Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Equilibrium Equations: V T V T
Equilibrium Equations: V T V T
Uploaded by
Jaor JnrCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Britten - The Foggy, Foggy DewDocument4 pagesBritten - The Foggy, Foggy DewAttila EndreffyNo ratings yet
- Transients: Multivector Review and Training CenterDocument18 pagesTransients: Multivector Review and Training CenterrenegadeNo ratings yet
- Topic6Multivibrators 2sppDocument8 pagesTopic6Multivibrators 2sppAbdul SheikhNo ratings yet
- 63-25-69 - Ec120 - Oil Cooler - SecanDocument7 pages63-25-69 - Ec120 - Oil Cooler - SecansebastienNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Property MethodsDocument23 pagesThermodynamic Property MethodsfarhaNo ratings yet
- SMPS TT 2022Document115 pagesSMPS TT 2022Kanekii HaiseNo ratings yet
- TR - NL X: ProcedureDocument6 pagesTR - NL X: ProcedureJesha KihampaNo ratings yet
- E I R Ir E Ir E Eir E E EirDocument1 pageE I R Ir E Ir E Eir E E Eirsrikanth0483287No ratings yet
- THE RF TRAP - Design and ImplementationDocument4 pagesTHE RF TRAP - Design and ImplementationTLALOC 1969No ratings yet
- Akre Kep S1 2018Document1 pageAkre Kep S1 2018gina soniaNo ratings yet
- Gaseous StateDocument19 pagesGaseous StateRajendra BhupathiNo ratings yet
- SDQSFDocument103 pagesSDQSFHuy Khôi HàNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 and 10Document13 pagesLecture 9 and 10Hyder GamingNo ratings yet
- Hornby High Level EquipmentDocument2 pagesHornby High Level EquipmentJohn GasparNo ratings yet
- Circuits ReportDocument2 pagesCircuits ReportJerry Arthur MartinezNo ratings yet
- Smps 3Document38 pagesSmps 3psychic_jason0071319No ratings yet
- Fallsem2016-17 6988 RM001 02-Aug-2016 Ece1001 EthDocument21 pagesFallsem2016-17 6988 RM001 02-Aug-2016 Ece1001 EthGaurav AgarNo ratings yet
- Fourier IntegralsDocument7 pagesFourier IntegralsOvi Poddar AntorNo ratings yet
- Electrical TransientsDocument13 pagesElectrical Transientsbenny bullNo ratings yet
- Appendix G: Maximum Power Transfer ConditionsDocument2 pagesAppendix G: Maximum Power Transfer ConditionsXxx CccNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Part 1Document6 pagesLesson 7 - Part 1Swifty SpotNo ratings yet
- StepByStep Pulse8EdDocument24 pagesStepByStep Pulse8Edpak tracksNo ratings yet
- 2008-01-01:【技術專題】Ten Fundamental Principles of Power ElectronicsDocument11 pages2008-01-01:【技術專題】Ten Fundamental Principles of Power ElectronicsDao DaoNo ratings yet
- 1E6 Electrical Engineering AC Circuit Analysis and Power Lecture 11: Series Resonant CircuitsDocument8 pages1E6 Electrical Engineering AC Circuit Analysis and Power Lecture 11: Series Resonant CircuitsKandi PrintNo ratings yet
- TGHGFFDocument21 pagesTGHGFFFikri AlfiansyahNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document16 pagesModule 4yakomi suraNo ratings yet
- DC-DC ConvertersDocument22 pagesDC-DC ConverterskanithanNo ratings yet
- Switch-Mode Power Supply: DC-DC ConvertersDocument19 pagesSwitch-Mode Power Supply: DC-DC ConvertersAbdullrahman Al-ShammaaNo ratings yet
- Flight C OC G C ( pG°30C 0 C VOL: I National Defense Defence NationeleDocument17 pagesFlight C OC G C ( pG°30C 0 C VOL: I National Defense Defence NationeleTateNo ratings yet
- The Analysis of The Global Ship Strengths in Vertical Plane With 3D-Fem Hull ModelsDocument31 pagesThe Analysis of The Global Ship Strengths in Vertical Plane With 3D-Fem Hull ModelsAlina NastasaNo ratings yet
- Request For Pre-AuthDocument17 pagesRequest For Pre-AuthKhan MohsinNo ratings yet
- QM 5 - Quantum Dynamics, Schrödinger EquationDocument11 pagesQM 5 - Quantum Dynamics, Schrödinger Equationkontakt.mfiedorowiczNo ratings yet
- KR10802 Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering: Chapter 6: RLCDocument69 pagesKR10802 Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering: Chapter 6: RLCPenziiNo ratings yet
- international phonetic alphabetDocument3 pagesinternational phonetic alphabetDayana MuñozNo ratings yet
- InductorsDocument22 pagesInductorsazafa netNo ratings yet
- InductorsDocument20 pagesInductorsVikash KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2Document8 pagesThermodynamics 2BINITHA MPNo ratings yet
- Topic1 PDFDocument72 pagesTopic1 PDFChitlet FrancheNo ratings yet
- BEF 12503 - Week 9 - AC Circuit Analysis Using Phasors and Equivalent Impedance ConceptDocument61 pagesBEF 12503 - Week 9 - AC Circuit Analysis Using Phasors and Equivalent Impedance Conceptfullmetal AesirNo ratings yet
- Ang 2005 A Practical GuideDocument5 pagesAng 2005 A Practical GuideAnna CampanatiNo ratings yet
- InductorsDocument22 pagesInductorsSatrianiRahmayanti67% (3)
- 74HC HCT158 CNV 2Document8 pages74HC HCT158 CNV 2MUHAMMAD SISWANTORONo ratings yet
- Vapor-Liquid EquilibriaDocument47 pagesVapor-Liquid EquilibriaKent GardoseNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Computational Neuroscience-2021-Lecture7Document35 pagesTheoretical and Computational Neuroscience-2021-Lecture7ali.lesani.1362No ratings yet
- BV Ramanna Convolution Finite Fourier Sine and Cosine TransformDocument18 pagesBV Ramanna Convolution Finite Fourier Sine and Cosine TransformxuzchxyzNo ratings yet
- The Chopper: By: Ruqaya MuatazDocument62 pagesThe Chopper: By: Ruqaya Muataznoor deenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Octahedral Substitution Reactions: 2P32 - Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. PilkingtonDocument13 pagesLecture 12 - Octahedral Substitution Reactions: 2P32 - Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. PilkingtonAlexa AlexiuNo ratings yet
- Ventilacion BloweDocument10 pagesVentilacion Blowemarco vasquezNo ratings yet
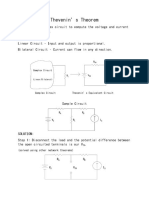
- KVL, KCL, Thevenin's Theorem and Norton's TheoremDocument9 pagesKVL, KCL, Thevenin's Theorem and Norton's TheoremHenok BelaynehNo ratings yet
- Class 4 - Dynamic Performance CharacteristicsDocument38 pagesClass 4 - Dynamic Performance CharacteristicsMaher Abu-ElolaNo ratings yet
- PosterDocument2 pagesPosterAndres OsorioNo ratings yet
- Guided Cantilever MethodDocument12 pagesGuided Cantilever MethodDan PastorNo ratings yet
- Foliations by Closed Cylinders in R3Document20 pagesFoliations by Closed Cylinders in R3Ike_CollpaNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current All DerivationsDocument7 pagesAlternating Current All DerivationsRonit VaskarNo ratings yet
- EE21L-2 - Basic Electrical Engineering, LabDocument7 pagesEE21L-2 - Basic Electrical Engineering, LabCedric Arcel CruzNo ratings yet
- EEE1001 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Thevenin's and Maximum Power Transfer TheoremDocument12 pagesEEE1001 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Thevenin's and Maximum Power Transfer TheoremISHAAAAAAAAAAANNo ratings yet
- Supp - 2021 - PRL - Purves - Quantum Theory Cannot Violate A Causal InequalityDocument11 pagesSupp - 2021 - PRL - Purves - Quantum Theory Cannot Violate A Causal InequalityYifan TangNo ratings yet
- Step Response of An RL CircuitDocument13 pagesStep Response of An RL CircuitROUNAK MANDALNo ratings yet
- Domenico Scarlatti Five PiecesDocument6 pagesDomenico Scarlatti Five PiecesMarco PipernoNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Trace Elements GeochronDocument38 pagesTrace Elements GeochronJaor JnrNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives and Fundamental QuestionsDocument18 pagesLearning Objectives and Fundamental QuestionsJaor JnrNo ratings yet
- Garg Et Al-2008-Journal of Geophysical Research - Solid Earth (1978-2012)Document32 pagesGarg Et Al-2008-Journal of Geophysical Research - Solid Earth (1978-2012)Jaor JnrNo ratings yet
- Bai 2012Document9 pagesBai 2012Jaor JnrNo ratings yet
- Massively Parallel Simulation of Oceanic-Gas-Hydrate ProductionDocument3 pagesMassively Parallel Simulation of Oceanic-Gas-Hydrate ProductionJaor JnrNo ratings yet
Equilibrium Equations: V T V T
Equilibrium Equations: V T V T
Uploaded by
Jaor JnrOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Equilibrium Equations: V T V T
Equilibrium Equations: V T V T
Uploaded by
Jaor JnrCopyright:
Available Formats
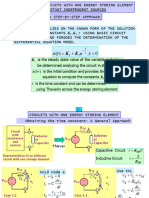
Equilibrium Equations
Equilibrium is attained when the chemical potentials of each component are equal in the
two phases:
iL T , V L , x L iR T , V R , x R
To simplify equilibrium calculations, the chemical potential is often written in the form
iL T ,V L , x L i0 T RT ln f i L T ,V L , x L
where the fugacity is defined as
L
f i L T , V L , x L iL xiL
NL
i
L Ni
VL VL
and the standard state chemical potential
2mkT 3/ 2
i0 T RT ln
h2
The advantage of introducing the fugacity is that the equilibrium equation is now given
by
fiL fiR
Note that the standard state contribution to the chemical potential will be the same in all
phases (which are at the same temperature.
The definition of the fugacity then leads to the simple equilibrium equations:
NL NR
iL iL iR iR
V V
or
NL NR
iL xiL L iR xiR R
V V
You might also like
- Britten - The Foggy, Foggy DewDocument4 pagesBritten - The Foggy, Foggy DewAttila EndreffyNo ratings yet
- Transients: Multivector Review and Training CenterDocument18 pagesTransients: Multivector Review and Training CenterrenegadeNo ratings yet
- Topic6Multivibrators 2sppDocument8 pagesTopic6Multivibrators 2sppAbdul SheikhNo ratings yet
- 63-25-69 - Ec120 - Oil Cooler - SecanDocument7 pages63-25-69 - Ec120 - Oil Cooler - SecansebastienNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Property MethodsDocument23 pagesThermodynamic Property MethodsfarhaNo ratings yet
- SMPS TT 2022Document115 pagesSMPS TT 2022Kanekii HaiseNo ratings yet
- TR - NL X: ProcedureDocument6 pagesTR - NL X: ProcedureJesha KihampaNo ratings yet
- E I R Ir E Ir E Eir E E EirDocument1 pageE I R Ir E Ir E Eir E E Eirsrikanth0483287No ratings yet
- THE RF TRAP - Design and ImplementationDocument4 pagesTHE RF TRAP - Design and ImplementationTLALOC 1969No ratings yet
- Akre Kep S1 2018Document1 pageAkre Kep S1 2018gina soniaNo ratings yet
- Gaseous StateDocument19 pagesGaseous StateRajendra BhupathiNo ratings yet
- SDQSFDocument103 pagesSDQSFHuy Khôi HàNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 and 10Document13 pagesLecture 9 and 10Hyder GamingNo ratings yet
- Hornby High Level EquipmentDocument2 pagesHornby High Level EquipmentJohn GasparNo ratings yet
- Circuits ReportDocument2 pagesCircuits ReportJerry Arthur MartinezNo ratings yet
- Smps 3Document38 pagesSmps 3psychic_jason0071319No ratings yet
- Fallsem2016-17 6988 RM001 02-Aug-2016 Ece1001 EthDocument21 pagesFallsem2016-17 6988 RM001 02-Aug-2016 Ece1001 EthGaurav AgarNo ratings yet
- Fourier IntegralsDocument7 pagesFourier IntegralsOvi Poddar AntorNo ratings yet
- Electrical TransientsDocument13 pagesElectrical Transientsbenny bullNo ratings yet
- Appendix G: Maximum Power Transfer ConditionsDocument2 pagesAppendix G: Maximum Power Transfer ConditionsXxx CccNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Part 1Document6 pagesLesson 7 - Part 1Swifty SpotNo ratings yet
- StepByStep Pulse8EdDocument24 pagesStepByStep Pulse8Edpak tracksNo ratings yet
- 2008-01-01:【技術專題】Ten Fundamental Principles of Power ElectronicsDocument11 pages2008-01-01:【技術專題】Ten Fundamental Principles of Power ElectronicsDao DaoNo ratings yet
- 1E6 Electrical Engineering AC Circuit Analysis and Power Lecture 11: Series Resonant CircuitsDocument8 pages1E6 Electrical Engineering AC Circuit Analysis and Power Lecture 11: Series Resonant CircuitsKandi PrintNo ratings yet
- TGHGFFDocument21 pagesTGHGFFFikri AlfiansyahNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document16 pagesModule 4yakomi suraNo ratings yet
- DC-DC ConvertersDocument22 pagesDC-DC ConverterskanithanNo ratings yet
- Switch-Mode Power Supply: DC-DC ConvertersDocument19 pagesSwitch-Mode Power Supply: DC-DC ConvertersAbdullrahman Al-ShammaaNo ratings yet
- Flight C OC G C ( pG°30C 0 C VOL: I National Defense Defence NationeleDocument17 pagesFlight C OC G C ( pG°30C 0 C VOL: I National Defense Defence NationeleTateNo ratings yet
- The Analysis of The Global Ship Strengths in Vertical Plane With 3D-Fem Hull ModelsDocument31 pagesThe Analysis of The Global Ship Strengths in Vertical Plane With 3D-Fem Hull ModelsAlina NastasaNo ratings yet
- Request For Pre-AuthDocument17 pagesRequest For Pre-AuthKhan MohsinNo ratings yet
- QM 5 - Quantum Dynamics, Schrödinger EquationDocument11 pagesQM 5 - Quantum Dynamics, Schrödinger Equationkontakt.mfiedorowiczNo ratings yet
- KR10802 Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering: Chapter 6: RLCDocument69 pagesKR10802 Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering: Chapter 6: RLCPenziiNo ratings yet
- international phonetic alphabetDocument3 pagesinternational phonetic alphabetDayana MuñozNo ratings yet
- InductorsDocument22 pagesInductorsazafa netNo ratings yet
- InductorsDocument20 pagesInductorsVikash KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2Document8 pagesThermodynamics 2BINITHA MPNo ratings yet
- Topic1 PDFDocument72 pagesTopic1 PDFChitlet FrancheNo ratings yet
- BEF 12503 - Week 9 - AC Circuit Analysis Using Phasors and Equivalent Impedance ConceptDocument61 pagesBEF 12503 - Week 9 - AC Circuit Analysis Using Phasors and Equivalent Impedance Conceptfullmetal AesirNo ratings yet
- Ang 2005 A Practical GuideDocument5 pagesAng 2005 A Practical GuideAnna CampanatiNo ratings yet
- InductorsDocument22 pagesInductorsSatrianiRahmayanti67% (3)
- 74HC HCT158 CNV 2Document8 pages74HC HCT158 CNV 2MUHAMMAD SISWANTORONo ratings yet
- Vapor-Liquid EquilibriaDocument47 pagesVapor-Liquid EquilibriaKent GardoseNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Computational Neuroscience-2021-Lecture7Document35 pagesTheoretical and Computational Neuroscience-2021-Lecture7ali.lesani.1362No ratings yet
- BV Ramanna Convolution Finite Fourier Sine and Cosine TransformDocument18 pagesBV Ramanna Convolution Finite Fourier Sine and Cosine TransformxuzchxyzNo ratings yet
- The Chopper: By: Ruqaya MuatazDocument62 pagesThe Chopper: By: Ruqaya Muataznoor deenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Octahedral Substitution Reactions: 2P32 - Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. PilkingtonDocument13 pagesLecture 12 - Octahedral Substitution Reactions: 2P32 - Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. PilkingtonAlexa AlexiuNo ratings yet
- Ventilacion BloweDocument10 pagesVentilacion Blowemarco vasquezNo ratings yet
- KVL, KCL, Thevenin's Theorem and Norton's TheoremDocument9 pagesKVL, KCL, Thevenin's Theorem and Norton's TheoremHenok BelaynehNo ratings yet
- Class 4 - Dynamic Performance CharacteristicsDocument38 pagesClass 4 - Dynamic Performance CharacteristicsMaher Abu-ElolaNo ratings yet
- PosterDocument2 pagesPosterAndres OsorioNo ratings yet
- Guided Cantilever MethodDocument12 pagesGuided Cantilever MethodDan PastorNo ratings yet
- Foliations by Closed Cylinders in R3Document20 pagesFoliations by Closed Cylinders in R3Ike_CollpaNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current All DerivationsDocument7 pagesAlternating Current All DerivationsRonit VaskarNo ratings yet
- EE21L-2 - Basic Electrical Engineering, LabDocument7 pagesEE21L-2 - Basic Electrical Engineering, LabCedric Arcel CruzNo ratings yet
- EEE1001 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Thevenin's and Maximum Power Transfer TheoremDocument12 pagesEEE1001 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Thevenin's and Maximum Power Transfer TheoremISHAAAAAAAAAAANNo ratings yet
- Supp - 2021 - PRL - Purves - Quantum Theory Cannot Violate A Causal InequalityDocument11 pagesSupp - 2021 - PRL - Purves - Quantum Theory Cannot Violate A Causal InequalityYifan TangNo ratings yet
- Step Response of An RL CircuitDocument13 pagesStep Response of An RL CircuitROUNAK MANDALNo ratings yet
- Domenico Scarlatti Five PiecesDocument6 pagesDomenico Scarlatti Five PiecesMarco PipernoNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Trace Elements GeochronDocument38 pagesTrace Elements GeochronJaor JnrNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives and Fundamental QuestionsDocument18 pagesLearning Objectives and Fundamental QuestionsJaor JnrNo ratings yet
- Garg Et Al-2008-Journal of Geophysical Research - Solid Earth (1978-2012)Document32 pagesGarg Et Al-2008-Journal of Geophysical Research - Solid Earth (1978-2012)Jaor JnrNo ratings yet
- Bai 2012Document9 pagesBai 2012Jaor JnrNo ratings yet
- Massively Parallel Simulation of Oceanic-Gas-Hydrate ProductionDocument3 pagesMassively Parallel Simulation of Oceanic-Gas-Hydrate ProductionJaor JnrNo ratings yet