings yet
- 1 - Anatomy of KidneysDocument22 pages1 - Anatomy of KidneysAHMAD YUNUSA GARBANo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary Tract BaruDocument68 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Tract BaruAdya ArradikhaNo ratings yet
- 8th Seminar TopoDocument36 pages8th Seminar TopoKarthick RajaNo ratings yet
- Ureter and Suprarenal GlandDocument9 pagesUreter and Suprarenal GlandOnwumerechimdikepreciousNo ratings yet
- Suprarenal GlandDocument13 pagesSuprarenal GlandAaa JjjjNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Shakar Mudrik Omer Asma Ibrahem Ismahel Supervisor: DR - Younis ZandyDocument24 pagesPrepared By: Shakar Mudrik Omer Asma Ibrahem Ismahel Supervisor: DR - Younis Zandyزيد مسعودNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.3 Adrenal GlandDocument15 pagesAnatomy Lec.3 Adrenal Glandزينب فؤاد موسىNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Suprarenal Glands f2f-s1b2-23Document17 pages7.2 Suprarenal Glands f2f-s1b2-23shlokNo ratings yet
- The Kidneys IDocument8 pagesThe Kidneys Ior1da2sa3No ratings yet
- Sistem Perkemihan - Hendriyan Sh. B.InggrisDocument13 pagesSistem Perkemihan - Hendriyan Sh. B.InggrisHaniyyahNo ratings yet
- UrinaryDocument18 pagesUrinaryaliofficial12355No ratings yet
- N Ephron 1111Document9 pagesN Ephron 1111Syed Sakline HossainNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Adrenal GlandsDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Adrenal GlandsAnastazia AdeelaNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument40 pagesKidneyOlaifa victorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology-KIDNEYSDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-KIDNEYSnessie dianne c. cuevasNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of The Retroperitoneum, Kidneys, and UretersDocument46 pagesSurgical Anatomy of The Retroperitoneum, Kidneys, and UretersDiana MarcusNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 2023-2024Document16 pagesEndocrine System 2023-2024michaelsoncole410No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The KidneyDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Kidneycatherine kate gulengNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology 1 1aDocument88 pagesRenal Physiology 1 1afentaw melkieNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Visceral OrgansDocument5 pagesAbdominal Visceral OrgansYudi Kelsi KaharapNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument2 pagesPancreasSam TagardaNo ratings yet
- UT AnatomyDocument35 pagesUT AnatomyAngel SaraNo ratings yet
- Lapsus InvaginasiDocument41 pagesLapsus InvaginasiHanda YaniNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesUrinary SystemAubrey Yu JaneaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Endocrine Glands: HypothalamusDocument10 pagesAnatomy of The Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamusgashbin latifNo ratings yet
- L1 - KidneyDocument27 pagesL1 - KidneyKhadeja JayashNo ratings yet
- Kerala University of Health Sciences (Kuhs) Expected Questions On First Year BSC Nursing Degree Examinations 2021Document5 pagesKerala University of Health Sciences (Kuhs) Expected Questions On First Year BSC Nursing Degree Examinations 2021ashna anilNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Kidney - ForDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Kidney - ForKristelle ModalesNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Kidney PDFDocument14 pagesThe Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Kidney PDFredderdatNo ratings yet
- The Adrenal Gland: Anatomy, Embryology & PhysiologyDocument29 pagesThe Adrenal Gland: Anatomy, Embryology & PhysiologyrajarshikNo ratings yet
- Location and External Anatomy of The KidneysDocument15 pagesLocation and External Anatomy of The KidneysKyla Malapit GarvidaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - de Jesus MDDocument3 pagesEndocrine System - de Jesus MDKerenTabuenaNo ratings yet
- The Adrenal Glands - Location - Structure - TeachMeAnatomy PDFDocument4 pagesThe Adrenal Glands - Location - Structure - TeachMeAnatomy PDFUsama KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Endokrin Mei 2019Document64 pagesAnatomi Endokrin Mei 2019insiya insiyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of PancreasDocument6 pagesAnatomy of PancreasNariska CooperNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocument43 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Systemandrea titus100% (1)
- Kidney and Kidneys Function 1Document5 pagesKidney and Kidneys Function 1nogakojasmrdiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy RCR1 RenalDocument3 pagesAnatomy RCR1 RenaleamcrawleyNo ratings yet
- Iii. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesIii. Anatomy and Physiologytedy_berNo ratings yet
- The KidneysDocument11 pagesThe KidneysJordan MosesNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland: Nani Murniat Departemen AnatomiDocument43 pagesAdrenal Gland: Nani Murniat Departemen Anatomisintia saputraNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocument41 pagesThe Urinary System: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin Universityraynhard b. fandresNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Ingles MédicoDocument14 pagesVocabulary Ingles MédicoMayra LandoNo ratings yet
- Kidney AnatomyDocument55 pagesKidney AnatomyMohammad zreadNo ratings yet
- 2 2018 04 12!08 19 02 PM PDFDocument61 pages2 2018 04 12!08 19 02 PM PDFMohammed ZewduNo ratings yet
- 9 The Endocrine SystemDocument10 pages9 The Endocrine SystemSenthereng MoaisiNo ratings yet
- Lect 4 Urinary SystemDocument42 pagesLect 4 Urinary Systemnightter4No ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument24 pagesUrinary Systemmahdia18No ratings yet
- Document 2Document6 pagesDocument 2nasaiyumi5No ratings yet
- Physio Renal Physiology Notes 1Document10 pagesPhysio Renal Physiology Notes 1Jeeson MichaelNo ratings yet
- DR Laxman Khanal Bpkihs 07-06-2013Document86 pagesDR Laxman Khanal Bpkihs 07-06-2013Bilal YimamNo ratings yet
- Seminar Cs 15 NovDocument24 pagesSeminar Cs 15 Novzeenatn1995No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy,: Renal /urinary SystemDocument62 pagesHuman Anatomy,: Renal /urinary Systemsapana shresthaNo ratings yet
- Kidneys and Suprarenal Glands - DR Nto, Nto JDocument34 pagesKidneys and Suprarenal Glands - DR Nto, Nto JMary-precious EgboNo ratings yet