Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sub 15698
Sub 15698
Uploaded by
Dea LeeteukCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ENT UK Revised Orbital Cellulitis Flow Chart 2017Document2 pagesENT UK Revised Orbital Cellulitis Flow Chart 2017Exo L1485No ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersDocument7 pagesChapter 22 Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersPeej Reyes100% (2)
- Rhinolith ArticlesDocument11 pagesRhinolith ArticlesdnllkzaNo ratings yet
- F013542830 PDFDocument3 pagesF013542830 PDFDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Rhinolithiasis With A Nasal Polyp: A Case Report: Ibrahim Ozcan, MD Murat Ozcan, MD Serdar Ensari, MD Huseyin Dere, MDDocument2 pagesRhinolithiasis With A Nasal Polyp: A Case Report: Ibrahim Ozcan, MD Murat Ozcan, MD Serdar Ensari, MD Huseyin Dere, MDHairunisa 0049No ratings yet
- Rhinolithiasis As Cause of Oronasal Fistula: Case ReportDocument3 pagesRhinolithiasis As Cause of Oronasal Fistula: Case ReportDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Rhinolith: A Case Report and Review of Literature: September 2010Document4 pagesRhinolith: A Case Report and Review of Literature: September 2010Syukri Be DeNo ratings yet
- Indian Journal of Clinical and Non Clinical Case Studies Article - No.3 (3), 2018: IJCNCS: ISSN.2456-8163Document8 pagesIndian Journal of Clinical and Non Clinical Case Studies Article - No.3 (3), 2018: IJCNCS: ISSN.2456-8163billy serataNo ratings yet
- Case Report - Fungus BallDocument13 pagesCase Report - Fungus BallAdrian ErindraNo ratings yet
- Rhinolith of EndogenosDocument3 pagesRhinolith of Endogenosnyayu syarahNo ratings yet
- A Large Rhinolith and Importance of Nasal Endoscopy: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesA Large Rhinolith and Importance of Nasal Endoscopy: A Case ReportIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- 2008 Article 29Document3 pages2008 Article 29Dea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Case Report Nasal Foreign Body NEW No IndentDocument13 pagesCase Report Nasal Foreign Body NEW No IndentheribertusNo ratings yet
- Huge Rhinolith in Adult: Yetişkinde Dev RinolitDocument3 pagesHuge Rhinolith in Adult: Yetişkinde Dev RinolitDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Rhinolith: A Forgotten Identity-Series of 18 Cases With Review of LiteratureDocument5 pagesRhinolith: A Forgotten Identity-Series of 18 Cases With Review of LiteratureGustamas Indra MaulanaNo ratings yet
- 272 537 1 SMDocument2 pages272 537 1 SMDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Left Ethmoidal Polyp Mimicking A Left Antral Mucous Retention CystDocument6 pagesLeft Ethmoidal Polyp Mimicking A Left Antral Mucous Retention CystInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Foreign Bodies in The NoseDocument37 pagesForeign Bodies in The NosenedvedcoxNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Matin Ghazizade, Mahboobe Asadi and Pouyan DarbaniDocument4 pagesCase Report: Matin Ghazizade, Mahboobe Asadi and Pouyan DarbanirizkiaNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis Associated With An Unusual Foreign Body: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesCase Report: Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis Associated With An Unusual Foreign Body: A Case Reporti made artaNo ratings yet
- Palatal Perforation: Case Report and Literature Review: 10.5005/jp-Journals-10039-1170Document4 pagesPalatal Perforation: Case Report and Literature Review: 10.5005/jp-Journals-10039-1170Maqbul AlamNo ratings yet
- Parotid Sialocele and Fistulae: Current Treatment Options: January 2011Document5 pagesParotid Sialocele and Fistulae: Current Treatment Options: January 2011g.abdulrhmanNo ratings yet
- FB in SinusDocument1 pageFB in SinusrajaalfatihNo ratings yet
- An Unusual Foreign Body As Cause of Chronic Sinusitis: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesAn Unusual Foreign Body As Cause of Chronic Sinusitis: A Case ReportmasyfuqNo ratings yet
- New Documents ENDocument3 pagesNew Documents ENAjmal KunjumonNo ratings yet
- Natural Treatment of Chronic RhinosinusitisDocument13 pagesNatural Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitisbandgar123No ratings yet
- Dentigerous Cyst With An Impacted Canine in The Maxillary Sinus: A Rare Entity!Document3 pagesDentigerous Cyst With An Impacted Canine in The Maxillary Sinus: A Rare Entity!PaTt Tyy RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine - Update For The Dental Practitioner Lumps and SwellingsDocument9 pagesOral Medicine - Update For The Dental Practitioner Lumps and SwellingsGowriNo ratings yet
- Nasal Myiasis in A Bedridden Patient and Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesNasal Myiasis in A Bedridden Patient and Literature Reviewintrovert ikonNo ratings yet
- Fulltext - Jdod v6 Id1141 1Document3 pagesFulltext - Jdod v6 Id1141 1Diandra Puspa WidyasariNo ratings yet
- AFP Clinical Nasal ObstructionDocument5 pagesAFP Clinical Nasal ObstructionTri OktarinaNo ratings yet
- Chronic RhinosinusitisDocument8 pagesChronic RhinosinusitisYunardi Singgo100% (1)
- Maxi Sinus AwayDocument74 pagesMaxi Sinus Awaysharmasoumankbtp622No ratings yet
- An Unusual Complication of Nasal Foreign Body in A Pediatric Patient A Case ReportDocument3 pagesAn Unusual Complication of Nasal Foreign Body in A Pediatric Patient A Case ReportputiridhaNo ratings yet
- Nasal Discharge & ObstructionDocument70 pagesNasal Discharge & ObstructionRajhmuniran KandasamyNo ratings yet
- Atrophic Rhinitis: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesAtrophic Rhinitis: A Case ReportSeven WarlordNo ratings yet
- Malignant Oncocytoma of The Nasal Cavity: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesMalignant Oncocytoma of The Nasal Cavity: A Case ReportInes Camilla PutriNo ratings yet
- Nasal ObstructionDocument26 pagesNasal ObstructionAkhil Krishna0% (1)
- Rhinotillexomania Manifesting As Empty Nose Syndrome-Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology-2020Document4 pagesRhinotillexomania Manifesting As Empty Nose Syndrome-Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology-2020Jose ManuelNo ratings yet
- Al Hafiz Djosan - Forum PPDS Unas L PadangDocument61 pagesAl Hafiz Djosan - Forum PPDS Unas L PadangAstrid GayatriNo ratings yet
- Nasal PolypsDocument43 pagesNasal PolypsManasa anonymous100% (2)
- ENT 2marksDocument10 pagesENT 2marksSaileekitha AjamoniNo ratings yet
- Lampiran RinosinusitisDocument92 pagesLampiran Rinosinusitislaringfaring updateNo ratings yet
- An Unusual Case of A Cheek Abscess in A Patient With Oral Submucous FibrosisDocument2 pagesAn Unusual Case of A Cheek Abscess in A Patient With Oral Submucous FibrosisnursitaNo ratings yet
- rjz074 PDFDocument3 pagesrjz074 PDFRegina Dwindarti DarostyNo ratings yet
- Plunging Ranula: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesPlunging Ranula: A Case ReportNadillaNo ratings yet
- Report Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis Associated With An Foreign Body: A Case ReportDocument8 pagesReport Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis Associated With An Foreign Body: A Case ReportaflisNo ratings yet
- Australian Dental Journal: Rhinosinusitis in Oral Medicine and DentistryDocument7 pagesAustralian Dental Journal: Rhinosinusitis in Oral Medicine and DentistryVishakha SabooNo ratings yet
- Articles Fernand Montreuil1949 Cyst of The Nasal VestibuleDocument8 pagesArticles Fernand Montreuil1949 Cyst of The Nasal Vestibuledieynaba baNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument6 pagesJurnalYazid Eriansyah PradantaNo ratings yet
- Hilde N Brand 2010Document4 pagesHilde N Brand 2010Amira TauhidaNo ratings yet
- A Rare Case Report - Nasal Columellar Schwannoma With Review of LiteratureDocument5 pagesA Rare Case Report - Nasal Columellar Schwannoma With Review of LiteratureIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Aspiration of Endo FileDocument3 pagesAspiration of Endo FileShivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- Nasopharyngeal Branchial CystDocument2 pagesNasopharyngeal Branchial CystSilva Neta OktariNo ratings yet
- Sublingual Ranula: Case Report and Review of Literature: June 2015Document4 pagesSublingual Ranula: Case Report and Review of Literature: June 2015Putri AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Sublingual Ranula: Case Report and Review of Literature: June 2015Document4 pagesSublingual Ranula: Case Report and Review of Literature: June 2015Putri AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Intra-Aural Tick Induced Facial PalsyDocument2 pagesIntra-Aural Tick Induced Facial PalsyAssaye NibretNo ratings yet
- ODONTOGENIC DISEASE of The MAXILLARY SINUS - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Document13 pagesODONTOGENIC DISEASE of The MAXILLARY SINUS - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Vinnie SinghNo ratings yet
- An Unusual Foreign Body As Cause of Chronic Sinusitis: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesAn Unusual Foreign Body As Cause of Chronic Sinusitis: A Case ReportKrisna Dwi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Jan/MarDocument8 pagesCase Report: Jan/Marintrovert ikonNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Patient With Hip PainDocument12 pagesEvaluation of The Patient With Hip PainDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Postmedj00378 0048 PDFDocument2 pagesPostmedj00378 0048 PDFDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Rhinolith A Brief Review of The Literature And: MarfatiaDocument2 pagesRhinolith A Brief Review of The Literature And: MarfatiaDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Huge Rhinolith in Adult: Yetişkinde Dev RinolitDocument3 pagesHuge Rhinolith in Adult: Yetişkinde Dev RinolitDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- 2008 Article 29Document3 pages2008 Article 29Dea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- F013542830 PDFDocument3 pagesF013542830 PDFDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Rhinolithiasis As Cause of Oronasal Fistula: Case ReportDocument3 pagesRhinolithiasis As Cause of Oronasal Fistula: Case ReportDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- 272 537 1 SMDocument2 pages272 537 1 SMDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Urticaria and AngioedemaDocument40 pagesUrticaria and AngioedemaDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- SPECIAL SENSES HearequismltasteDocument22 pagesSPECIAL SENSES HearequismltasteDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- English Book ReadingDocument33 pagesEnglish Book ReadingDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Atlas of Pediatric EntDocument72 pagesEndoscopic Atlas of Pediatric EntAyman Yakout100% (1)
- Ent PointsDocument9 pagesEnt PointsSaiNo ratings yet
- OPTHADocument297 pagesOPTHAroveenaNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Sinus Surgery ConsentDocument3 pagesEndoscopic Sinus Surgery ConsentNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Rhino 2Document4 pagesJurnal Rhino 2Wan Andre Nugraha BarosNo ratings yet
- Nose & Sinus Dysfunction - TCMDocument4 pagesNose & Sinus Dysfunction - TCMpar_avionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Upper Airway or Respiratory DisordersDocument6 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Upper Airway or Respiratory DisordersLuna MarieNo ratings yet
- RinolithDocument16 pagesRinolithGustamas Indra MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Rhino PharyngitisDocument27 pagesRhino PharyngitisinriantoNo ratings yet
- AnglishtPROGRAM ORLDocument2 pagesAnglishtPROGRAM ORLEriola FrrokuNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 (SOAP Note) .PPTX Version 1 (2) (3 Files Merged)Document115 pagesLab 1 (SOAP Note) .PPTX Version 1 (2) (3 Files Merged)Mohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- PracticalDocument89 pagesPracticalAthEer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Non Allergic RhinitisDocument42 pagesNon Allergic RhinitisKadek Seruni KusumanegaraNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy NotesDocument15 pagesGeneral Anatomy NotesEmerald BunnyNo ratings yet
- Nasal PolypsDocument3 pagesNasal PolypsJoyVee Pillagara-De LeonNo ratings yet
- Simply Put - ENT NOSE LECTURESDocument38 pagesSimply Put - ENT NOSE LECTURESCedric KyekyeNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Indications For The Caldwell-Luc Procedure: Keith E. Matheny,, and James A. DuncavageDocument4 pagesContemporary Indications For The Caldwell-Luc Procedure: Keith E. Matheny,, and James A. DuncavageLesly Caman gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Neurological Consequences of Scuba Diving With Chronic SinusitisDocument3 pagesNeurological Consequences of Scuba Diving With Chronic SinusitisDCvdsNo ratings yet
- Nasal Vestibular Furunculosis Summarised Case SeriesDocument7 pagesNasal Vestibular Furunculosis Summarised Case SeriesGadNo ratings yet
- Ent MCQDocument5 pagesEnt MCQMayar MohammadNo ratings yet
- Respiratory BSNMedsurgDocument27 pagesRespiratory BSNMedsurgLeobert Yancy SalosagcolNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Sinus Disease - Power Point PresentationDocument45 pagesMaxillary Sinus Disease - Power Point PresentationRohan Grover100% (1)
- 3 s2.0 B9781455748013003301 MainDocument120 pages3 s2.0 B9781455748013003301 MainInzamam Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- ID For ABIM - Parham 2014Document140 pagesID For ABIM - Parham 2014Jeronim H'gharNo ratings yet
- Upper Respıratory Tract InfectıonsDocument68 pagesUpper Respıratory Tract InfectıonsMekdes ZewdeNo ratings yet
- The Common Cold GuideDocument27 pagesThe Common Cold Guidehappyscottlee3438No ratings yet
- Maxillarysinus 170705134531 PDFDocument93 pagesMaxillarysinus 170705134531 PDFmelaniaNo ratings yet
- Post-Operative Complications After Extraction - A Review of LiteratureDocument5 pagesPost-Operative Complications After Extraction - A Review of Literature072 Adira Khansa MahdiyaNo ratings yet
Sub 15698
Sub 15698
Uploaded by
Dea LeeteukOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sub 15698
Sub 15698
Uploaded by
Dea LeeteukCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR)
ISSN (Online): 2319-7064
Index Copernicus Value (2013): 6.14 | Impact Factor (2013): 4.438
An Unusual and Forgotten Foreign Body Nose
Presenting as Rhinolith
Dr. Dimple Sahni1, Dr. Harpuneet2
1
Assistant Professor, Department of ENT, Government Medical College, Patiala, Punjab India
2
Junior Resident, Department of ENT, Govt. Medical College, Patiala, Punjab India
Abstract: Rhinoliths are uncommon clinical entities reported in clinical practice as unusual cause of unilateral nasal obstruction and
foul smelling nasal discharge. Rhinolith is calcified material found in the nasal cavity. It should be suspected when patient presents with
unilateral nasal blocked and foul smelling nasal discharge with stony mass on clinical examination and proved radiologically. We report
the case of a 30 year old female with left sided (LT) nasal obstruction and foul smelling discharge for 15 years suspected as being due to
foreign body (rubber band) present since childhood and forgotten by the patient. The salient features of such rhinoliths and their
relevance to clinical practice are discussed , so as to enable the attending clinician to be aware of this forgotten entity, which requires a
high index of suspicion. On anterior rhinoscopy a stony hard mass (Rhinolith was seen filling left nasal cavity. Under General
anaesthesia stone was removed in toto from left nasal cavity.
Keywords: Rhinolith, Foreign body nose, Calcareous concretions, Serosanginous discharge, Functional endoscopic sinus surgery.
1. Background history may range from months to decades (7) .women are
more commonly effected than men (8). The diagnosis is
Rhinolith (from the Greek rhino meaning nose, and lithos established on the basis of history endoscopic findings and
meaning stone) are rare . An uncommon medical imaging techniques. Surgical removal is the treatment of
phenomenon , requiring high index of suspicion .They are choice. During surgery, these are friable and crumble readily
calcareous concretions that are formed by the deposition of under pressure.
salts around a nucleus which could be a desiccated blood
clot, insipissated mucous plug, ectopic teeth, bone fragment 2. Case Report
or a small foreign body, thus becoming the focal point for
encrustation. Nasal foreign bodies can either be endogenous A 30 year old female presented with complaints of left sided
or exogenous. Foreign bodies normally access the site progressive nasal discharge, foul smelling and muco-
anteriorly, but they may occasionally reach the nasal cavity purulent in nature since 15 years. Progressive left sided
through the posterior choanae owing to cough or vomiting. nasal obstruction with resultant difficulty in breathing,
Foreign bodies are normally introduced during childhood, especially during sleep for the last 15 years. Of and on
occupying the nasal floor in most situations. A wide range of bloody nasal discharge for the last five years. History of left
objects including metal, plastic, organic materials, and live sided headache in region of forehead was reported. There
insects find their way into the nose, either accidentally or were no other constitutional symptoms. There was no
deliberately. history of trauma, foreign body insertion or any systemic
illness given by the patient. Otorhinolaryngeal clinical
Presence of a nucleus (endogenous/exogenous). Induces examination revealed deviated nasal septum towards the
local inflammatory reaction. Leading to deposits of salts like right side. There was a hard mass filling the left nasal cavity
calcium carbonate and phosphate, magnesium, iron and which was irregular in shape with a rough surface and was
aluminium, in addition to organic substances such as slightly mobile with hard, bony feel but tender and with
glutamic acid and glycine, which originate from the nasal bleeding tendency. A diagnosis of rhinolith was clinically
mucous secretions, tears, and inflammatory exudates. made. NCCT PNS Coronal view was done which confirmed
Leading to slow and progressive increases in size. They may rhinolith. (Figure 1) The patient was admitted for removal of
cause pressure necrosis of the nasal septum or lateral wall of the rhinolith under general anaesthesia.
nose.
The Symptoms are Progressive unilateral nasal discharge,
which may be serosanguinous in nature but usually purulent
and fetid. Nasal obstruction, Epistaxis, Cacosmia. Swelling
of the nose and face, headaches, facial pain and epiphora
could be some of the other less common symptoms. Usually
unilateral and solitary. The surface of a rhinollith is
mulberry like, may be grey or brownish pink in colour. On
probing, the presence of a stony hard structure could be
identified. It appears radiologically as densely calcified
mass in the nasal cavity, with displacement and expansion of
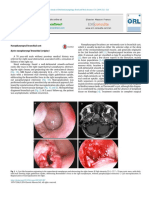
the adjacent bony landmarks. The duration of medical Figure 1
Volume 4 Issue 1, January 2015
www.ijsr.net
Paper ID: SUB15698 2468
Licensed Under Creative Commons Attribution CC BY
International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR)
ISSN (Online): 2319-7064
Index Copernicus Value (2013): 6.14 | Impact Factor (2013): 4.438
3. Treatment
Under General Anaesthesia, the nasal cavities were
inspected by 0 degree nasal endoscope. The nasopharynx
was inspected was found to be normal. A rhinolith was
found lying impacted in the inferior meatus, between the
inferior turbinate and septum in the middle of the left nasal
cavity, also extending to lie between septum and middle
turbinate, between middle turbinate and lateral wall of nose
and in the middle meatus. Functional endoscopic sinus
surgery was done. (Figure 2) It was gently probed and
removed in multiple pieces. (Figure 3) During removal from
inferior meatus, it was found impacted and on removal, a
rubber band was seen, embedded in the rhinolith. (Figure 4) Figure 4
4. Discussion
Bartholin first described rhinolith in 1654, since then more
than 600 cases have been reported.(1,2,3) Rhinoliths are
rare. They are calcareous concretions that are formed by the
deposition of salts on an intranasal foreign body. Although
the pathogenesis remains unclear, a number of factors are
thought to be involved in their formation. These include :
entry and impaction of a foreign body into the nasal cavity,
acute and chronic inflammation, obstruction and stagnation
of nasal secretions and precipitation of mineral salts.
Rhinolith needs time to be formed which is suggested to be
around 15 years.(4) Patients are mostly asymptomatic for
many years following lodgment of the foreign body, which
tends to be forgotten. As the size increases over the years,
patients commonly present with: Nasal obstruction,
Rhinorrhea, Epistaxis, Sinusitis.Other less common
symptoms include facial pain and headache. As it grows
Figure 2 further, it compromises blood supply causing pressure
necrosis, erosion and perforation of surrounding structures
The estimated blood loss was approximately 100 ml. like hard palate or nasal septum.
Septoplasty was performed on right side. Both nasal cavities
were packed with one merocele pack on each side after Diagnosis can be established by keeping a high index of
obtaining haemostasis. The patient was smoothly extubated suspicion based on: symptomatology, history of foreign
and transferred to the recovery room. The merocel packs body introduction into the nose, physical examination and
were removed on third post-operative day with the patient complementary tests. Diagnostic nasal endoscopy is a very
experiencing marked relief of his symptoms. She was useful procedure as it makes diagnosis and assessment of
discharged with antibiotic cover and nasal decongestants. neighboring structures easier. Rhinolith is found frequently
as incidental finding during rhinoscopy, as irregular, hard
dark mass with greenish foul smelling crusts all
around.(7,8,9)
Radiological investigations such as plain X-ray and CT scan,
support the diagnosis through the presence of calcified
concretions in the nasal fossa, help to rule out complications,
support the planning of surgical approach. Computed
tomography of the paranasal sinuses can accurately
determine the site and size of the rhinolith and identify
coexisting sinus disease which may also require
treatment.(10) Maclntyre was the first to describe rhinolith
radiographically in 1900.(5,6) Rhinolith may present with
variable opacities depending upon the nature of the origin.
Diagnosis is sometime also made incidentally through
Figure 3 routine examination or revealed by imaging examinations
conducted for other reasons, such as dental treatment.
Volume 4 Issue 1, January 2015
www.ijsr.net
Paper ID: SUB15698 2469
Licensed Under Creative Commons Attribution CC BY
International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR)
ISSN (Online): 2319-7064
Index Copernicus Value (2013): 6.14 | Impact Factor (2013): 4.438
Differential diagnosis includes: ectopic tooth, benign lesions [10] Hadi U, Ghossaini S, Zaytoun G. Rhinolithiasis: a
such as osteoma and odontogenic tumours, malignant forgotten entity. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2002.
lesions like osteosarcoma Jan;126(1):48-51 10.1067
Medical treatment has not shown to be effective in these Author Profile
cases. Treatment of choice is surgical that is endoscopic
removal and in extremely rare conditions, it needs external Dr. Dimple Sahni is MS ENT and working as a
approach like lateral rhinotomy. Usage of local and systemic Assistant Professor, Dept. of ENT, Govt. Medical
antibiotics after removal of rhinolith improves the recovery. College, Patiala-147001, Punjab (INDIA) Her area of
research interest includes Rhinology
5. Conclusion
Dr. Harpuneet, Junior Resident, ENT, Govt. Medical College,
A typical history clinical science diagnostic endoscopy and Patiala-147001, Punjab (India)
radiographs of nose and paranasal sinuses showing a
calcified mass in the nasal cavity points to presence of
rhinolith. So, in this case, foreign body which acted as nidus
for rhinolith was found to be a rubber band which is a very
unusual foreign body, never seen before in any case of
foreign body nose in our hospital setting. Also, patient was
unaware of any foreign body inserted during childhood.
Although Rhinoliths are rare, attending clinicians should be
aware of this entity. It requires a high index of suspicion
when dealing with nasal symptoms such as progressive
unilateral nasal obstruction, rhinorrhea (usually purulent and
fetid), cacosmia and unilateral nasal bleeding.
6. Future Scope
To study the incidence and prevalence and need for early
diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications.
7. Source of Funding: None
8. Conflict of Interest: None
References
[1] Pitt SK, Rout PG. Rhinoliths presenting during
routine radiography: Two cases. Dent Update 2000;
27: 505-7.
[2] Appleton SS, Kimbrough RE, Engstrom HI.
Rhinolithiasis: A review. Oral surg Oral med Oral
Pathol 1988; 65: 693-8
[3] C. J. Polson, On rhinoliths, Journal of Laryngology
and Otology, vol. 58, no.3, pp.79116, 1943.
[4] Shaw LC. Rhinolith of endogenous origin: A rare
entity. Surg Pract 2007; 11: 48-50.
[5] Royal SA, Gardner RE. Rhinolithiasis: An unusual
pediatric nasal mass. Pediatr Radiol 1998; 28: 55-5.
[6] K. Patil, M. V. Guledgud, and S. N. Malleshi,
Rhinolith, Indian Journal of Dental Research, vol.
20, no. 1, pp. 114116, 2009.
[7] Jain RK., Frammer HH. (1982): Incidental finding of
rhinoliths in panoramic radiography. New York State
Dental Journal. 48: 530-532.
[8] A. Mustafa and S. Nishori, Rhinolith caused from
undetected foreign body: a case report, Kosova
Journal of Surgery, vol. 2, pp. 3235, 2008.
[9] R. K. Singh, S. Varshney, S. S. Bist, N. Gupta, R.
Bhatia, and S. Kishor, A case of rhinolithiasis, "
Online Journal of Health and Allied Sciences, vol. 7,
no. 2, article 7, 2008.
Volume 4 Issue 1, January 2015
www.ijsr.net
Paper ID: SUB15698 2470
Licensed Under Creative Commons Attribution CC BY
You might also like
- ENT UK Revised Orbital Cellulitis Flow Chart 2017Document2 pagesENT UK Revised Orbital Cellulitis Flow Chart 2017Exo L1485No ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersDocument7 pagesChapter 22 Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersPeej Reyes100% (2)
- Rhinolith ArticlesDocument11 pagesRhinolith ArticlesdnllkzaNo ratings yet
- F013542830 PDFDocument3 pagesF013542830 PDFDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Rhinolithiasis With A Nasal Polyp: A Case Report: Ibrahim Ozcan, MD Murat Ozcan, MD Serdar Ensari, MD Huseyin Dere, MDDocument2 pagesRhinolithiasis With A Nasal Polyp: A Case Report: Ibrahim Ozcan, MD Murat Ozcan, MD Serdar Ensari, MD Huseyin Dere, MDHairunisa 0049No ratings yet
- Rhinolithiasis As Cause of Oronasal Fistula: Case ReportDocument3 pagesRhinolithiasis As Cause of Oronasal Fistula: Case ReportDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Rhinolith: A Case Report and Review of Literature: September 2010Document4 pagesRhinolith: A Case Report and Review of Literature: September 2010Syukri Be DeNo ratings yet
- Indian Journal of Clinical and Non Clinical Case Studies Article - No.3 (3), 2018: IJCNCS: ISSN.2456-8163Document8 pagesIndian Journal of Clinical and Non Clinical Case Studies Article - No.3 (3), 2018: IJCNCS: ISSN.2456-8163billy serataNo ratings yet
- Case Report - Fungus BallDocument13 pagesCase Report - Fungus BallAdrian ErindraNo ratings yet
- Rhinolith of EndogenosDocument3 pagesRhinolith of Endogenosnyayu syarahNo ratings yet
- A Large Rhinolith and Importance of Nasal Endoscopy: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesA Large Rhinolith and Importance of Nasal Endoscopy: A Case ReportIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- 2008 Article 29Document3 pages2008 Article 29Dea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Case Report Nasal Foreign Body NEW No IndentDocument13 pagesCase Report Nasal Foreign Body NEW No IndentheribertusNo ratings yet
- Huge Rhinolith in Adult: Yetişkinde Dev RinolitDocument3 pagesHuge Rhinolith in Adult: Yetişkinde Dev RinolitDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Rhinolith: A Forgotten Identity-Series of 18 Cases With Review of LiteratureDocument5 pagesRhinolith: A Forgotten Identity-Series of 18 Cases With Review of LiteratureGustamas Indra MaulanaNo ratings yet
- 272 537 1 SMDocument2 pages272 537 1 SMDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Left Ethmoidal Polyp Mimicking A Left Antral Mucous Retention CystDocument6 pagesLeft Ethmoidal Polyp Mimicking A Left Antral Mucous Retention CystInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Foreign Bodies in The NoseDocument37 pagesForeign Bodies in The NosenedvedcoxNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Matin Ghazizade, Mahboobe Asadi and Pouyan DarbaniDocument4 pagesCase Report: Matin Ghazizade, Mahboobe Asadi and Pouyan DarbanirizkiaNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis Associated With An Unusual Foreign Body: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesCase Report: Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis Associated With An Unusual Foreign Body: A Case Reporti made artaNo ratings yet
- Palatal Perforation: Case Report and Literature Review: 10.5005/jp-Journals-10039-1170Document4 pagesPalatal Perforation: Case Report and Literature Review: 10.5005/jp-Journals-10039-1170Maqbul AlamNo ratings yet
- Parotid Sialocele and Fistulae: Current Treatment Options: January 2011Document5 pagesParotid Sialocele and Fistulae: Current Treatment Options: January 2011g.abdulrhmanNo ratings yet
- FB in SinusDocument1 pageFB in SinusrajaalfatihNo ratings yet
- An Unusual Foreign Body As Cause of Chronic Sinusitis: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesAn Unusual Foreign Body As Cause of Chronic Sinusitis: A Case ReportmasyfuqNo ratings yet
- New Documents ENDocument3 pagesNew Documents ENAjmal KunjumonNo ratings yet
- Natural Treatment of Chronic RhinosinusitisDocument13 pagesNatural Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitisbandgar123No ratings yet
- Dentigerous Cyst With An Impacted Canine in The Maxillary Sinus: A Rare Entity!Document3 pagesDentigerous Cyst With An Impacted Canine in The Maxillary Sinus: A Rare Entity!PaTt Tyy RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine - Update For The Dental Practitioner Lumps and SwellingsDocument9 pagesOral Medicine - Update For The Dental Practitioner Lumps and SwellingsGowriNo ratings yet
- Nasal Myiasis in A Bedridden Patient and Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesNasal Myiasis in A Bedridden Patient and Literature Reviewintrovert ikonNo ratings yet
- Fulltext - Jdod v6 Id1141 1Document3 pagesFulltext - Jdod v6 Id1141 1Diandra Puspa WidyasariNo ratings yet
- AFP Clinical Nasal ObstructionDocument5 pagesAFP Clinical Nasal ObstructionTri OktarinaNo ratings yet
- Chronic RhinosinusitisDocument8 pagesChronic RhinosinusitisYunardi Singgo100% (1)
- Maxi Sinus AwayDocument74 pagesMaxi Sinus Awaysharmasoumankbtp622No ratings yet
- An Unusual Complication of Nasal Foreign Body in A Pediatric Patient A Case ReportDocument3 pagesAn Unusual Complication of Nasal Foreign Body in A Pediatric Patient A Case ReportputiridhaNo ratings yet
- Nasal Discharge & ObstructionDocument70 pagesNasal Discharge & ObstructionRajhmuniran KandasamyNo ratings yet
- Atrophic Rhinitis: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesAtrophic Rhinitis: A Case ReportSeven WarlordNo ratings yet
- Malignant Oncocytoma of The Nasal Cavity: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesMalignant Oncocytoma of The Nasal Cavity: A Case ReportInes Camilla PutriNo ratings yet
- Nasal ObstructionDocument26 pagesNasal ObstructionAkhil Krishna0% (1)
- Rhinotillexomania Manifesting As Empty Nose Syndrome-Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology-2020Document4 pagesRhinotillexomania Manifesting As Empty Nose Syndrome-Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology-2020Jose ManuelNo ratings yet
- Al Hafiz Djosan - Forum PPDS Unas L PadangDocument61 pagesAl Hafiz Djosan - Forum PPDS Unas L PadangAstrid GayatriNo ratings yet
- Nasal PolypsDocument43 pagesNasal PolypsManasa anonymous100% (2)
- ENT 2marksDocument10 pagesENT 2marksSaileekitha AjamoniNo ratings yet
- Lampiran RinosinusitisDocument92 pagesLampiran Rinosinusitislaringfaring updateNo ratings yet
- An Unusual Case of A Cheek Abscess in A Patient With Oral Submucous FibrosisDocument2 pagesAn Unusual Case of A Cheek Abscess in A Patient With Oral Submucous FibrosisnursitaNo ratings yet
- rjz074 PDFDocument3 pagesrjz074 PDFRegina Dwindarti DarostyNo ratings yet
- Plunging Ranula: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesPlunging Ranula: A Case ReportNadillaNo ratings yet
- Report Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis Associated With An Foreign Body: A Case ReportDocument8 pagesReport Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis Associated With An Foreign Body: A Case ReportaflisNo ratings yet
- Australian Dental Journal: Rhinosinusitis in Oral Medicine and DentistryDocument7 pagesAustralian Dental Journal: Rhinosinusitis in Oral Medicine and DentistryVishakha SabooNo ratings yet
- Articles Fernand Montreuil1949 Cyst of The Nasal VestibuleDocument8 pagesArticles Fernand Montreuil1949 Cyst of The Nasal Vestibuledieynaba baNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument6 pagesJurnalYazid Eriansyah PradantaNo ratings yet
- Hilde N Brand 2010Document4 pagesHilde N Brand 2010Amira TauhidaNo ratings yet
- A Rare Case Report - Nasal Columellar Schwannoma With Review of LiteratureDocument5 pagesA Rare Case Report - Nasal Columellar Schwannoma With Review of LiteratureIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Aspiration of Endo FileDocument3 pagesAspiration of Endo FileShivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- Nasopharyngeal Branchial CystDocument2 pagesNasopharyngeal Branchial CystSilva Neta OktariNo ratings yet
- Sublingual Ranula: Case Report and Review of Literature: June 2015Document4 pagesSublingual Ranula: Case Report and Review of Literature: June 2015Putri AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Sublingual Ranula: Case Report and Review of Literature: June 2015Document4 pagesSublingual Ranula: Case Report and Review of Literature: June 2015Putri AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Intra-Aural Tick Induced Facial PalsyDocument2 pagesIntra-Aural Tick Induced Facial PalsyAssaye NibretNo ratings yet
- ODONTOGENIC DISEASE of The MAXILLARY SINUS - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Document13 pagesODONTOGENIC DISEASE of The MAXILLARY SINUS - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Vinnie SinghNo ratings yet
- An Unusual Foreign Body As Cause of Chronic Sinusitis: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesAn Unusual Foreign Body As Cause of Chronic Sinusitis: A Case ReportKrisna Dwi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Jan/MarDocument8 pagesCase Report: Jan/Marintrovert ikonNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Patient With Hip PainDocument12 pagesEvaluation of The Patient With Hip PainDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Postmedj00378 0048 PDFDocument2 pagesPostmedj00378 0048 PDFDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Rhinolith A Brief Review of The Literature And: MarfatiaDocument2 pagesRhinolith A Brief Review of The Literature And: MarfatiaDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Huge Rhinolith in Adult: Yetişkinde Dev RinolitDocument3 pagesHuge Rhinolith in Adult: Yetişkinde Dev RinolitDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- 2008 Article 29Document3 pages2008 Article 29Dea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- F013542830 PDFDocument3 pagesF013542830 PDFDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Rhinolithiasis As Cause of Oronasal Fistula: Case ReportDocument3 pagesRhinolithiasis As Cause of Oronasal Fistula: Case ReportDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- 272 537 1 SMDocument2 pages272 537 1 SMDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Urticaria and AngioedemaDocument40 pagesUrticaria and AngioedemaDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- SPECIAL SENSES HearequismltasteDocument22 pagesSPECIAL SENSES HearequismltasteDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- English Book ReadingDocument33 pagesEnglish Book ReadingDea LeeteukNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Atlas of Pediatric EntDocument72 pagesEndoscopic Atlas of Pediatric EntAyman Yakout100% (1)
- Ent PointsDocument9 pagesEnt PointsSaiNo ratings yet
- OPTHADocument297 pagesOPTHAroveenaNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Sinus Surgery ConsentDocument3 pagesEndoscopic Sinus Surgery ConsentNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Rhino 2Document4 pagesJurnal Rhino 2Wan Andre Nugraha BarosNo ratings yet
- Nose & Sinus Dysfunction - TCMDocument4 pagesNose & Sinus Dysfunction - TCMpar_avionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Upper Airway or Respiratory DisordersDocument6 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Upper Airway or Respiratory DisordersLuna MarieNo ratings yet
- RinolithDocument16 pagesRinolithGustamas Indra MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Rhino PharyngitisDocument27 pagesRhino PharyngitisinriantoNo ratings yet
- AnglishtPROGRAM ORLDocument2 pagesAnglishtPROGRAM ORLEriola FrrokuNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 (SOAP Note) .PPTX Version 1 (2) (3 Files Merged)Document115 pagesLab 1 (SOAP Note) .PPTX Version 1 (2) (3 Files Merged)Mohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- PracticalDocument89 pagesPracticalAthEer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Non Allergic RhinitisDocument42 pagesNon Allergic RhinitisKadek Seruni KusumanegaraNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy NotesDocument15 pagesGeneral Anatomy NotesEmerald BunnyNo ratings yet
- Nasal PolypsDocument3 pagesNasal PolypsJoyVee Pillagara-De LeonNo ratings yet
- Simply Put - ENT NOSE LECTURESDocument38 pagesSimply Put - ENT NOSE LECTURESCedric KyekyeNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Indications For The Caldwell-Luc Procedure: Keith E. Matheny,, and James A. DuncavageDocument4 pagesContemporary Indications For The Caldwell-Luc Procedure: Keith E. Matheny,, and James A. DuncavageLesly Caman gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Neurological Consequences of Scuba Diving With Chronic SinusitisDocument3 pagesNeurological Consequences of Scuba Diving With Chronic SinusitisDCvdsNo ratings yet
- Nasal Vestibular Furunculosis Summarised Case SeriesDocument7 pagesNasal Vestibular Furunculosis Summarised Case SeriesGadNo ratings yet
- Ent MCQDocument5 pagesEnt MCQMayar MohammadNo ratings yet
- Respiratory BSNMedsurgDocument27 pagesRespiratory BSNMedsurgLeobert Yancy SalosagcolNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Sinus Disease - Power Point PresentationDocument45 pagesMaxillary Sinus Disease - Power Point PresentationRohan Grover100% (1)
- 3 s2.0 B9781455748013003301 MainDocument120 pages3 s2.0 B9781455748013003301 MainInzamam Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- ID For ABIM - Parham 2014Document140 pagesID For ABIM - Parham 2014Jeronim H'gharNo ratings yet
- Upper Respıratory Tract InfectıonsDocument68 pagesUpper Respıratory Tract InfectıonsMekdes ZewdeNo ratings yet
- The Common Cold GuideDocument27 pagesThe Common Cold Guidehappyscottlee3438No ratings yet
- Maxillarysinus 170705134531 PDFDocument93 pagesMaxillarysinus 170705134531 PDFmelaniaNo ratings yet
- Post-Operative Complications After Extraction - A Review of LiteratureDocument5 pagesPost-Operative Complications After Extraction - A Review of Literature072 Adira Khansa MahdiyaNo ratings yet