Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Finite Element Method FINAL EXAM SEM I 2012/2013 Q2: F A, E K
Finite Element Method FINAL EXAM SEM I 2012/2013 Q2: F A, E K
Uploaded by
syazwanaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Assignment 1: BDA 31003 Finite Element MethodDocument3 pagesAssignment 1: BDA 31003 Finite Element MethodIzwan SaifudinNo ratings yet
- Military Technological College Oman: in Collaboration With The University of Portsmouth, UKDocument4 pagesMilitary Technological College Oman: in Collaboration With The University of Portsmouth, UKZoay7 I 6No ratings yet
- 2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document5 pages2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Ashish pathareNo ratings yet
- QP293A2 20MET201 Mechanics of SolidsDocument4 pagesQP293A2 20MET201 Mechanics of SolidsJASON CHERIAN MENo ratings yet
- 18me52 Dme 1 Febarch 2022Document22 pages18me52 Dme 1 Febarch 2022Thirumal K SNo ratings yet
- 2859 10660 1 PBDocument16 pages2859 10660 1 PBlaich_mustaNo ratings yet
- (Common To CE, CEE) : 0 S - 5 0 C - 5 0 S 5 2 C 5 2Document2 pages(Common To CE, CEE) : 0 S - 5 0 C - 5 0 S 5 2 C 5 2AYRUSNo ratings yet
- Rr210102 Strength of Materials IDocument8 pagesRr210102 Strength of Materials ISrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Diploma Board Examination - June 2021Document4 pagesDiploma Board Examination - June 2021Maruthi Groupof InstitutionsNo ratings yet
- QBank FEMDocument12 pagesQBank FEMShivam ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: I B. Tech I Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, Oct/Nov - 2018 Engineering MechanicsDocument12 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: I B. Tech I Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, Oct/Nov - 2018 Engineering MechanicsArivaNo ratings yet
- Structures Combine (Year 2pp)Document37 pagesStructures Combine (Year 2pp)KrisNo ratings yet
- Engineering StructureDocument17 pagesEngineering Structuremohamedelamari04No ratings yet
- MECH-ND-2021-ME 8692-FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS-854780751-40839(ME8692)Document4 pagesMECH-ND-2021-ME 8692-FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS-854780751-40839(ME8692)sivananth.mechNo ratings yet
- 2020 10 28SupplementaryCE201CE201 I Ktu QbankDocument3 pages2020 10 28SupplementaryCE201CE201 I Ktu Qbankprasidh msNo ratings yet
- Ame014 QPDocument3 pagesAme014 QPMech HodNo ratings yet
- S & A Lab Set - 1Document11 pagesS & A Lab Set - 1raveen_82mechNo ratings yet
- Beng (Hons) Mechanical Engineering Two Final Examination 6 Finite Element and Difference Solutions Module No: Ame6006Document9 pagesBeng (Hons) Mechanical Engineering Two Final Examination 6 Finite Element and Difference Solutions Module No: Ame6006Sameera AlweeraNo ratings yet
- Civil715 S1 2019Document8 pagesCivil715 S1 2019Cheng FuNo ratings yet
- 2018 April CE201-D - Ktu QbankDocument2 pages2018 April CE201-D - Ktu Qbanklakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2jermainpeart4No ratings yet
- Tutor Marked Assignment: BtwreDocument41 pagesTutor Marked Assignment: BtwrePranita JoshiNo ratings yet
- FEA Model ExamDocument12 pagesFEA Model Exam20mec06sriramNo ratings yet
- DE5302 Strength of Materials. Semester 1, 2018 Exam and FormulaeDocument15 pagesDE5302 Strength of Materials. Semester 1, 2018 Exam and FormulaeGopal KrishanNo ratings yet
- CIV3506 2022 Assign2 Exemplary2Document33 pagesCIV3506 2022 Assign2 Exemplary2Neil WayneNo ratings yet
- B C192020 Pages: 3: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 MarksDocument3 pagesB C192020 Pages: 3: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Markslakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- MAKEUPDocument3 pagesMAKEUPRambo 420No ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 5 Aktuell Page SetupDocument33 pages07 Chapter 5 Aktuell Page SetupHO Vinh-QuynhNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityhemalNo ratings yet
- Me62o June2021Document3 pagesMe62o June2021Rambo 420No ratings yet
- Machine Design QP KtuDocument3 pagesMachine Design QP KtuAbhijith JoseNo ratings yet
- ME401 RegularDocument3 pagesME401 RegularAmal SNo ratings yet
- OctoberNovember 2021Document2 pagesOctoberNovember 2021anil kumarNo ratings yet
- Diploma QPDocument4 pagesDiploma QPSundarasetty HarishbabuNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis QBDocument3 pagesStructural Analysis QBAbanishAmpNo ratings yet
- JJEB O Phy P2 2017Document6 pagesJJEB O Phy P2 2017William OkongoNo ratings yet
- Docs Me Fem Assignments 2013Document8 pagesDocs Me Fem Assignments 2013Sanju ReddyNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AE, MSNT)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AE, MSNT)Sreedhar MNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Members I Jan 2023Document12 pagesDesign of Machine Members I Jan 2023chinniparamesh92No ratings yet
- Structures E2 2019-2020 GivenDocument11 pagesStructures E2 2019-2020 GivenSarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- P15meo754 W3Document3 pagesP15meo754 W3ranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Unit I 1. A) Derive The Relationship Between The Elastic Modulii. (8 Marks)Document3 pagesUnit I 1. A) Derive The Relationship Between The Elastic Modulii. (8 Marks)srihari_bhadabhagniNo ratings yet
- LE1 Problem Set PDFDocument14 pagesLE1 Problem Set PDFJunhong BapNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural MechanicsDocument7 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural Mechanicssky willaNo ratings yet
- Diploma Quasion PapersDocument4 pagesDiploma Quasion PapersSundarasetty HarishbabuNo ratings yet
- Ace102 - Strength of MaterialsDocument3 pagesAce102 - Strength of Materialspreetijan07No ratings yet
- 2020 10 28SupplementaryME201ME201 I Ktu QbankDocument3 pages2020 10 28SupplementaryME201ME201 I Ktu Qbankred18ggmuNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Venkat.G SuryaNo ratings yet
- Structures E2 2018-2019 GivenDocument10 pagesStructures E2 2018-2019 GivenSarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural MechanicsDocument8 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural Mechanicssky willaNo ratings yet
- End Sem 2019 Determinate StructureDocument2 pagesEnd Sem 2019 Determinate Structuretenzinlhamo.199No ratings yet
- WWW - Mana R e Sults - Co.in: Mechanics of SolidsDocument14 pagesWWW - Mana R e Sults - Co.in: Mechanics of Solidsmahendra babu mekalaNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIDocument7 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIkundayi shavaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Subject Code: Date: 02/01/2016 Subject Name: Time: 2:30 PM To 5:00 PM Total Marks: 70Document2 pagesGujarat Technological University: Subject Code: Date: 02/01/2016 Subject Name: Time: 2:30 PM To 5:00 PM Total Marks: 70rameshNo ratings yet
- EVALUATION OF MECHANICAL ANCHORAGE OF Beam Column JointDocument9 pagesEVALUATION OF MECHANICAL ANCHORAGE OF Beam Column JointDr Ahmed Al-RubaieNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics 2015 PaperDocument6 pagesStructural Mechanics 2015 PaperAlexNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 FinalDocument2 pagesTutorial 5 FinalAtul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Discrete-continuum Coupling Method to Simulate Highly Dynamic Multi-scale Problems: Simulation of Laser-induced Damage in Silica Glass, Volume 2From EverandDiscrete-continuum Coupling Method to Simulate Highly Dynamic Multi-scale Problems: Simulation of Laser-induced Damage in Silica Glass, Volume 2No ratings yet
Finite Element Method FINAL EXAM SEM I 2012/2013 Q2: F A, E K
Finite Element Method FINAL EXAM SEM I 2012/2013 Q2: F A, E K
Uploaded by
syazwanaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Finite Element Method FINAL EXAM SEM I 2012/2013 Q2: F A, E K
Finite Element Method FINAL EXAM SEM I 2012/2013 Q2: F A, E K
Uploaded by
syazwanaCopyright:
Available Formats
FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
FINAL EXAM SEM I 2012/2013
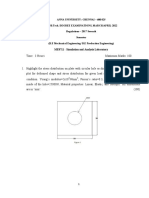
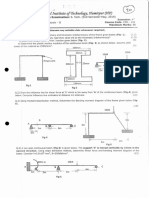
Q2 A mechanical structure consists of a rod and a heavy spring. The rod (with the cross
section, A = 0.002 m2 and modulus of elasticity, E = 200 GPa) and the spring (with the
spring constant, k = 40 MN/m) are attached together. The end of the rod that is not
connected to the spring is rigidly fixed to the wall. At the connection point to the spring,
the rod is axially pulled, F = 1000 kN as shown in Figure Q2 below. In front of the
spring there is a fixed wall, so that the end spring will deform maximum 2 mm.
A, E F k
1m 2 mm
Figure Q2: Axial Structure Under Loading
(a) Draw the finite element model consists of 2 elements. Indicate clearly the node
and element numbers. Specify also the constraints (boundary conditions) of your
model
(5 marks)
(b) Find the stiffness matrix of each element.
(5 marks)
(c) Determine the global stiffness matrix of the structure before and after constraints
(you can use either direct elimination method or penalty method).
(10 marks)
(d) Find the deformation of each node.
(5 marks)
Example 1:
The rod circular cross section A2 0.0025m , A3 0.009m , modulus of elasticity, E 70 GPa
2 2
and the spring ( k 60 MN/m ) are attached together. At the connection point to the spring, the
rod is axially pulled, F 200 kN . Find the deformation of each node.
You might also like
- Assignment 1: BDA 31003 Finite Element MethodDocument3 pagesAssignment 1: BDA 31003 Finite Element MethodIzwan SaifudinNo ratings yet
- Military Technological College Oman: in Collaboration With The University of Portsmouth, UKDocument4 pagesMilitary Technological College Oman: in Collaboration With The University of Portsmouth, UKZoay7 I 6No ratings yet
- 2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document5 pages2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Ashish pathareNo ratings yet
- QP293A2 20MET201 Mechanics of SolidsDocument4 pagesQP293A2 20MET201 Mechanics of SolidsJASON CHERIAN MENo ratings yet
- 18me52 Dme 1 Febarch 2022Document22 pages18me52 Dme 1 Febarch 2022Thirumal K SNo ratings yet
- 2859 10660 1 PBDocument16 pages2859 10660 1 PBlaich_mustaNo ratings yet
- (Common To CE, CEE) : 0 S - 5 0 C - 5 0 S 5 2 C 5 2Document2 pages(Common To CE, CEE) : 0 S - 5 0 C - 5 0 S 5 2 C 5 2AYRUSNo ratings yet
- Rr210102 Strength of Materials IDocument8 pagesRr210102 Strength of Materials ISrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Diploma Board Examination - June 2021Document4 pagesDiploma Board Examination - June 2021Maruthi Groupof InstitutionsNo ratings yet
- QBank FEMDocument12 pagesQBank FEMShivam ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: I B. Tech I Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, Oct/Nov - 2018 Engineering MechanicsDocument12 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: I B. Tech I Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, Oct/Nov - 2018 Engineering MechanicsArivaNo ratings yet
- Structures Combine (Year 2pp)Document37 pagesStructures Combine (Year 2pp)KrisNo ratings yet
- Engineering StructureDocument17 pagesEngineering Structuremohamedelamari04No ratings yet
- MECH-ND-2021-ME 8692-FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS-854780751-40839(ME8692)Document4 pagesMECH-ND-2021-ME 8692-FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS-854780751-40839(ME8692)sivananth.mechNo ratings yet
- 2020 10 28SupplementaryCE201CE201 I Ktu QbankDocument3 pages2020 10 28SupplementaryCE201CE201 I Ktu Qbankprasidh msNo ratings yet
- Ame014 QPDocument3 pagesAme014 QPMech HodNo ratings yet
- S & A Lab Set - 1Document11 pagesS & A Lab Set - 1raveen_82mechNo ratings yet
- Beng (Hons) Mechanical Engineering Two Final Examination 6 Finite Element and Difference Solutions Module No: Ame6006Document9 pagesBeng (Hons) Mechanical Engineering Two Final Examination 6 Finite Element and Difference Solutions Module No: Ame6006Sameera AlweeraNo ratings yet
- Civil715 S1 2019Document8 pagesCivil715 S1 2019Cheng FuNo ratings yet
- 2018 April CE201-D - Ktu QbankDocument2 pages2018 April CE201-D - Ktu Qbanklakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2jermainpeart4No ratings yet
- Tutor Marked Assignment: BtwreDocument41 pagesTutor Marked Assignment: BtwrePranita JoshiNo ratings yet
- FEA Model ExamDocument12 pagesFEA Model Exam20mec06sriramNo ratings yet
- DE5302 Strength of Materials. Semester 1, 2018 Exam and FormulaeDocument15 pagesDE5302 Strength of Materials. Semester 1, 2018 Exam and FormulaeGopal KrishanNo ratings yet
- CIV3506 2022 Assign2 Exemplary2Document33 pagesCIV3506 2022 Assign2 Exemplary2Neil WayneNo ratings yet
- B C192020 Pages: 3: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 MarksDocument3 pagesB C192020 Pages: 3: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Markslakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- MAKEUPDocument3 pagesMAKEUPRambo 420No ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 5 Aktuell Page SetupDocument33 pages07 Chapter 5 Aktuell Page SetupHO Vinh-QuynhNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityhemalNo ratings yet
- Me62o June2021Document3 pagesMe62o June2021Rambo 420No ratings yet
- Machine Design QP KtuDocument3 pagesMachine Design QP KtuAbhijith JoseNo ratings yet
- ME401 RegularDocument3 pagesME401 RegularAmal SNo ratings yet
- OctoberNovember 2021Document2 pagesOctoberNovember 2021anil kumarNo ratings yet
- Diploma QPDocument4 pagesDiploma QPSundarasetty HarishbabuNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis QBDocument3 pagesStructural Analysis QBAbanishAmpNo ratings yet
- JJEB O Phy P2 2017Document6 pagesJJEB O Phy P2 2017William OkongoNo ratings yet
- Docs Me Fem Assignments 2013Document8 pagesDocs Me Fem Assignments 2013Sanju ReddyNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AE, MSNT)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AE, MSNT)Sreedhar MNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Members I Jan 2023Document12 pagesDesign of Machine Members I Jan 2023chinniparamesh92No ratings yet
- Structures E2 2019-2020 GivenDocument11 pagesStructures E2 2019-2020 GivenSarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- P15meo754 W3Document3 pagesP15meo754 W3ranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Unit I 1. A) Derive The Relationship Between The Elastic Modulii. (8 Marks)Document3 pagesUnit I 1. A) Derive The Relationship Between The Elastic Modulii. (8 Marks)srihari_bhadabhagniNo ratings yet
- LE1 Problem Set PDFDocument14 pagesLE1 Problem Set PDFJunhong BapNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural MechanicsDocument7 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural Mechanicssky willaNo ratings yet
- Diploma Quasion PapersDocument4 pagesDiploma Quasion PapersSundarasetty HarishbabuNo ratings yet
- Ace102 - Strength of MaterialsDocument3 pagesAce102 - Strength of Materialspreetijan07No ratings yet
- 2020 10 28SupplementaryME201ME201 I Ktu QbankDocument3 pages2020 10 28SupplementaryME201ME201 I Ktu Qbankred18ggmuNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Venkat.G SuryaNo ratings yet
- Structures E2 2018-2019 GivenDocument10 pagesStructures E2 2018-2019 GivenSarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural MechanicsDocument8 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural Mechanicssky willaNo ratings yet
- End Sem 2019 Determinate StructureDocument2 pagesEnd Sem 2019 Determinate Structuretenzinlhamo.199No ratings yet
- WWW - Mana R e Sults - Co.in: Mechanics of SolidsDocument14 pagesWWW - Mana R e Sults - Co.in: Mechanics of Solidsmahendra babu mekalaNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIDocument7 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIkundayi shavaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Subject Code: Date: 02/01/2016 Subject Name: Time: 2:30 PM To 5:00 PM Total Marks: 70Document2 pagesGujarat Technological University: Subject Code: Date: 02/01/2016 Subject Name: Time: 2:30 PM To 5:00 PM Total Marks: 70rameshNo ratings yet
- EVALUATION OF MECHANICAL ANCHORAGE OF Beam Column JointDocument9 pagesEVALUATION OF MECHANICAL ANCHORAGE OF Beam Column JointDr Ahmed Al-RubaieNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics 2015 PaperDocument6 pagesStructural Mechanics 2015 PaperAlexNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 FinalDocument2 pagesTutorial 5 FinalAtul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Discrete-continuum Coupling Method to Simulate Highly Dynamic Multi-scale Problems: Simulation of Laser-induced Damage in Silica Glass, Volume 2From EverandDiscrete-continuum Coupling Method to Simulate Highly Dynamic Multi-scale Problems: Simulation of Laser-induced Damage in Silica Glass, Volume 2No ratings yet