Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fever in A Child
Fever in A Child
Uploaded by
Has MasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fever in A Child
Fever in A Child
Uploaded by
Has MasCopyright:
Available Formats
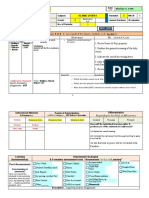
Risk stratification
Please see the link for the complete table, below is a modified version
Green - low risk Amber - intermediate risk Red - high risk
Colour Normal colour Pallor reported by Pale/mottled/ashen/blue
parent/carer
Activity Responds Not responding normally to No response to social cues
normally to social social cues Appears ill to a healthcare
cues No smile professional
Content/smiles Wakes only with prolonged Does not wake or if roused
Stays awake or stimulation does not stay awake
awakens quickly Decreased activity Weak, high-pitched or
Strong normal continuous cry
cry/not crying
Respiratory Nasal flaring Grunting
Tachypnoea: respiratory Tachypnoea: respiratory
rate rate >60 breaths/minute
Moderate or severe chest
indrawing
>50 breaths/minute,
age 6-12 months;
>40 breaths/minute,
age >12 months
Oxygen saturation <=95%
in air
Crackles in the chest
Circulation Normal skin and Tachycardia: Reduced skin turgor
and hydration eyes
Moist mucous
membranes >160 beats/minute,
age <12 months
>150 beats/minute,
age 12-24 months
>140 beats/minute,
age 2-5 years
Capillary refill time >=3
seconds
Dry mucous membranes
Poor feeding in infants
Reduced urine output
Green - low risk Amber - intermediate risk Red - high risk
Other No amber or red Age 3-6 months, Age <3 months, temperature
signs temperature >=39C >=38C
Fever for >=5 days Non-blanching rash
Rigors Bulging fontanelle
Swelling of a limb or joint Neck stiffness
Non-weight bearing Status epilepticus
limb/not using an extremity Focal neurological signs
Focal seizures
Management
If green:
Child can be managed at home with appropriate care advice, including when to seek further
help
If amber:
provide parents with a safety net or refer to a paediatric specialist for further assessment
a safety net includes verbal or written information on warning symptoms and how further
healthcare can be accessed, a follow-up appointment, liaison with other healthcare
professionals, e.g. out-of-hours providers, for further follow-up
If red:
refer child urgently to a paediatric specialist
Other key points include
oral antibiotics should not be prescribed to children with fever without apparent source
if a pneumonia is suspected but the child is not going to be referred to hospital then a chest
x-ray does not need to be routinely performed
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- AMET Botox and FillerDocument186 pagesAMET Botox and Fillerhesham100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Deconstrucing The OsceDocument129 pagesDeconstrucing The OsceHas Mas100% (1)
- Far160 - Question 5 Tutorial Chapter 1Document2 pagesFar160 - Question 5 Tutorial Chapter 1Syaza AisyahNo ratings yet
- 5 Things All Patients Want To KNOWDocument4 pages5 Things All Patients Want To KNOWHas MasNo ratings yet
- Consultation Models - TypesDocument19 pagesConsultation Models - TypesHas MasNo ratings yet
- FP Curriculum Resource PDFDocument24 pagesFP Curriculum Resource PDFHas MasNo ratings yet
- Value and Quality Innovations in Acute and Emergency CareDocument246 pagesValue and Quality Innovations in Acute and Emergency CareHas MasNo ratings yet
- (PDFmedbook - Info) BiochemistryDocument290 pages(PDFmedbook - Info) BiochemistryHas MasNo ratings yet
- PlabRight Notes 2014 PDFDocument270 pagesPlabRight Notes 2014 PDFHas Mas100% (2)
- Ab PomDocument2 pagesAb PomErica CalzadaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Hand OutsDocument3 pagesPurposive Communication Hand OutsBhoxzs Mel Ikaw Lng0% (1)
- Here: Kali Linux Using Tutorial PDFDocument2 pagesHere: Kali Linux Using Tutorial PDFr00TNo ratings yet
- Getachew AlemuDocument4 pagesGetachew AlemuGetachew AlemuNo ratings yet
- Resolution For Improving Sip1Document2 pagesResolution For Improving Sip1ARGIE DEJECASION100% (2)
- The Zapotecs Official Presentation 1Document4 pagesThe Zapotecs Official Presentation 1api-249845382No ratings yet
- G Ish 401 Chapter 7 SlaughteringDocument75 pagesG Ish 401 Chapter 7 Slaughteringnrnvbihah26No ratings yet
- Date Sunday, April 14, 2019 Date: Sha'ban 9, 1440Document7 pagesDate Sunday, April 14, 2019 Date: Sha'ban 9, 1440Ahmad SaadNo ratings yet
- VISHNU CV With ExperianceDocument2 pagesVISHNU CV With ExperianceoNo ratings yet
- WerpapointDocument14 pagesWerpapointPaula Mae RubialesNo ratings yet
- R514A CVHE Centravac Centrifugal Chiller Dimension DrawingsDocument13 pagesR514A CVHE Centravac Centrifugal Chiller Dimension DrawingsBegundalz PotterNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document8 pagesUnit 4lomash2018No ratings yet
- User Manual RedpackAPI English 1.0Document23 pagesUser Manual RedpackAPI English 1.0GogodzillaNo ratings yet
- Acroname EnglishDocument44 pagesAcroname EnglishNissan NavaraNo ratings yet
- Water Managment PlanDocument31 pagesWater Managment Planmehmal malikNo ratings yet
- R BalajiDocument81 pagesR BalajiBalaji radhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- JL - Langkat 88 Singgahan-Pelem Pare - Kediri - Jawa Timur 64213 Phone: 0354-396 561 Moblie: 0852 3111 1117-0858 8888 1117Document2 pagesJL - Langkat 88 Singgahan-Pelem Pare - Kediri - Jawa Timur 64213 Phone: 0354-396 561 Moblie: 0852 3111 1117-0858 8888 1117Mita KusniasariNo ratings yet
- 2017 CenturionDocument2 pages2017 Centurionceo9871No ratings yet
- Chufamix Recipe Book EngDocument100 pagesChufamix Recipe Book EnglollibravoNo ratings yet
- Local Controller - 250WDocument4 pagesLocal Controller - 250WSyed Muzzaffar HussainNo ratings yet
- Spes Gardening Accomplishment FormDocument2 pagesSpes Gardening Accomplishment FormOliver MendozaNo ratings yet
- Accommodation Theory: Irsalina Rachma Viramdani Khusnen Khoirin NadaDocument11 pagesAccommodation Theory: Irsalina Rachma Viramdani Khusnen Khoirin NadaSudeshna DeyNo ratings yet
- OOP MSBTE Question Paper Winter 2008Document2 pagesOOP MSBTE Question Paper Winter 2008api-3728136No ratings yet
- Nursing Home Private Hospital / ICU Nursing Chart: 6 HR 18 HRDocument2 pagesNursing Home Private Hospital / ICU Nursing Chart: 6 HR 18 HRdavidNo ratings yet
- Association of Indian Universities: Competitions On Four Zone Basis (Women)Document10 pagesAssociation of Indian Universities: Competitions On Four Zone Basis (Women)Aseem Singh SodhiNo ratings yet
- Under Keel Clearnace (Filled-Up)Document1 pageUnder Keel Clearnace (Filled-Up)CHERRY ANN OLAJAYNo ratings yet
- Groupwork Consumer BehaviourDocument14 pagesGroupwork Consumer BehaviourMaisarahNo ratings yet
- Diet PDFDocument11 pagesDiet PDFAarcamNo ratings yet