Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conductor Temperature: Method B
Conductor Temperature: Method B
Uploaded by
Udomkarn SmtCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lab 7 RC Time ConstantDocument8 pagesLab 7 RC Time ConstantMalith Madushan100% (1)
- MD 11fgnDocument3 pagesMD 11fgnMcDonnell Douglas MD-110% (7)
- Project Proposal On Dairy FarmDocument26 pagesProject Proposal On Dairy Farmvector dairy88% (8)
- Australian Professional Standards For TeachersDocument1 pageAustralian Professional Standards For Teachersapi-365080091No ratings yet
- Mainframe Admin Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesMainframe Admin Course SyllabusENDLURI DEEPAK KUMARNo ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator and RC Coupled Ce Amplifier - Lab ExperimentDocument8 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator and RC Coupled Ce Amplifier - Lab ExperimentMani BharathiNo ratings yet
- Relay Calculation SummaryDocument4 pagesRelay Calculation SummaryAnonymous kjvaeVJNNo ratings yet
- Cs Lab Manual in PDFDocument56 pagesCs Lab Manual in PDFvasukonetiNo ratings yet
- Daycounter Inc - Snubber Circuit Design CalculatorsDocument5 pagesDaycounter Inc - Snubber Circuit Design CalculatorsLaercio Marques100% (1)
- Snubber PDFDocument5 pagesSnubber PDFJ Milk SilvaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Attenuators and Compensation: R R V R V R R R V VDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Attenuators and Compensation: R R V R V R R R V Vnithinjose4uNo ratings yet
- TL431 Design Tips2 PDFDocument10 pagesTL431 Design Tips2 PDF3degreesNo ratings yet
- Applications To Sizing Circuit Breakers (ANSI C37)Document22 pagesApplications To Sizing Circuit Breakers (ANSI C37)freddy riveraNo ratings yet
- Oral PEADocument34 pagesOral PEAatefdinNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Input Filter - Flo: GraphicDocument2 pagesCapacitor Input Filter - Flo: GraphicSeijuro AkashiNo ratings yet
- MiCOM P54 X - Current Diff Prot Relays - CT RequirementDocument5 pagesMiCOM P54 X - Current Diff Prot Relays - CT RequirementpayNo ratings yet
- Figure 2. Voltage Mode Amplifier CircuitDocument2 pagesFigure 2. Voltage Mode Amplifier CircuitHadi KhanmohammadiNo ratings yet
- A PWM Circuit Using Operational AmplifiersDocument7 pagesA PWM Circuit Using Operational Amplifiershamza abdo mohamoud100% (1)
- Op Amp Manual Sem 1st....Document7 pagesOp Amp Manual Sem 1st....diljitdosanjhfan24No ratings yet
- 3 - 2b Transformer Energization - ModelingDocument7 pages3 - 2b Transformer Energization - ModelingNalex GeeNo ratings yet
- Universal Block DiagramDocument6 pagesUniversal Block Diagramapneetsandhu1234No ratings yet
- Analog Basics:: Waveforms, Ac and DCDocument30 pagesAnalog Basics:: Waveforms, Ac and DCvenkumaniNo ratings yet
- Uses of CapacitorsDocument4 pagesUses of Capacitorswilliamx1978No ratings yet
- Lab #6Document4 pagesLab #6darline.ferrerNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EENG200 - Updated 23-24Document23 pagesLab Manual EENG200 - Updated 23-24What's new ?No ratings yet
- An 4134Document14 pagesAn 4134shri.bhairavkar6977No ratings yet
- 1.RC CircuitsDocument7 pages1.RC CircuitsNaveen ChNo ratings yet
- TAN DELTA Application NotesDocument34 pagesTAN DELTA Application NotesKamlesh MhatreNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier 741 As Wein Bridge Oscillator 1Document4 pagesOperational Amplifier 741 As Wein Bridge Oscillator 1Deepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- 18eel66 Lab ManualDocument53 pages18eel66 Lab ManualVasanthNo ratings yet
- Amplifier Frequency ResponseDocument24 pagesAmplifier Frequency ResponsejaltitiNo ratings yet
- 6 Log Anti Log AmplifiersDocument32 pages6 Log Anti Log AmplifiersAnonymous eWMnRr70q0% (1)
- R - KZ I: A 12-Bit ADC Successive-Approximation-Type With Digital Error CorrectionDocument10 pagesR - KZ I: A 12-Bit ADC Successive-Approximation-Type With Digital Error CorrectionMiguel BrunoNo ratings yet
- Hybrid PieDocument6 pagesHybrid PieAman GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ty Man V ACDocument17 pagesTy Man V AC10 Joshua MasterNo ratings yet
- Frequency Characteristics of AC Circuits: RLC Circuits and ResonanceDocument39 pagesFrequency Characteristics of AC Circuits: RLC Circuits and ResonanceOng Xuan YaoNo ratings yet
- Transformer Protection 2012-1Document43 pagesTransformer Protection 2012-1muaz_aminu1422100% (2)
- Monty B Bode Plots and First Order Filters ReportDocument11 pagesMonty B Bode Plots and First Order Filters ReportMonts 42No ratings yet
- Dist Cord (R)Document12 pagesDist Cord (R)1453hNo ratings yet
- Multivibrators - Record PartDocument6 pagesMultivibrators - Record PartAlfred D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Step-ByStep Flyback SMPS DesignDocument6 pagesStep-ByStep Flyback SMPS DesignPhạm Văn TưởngNo ratings yet
- Lab 5: Voltage RegulatorDocument7 pagesLab 5: Voltage RegulatorMansi NanavatiNo ratings yet
- Mixed Signal Analysis of First Order Low Pass FilterDocument3 pagesMixed Signal Analysis of First Order Low Pass FilterAhdelNo ratings yet
- Transient Response of RC CircuitDocument5 pagesTransient Response of RC CircuitJayesh Ruikar100% (1)
- EEE 54 DP1 Documentation - Mendoza - SorianoDocument2 pagesEEE 54 DP1 Documentation - Mendoza - SorianoDarl John MendozaNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Relay PDFDocument17 pagesOvercurrent Relay PDFtranhuutuongNo ratings yet
- Design of Electrical SystemsDocument621 pagesDesign of Electrical SystemsPardeep KhosaNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryDocument6 pagesRC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryMuhammad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Experiment 21 RC Time Constants: Advanced ReadingDocument2 pagesExperiment 21 RC Time Constants: Advanced ReadingAlicia AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument28 pagesCourse OutlineIdrisa Mussa ChubwaNo ratings yet
- RC CircuitsDocument11 pagesRC Circuits2456903No ratings yet
- Implementing The TL431 Feedback LoopDocument10 pagesImplementing The TL431 Feedback LoopAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Discussion of The Sample and Hold Circuit and The Time Required To Get and Hold The VoltageDocument22 pagesDiscussion of The Sample and Hold Circuit and The Time Required To Get and Hold The VoltagewolverinepNo ratings yet
- Numerical Overcurrent Relay and Relay CoordinationDocument7 pagesNumerical Overcurrent Relay and Relay Coordinationvoyimat216No ratings yet
- Circuit BreakerDocument50 pagesCircuit BreakerDeanna GrahamNo ratings yet
- Protection Relays Setting Calculation Rev 4Document55 pagesProtection Relays Setting Calculation Rev 4Aatif Usmani100% (1)
- Analog1 Final 6Document15 pagesAnalog1 Final 6Sourav SinhaNo ratings yet
- Fly BackDocument20 pagesFly BackĐặng Văn TàiNo ratings yet
- Compensating The RHPZ in A CCM Boost Converter - The Analytical Way - Jun 2009Document4 pagesCompensating The RHPZ in A CCM Boost Converter - The Analytical Way - Jun 2009QuickerManNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Relaying For Feeder ProtectionDocument20 pagesOvercurrent Relaying For Feeder ProtectionVinodNo ratings yet
- Durgapur: National Institute of TechnologyDocument10 pagesDurgapur: National Institute of TechnologyBishal SinghNo ratings yet
- HWR FWR ParametersDocument6 pagesHWR FWR ParametersRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- 002 Lab2-Fa10Document4 pages002 Lab2-Fa10xendikaNo ratings yet
- 1995 Transmission Line Design ProcessDocument10 pages1995 Transmission Line Design Processjoydeep_d3232No ratings yet
- Conductor TAIHAN Size ChartsDocument40 pagesConductor TAIHAN Size ChartsUdomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- IEC StandardDocument23 pagesIEC StandardSyedAhsanAbbasBokhari0% (1)
- STR 180Document2 pagesSTR 180Udomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Tower Footing Resistance Effected Back Flashover Across Insulator in A Transmission SystemDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Tower Footing Resistance Effected Back Flashover Across Insulator in A Transmission SystemUdomkarn Smt100% (1)
- FLL 431Document1 pageFLL 431Udomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- Design of Transmission Lines, Structures, and FoundationsDocument8 pagesDesign of Transmission Lines, Structures, and FoundationsUdomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- Solution Methods of Overhead Transmission Line Mechanics: Ladislav VARGA, Stanislav ILENIN, Vladimír CHLADNÝDocument4 pagesSolution Methods of Overhead Transmission Line Mechanics: Ladislav VARGA, Stanislav ILENIN, Vladimír CHLADNÝUdomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- App HDocument1 pageApp HUdomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- Glossary: A Accelerated ErosionDocument13 pagesGlossary: A Accelerated ErosionUdomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Endurance Present KnowledgeDocument30 pagesFatigue Endurance Present KnowledgeUdomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- SF Hose Cat 2017Document40 pagesSF Hose Cat 2017Ahmed Abdelaty100% (1)
- Job Notification NHM Odisha Recruitment 2015 16 For 19 District Programme Manager Other PostsDocument12 pagesJob Notification NHM Odisha Recruitment 2015 16 For 19 District Programme Manager Other PostsJeshiNo ratings yet
- Crown Amplifiers Catalog PDFDocument68 pagesCrown Amplifiers Catalog PDFArjay DomisiwNo ratings yet
- Wandering Heroes of Ogre Gate - House of Paper ShadowsDocument97 pagesWandering Heroes of Ogre Gate - House of Paper ShadowsSamuel Smallman75% (4)
- UP Series: Grundfos Product GuideDocument84 pagesUP Series: Grundfos Product GuideGrundfosEgyptNo ratings yet
- Ideal Dilute and Real SolutionsDocument9 pagesIdeal Dilute and Real SolutionsJksgNo ratings yet
- PRIsDocument11 pagesPRIsbobby choudharyNo ratings yet
- Product Environmental Profile: Canalis KNA 40A To 160ADocument7 pagesProduct Environmental Profile: Canalis KNA 40A To 160AJavier LazoNo ratings yet
- Historical Background of LubricantsDocument21 pagesHistorical Background of LubricantsDinesh babuNo ratings yet
- ICC 70 AdministratorsGuide en PDFDocument92 pagesICC 70 AdministratorsGuide en PDFMarie ManuelNo ratings yet
- Lavon 2004Document7 pagesLavon 2004Tazkiyatul Asma'iNo ratings yet
- Lab Reproductive SDocument8 pagesLab Reproductive SJoyce TorcuatorNo ratings yet
- Basics of News WritingDocument31 pagesBasics of News WritingAngela Mae VillalunaNo ratings yet
- 12life Saving RulesDocument33 pages12life Saving RulesLakshmi Kanth P100% (1)
- Experiment 7: Investigating The Change of Volume in The Change of Temperature (Document2 pagesExperiment 7: Investigating The Change of Volume in The Change of Temperature (EDWIN SIMBARASHE MASUNUNGURENo ratings yet
- Controller Job DescriptionDocument1 pageController Job Descriptionmarco thompson100% (2)
- Plasticity - Rubber PDFDocument3 pagesPlasticity - Rubber PDFsujudNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 - 2020 PDFLusambo SimpasaNo ratings yet
- The Role of IRCTC Train Booking AgentsDocument7 pagesThe Role of IRCTC Train Booking AgentsRahul officalNo ratings yet
- Perfect Manpower Consultancy (Invoice) of Mr. Inamullah SheikhDocument1 pagePerfect Manpower Consultancy (Invoice) of Mr. Inamullah Sheikhvikrant jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Types of Cracks in Concrete BeamsDocument3 pagesTypes of Cracks in Concrete BeamsFatin UmyarahNo ratings yet
- Br2e Adv Readingfile03Document2 pagesBr2e Adv Readingfile03PressCall AcademyNo ratings yet
- Dressmaking 10 - 1st PT - TOS - Key To Correction 2Document8 pagesDressmaking 10 - 1st PT - TOS - Key To Correction 2Sonia CanaNo ratings yet
- PHD Pharma 23 IdDocument1 pagePHD Pharma 23 Idos krishnaNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 13 KINETIC THEORY With SOLUTIONSDocument6 pagesPhysics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 13 KINETIC THEORY With SOLUTIONSSk ShivamNo ratings yet
- SADP User Manual (V2.0)Document10 pagesSADP User Manual (V2.0)tehixazNo ratings yet
Conductor Temperature: Method B
Conductor Temperature: Method B
Uploaded by
Udomkarn SmtOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conductor Temperature: Method B
Conductor Temperature: Method B
Uploaded by
Udomkarn SmtCopyright:
Available Formats
DIgSILENT PowerFactory Short-Circuit Calculations
Conductor Temperature
When activating this option, the initial (pre-fault) conductor temperature can be set man-
ually. This will influence the calculated maximum temperature of the conductors, as
caused by the short-circuit currents.
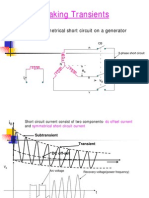
Decaying Aperiodic Component
Allows for the calculation of the DC current component for which the decaying time has
to be given. According to the IEC/IEC standard, the methods B, C and C' can be selected.
The symbols used mean:
Tb Breaker Time (see short-circuit command)
fn Nominal frequency
Ik" Initial short-circuit current
Method B: Using the complex calculated equivalent impedance of the network
with a security factor of 1.15:
R
T b ----
X
i DC = 2 I k e
Method C: Using the R/X ratio calculated with the equivalent frequency method.
The equivalent frequency is depending on the breaking time (see table
11.1). This method is recommended for maximum accuracy.
Table 11.1:
fn * Tb <1 < 2.5 <5 < 12.5
fc / fn 0.27 0.15 0.092 0.055
R
T b -----f
Xf
i DC = 2 I k e
R R fc
------f = ------c -----------
Xf X c f nom
The ratio Rc/Xc is the equivalent impedance calculate at frequency:
fc
f c = ----------- f nom
f nom
Method C': Using the R/X ratio like for the peak short-circuit current, thus selecting
the ratio fc/fn = 0.4. This options speeds up the calculation, as no
additional equivalent impedance must be calculated.
Peak-Shc Current (Meshed network)
In accordance with the IEC/VDE standard, the following methods for calculating kappa
11 - 9
You might also like
- Lab 7 RC Time ConstantDocument8 pagesLab 7 RC Time ConstantMalith Madushan100% (1)
- MD 11fgnDocument3 pagesMD 11fgnMcDonnell Douglas MD-110% (7)
- Project Proposal On Dairy FarmDocument26 pagesProject Proposal On Dairy Farmvector dairy88% (8)
- Australian Professional Standards For TeachersDocument1 pageAustralian Professional Standards For Teachersapi-365080091No ratings yet
- Mainframe Admin Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesMainframe Admin Course SyllabusENDLURI DEEPAK KUMARNo ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator and RC Coupled Ce Amplifier - Lab ExperimentDocument8 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator and RC Coupled Ce Amplifier - Lab ExperimentMani BharathiNo ratings yet
- Relay Calculation SummaryDocument4 pagesRelay Calculation SummaryAnonymous kjvaeVJNNo ratings yet
- Cs Lab Manual in PDFDocument56 pagesCs Lab Manual in PDFvasukonetiNo ratings yet
- Daycounter Inc - Snubber Circuit Design CalculatorsDocument5 pagesDaycounter Inc - Snubber Circuit Design CalculatorsLaercio Marques100% (1)
- Snubber PDFDocument5 pagesSnubber PDFJ Milk SilvaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Attenuators and Compensation: R R V R V R R R V VDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Attenuators and Compensation: R R V R V R R R V Vnithinjose4uNo ratings yet
- TL431 Design Tips2 PDFDocument10 pagesTL431 Design Tips2 PDF3degreesNo ratings yet
- Applications To Sizing Circuit Breakers (ANSI C37)Document22 pagesApplications To Sizing Circuit Breakers (ANSI C37)freddy riveraNo ratings yet
- Oral PEADocument34 pagesOral PEAatefdinNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Input Filter - Flo: GraphicDocument2 pagesCapacitor Input Filter - Flo: GraphicSeijuro AkashiNo ratings yet
- MiCOM P54 X - Current Diff Prot Relays - CT RequirementDocument5 pagesMiCOM P54 X - Current Diff Prot Relays - CT RequirementpayNo ratings yet
- Figure 2. Voltage Mode Amplifier CircuitDocument2 pagesFigure 2. Voltage Mode Amplifier CircuitHadi KhanmohammadiNo ratings yet
- A PWM Circuit Using Operational AmplifiersDocument7 pagesA PWM Circuit Using Operational Amplifiershamza abdo mohamoud100% (1)
- Op Amp Manual Sem 1st....Document7 pagesOp Amp Manual Sem 1st....diljitdosanjhfan24No ratings yet
- 3 - 2b Transformer Energization - ModelingDocument7 pages3 - 2b Transformer Energization - ModelingNalex GeeNo ratings yet
- Universal Block DiagramDocument6 pagesUniversal Block Diagramapneetsandhu1234No ratings yet
- Analog Basics:: Waveforms, Ac and DCDocument30 pagesAnalog Basics:: Waveforms, Ac and DCvenkumaniNo ratings yet
- Uses of CapacitorsDocument4 pagesUses of Capacitorswilliamx1978No ratings yet
- Lab #6Document4 pagesLab #6darline.ferrerNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EENG200 - Updated 23-24Document23 pagesLab Manual EENG200 - Updated 23-24What's new ?No ratings yet
- An 4134Document14 pagesAn 4134shri.bhairavkar6977No ratings yet
- 1.RC CircuitsDocument7 pages1.RC CircuitsNaveen ChNo ratings yet
- TAN DELTA Application NotesDocument34 pagesTAN DELTA Application NotesKamlesh MhatreNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier 741 As Wein Bridge Oscillator 1Document4 pagesOperational Amplifier 741 As Wein Bridge Oscillator 1Deepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- 18eel66 Lab ManualDocument53 pages18eel66 Lab ManualVasanthNo ratings yet
- Amplifier Frequency ResponseDocument24 pagesAmplifier Frequency ResponsejaltitiNo ratings yet
- 6 Log Anti Log AmplifiersDocument32 pages6 Log Anti Log AmplifiersAnonymous eWMnRr70q0% (1)
- R - KZ I: A 12-Bit ADC Successive-Approximation-Type With Digital Error CorrectionDocument10 pagesR - KZ I: A 12-Bit ADC Successive-Approximation-Type With Digital Error CorrectionMiguel BrunoNo ratings yet
- Hybrid PieDocument6 pagesHybrid PieAman GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ty Man V ACDocument17 pagesTy Man V AC10 Joshua MasterNo ratings yet
- Frequency Characteristics of AC Circuits: RLC Circuits and ResonanceDocument39 pagesFrequency Characteristics of AC Circuits: RLC Circuits and ResonanceOng Xuan YaoNo ratings yet
- Transformer Protection 2012-1Document43 pagesTransformer Protection 2012-1muaz_aminu1422100% (2)
- Monty B Bode Plots and First Order Filters ReportDocument11 pagesMonty B Bode Plots and First Order Filters ReportMonts 42No ratings yet
- Dist Cord (R)Document12 pagesDist Cord (R)1453hNo ratings yet
- Multivibrators - Record PartDocument6 pagesMultivibrators - Record PartAlfred D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Step-ByStep Flyback SMPS DesignDocument6 pagesStep-ByStep Flyback SMPS DesignPhạm Văn TưởngNo ratings yet
- Lab 5: Voltage RegulatorDocument7 pagesLab 5: Voltage RegulatorMansi NanavatiNo ratings yet
- Mixed Signal Analysis of First Order Low Pass FilterDocument3 pagesMixed Signal Analysis of First Order Low Pass FilterAhdelNo ratings yet
- Transient Response of RC CircuitDocument5 pagesTransient Response of RC CircuitJayesh Ruikar100% (1)
- EEE 54 DP1 Documentation - Mendoza - SorianoDocument2 pagesEEE 54 DP1 Documentation - Mendoza - SorianoDarl John MendozaNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Relay PDFDocument17 pagesOvercurrent Relay PDFtranhuutuongNo ratings yet
- Design of Electrical SystemsDocument621 pagesDesign of Electrical SystemsPardeep KhosaNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryDocument6 pagesRC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryMuhammad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Experiment 21 RC Time Constants: Advanced ReadingDocument2 pagesExperiment 21 RC Time Constants: Advanced ReadingAlicia AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument28 pagesCourse OutlineIdrisa Mussa ChubwaNo ratings yet
- RC CircuitsDocument11 pagesRC Circuits2456903No ratings yet
- Implementing The TL431 Feedback LoopDocument10 pagesImplementing The TL431 Feedback LoopAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Discussion of The Sample and Hold Circuit and The Time Required To Get and Hold The VoltageDocument22 pagesDiscussion of The Sample and Hold Circuit and The Time Required To Get and Hold The VoltagewolverinepNo ratings yet
- Numerical Overcurrent Relay and Relay CoordinationDocument7 pagesNumerical Overcurrent Relay and Relay Coordinationvoyimat216No ratings yet
- Circuit BreakerDocument50 pagesCircuit BreakerDeanna GrahamNo ratings yet
- Protection Relays Setting Calculation Rev 4Document55 pagesProtection Relays Setting Calculation Rev 4Aatif Usmani100% (1)
- Analog1 Final 6Document15 pagesAnalog1 Final 6Sourav SinhaNo ratings yet
- Fly BackDocument20 pagesFly BackĐặng Văn TàiNo ratings yet
- Compensating The RHPZ in A CCM Boost Converter - The Analytical Way - Jun 2009Document4 pagesCompensating The RHPZ in A CCM Boost Converter - The Analytical Way - Jun 2009QuickerManNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Relaying For Feeder ProtectionDocument20 pagesOvercurrent Relaying For Feeder ProtectionVinodNo ratings yet
- Durgapur: National Institute of TechnologyDocument10 pagesDurgapur: National Institute of TechnologyBishal SinghNo ratings yet
- HWR FWR ParametersDocument6 pagesHWR FWR ParametersRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- 002 Lab2-Fa10Document4 pages002 Lab2-Fa10xendikaNo ratings yet
- 1995 Transmission Line Design ProcessDocument10 pages1995 Transmission Line Design Processjoydeep_d3232No ratings yet
- Conductor TAIHAN Size ChartsDocument40 pagesConductor TAIHAN Size ChartsUdomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- IEC StandardDocument23 pagesIEC StandardSyedAhsanAbbasBokhari0% (1)
- STR 180Document2 pagesSTR 180Udomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Tower Footing Resistance Effected Back Flashover Across Insulator in A Transmission SystemDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Tower Footing Resistance Effected Back Flashover Across Insulator in A Transmission SystemUdomkarn Smt100% (1)
- FLL 431Document1 pageFLL 431Udomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- Design of Transmission Lines, Structures, and FoundationsDocument8 pagesDesign of Transmission Lines, Structures, and FoundationsUdomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- Solution Methods of Overhead Transmission Line Mechanics: Ladislav VARGA, Stanislav ILENIN, Vladimír CHLADNÝDocument4 pagesSolution Methods of Overhead Transmission Line Mechanics: Ladislav VARGA, Stanislav ILENIN, Vladimír CHLADNÝUdomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- App HDocument1 pageApp HUdomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- Glossary: A Accelerated ErosionDocument13 pagesGlossary: A Accelerated ErosionUdomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Endurance Present KnowledgeDocument30 pagesFatigue Endurance Present KnowledgeUdomkarn SmtNo ratings yet
- SF Hose Cat 2017Document40 pagesSF Hose Cat 2017Ahmed Abdelaty100% (1)
- Job Notification NHM Odisha Recruitment 2015 16 For 19 District Programme Manager Other PostsDocument12 pagesJob Notification NHM Odisha Recruitment 2015 16 For 19 District Programme Manager Other PostsJeshiNo ratings yet
- Crown Amplifiers Catalog PDFDocument68 pagesCrown Amplifiers Catalog PDFArjay DomisiwNo ratings yet
- Wandering Heroes of Ogre Gate - House of Paper ShadowsDocument97 pagesWandering Heroes of Ogre Gate - House of Paper ShadowsSamuel Smallman75% (4)
- UP Series: Grundfos Product GuideDocument84 pagesUP Series: Grundfos Product GuideGrundfosEgyptNo ratings yet
- Ideal Dilute and Real SolutionsDocument9 pagesIdeal Dilute and Real SolutionsJksgNo ratings yet
- PRIsDocument11 pagesPRIsbobby choudharyNo ratings yet
- Product Environmental Profile: Canalis KNA 40A To 160ADocument7 pagesProduct Environmental Profile: Canalis KNA 40A To 160AJavier LazoNo ratings yet
- Historical Background of LubricantsDocument21 pagesHistorical Background of LubricantsDinesh babuNo ratings yet
- ICC 70 AdministratorsGuide en PDFDocument92 pagesICC 70 AdministratorsGuide en PDFMarie ManuelNo ratings yet
- Lavon 2004Document7 pagesLavon 2004Tazkiyatul Asma'iNo ratings yet
- Lab Reproductive SDocument8 pagesLab Reproductive SJoyce TorcuatorNo ratings yet
- Basics of News WritingDocument31 pagesBasics of News WritingAngela Mae VillalunaNo ratings yet
- 12life Saving RulesDocument33 pages12life Saving RulesLakshmi Kanth P100% (1)
- Experiment 7: Investigating The Change of Volume in The Change of Temperature (Document2 pagesExperiment 7: Investigating The Change of Volume in The Change of Temperature (EDWIN SIMBARASHE MASUNUNGURENo ratings yet
- Controller Job DescriptionDocument1 pageController Job Descriptionmarco thompson100% (2)
- Plasticity - Rubber PDFDocument3 pagesPlasticity - Rubber PDFsujudNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 - 2020 PDFLusambo SimpasaNo ratings yet
- The Role of IRCTC Train Booking AgentsDocument7 pagesThe Role of IRCTC Train Booking AgentsRahul officalNo ratings yet
- Perfect Manpower Consultancy (Invoice) of Mr. Inamullah SheikhDocument1 pagePerfect Manpower Consultancy (Invoice) of Mr. Inamullah Sheikhvikrant jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Types of Cracks in Concrete BeamsDocument3 pagesTypes of Cracks in Concrete BeamsFatin UmyarahNo ratings yet
- Br2e Adv Readingfile03Document2 pagesBr2e Adv Readingfile03PressCall AcademyNo ratings yet
- Dressmaking 10 - 1st PT - TOS - Key To Correction 2Document8 pagesDressmaking 10 - 1st PT - TOS - Key To Correction 2Sonia CanaNo ratings yet
- PHD Pharma 23 IdDocument1 pagePHD Pharma 23 Idos krishnaNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 13 KINETIC THEORY With SOLUTIONSDocument6 pagesPhysics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 13 KINETIC THEORY With SOLUTIONSSk ShivamNo ratings yet
- SADP User Manual (V2.0)Document10 pagesSADP User Manual (V2.0)tehixazNo ratings yet